Unveiling The Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide To Indonesia’s Geographic Landscape
Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Indonesia’s Geographic Landscape
Related Articles: Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Indonesia’s Geographic Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Indonesia’s Geographic Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Indonesia’s Geographic Landscape

Indonesia, an archipelago nation spanning over 17,000 islands, boasts a captivating tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and biodiversity. Understanding its complex geography is crucial to appreciating its rich history, diverse ecosystems, and the challenges and opportunities it faces. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Indonesia’s geography, exploring its diverse terrain, natural resources, and the impact of its unique geographical features on its people and environment.
A Mosaic of Islands: The Geographic Framework of Indonesia
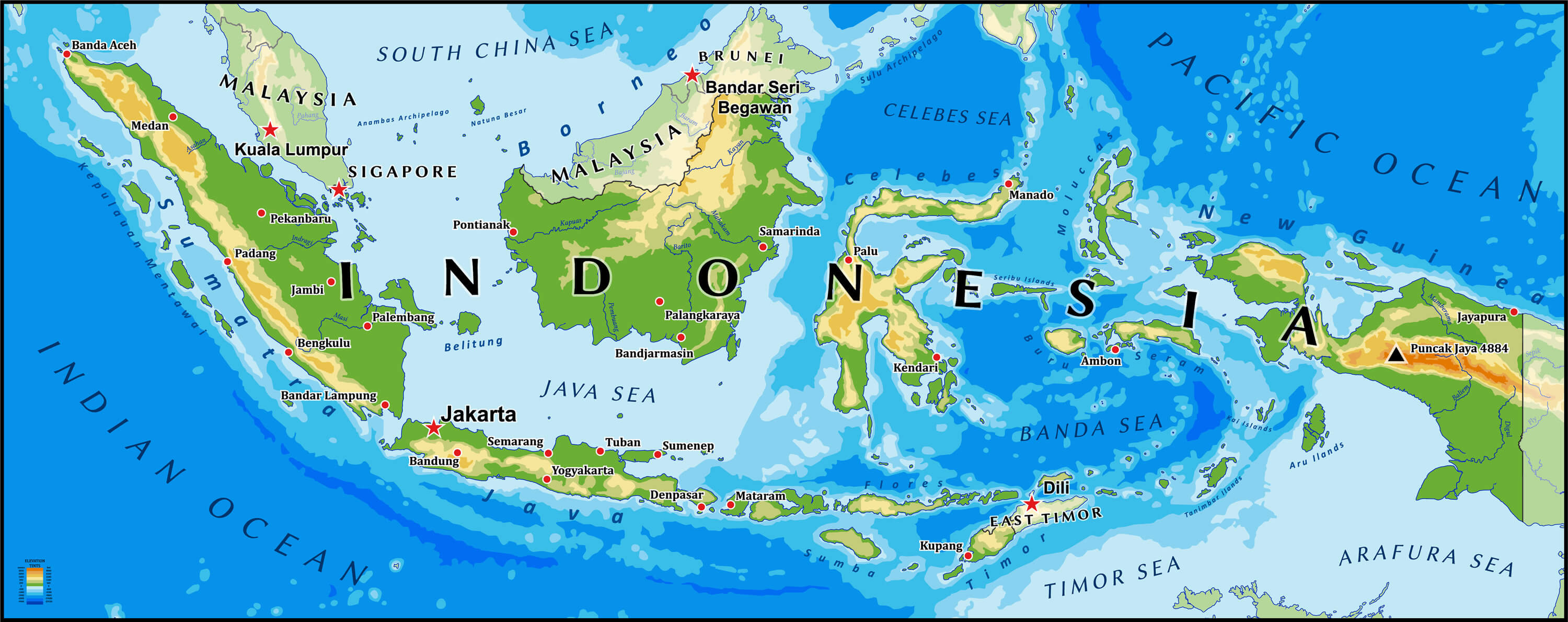
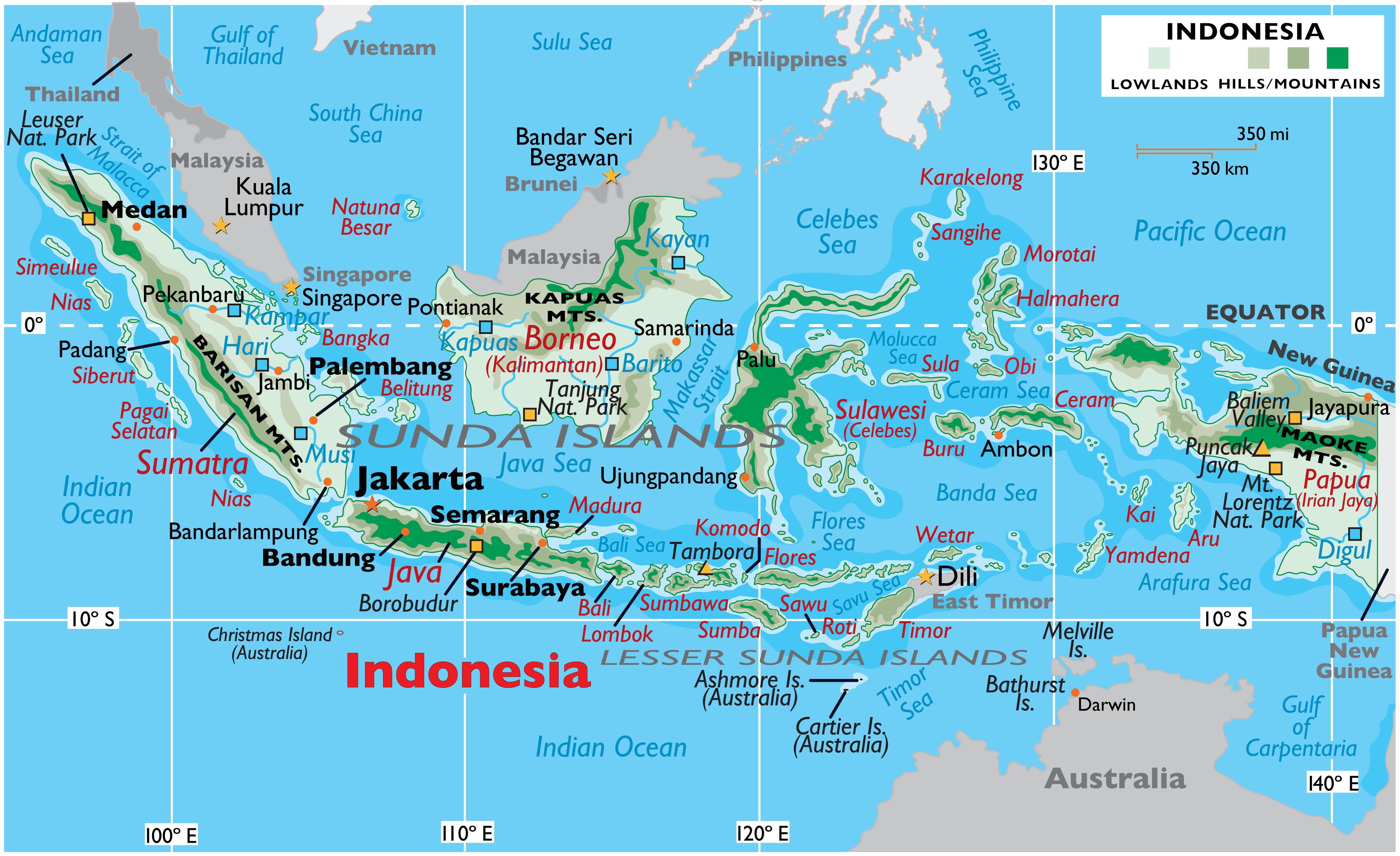
Indonesia’s geographical position, straddling the equator and nestled between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, plays a pivotal role in shaping its climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscape. The nation’s vast archipelago can be broadly categorized into five main island groups:
