Unveiling The Land Of Indiana: A Topographic Exploration
Unveiling the Land of Indiana: A Topographic Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Land of Indiana: A Topographic Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Land of Indiana: A Topographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Land of Indiana: A Topographic Exploration
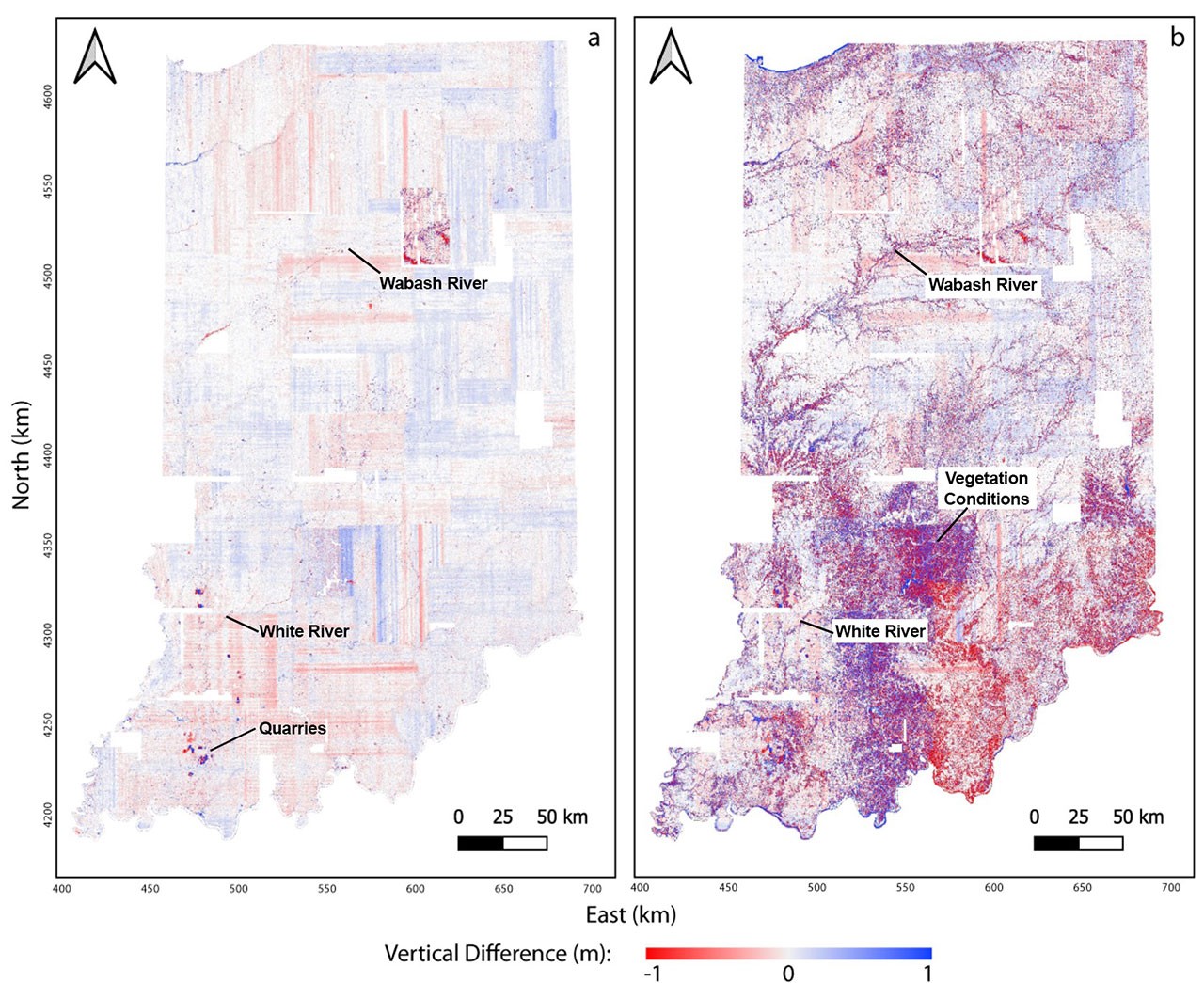
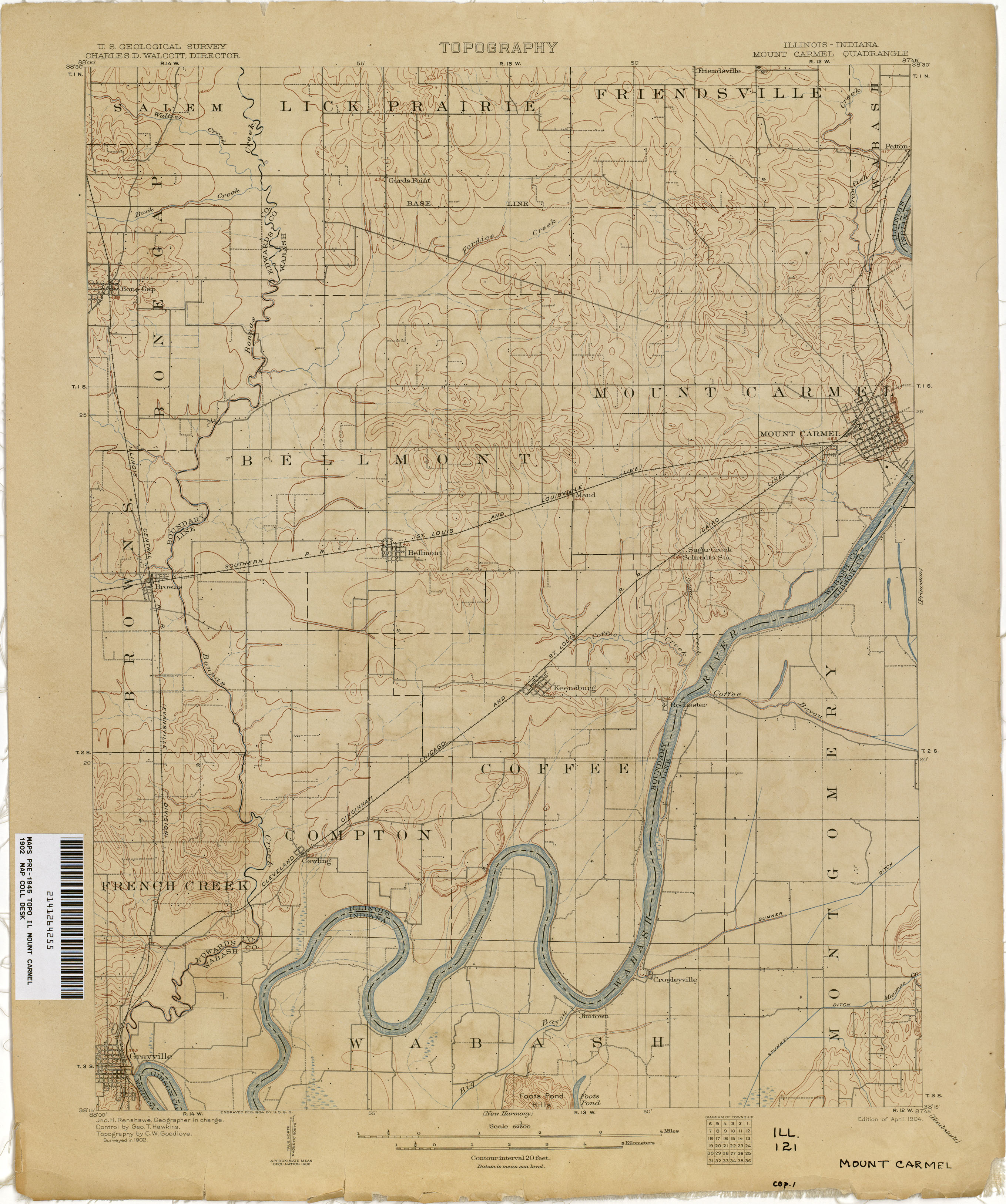
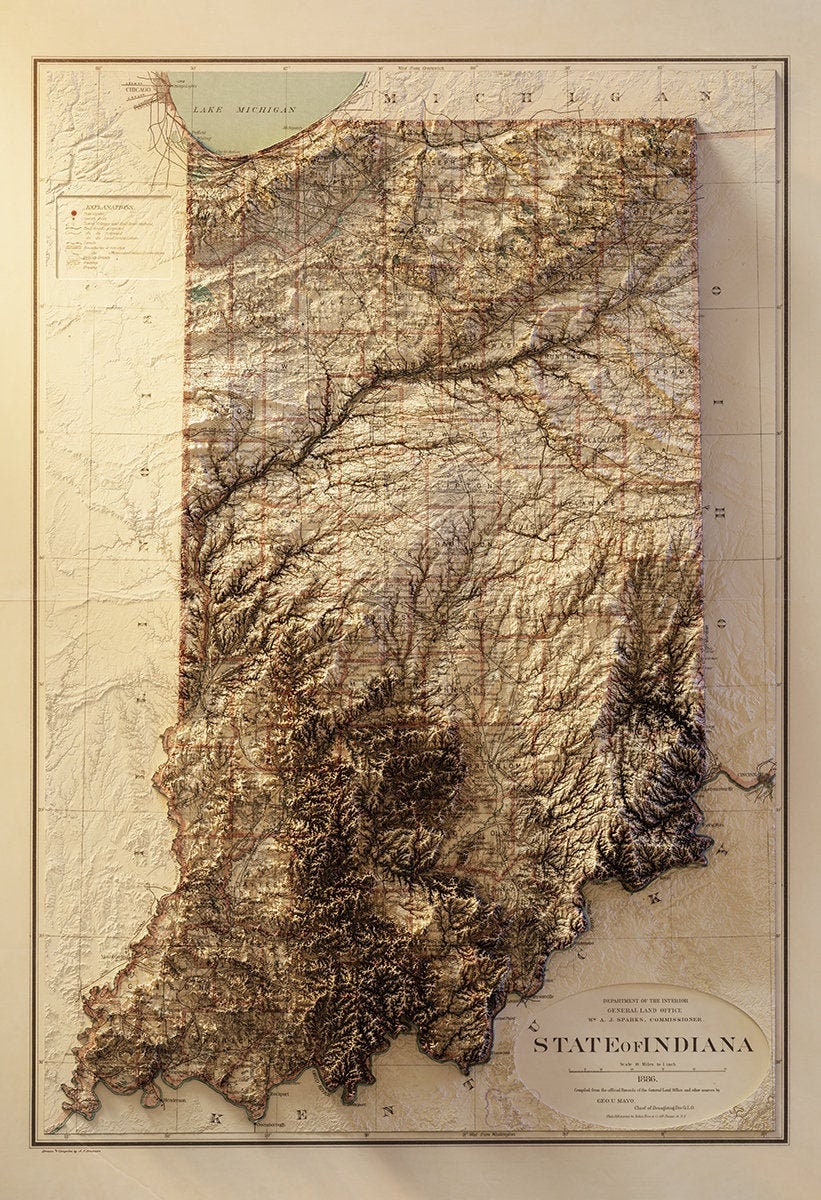
The state of Indiana, nestled in the heart of the American Midwest, presents a diverse landscape that is best understood through the lens of its topographic map. This map, a visual representation of the state’s elevation and landforms, provides a detailed understanding of the natural features that shape Indiana’s environment and influence its history, culture, and development.
Understanding the Terrain: A Visual Guide to Indiana’s Landscape
Indiana’s topographic map reveals a tapestry of contrasting features, ranging from the rolling hills of the Crawford Upland to the flat plains of the Wabash River Valley. The map’s contour lines, representing lines of equal elevation, depict the subtle changes in elevation that define the state’s diverse terrain.
- The Southern Uplands: The southern portion of Indiana is characterized by the rugged Crawford Upland, a region of high elevation and steep slopes. This area, known for its karst topography, features sinkholes, caves, and springs, remnants of ancient limestone formations.
