Unveiling The Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration Of Topographic Maps In Indonesia
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps in Indonesia
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps in Indonesia
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps in Indonesia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps in Indonesia
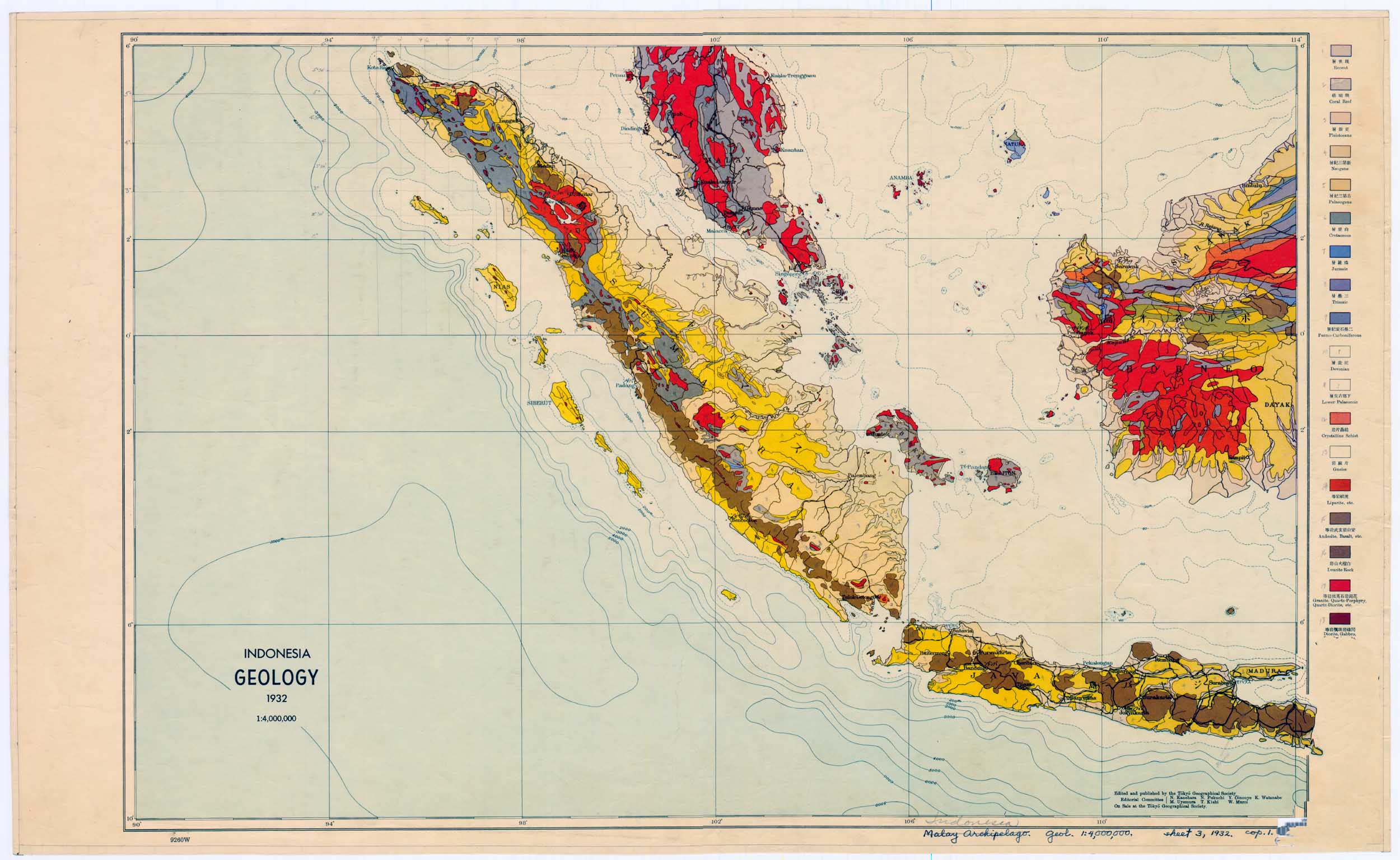
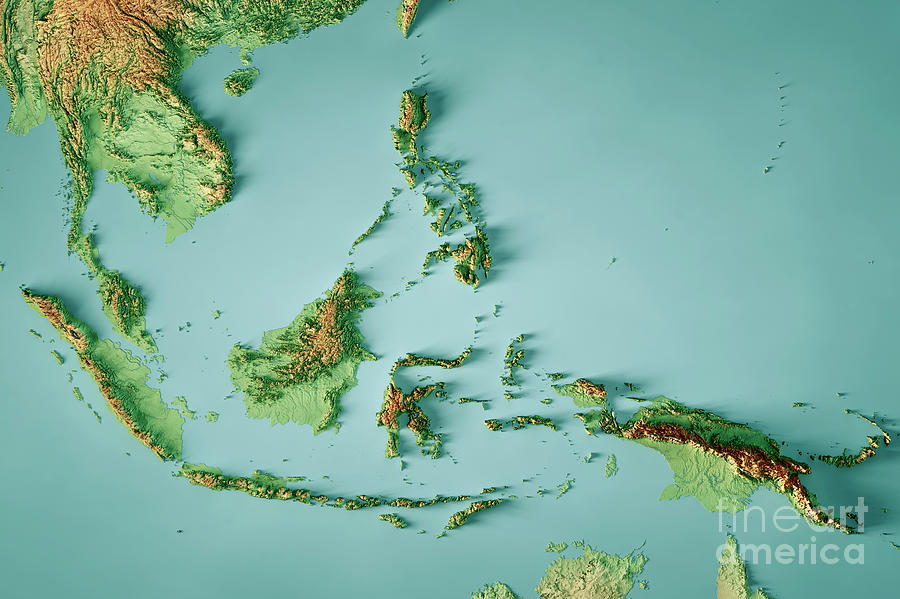
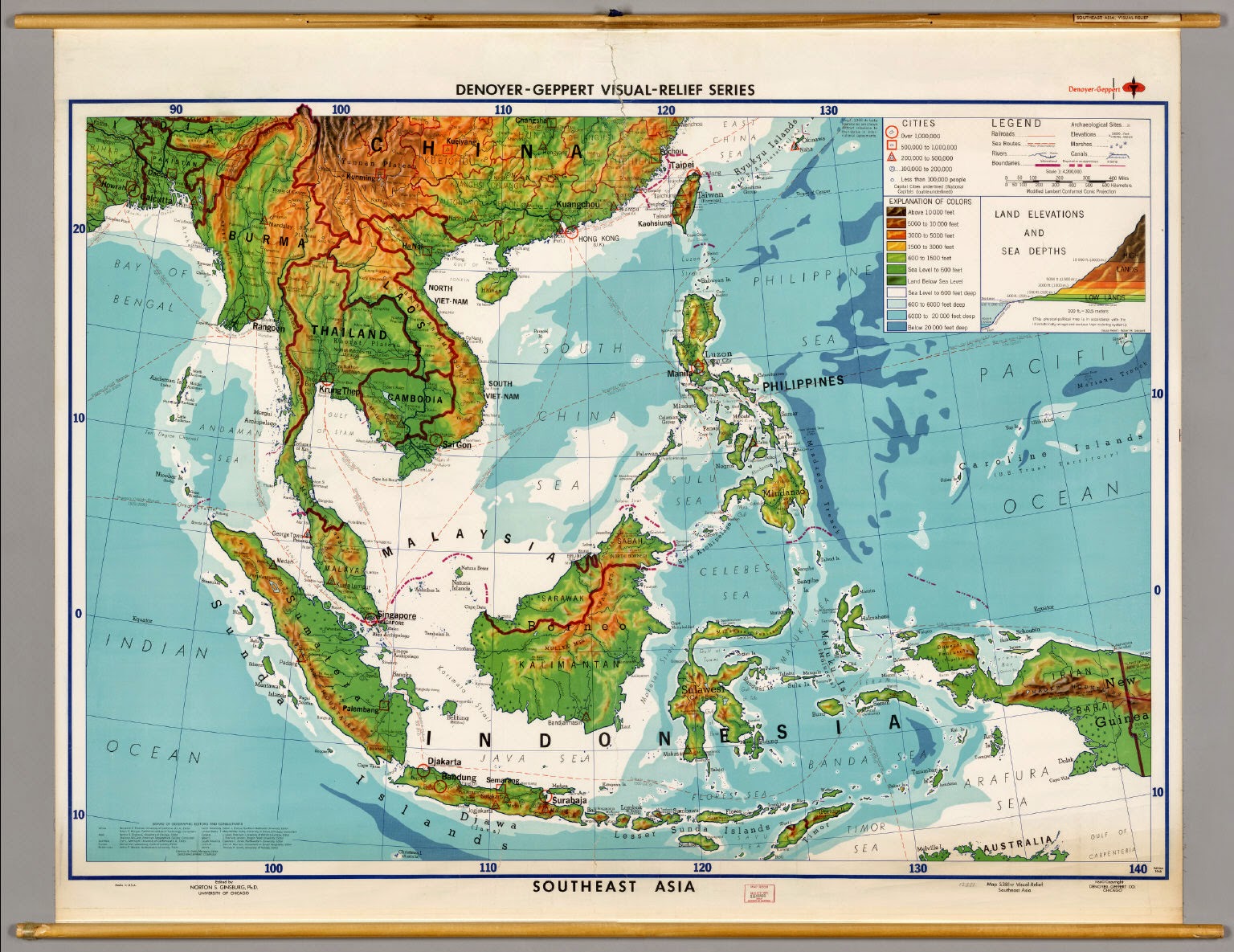
Indonesia, a sprawling archipelago nation, boasts a diverse and dynamic landscape. From towering volcanic peaks to lush rainforests and sprawling plains, its geography presents a tapestry of intricate features. To navigate and understand this complex terrain, topographic maps have proven invaluable tools, offering a detailed visual representation of the country’s physical characteristics. This article delves into the significance of topographic maps in Indonesia, exploring their creation, uses, and benefits, while also addressing frequently asked questions and offering practical tips for their utilization.
