Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: The SMAP Mission And Its Contributions To Understanding Our Planet
Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: The SMAP Mission and its Contributions to Understanding Our Planet
Related Articles: Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: The SMAP Mission and its Contributions to Understanding Our Planet
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: The SMAP Mission and its Contributions to Understanding Our Planet. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: The SMAP Mission and its Contributions to Understanding Our Planet

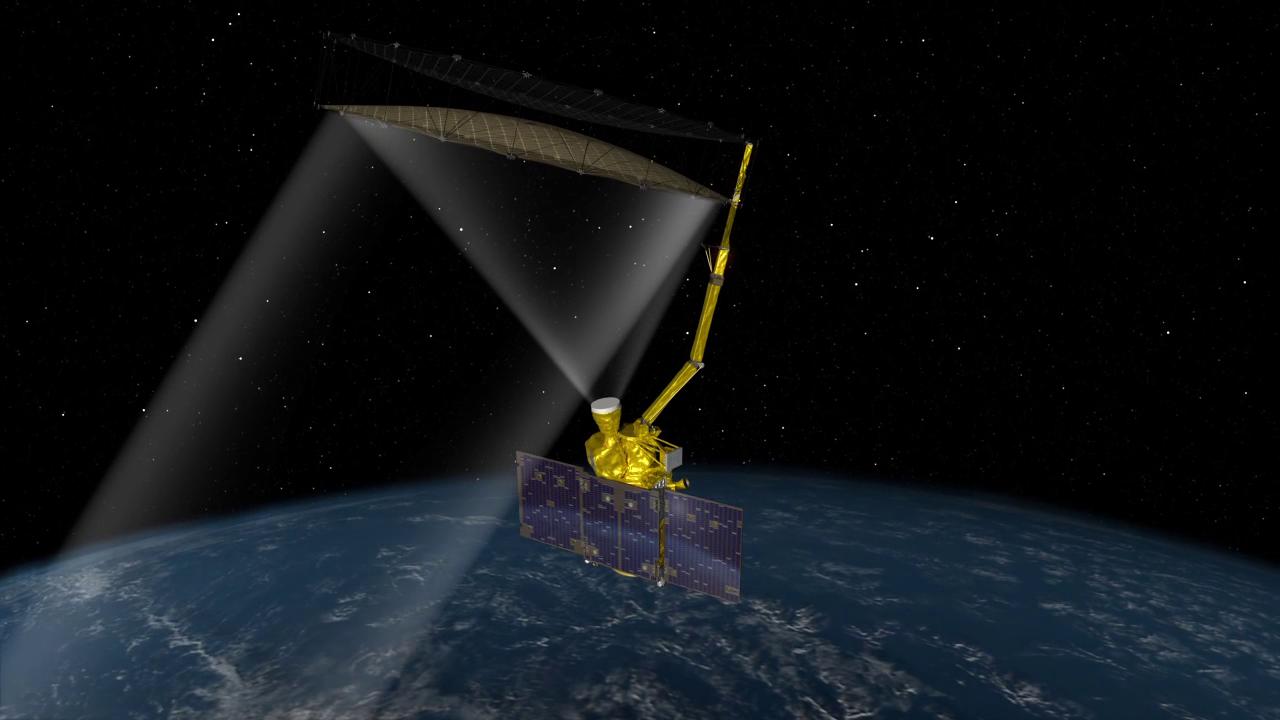
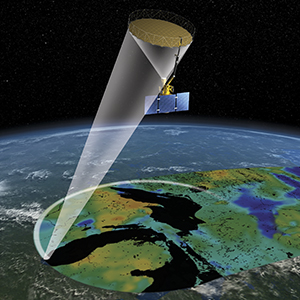
The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, a collaborative effort between NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and the University of California, Irvine, was a groundbreaking endeavor in Earth observation. Launched in January 2014, SMAP’s primary objective was to provide global, high-resolution measurements of soil moisture and freeze/thaw state. This data proved invaluable for understanding a wide range of Earth processes, including the global water cycle, climate change, and agricultural productivity.