- The Central Lowlands: The heart of Indiana is dominated by the Central Lowlands, a region of gently rolling hills and valleys. This area is characterized by fertile soils, making it ideal for agriculture. The Wabash River, flowing through the center of the state, plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape, creating fertile floodplains and influencing the region’s settlement patterns.
- The Northern Lake Region: The northern part of Indiana is home to the Great Lakes region, with its distinctive shoreline and expansive wetlands. The presence of Lake Michigan and its surrounding ecosystems contribute to the unique ecological character of this area.
Beyond Elevation: Uncovering the Significance of Indiana’s Topography
The topographic map is not merely a visual representation of landforms; it serves as a powerful tool for understanding the intricate relationship between the natural environment and human activity in Indiana.
- Impact on Settlement and Development: The state’s topography has played a significant role in shaping its settlement patterns. The fertile valleys and plains of the Central Lowlands attracted early settlers, leading to the development of major agricultural centers. In contrast, the rugged terrain of the Crawford Upland posed challenges to settlement, resulting in a more dispersed population.
- Influence on Infrastructure and Transportation: Indiana’s topography has influenced the development of its transportation infrastructure. The presence of major rivers like the Wabash and Ohio provided natural waterways for early transportation and trade. Today, the state’s road and rail networks are largely shaped by its terrain, with highways and railroads following the contours of the land.
- Ecological Significance: Indiana’s topography is intricately linked to its diverse ecosystems. The state’s rolling hills support a variety of habitats, from hardwood forests to prairie grasslands. The presence of wetlands and lakes provides critical breeding grounds for migratory birds and supports a rich biodiversity.
Navigating the Map: A Guide to Understanding the Details
To effectively interpret the information presented on an Indiana topographic map, it is essential to understand the key elements:
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s slopes and valleys. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
- Elevation: The map typically includes a scale that indicates the elevation of different points on the map. This information allows users to determine the relative height of different areas.
- Land Features: The map identifies various land features, including rivers, lakes, forests, and urban areas. These elements provide context and help users understand the relationship between topography and human activity.
The Importance of a Topographic Map in Modern Times
While traditional paper maps are still valuable, the advent of digital mapping technologies has revolutionized the way we interact with topographic information. Online platforms and mobile applications provide interactive maps that allow users to explore the terrain in greater detail, navigate specific areas, and access real-time information such as weather conditions and traffic updates.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Indiana’s Topography
Q: What is the highest point in Indiana?
A: The highest point in Indiana is Hoosier Hill, located in the Crawford Upland, with an elevation of 1,257 feet (383 meters).
Q: What is the lowest point in Indiana?
A: The lowest point in Indiana is the Ohio River at the state’s southwestern border, with an elevation of 250 feet (76 meters).
Q: How does Indiana’s topography influence its climate?
A: Indiana’s topography plays a role in its climate by influencing air circulation patterns. The state’s elevation changes create variations in temperature and precipitation, with the higher elevations experiencing cooler temperatures and more rainfall.
Q: How does Indiana’s topography impact its agriculture?
A: The fertile soils of the Central Lowlands make Indiana a major agricultural producer. The state’s rolling hills and valleys provide ideal conditions for growing crops like corn, soybeans, and wheat.
Q: What are some of the challenges posed by Indiana’s topography?
A: Indiana’s topography can present challenges in areas like transportation and development. The rugged terrain of the Crawford Upland can make road construction and infrastructure development more difficult.
Tips for Using a Topographic Map
- Start with a general overview: Familiarize yourself with the overall layout of the map and the major land features.
- Focus on the contour lines: Pay close attention to the spacing and direction of the contour lines to understand the terrain’s slope and elevation changes.
- Use the elevation scale: Refer to the elevation scale to determine the height of specific points on the map.
- Combine with other information: Use the topographic map in conjunction with other resources, such as weather reports, road maps, and historical data, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the area.
