Unveiling Indonesia’s Spatial Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis Of The PT Map
Unveiling Indonesia’s Spatial Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of the PT Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Indonesia’s Spatial Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of the PT Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Indonesia’s Spatial Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of the PT Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Indonesia’s Spatial Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of the PT Map

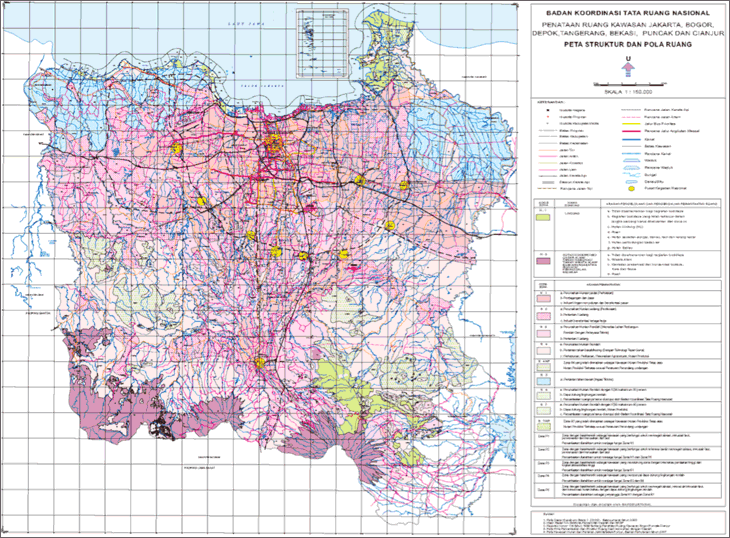
Indonesia, a vast archipelago nation sprawling across a multitude of islands, presents a complex and intricate spatial landscape. Understanding this landscape is crucial for effective planning, development, and management of its diverse resources. The "PT Map," or "Peta Tematik," a thematic map, serves as a vital tool for navigating and interpreting this complexity, offering a comprehensive and layered perspective on Indonesia’s geography, environment, and socio-economic characteristics.
The Essence of the PT Map: A Multifaceted View
The PT Map transcends the limitations of a simple geographical representation. It goes beyond mere lines and boundaries, incorporating thematic layers that reveal the intricate interplay of various factors shaping Indonesia’s landscape. These layers encompass a wide spectrum of information, including:
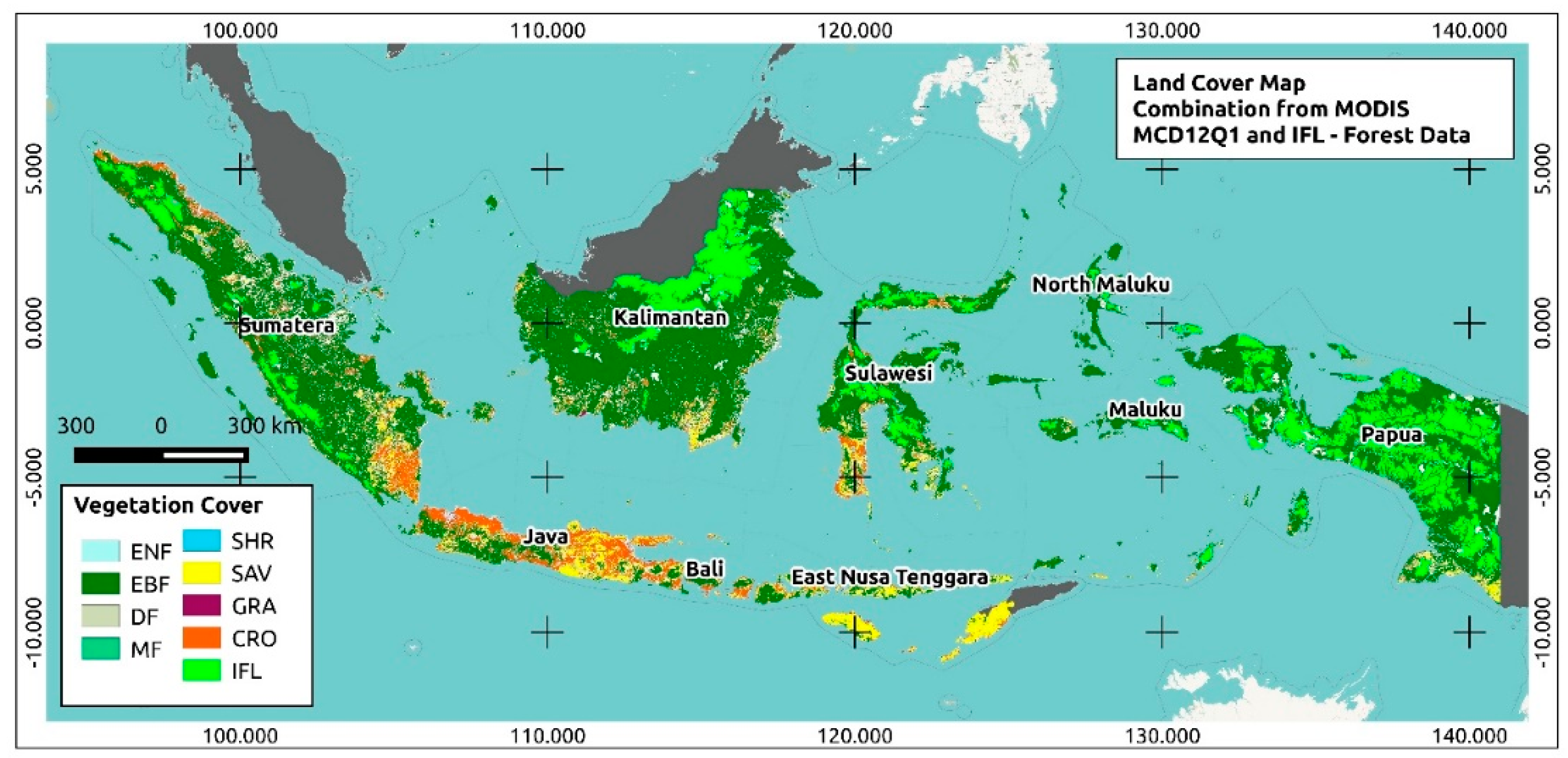