Understanding the Topography of Indonesia: A Visual Guide
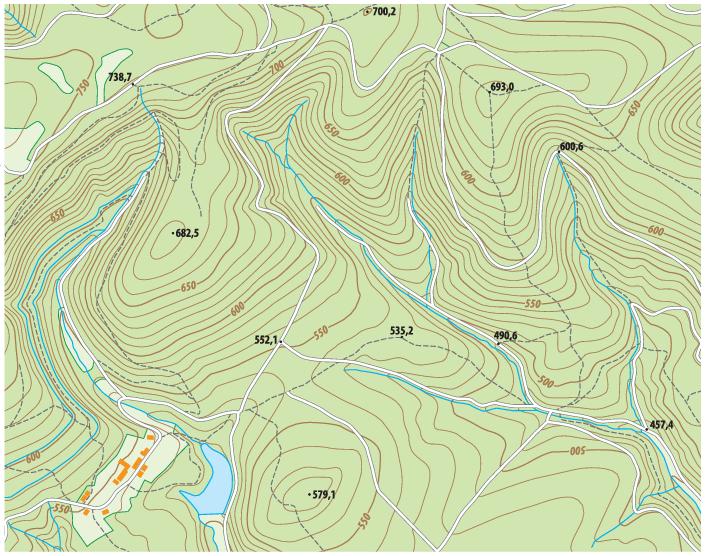
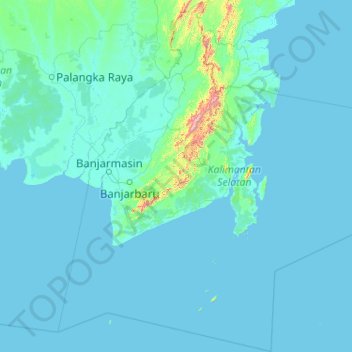
Topographic maps are specialized cartographic representations that depict the Earth’s surface, showcasing elevation, landforms, and key geographical features. They utilize contour lines, a system of interconnected lines that connect points of equal elevation, to portray the terrain’s three-dimensional shape.
The intricate network of contour lines on a topographic map provides a wealth of information, allowing users to:
- Visualize the terrain: Contour lines effectively represent the elevation changes, revealing the presence of hills, valleys, mountains, and plateaus.
- Determine elevation: By reading the numerical values associated with contour lines, users can ascertain the precise elevation of any point on the map.
- Identify landforms: Topographic maps depict various landforms, such as rivers, lakes, forests, and urban areas, providing a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Plan routes and activities: Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic maps to plan safe and efficient routes, considering elevation changes, obstacles, and potential hazards.
The Importance of Topographic Maps in Indonesia:
Indonesia’s unique geography, characterized by volcanic activity, seismic instability, and a vast archipelago, makes topographic maps indispensable for a wide range of activities and sectors. These maps serve as essential tools for:
- Disaster Management and Mitigation: Topographic maps play a crucial role in disaster preparedness and response. By accurately representing the terrain, they facilitate the identification of vulnerable areas prone to landslides, floods, and earthquakes. This information enables authorities to develop effective mitigation strategies, evacuation plans, and resource allocation for disaster relief efforts.
- Infrastructure Development: Topographic maps guide the planning and construction of roads, bridges, dams, and other infrastructure projects. They help engineers and planners assess the feasibility of projects, identify potential challenges related to terrain, and optimize design for optimal functionality and safety.