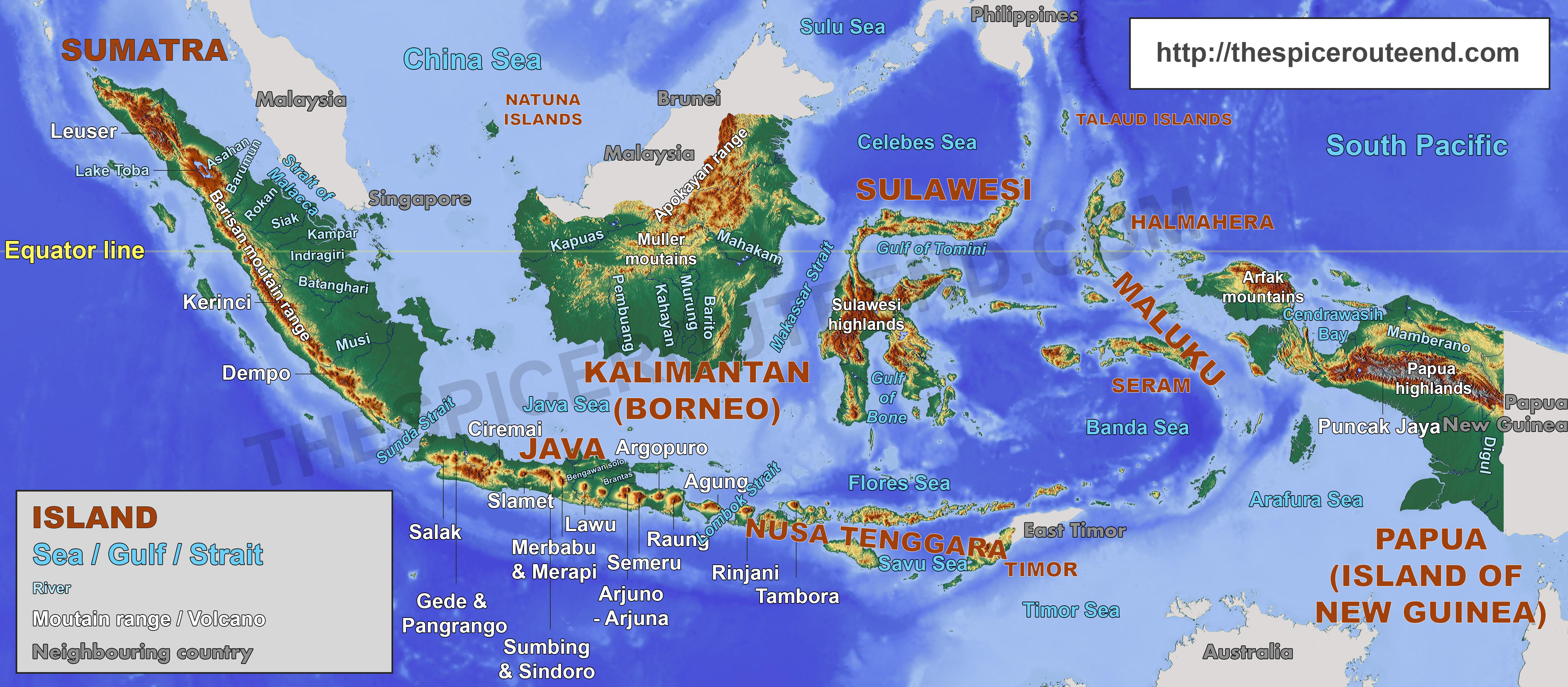
- Sumatra: The westernmost and sixth-largest island globally, Sumatra is known for its dense rainforests, active volcanoes, and rich biodiversity. Its eastern coastline is dominated by the Barisan Mountains, while its western coast faces the Indian Ocean.
- Java: The most populous island in the world, Java is a densely populated landmass dominated by volcanic mountains and fertile plains. It is home to the capital city, Jakarta, and boasts a rich cultural heritage.
- Kalimantan (Borneo): The third-largest island globally, Kalimantan is divided between Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei. Its vast rainforests, rich in biodiversity, are a vital carbon sink and home to indigenous communities.
- Sulawesi: Shaped like a human hand, Sulawesi is characterized by its mountainous terrain, numerous bays and peninsulas, and a unique biodiversity. It is home to several endemic species and is known for its vibrant cultural heritage.
- Irian Jaya (New Guinea): The second-largest island globally, Irian Jaya is divided between Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. Its rugged terrain, dense rainforests, and diverse ecosystems are home to unique indigenous cultures and a rich biodiversity.
Beyond the Islands: Exploring Indonesia’s Diverse Terrain
Indonesia’s diverse terrain extends beyond its islands, encompassing a wide range of landscapes, including:
- Volcanoes: Indonesia is home to over 150 active volcanoes, forming a significant part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. These volcanoes contribute to fertile soils, geothermal energy, and breathtaking natural beauty, but also pose significant risks due to eruptions and seismic activity.
- Mountains: The country is home to numerous mountain ranges, including the Jayawijaya Mountains in Irian Jaya, which boast the highest peak in Southeast Asia, Puncak Jaya. These mountains are vital for water resources, biodiversity, and tourism.
- Rainforests: Indonesia boasts vast rainforests, including the world’s third-largest rainforest in Kalimantan. These forests are crucial for biodiversity, climate regulation, and the livelihoods of indigenous communities.
- Coastal Areas: With thousands of kilometers of coastline, Indonesia possesses a vast network of beaches, estuaries, and coral reefs. These areas are crucial for fishing, tourism, and coastal ecosystems.
- Rivers: Indonesia’s network of rivers, including the Kapuas, Mahakam, and Musi Rivers, are vital for transportation, irrigation, and hydropower generation.
