Unveiling Indiana’s Landscape: A Comprehensive Look At The State’s Topography
Unveiling Indiana’s Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Topography
Related Articles: Unveiling Indiana’s Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Topography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Indiana’s Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Indiana’s Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Topography

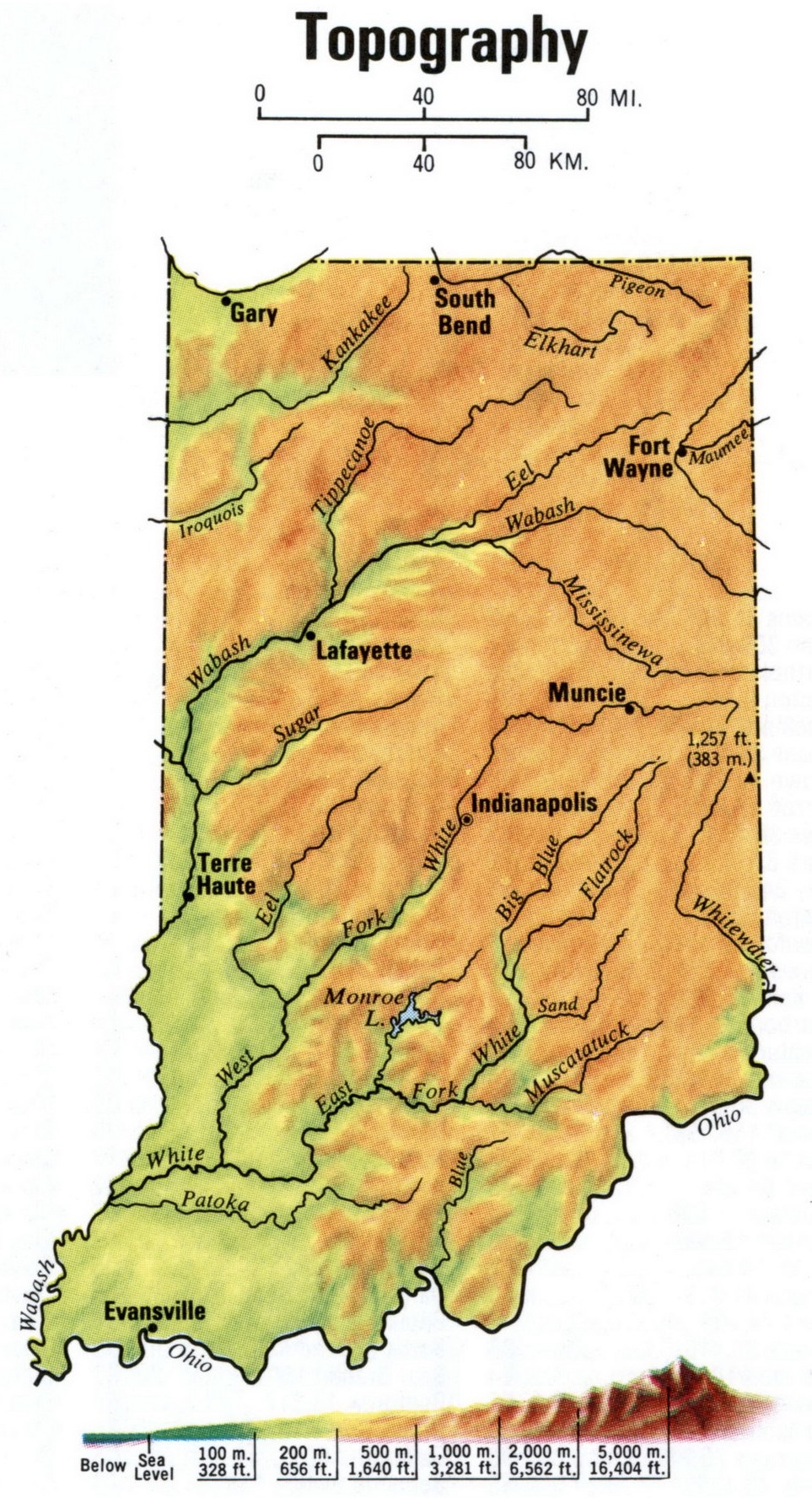
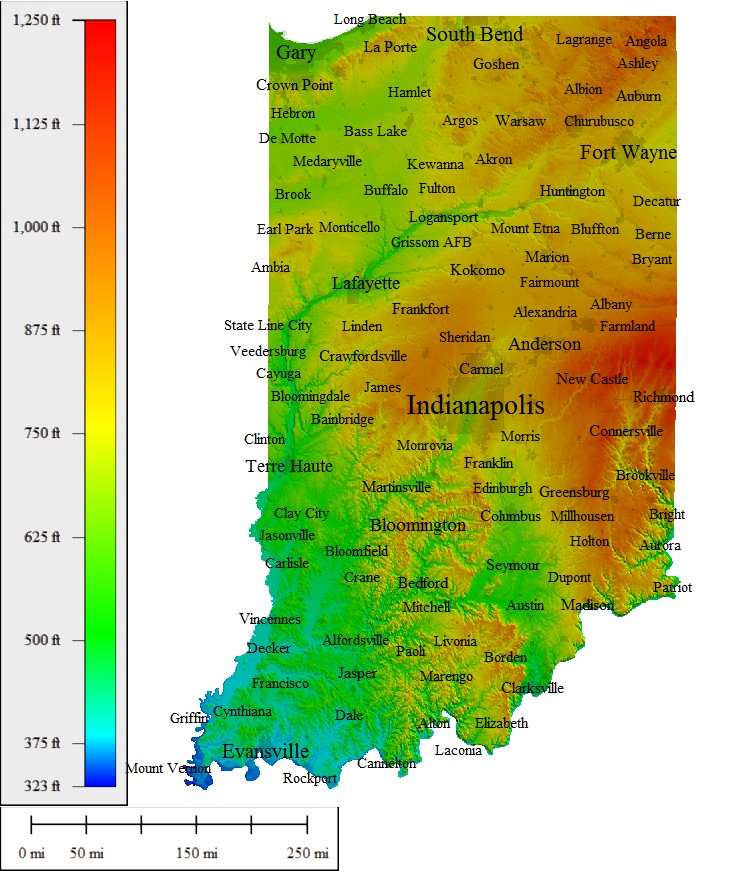
Indiana, nestled in the heart of the American Midwest, boasts a diverse and captivating landscape that is best understood through the lens of its topographical map. This intricate representation of the state’s elevation, landforms, and water features provides a valuable tool for comprehending the physical characteristics that shape Indiana’s natural beauty, environmental dynamics, and human settlements.
Navigating the Terrain: A Geographical Overview
Indiana’s topography is characterized by a gentle, rolling landscape, with elevations ranging from a low of 258 feet above sea level in the Wabash River valley to a high of 1,257 feet at the state’s highest point, Hoosier Hill. This relatively low elevation difference, coupled with the dominance of the central lowlands, contributes to the state’s predominantly flat to gently undulating terrain. However, this seemingly uniform landscape conceals a fascinating tapestry of diverse geographical features.
