Unveiling The Network Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Nmap And Wireless Network Scanning
Unveiling the Network Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap and Wireless Network Scanning
Related Articles: Unveiling the Network Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap and Wireless Network Scanning
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Network Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap and Wireless Network Scanning. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Network Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap and Wireless Network Scanning
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, understanding the intricacies of network security is paramount. Network scanning, a crucial component of this understanding, empowers individuals and organizations to identify vulnerabilities, assess security posture, and ultimately, bolster their defenses. This article delves into the world of Nmap, a powerful and versatile network scanning tool, and explores its application in the realm of wireless networks.
Understanding Nmap: The Network Mapper
Nmap, short for Network Mapper, is a free and open-source utility that allows users to discover hosts and services on a network. This network scanner employs a variety of techniques to gather information, including:
- Port Scanning: Identifying open ports on target systems, revealing potential services running on those ports. This provides insights into the applications and protocols accessible on the network.
- Host Discovery: Detecting active hosts on the network, even those not actively responding to standard network requests.
- Operating System Detection: Identifying the operating systems running on discovered hosts, aiding in vulnerability assessment and exploitation.
- Service Version Detection: Determining the specific versions of services running on open ports, enabling the identification of known vulnerabilities and outdated software.
The Significance of Wireless Network Scanning
Wireless networks, while offering convenience and mobility, introduce unique security challenges. The open nature of wireless communication makes them susceptible to various threats, including:
- Eavesdropping: Unsecured wireless networks can be easily intercepted, exposing sensitive data to unauthorized access.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Malicious actors can intercept communication between devices on the network, potentially stealing credentials or injecting malicious code.
- Denial-of-Service Attacks: Attackers can disrupt network connectivity by flooding the network with traffic, making it unusable for legitimate users.
Wireless network scanning using Nmap plays a vital role in mitigating these risks by:
- Identifying Vulnerable Access Points: Detecting open or weakly protected wireless access points, allowing for immediate remediation.
- Discovering Unauthorized Devices: Identifying devices connected to the network that are not authorized, potentially indicating a security breach.
- Assessing Network Security Posture: Providing a comprehensive view of the network’s security configuration, highlighting potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement.
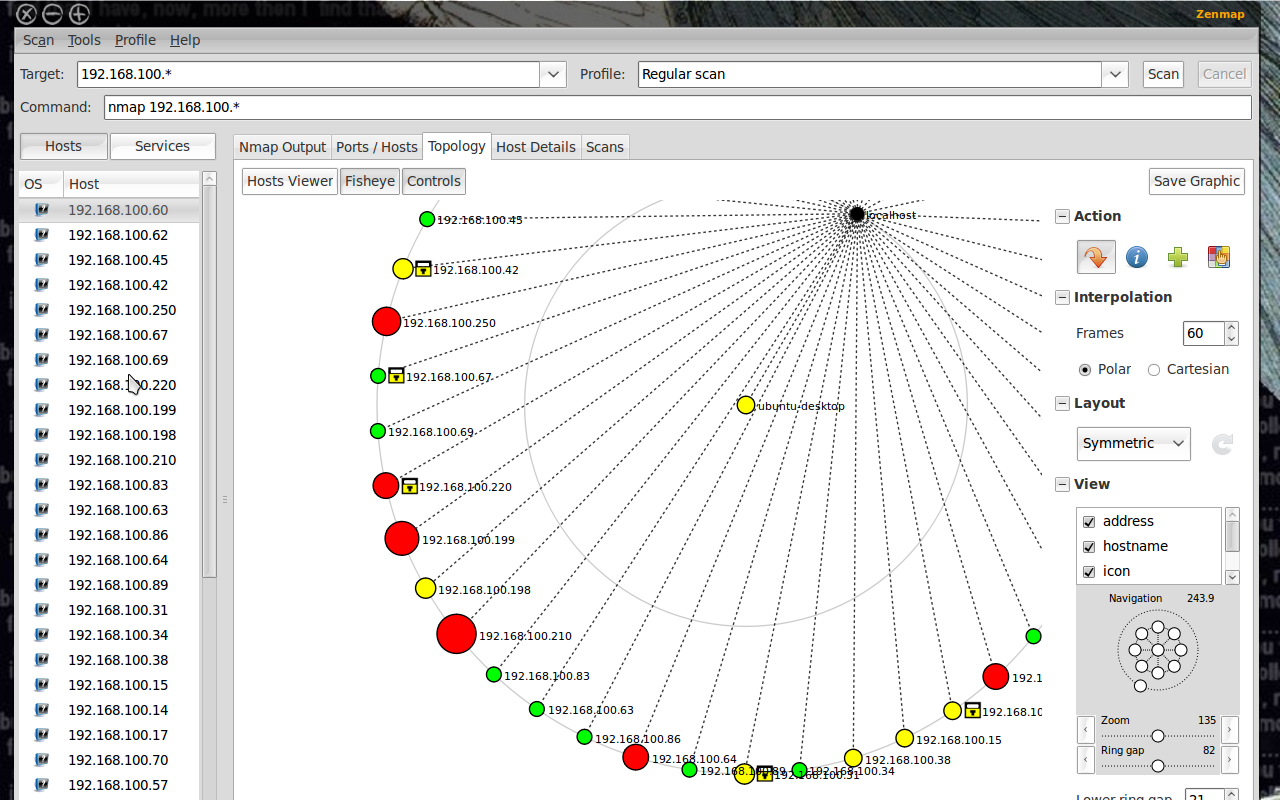
Navigating Nmap for Wireless Network Scanning
Nmap offers a wide array of options and capabilities for scanning wireless networks. Here’s a breakdown of key commands and techniques:
-
Basic Scanning: The simplest form of scanning involves using the
nmapcommand with the target network address. For example,nmap 192.168.1.0/24scans all devices within the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet. -
Wireless Scanning: Nmap can be used to scan wireless networks by specifying the interface and the