Natural Resources: A Bounty of Wealth
Indonesia’s diverse geography has endowed the nation with a wealth of natural resources, including:
- Minerals: The country is rich in mineral resources, including tin, nickel, copper, and gold. These resources are crucial for industrial development and economic growth.
- Oil and Gas: Indonesia is a significant producer of oil and gas, with reserves concentrated in Sumatra, Java, and Kalimantan. These resources play a crucial role in the country’s energy sector.
- Forests: Indonesia’s vast forests are a valuable resource for timber, pulp, and paper production. They also play a vital role in biodiversity conservation and climate regulation.
- Fisheries: With vast coastal areas and abundant marine life, Indonesia has a thriving fishing industry. This sector is crucial for food security and livelihoods.
- Agriculture: Indonesia’s fertile soils and tropical climate support a diverse agricultural sector, producing rice, palm oil, rubber, coffee, and other commodities.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Geographic Landscape
Indonesia’s unique geography presents both challenges and opportunities. Some of the key issues include:
- Natural Disasters: Due to its location in the Pacific Ring of Fire, Indonesia is prone to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and landslides. These natural disasters pose a significant threat to infrastructure, livelihoods, and human life.
- Environmental Degradation: Deforestation, pollution, and unsustainable land use practices are major environmental challenges facing Indonesia. These issues impact biodiversity, climate change, and the livelihoods of local communities.
- Transportation and Connectivity: The archipelago’s vast distances and fragmented geography pose challenges for transportation and connectivity. This can hinder economic development and social mobility.
- Resource Management: The abundance of natural resources also presents challenges in terms of sustainable management and equitable distribution. Overexploitation and environmental degradation pose risks to future generations.
Despite these challenges, Indonesia’s geography also presents opportunities:
- Tourism: Indonesia’s diverse landscapes, rich culture, and stunning natural beauty attract millions of tourists annually. This sector has the potential for significant economic growth and job creation.
- Renewable Energy: Indonesia’s abundant geothermal, solar, and wind resources offer opportunities for developing a sustainable energy sector. This can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Indonesia’s unique biodiversity offers opportunities for research, conservation, and sustainable development. This can contribute to global efforts to protect endangered species and ecosystems.
- Maritime Economy: With its vast coastline and strategic location, Indonesia has the potential to become a leading maritime nation. This can boost trade, transportation, and economic growth.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Indonesia’s Geography
Q: What is the significance of Indonesia’s location in the Pacific Ring of Fire?
A: Indonesia’s location in the Pacific Ring of Fire makes it prone to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis. While these events pose significant risks, they also contribute to fertile soils and geothermal energy resources.
Q: How does Indonesia’s geography impact its climate?
A: Indonesia’s equatorial location and vast archipelago result in a tropical climate characterized by high humidity, abundant rainfall, and consistent temperatures. This climate supports a diverse range of ecosystems and influences agricultural production.
Q: What are the main challenges faced by Indonesia in managing its natural resources?
A: Indonesia faces challenges in managing its vast natural resources, including deforestation, illegal mining, and overfishing. These issues threaten biodiversity, climate change, and the livelihoods of local communities.
Q: How does Indonesia’s geography impact its cultural diversity?
A: Indonesia’s fragmented geography has fostered a rich tapestry of cultures and traditions. The isolation of different islands and regions has allowed unique languages, customs, and beliefs to develop.
Q: What are the opportunities presented by Indonesia’s geography for future development?
A: Indonesia’s geography offers opportunities for sustainable tourism, renewable energy development, biodiversity conservation, and a thriving maritime economy. These sectors have the potential to contribute to economic growth and social development.
Tips: Navigating Indonesia’s Geographic Landscape
- Research and Plan: Before traveling to Indonesia, research the specific islands and regions you plan to visit, considering their unique geography, climate, and potential hazards.
- Be Prepared for Diverse Terrain: Pack appropriate clothing and footwear for different terrains, from beaches to mountains and rainforests.
- Respect Local Cultures: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, especially when visiting indigenous communities.
- Be Aware of Environmental Impacts: Practice responsible tourism and avoid activities that contribute to environmental degradation.
- Stay Informed about Natural Disasters: Monitor weather forecasts and official advisories regarding potential natural disasters.
Conclusion: A Land of Contrasts and Potential
Indonesia’s vast archipelago, with its diverse terrain, natural resources, and vibrant cultures, presents a fascinating case study in the interplay of geography and human development. The challenges and opportunities presented by its unique landscape are intertwined, demanding careful consideration and sustainable practices. Understanding the complex geography of Indonesia is crucial for appreciating its rich heritage, navigating its challenges, and harnessing its potential for a sustainable future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Indonesia’s Geographic Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!