The Defining Features: Landforms and Waterbodies
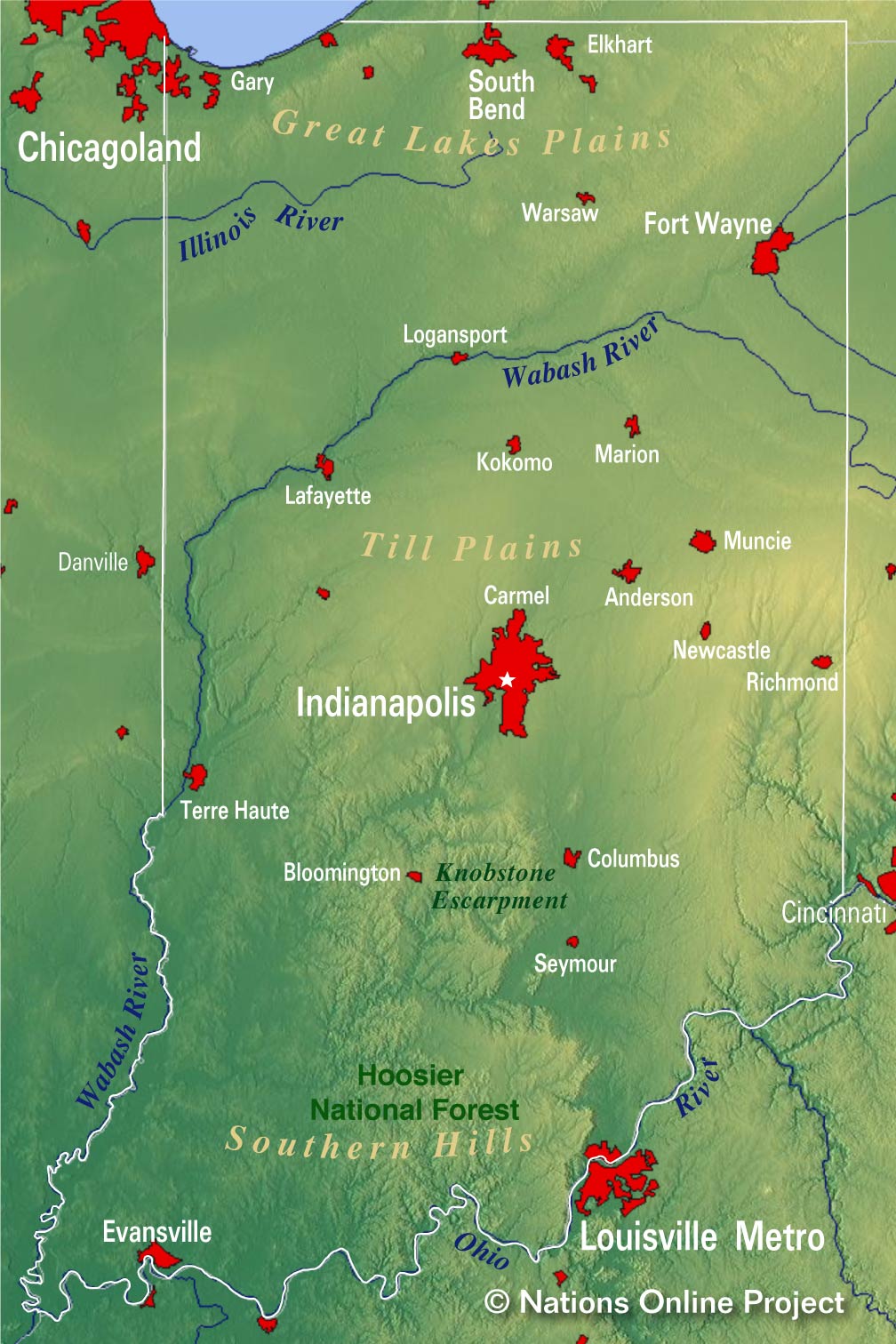
1. The Physiographic Regions: The state’s topography is further defined by its distinct physiographic regions, each possessing its own unique characteristics:
- The Interior Low Plateau: Occupying the central and southern portions of the state, this region is characterized by gently rolling hills, deeply incised valleys, and numerous sinkholes. The presence of karst topography, formed by the dissolution of soluble bedrock, contributes to the region’s distinctive landscape.
- The Central Lowland: This region, encompassing the majority of Indiana’s northern and western areas, features a relatively flat to gently rolling plain. The presence of glacial deposits and outwash plains, remnants of past ice ages, contributes to the region’s fertile soil and agricultural productivity.
- The Eastern Highland Rim: Located in the southeastern corner of the state, this region is marked by a higher elevation and a more rugged landscape, with steep hills and narrow valleys. The presence of Paleozoic sedimentary rocks contributes to the region’s rich fossil record.