- Physical Geography: Elevations, terrain, land cover, and hydrological features provide a foundation for understanding the natural environment.
- Climate and Weather: Rainfall patterns, temperature variations, and seasonal shifts highlight the influence of climate on the country’s diverse ecosystems.
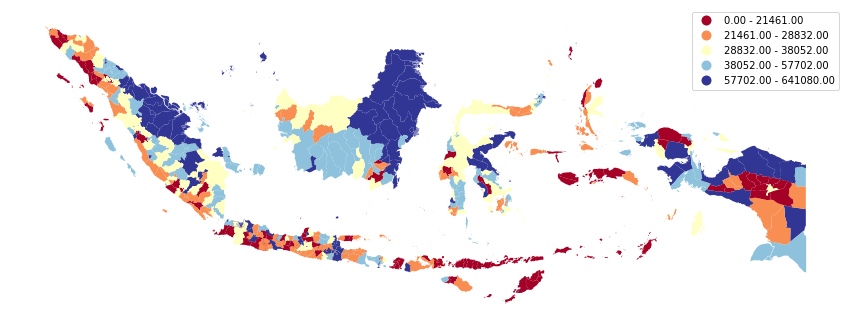
- Population Distribution: Demographics, population density, and urban centers offer insights into human settlement patterns and their impact on the environment.
- Infrastructure: Road networks, transportation hubs, and communication infrastructure showcase the connectivity and accessibility of different regions.
- Economic Activity: Agricultural zones, mining areas, industrial hubs, and tourism hotspots illuminate the economic landscape and its spatial distribution.
- Environmental Resources: Forests, wetlands, protected areas, and natural resources provide a framework for understanding the ecological value and vulnerabilities of different regions.
- Social and Cultural Indicators: Language, ethnicity, religion, and cultural heritage offer a nuanced understanding of the diverse communities inhabiting Indonesia.
Beyond Visualization: The Power of Data Integration
The PT Map is more than just a visual representation. It serves as a platform for integrating diverse datasets, enabling analysis and decision-making based on a holistic understanding of spatial relationships. This integration allows for:
- Spatial Analysis: Identifying patterns, trends, and correlations between different thematic layers, revealing hidden relationships and insights.