Conclusion: A Deeper Appreciation for Indiana’s Land
The topographic map of Indiana serves as a powerful tool for understanding the state’s unique landscape and its intricate relationship with human activity. By revealing the subtle variations in elevation, the map provides insights into the state’s diverse ecosystems, settlement patterns, and infrastructure development. Through the lens of this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the natural beauty and the historical significance of Indiana’s diverse terrain.
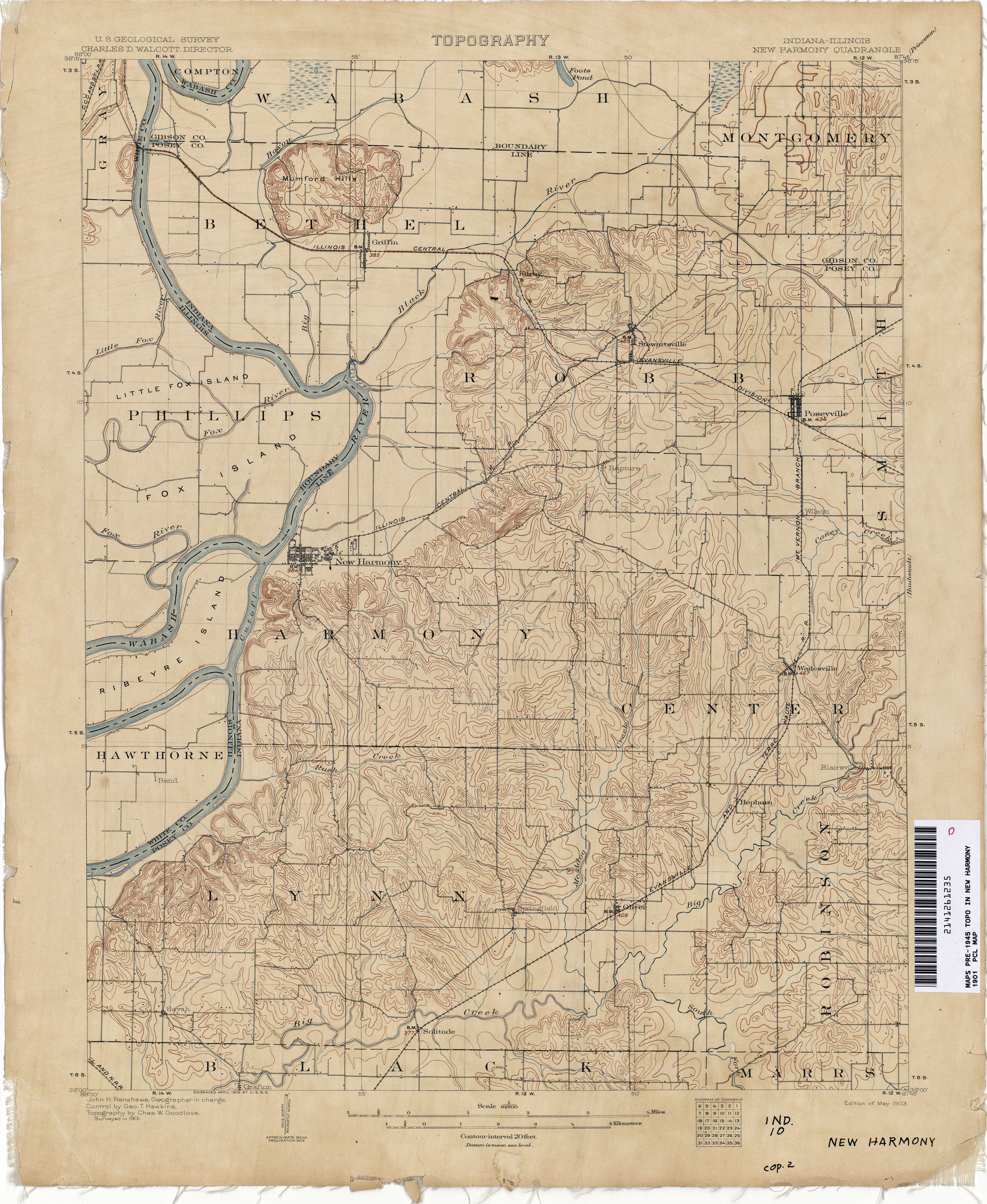
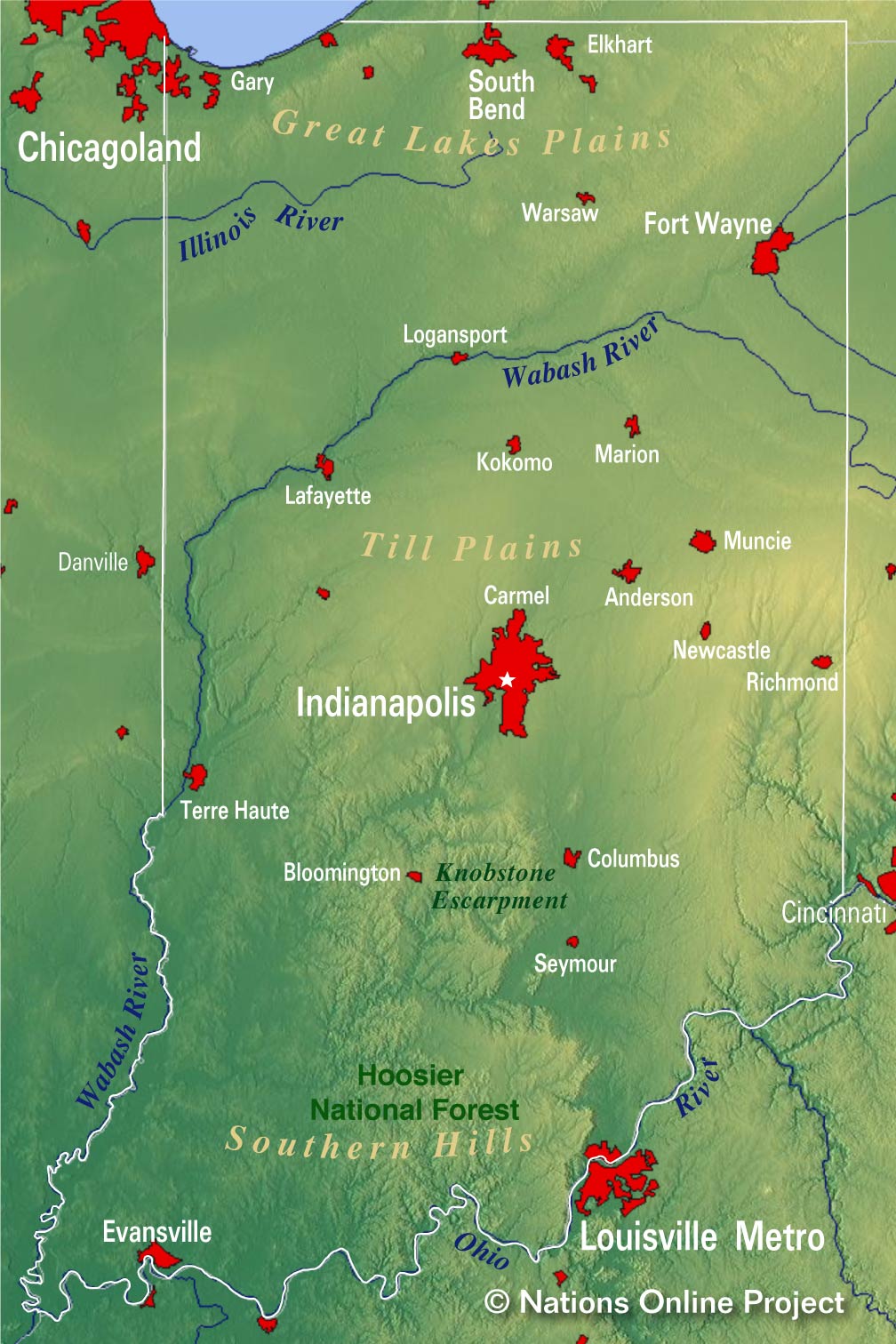
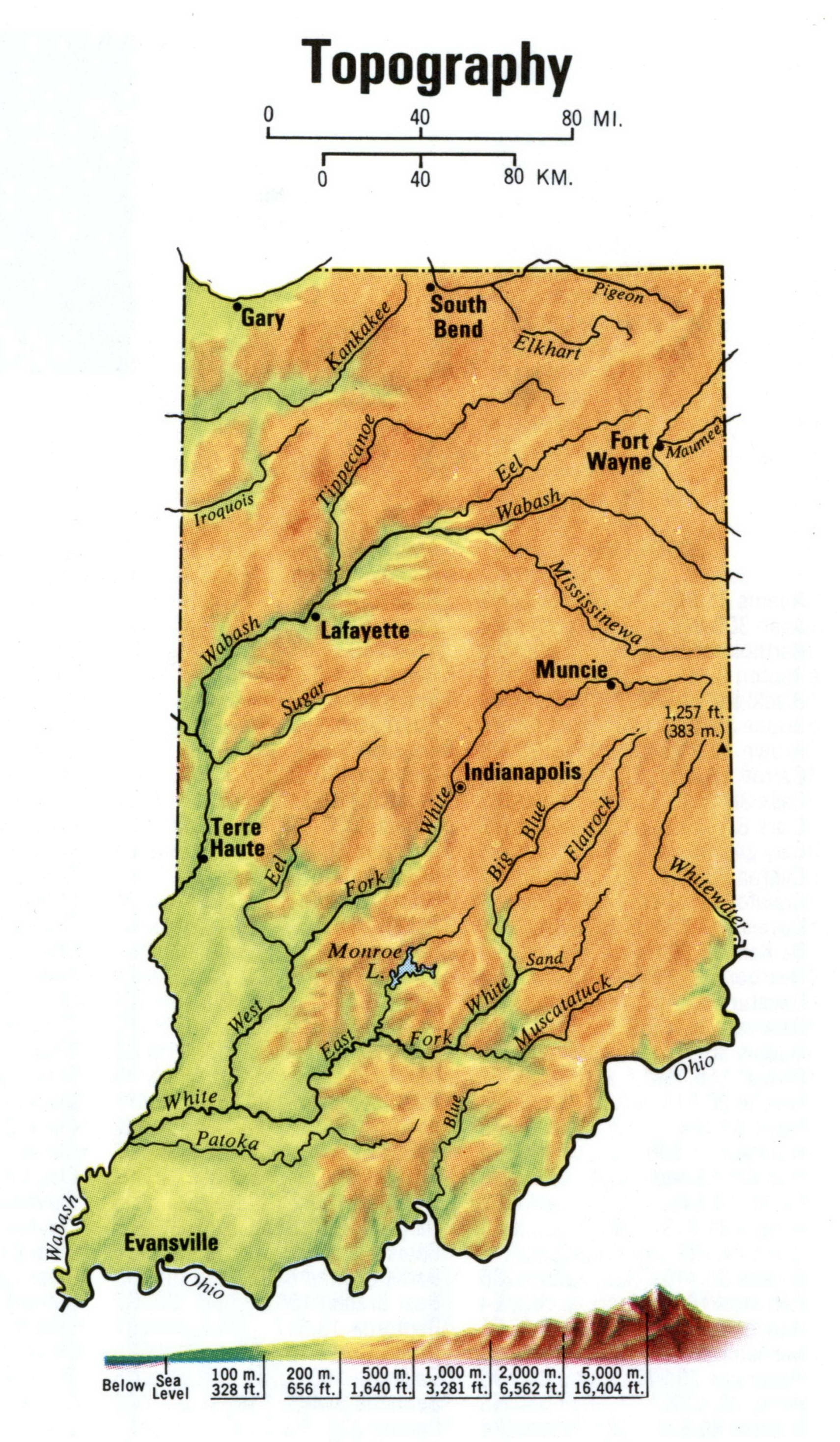



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Land of Indiana: A Topographic Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!