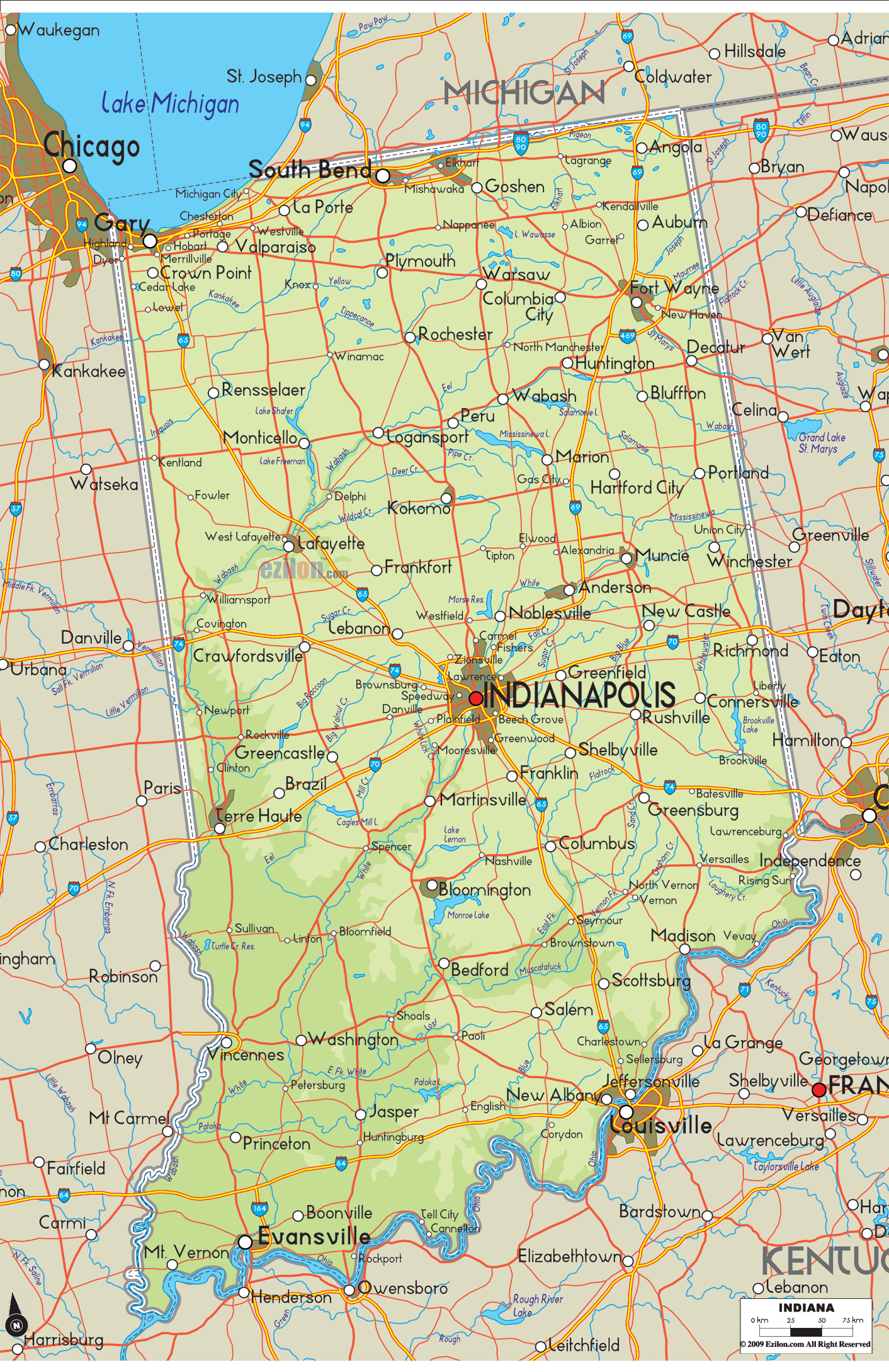
2. The Rivers and Streams: A network of rivers and streams crisscrosses Indiana, playing a crucial role in shaping its landscape and providing vital transportation corridors. The state’s major rivers, including the Wabash, Ohio, White, and East Fork White rivers, have carved out valleys and floodplains that are essential for agriculture and urban development.