SMAP’s Unique Approach: A Fusion of Active and Passive Sensing
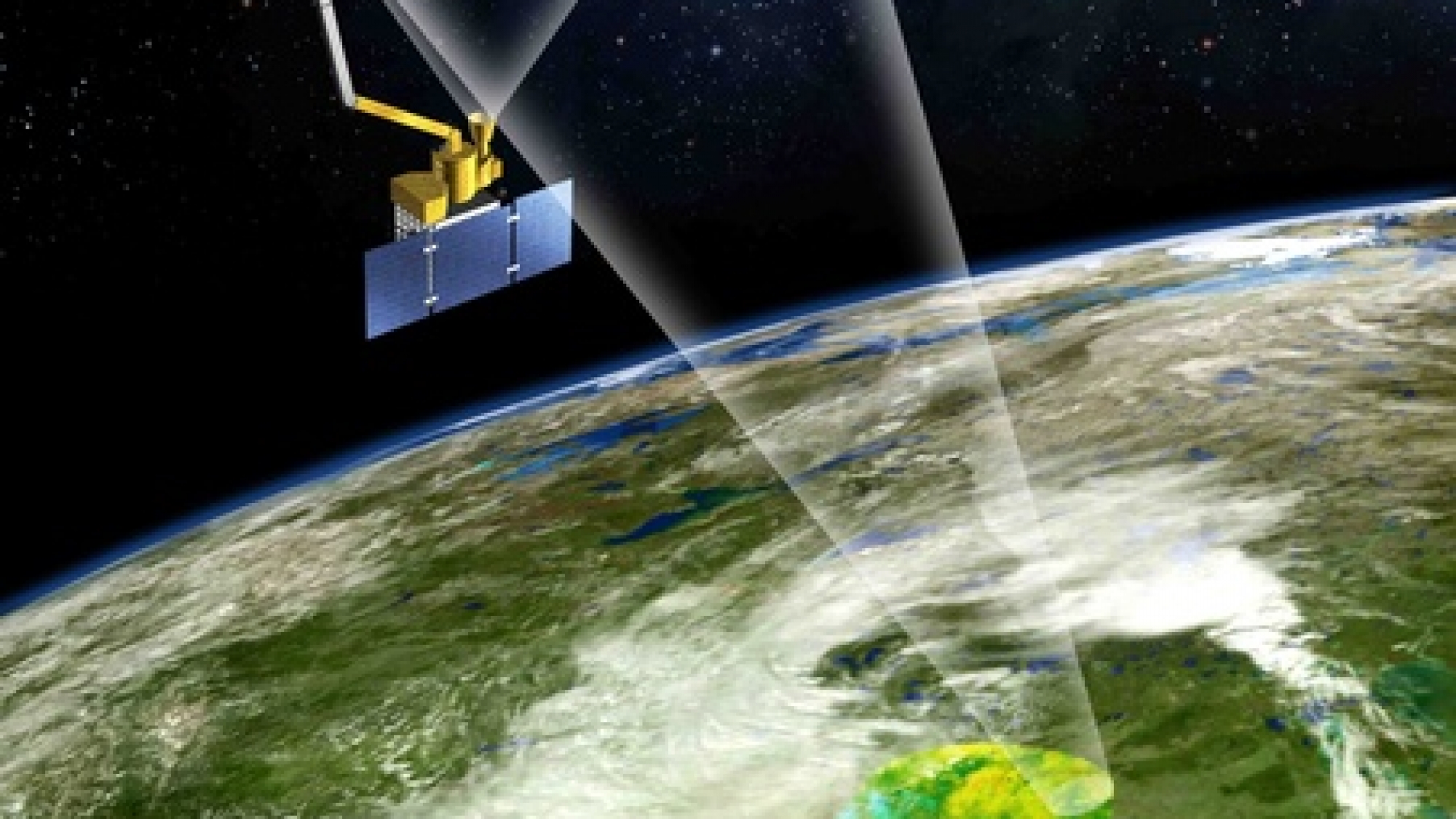
SMAP’s innovative design incorporated both active and passive microwave sensing techniques, allowing for comprehensive and detailed observations. The active sensor, a radar instrument, emitted microwaves towards the Earth’s surface and measured the reflected signal. This provided information about the surface roughness and the presence of liquid water in the soil.