- Resource Management: Optimizing resource allocation and utilization based on spatial distribution and accessibility.
- Disaster Preparedness: Assessing vulnerability and risk factors, enabling proactive planning and mitigation strategies for natural hazards.
- Infrastructure Development: Planning and prioritizing infrastructure projects based on spatial needs and connectivity.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracking changes in land cover, deforestation, and pollution, providing data for informed conservation efforts.
The PT Map: A Foundation for Sustainable Development
The PT Map serves as a cornerstone for sustainable development in Indonesia, enabling informed decision-making across various sectors. Its applications span:
- Land Use Planning: Optimizing land use for agriculture, urban development, and conservation based on environmental and social considerations.
- Natural Resource Management: Managing water resources, forests, and mineral reserves sustainably, balancing economic needs with ecological integrity.
- Urban Planning: Designing sustainable cities that prioritize accessibility, public transportation, and environmental sustainability.
- Environmental Protection: Identifying areas of high biodiversity, ecological sensitivity, and pollution hotspots, guiding conservation and remediation efforts.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: Mapping areas prone to earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, and other hazards, enabling proactive risk mitigation strategies.
FAQs about the PT Map
1. What are the different types of PT Maps available for Indonesia?
The PT Map encompasses a wide range of thematic maps, each focusing on specific aspects of the landscape. Examples include:
- Land Cover Map: Depicting different land cover types like forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
- Soil Map: Showing soil types and their suitability for different agricultural activities.
- Climate Map: Representing temperature, rainfall, and other climatic variables.
- Population Density Map: Illustrating population distribution across different regions.
- Infrastructure Map: Displaying road networks, transportation hubs, and communication infrastructure.
- Environmental Impact Map: Highlighting areas affected by pollution, deforestation, and other environmental stressors.
2. How can I access the PT Map for Indonesia?
The PT Map is available through various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: The Indonesian Ministry of Environment and Forestry (KLHK) and the National Geographic Agency (BIG) are primary sources for PT Maps.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research institutions often develop and disseminate PT Maps for specific research purposes.
- Online Platforms: Several online platforms offer access to PT Maps, including the Indonesian Geospatial Portal and the Global Land Cover Facility.
3. How is the PT Map updated and maintained?
The PT Map is constantly updated and maintained through a combination of:
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide data for mapping land cover, vegetation, and other features.
- Ground Truthing: Field surveys and data collection validate and refine the information obtained from remote sensing.
- Collaboration: Partnerships between government agencies, research institutions, and private organizations ensure ongoing data collection and updates.
4. What are the limitations of the PT Map?
While the PT Map offers valuable insights, it is important to acknowledge its limitations:
- Data Availability: Data availability and accuracy can vary across different regions and thematic layers.
- Spatial Resolution: The level of detail provided by the PT Map can be limited by the spatial resolution of the data used.
- Temporal Variability: The PT Map represents a snapshot in time, and changes in the landscape can occur over time.
- Interpretation: The interpretation of the PT Map requires expertise and understanding of the data and its limitations.
Tips for Using the PT Map
- Understand the Data Sources: Familiarize yourself with the data sources and their limitations before interpreting the PT Map.
- Consider the Spatial Scale: The PT Map can be used at different scales, from regional to local, affecting the level of detail and analysis.
- Integrate with Other Data: Combine the PT Map with other datasets, such as socio-economic data or environmental monitoring data, for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Consult with Experts: Seek guidance from experts in relevant fields to ensure accurate interpretation and informed decision-making.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for a Sustainable Future
The PT Map is a powerful tool for understanding and navigating Indonesia’s complex spatial landscape. It serves as a foundation for informed decision-making in various sectors, promoting sustainable development and resource management. By integrating diverse data, facilitating spatial analysis, and fostering collaboration, the PT Map empowers Indonesia to address its challenges and build a brighter future. Its ongoing development and accessibility ensure its continued relevance as a vital resource for navigating the complexities of Indonesia’s unique and dynamic landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Indonesia’s Spatial Landscape: A Comprehensive Analysis of the PT Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!