- Resource Management: Indonesia’s natural resources, including forests, minerals, and water, are vital for its economy. Topographic maps aid in resource exploration, mapping, and management, ensuring sustainable utilization and minimizing environmental impact.
- Scientific Research: Geologists, ecologists, and other researchers utilize topographic maps to study the Earth’s surface, analyze geological formations, understand ecological patterns, and conduct environmental monitoring.
- Tourism and Recreation: Topographic maps empower tourists and outdoor enthusiasts to explore Indonesia’s diverse landscapes, navigate trails, plan hiking expeditions, and discover hidden gems.
The Evolution of Topographic Maps in Indonesia:
The creation of topographic maps in Indonesia has evolved over time, reflecting technological advancements and the growing demand for detailed and accurate cartographic representations.
- Early Mapping Efforts: Early topographic maps of Indonesia were primarily based on manual surveys and aerial photography, often limited in detail and accuracy.
- Satellite Imagery and Digital Mapping: The advent of satellite imagery and digital mapping technologies revolutionized topographic mapping in Indonesia. Advanced sensors and algorithms enable the creation of high-resolution maps, incorporating detailed elevation data and providing a comprehensive view of the terrain.
- Open-Source Data and Citizen Science: The availability of open-source data and citizen science initiatives has further democratized access to topographic information, allowing researchers, developers, and the general public to contribute to and utilize these valuable resources.
FAQs about Topographic Maps in Indonesia:
1. Where can I find topographic maps of Indonesia?
Topographic maps of Indonesia are available from various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: The Indonesian Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (ESDM) and the National Agency for Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysics (BMKG) provide topographic maps and geospatial data.
- Private Companies: Several private companies specialize in geospatial data and offer topographic maps for sale or subscription.
- Online Platforms: Online platforms like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap provide access to topographic data and maps, often integrated with other features like satellite imagery and street views.
2. What are the different types of topographic maps available for Indonesia?
Topographic maps of Indonesia are available in various scales and formats, each catering to specific needs:
- Small-scale maps: These maps cover large areas, typically showing major features like mountain ranges, rivers, and cities. They are suitable for regional planning and general overview.
- Medium-scale maps: These maps provide more detail and cover smaller areas, often focusing on specific regions or provinces. They are useful for local planning, resource management, and outdoor activities.
- Large-scale maps: These maps offer the highest level of detail, focusing on specific areas like cities, national parks, or hiking trails. They are essential for navigation, infrastructure development, and detailed analysis.
3. How can I interpret topographic maps of Indonesia?
Interpreting topographic maps requires understanding the symbols and conventions used to represent terrain features. Key elements include:
- Contour lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, indicating the shape of the terrain.
- Elevation values: Numbers associated with contour lines indicate the elevation in meters or feet.
- Landform symbols: Specific symbols represent features like rivers, lakes, forests, and urban areas.
- Scale: The scale indicates the ratio between the map distance and the actual distance on the ground.
4. Are topographic maps of Indonesia updated regularly?
Topographic maps of Indonesia are updated periodically, but the frequency varies depending on the map scale, source, and the availability of new data. Government agencies and private companies strive to maintain accurate and up-to-date maps, incorporating new information from satellite imagery, surveys, and field observations.
5. How can I use topographic maps for planning outdoor activities in Indonesia?
Topographic maps are invaluable tools for planning outdoor activities in Indonesia, offering crucial information for:
- Route planning: Identify trails, elevation changes, and potential obstacles.
- Safety assessment: Assess risks like steep slopes, water crossings, and potential hazards.
- Resource planning: Locate campsites, water sources, and other essential resources.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps in Indonesia:
- Choose the appropriate scale: Select a map with a scale suitable for your specific activity and area of interest.
- Understand the map symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used to represent terrain features, elevation, and other relevant information.
- Consider the date of publication: Ensure that the map is up-to-date, especially for areas prone to changes in terrain or infrastructure.
- Use a compass and GPS: A compass and GPS device can enhance navigation and provide accurate location information.
- Mark your route: Use a pencil or marker to highlight your planned route on the map for easy reference.
Conclusion:
Topographic maps of Indonesia serve as indispensable tools for understanding, navigating, and managing the country’s complex and diverse landscape. They provide valuable information for disaster management, infrastructure development, resource management, scientific research, tourism, and outdoor recreation. As technology continues to advance, the creation and utilization of topographic maps in Indonesia are poised to evolve further, offering increasingly detailed and accurate representations of the nation’s physical environment. By embracing these powerful cartographic resources, Indonesia can continue to navigate its unique geography, harness its natural resources, and foster sustainable development for the benefit of its people and the environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Maps in Indonesia. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!