Simultaneously, the passive sensor, a radiometer, measured the naturally emitted microwave radiation from the Earth’s surface. This allowed for the determination of soil moisture content and the identification of frozen ground. By combining these two techniques, SMAP provided a more complete picture of soil moisture dynamics than any previous mission.
A Multifaceted Impact: From Water Cycle Understanding to Climate Change Monitoring
SMAP’s data has significantly advanced our understanding of the Earth’s water cycle, a crucial element in global climate systems. Soil moisture plays a critical role in regulating evaporation and transpiration, influencing precipitation patterns and water availability. SMAP’s high-resolution measurements provided unprecedented insights into these processes, enabling scientists to better model and predict water resource availability, drought conditions, and flood risks.
Beyond the water cycle, SMAP’s data has also contributed to our understanding of climate change. Soil moisture is a key factor in regulating the Earth’s energy balance, influencing the amount of solar radiation absorbed and reflected by the surface. SMAP’s measurements provided valuable data for monitoring changes in soil moisture patterns and their impact on climate variability.
Applications Beyond Science: Supporting Agriculture and Disaster Management
SMAP’s data has also found practical applications in various sectors, particularly in agriculture and disaster management. Farmers can utilize SMAP’s soil moisture data to optimize irrigation schedules, improving water use efficiency and reducing water consumption. This is particularly crucial in regions facing water scarcity.
SMAP’s data has also been used to monitor drought conditions and predict potential crop failures, enabling timely intervention and mitigating agricultural losses. In disaster management, SMAP’s freeze/thaw data has proven useful in assessing the risk of landslides and avalanches, helping to improve preparedness and response efforts.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about SMAP
Q: What is the significance of measuring soil moisture?
A: Soil moisture is a crucial variable in understanding the Earth’s water cycle, climate change, and agricultural productivity. It influences evaporation rates, precipitation patterns, water availability, and plant growth.
Q: How does SMAP’s data benefit agriculture?
A: SMAP’s soil moisture data helps farmers optimize irrigation schedules, leading to improved water use efficiency and reduced water consumption. It also assists in monitoring drought conditions and predicting potential crop failures.
Q: What are the limitations of SMAP’s data?
A: SMAP’s data is primarily focused on surface soil moisture, with limited information about deeper soil layers. Additionally, the data is affected by factors like vegetation cover and topography.
Q: What is the future of soil moisture monitoring?
A: Future soil moisture monitoring missions will likely focus on developing higher-resolution sensors, extending coverage to deeper soil layers, and integrating data from multiple sources to improve accuracy and understanding.
Tips for Using SMAP Data
- Understand the data limitations: SMAP data is primarily focused on surface soil moisture and is affected by factors like vegetation cover and topography.
- Utilize data visualization tools: Visualizing SMAP data can help identify patterns and trends, facilitating better understanding and analysis.
- Combine SMAP data with other datasets: Integrating SMAP data with other relevant datasets, such as meteorological data, can provide a more comprehensive picture of the studied phenomena.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Scientific Advancements and Practical Applications
The SMAP mission, while concluding in 2018, left behind a legacy of scientific advancements and practical applications. Its data has significantly advanced our understanding of the Earth’s water cycle, climate change, and agricultural productivity. SMAP’s legacy continues to inspire future missions and research, driving further exploration and understanding of our planet. As we continue to face challenges related to climate change and water resource management, the insights gained from SMAP will remain invaluable for informing policy decisions and developing sustainable solutions.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Earth’s Secrets: The SMAP Mission and its Contributions to Understanding Our Planet. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!