-Toption to increase scanning speed. For instance,nmap -T4 -i wlan0 192.168.1.1scans the network using thewlan0interface with increased speed. -
Service and Version Detection: The
-sVoption allows for the identification of services and their versions running on discovered hosts. This is crucial for pinpointing potential vulnerabilities. -
Operating System Detection: The
-Ooption enables Nmap to identify the operating systems running on discovered hosts, aiding in vulnerability assessment. - Script Scanning: Nmap’s scripting engine allows for the execution of custom scripts during scans. This enables the detection of specific vulnerabilities or the collection of detailed information about discovered services.
Nmap’s Role in Wireless Security Audits
Nmap is a valuable tool for conducting comprehensive wireless security audits. By combining its scanning capabilities with custom scripts and configuration options, security professionals can gain a deep understanding of the network’s security posture and identify potential vulnerabilities.
FAQs on Nmap and Wireless Network Scanning
Q1: Is it legal to scan networks using Nmap?
A1: The legality of network scanning varies depending on jurisdiction and the target network. Scanning public networks is generally permissible, while scanning private networks without authorization may be illegal.
Q2: How can I prevent my network from being scanned?
A2: Employing strong security measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists can help mitigate the risk of unauthorized scanning.
Q3: What are the ethical considerations of network scanning?
A3: It is crucial to obtain consent before scanning private networks and to respect privacy concerns. Additionally, scanning should be conducted in a responsible and ethical manner, avoiding malicious activities or disrupting network operations.
Q4: Can Nmap be used for penetration testing?
A4: Yes, Nmap is a valuable tool for penetration testing, allowing ethical hackers to identify vulnerabilities and assess the security of a network.
Q5: What are some best practices for using Nmap for wireless network scanning?
A5: Always obtain consent before scanning a network, use appropriate scanning options to avoid disrupting network operations, and follow ethical guidelines.
Tips for Effective Wireless Network Scanning with Nmap
-
Specify the Target Network: Use the
-Toption to increase scanning speed and focus on the target network. -
Customize Scanning Options: Utilize options like
-sVand-Oto gather detailed information about discovered hosts and services. - Employ Script Scanning: Leverage Nmap’s scripting engine to automate the detection of specific vulnerabilities or collect additional information.
- Analyze Scan Results: Carefully examine scan results to identify potential vulnerabilities and prioritize remediation efforts.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update Nmap and its scripts to ensure access to the latest vulnerabilities and scanning capabilities.
Conclusion: Empowering Network Security
Nmap is a powerful and versatile tool for scanning wireless networks, providing valuable insights into network security posture and potential vulnerabilities. By leveraging its capabilities responsibly and ethically, individuals and organizations can strengthen their defenses, mitigate risks, and ensure the integrity of their wireless networks. In an era of increasing cyber threats, understanding and effectively utilizing tools like Nmap is essential for building a resilient and secure digital environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Network Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nmap and Wireless Network Scanning. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!