3. The Lakes and Wetlands: While not as prominent as in other states, Indiana boasts a number of lakes and wetlands, adding to its diverse ecological tapestry. Glacial lakes, such as Lake Wawasee and Lake James, offer recreational opportunities, while wetlands, such as the Kankakee River marshes, provide vital habitats for numerous species.
4. The Karst Topography: In the southern and central portions of the state, the presence of soluble bedrock, primarily limestone and dolomite, has led to the formation of karst topography. This unique landscape is characterized by sinkholes, caves, and underground streams, contributing to the state’s diverse and sometimes hidden geological features.
Understanding the Importance: The Benefits of Topographical Maps
The topographical map of Indiana serves as a vital tool for understanding the state’s physical characteristics and their implications for various aspects of life:
1. Environmental Management: Topographical maps provide valuable insights into the distribution of natural resources, such as water, soil, and minerals. This information is crucial for effective environmental management, including water resource planning, soil conservation, and land use regulation.
2. Infrastructure Development: The map’s depiction of elevation, slopes, and drainage patterns is essential for planning and designing infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and pipelines. Understanding the terrain allows for efficient and sustainable development, minimizing environmental impact.
3. Agriculture and Forestry: The map’s representation of soil types, drainage patterns, and elevation is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices and forestry management. This information helps farmers make informed decisions regarding crop selection, irrigation, and soil conservation, while foresters utilize it for planning reforestation and managing timber resources.
4. Recreation and Tourism: Topographical maps are essential for planning outdoor recreational activities, such as hiking, biking, and camping. They provide information about trails, elevations, and potential hazards, ensuring safe and enjoyable experiences for visitors.
5. Emergency Response: During natural disasters, such as floods or earthquakes, topographical maps play a crucial role in guiding emergency response efforts. They provide information about potential flood zones, evacuation routes, and accessibility, enabling efficient rescue and relief operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the highest point in Indiana?
The highest point in Indiana is Hoosier Hill, located in the southeastern portion of the state, with an elevation of 1,257 feet above sea level.
2. What is the lowest point in Indiana?
The lowest point in Indiana is located in the Wabash River valley, with an elevation of 258 feet above sea level.
3. What are the major rivers in Indiana?
The major rivers in Indiana include the Wabash, Ohio, White, and East Fork White rivers.
4. What are the different physiographic regions of Indiana?
Indiana is divided into three major physiographic regions: the Interior Low Plateau, the Central Lowland, and the Eastern Highland Rim.
5. What are the key features of karst topography in Indiana?
Karst topography in Indiana is characterized by sinkholes, caves, and underground streams, formed by the dissolution of soluble bedrock, primarily limestone and dolomite.
Tips for Understanding Topographical Maps
1. Understand the Map’s Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the standard symbols used on topographical maps, such as contour lines, elevation points, and water features.
2. Analyze Contour Lines: Contour lines represent points of equal elevation. By studying their spacing and patterns, you can visualize the shape of the terrain and identify slopes, valleys, and ridges.
3. Interpret Elevation Data: Elevation points and contour lines provide information about the height of the land. This data is essential for understanding the overall topography and identifying potential hazards.
4. Identify Drainage Patterns: Rivers, streams, and lakes are depicted on topographical maps. Analyze their location and flow patterns to understand the drainage system and potential flood risks.
5. Utilize Online Resources: Numerous online resources, such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS) website, provide access to topographical maps and data, allowing for further exploration and analysis.
Conclusion
The topographical map of Indiana offers a fascinating glimpse into the state’s physical landscape, revealing its diverse terrain, unique landforms, and intricate water features. By understanding the information presented on these maps, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the state’s natural beauty, its environmental dynamics, and the challenges and opportunities presented by its topography. From guiding infrastructure development to informing environmental management practices, topographical maps serve as an invaluable tool for understanding and interacting with Indiana’s captivating landscape.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Indiana’s Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Topography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!