Unraveling The Landscape: A Comprehensive Look At Jamaica’s Topographical Map
Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Jamaica’s Topographical Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Jamaica’s Topographical Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Jamaica’s Topographical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Jamaica’s Topographical Map

Jamaica, the island nation nestled in the Caribbean Sea, boasts a diverse and captivating landscape. Its topography, a tapestry woven with rolling hills, rugged mountains, fertile valleys, and sprawling coastlines, is a crucial factor shaping its unique ecosystem, cultural heritage, and economic development. This article delves into the intricacies of Jamaica’s topographical map, exploring its significance in understanding the island’s physical characteristics, natural resources, and human interactions with the environment.
A Tapestry of Elevation: Unveiling the Island’s Structure
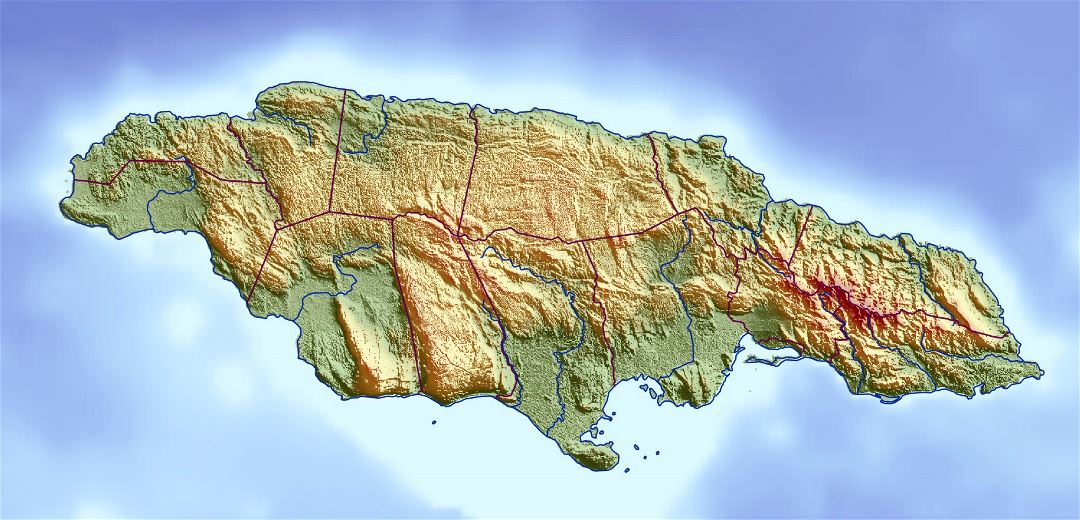
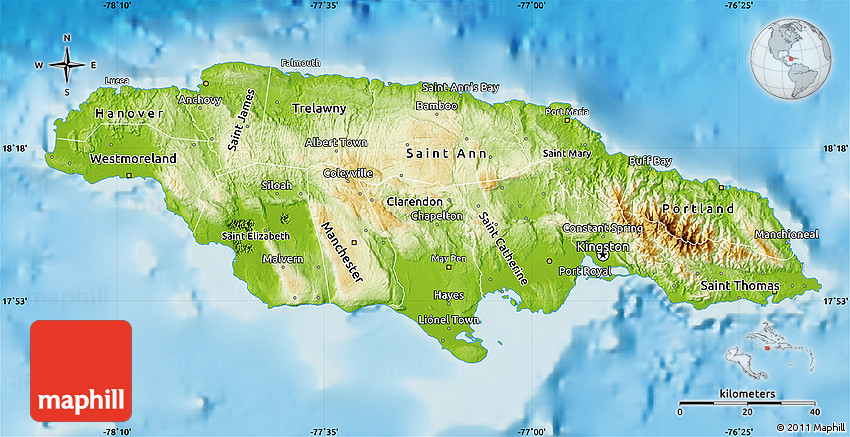
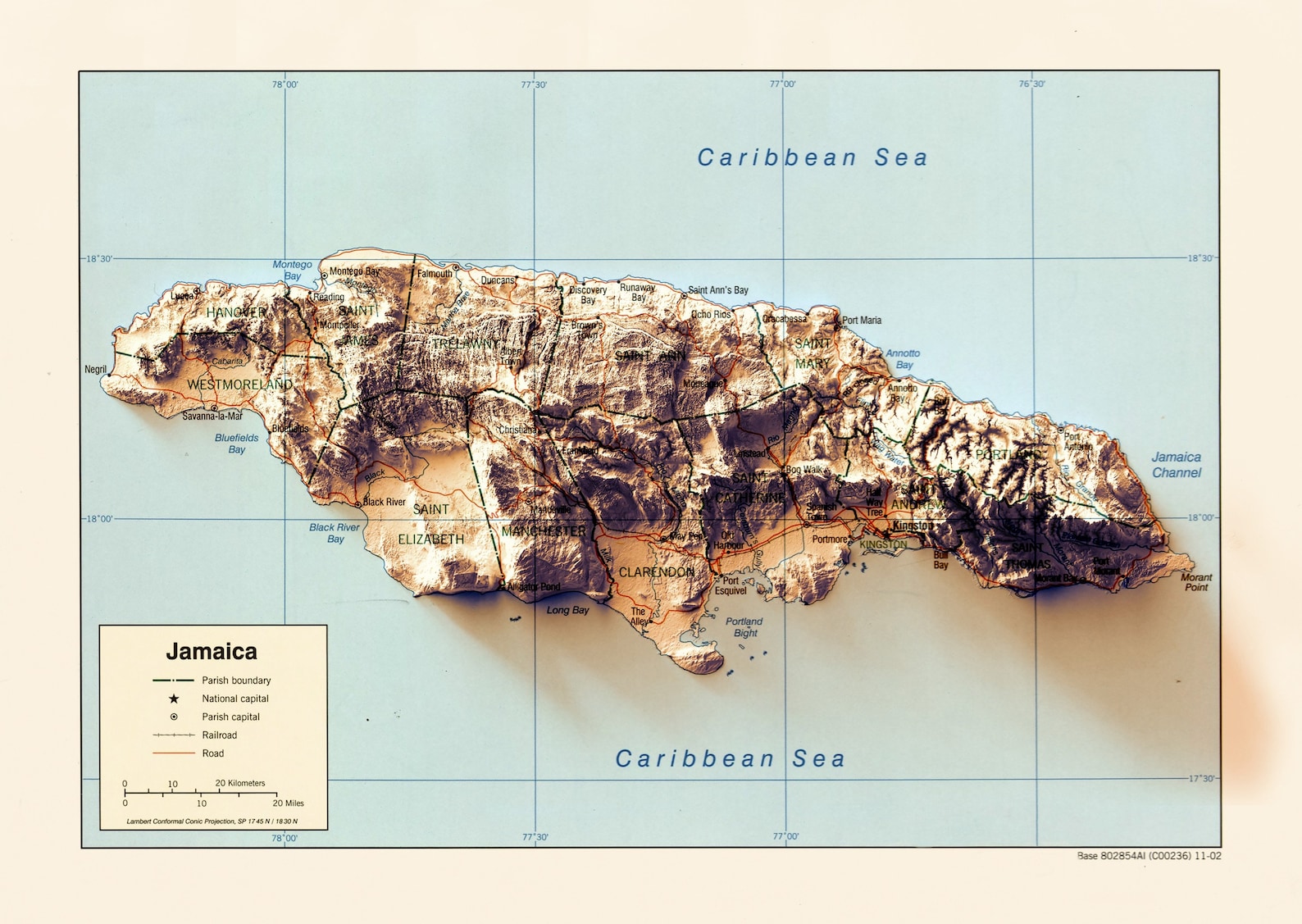
Jamaica’s topographical map, a visual representation of its elevation and landforms, reveals a fascinating interplay of geological forces. The island’s central spine, the Blue Mountain range, dominates the landscape, culminating in the majestic Blue Mountain Peak, the highest point in the Caribbean at 2,256 meters. This range, formed by volcanic activity millions of years ago, acts as a natural watershed, influencing rainfall patterns and the distribution of vegetation.
Moving westward, the island’s topography transitions into the Cockpit Country, a unique karst landscape characterized by sinkholes, caves, and steep-sided hills. This rugged terrain, formed by the dissolution of limestone bedrock, presents a challenging but beautiful landscape, home to endemic species and a rich cultural heritage.
The eastern and southern portions of Jamaica showcase a gentler topography, characterized by rolling hills and coastal plains. These areas, often fertile and suitable for agriculture, have played a pivotal role in shaping Jamaica’s economic landscape, supporting its agricultural production and tourism industry.
Beyond Elevation: Understanding the Importance of Topographical Features
The topographical map of Jamaica transcends a mere representation of elevation; it offers valuable insights into the island’s natural resources, ecological processes, and human settlement patterns.
1. A Lifeline for Water Resources: The Blue Mountain range acts as a crucial water source for Jamaica, capturing rainfall and feeding numerous rivers and streams. These waterways provide essential drinking water for the population, support irrigation for agriculture, and contribute to the island’s hydropower generation. Understanding the topography of these watersheds is essential for managing water resources sustainably and mitigating the risks of drought and flooding.
2. Shaping the Island’s Biodiversity: Jamaica’s diverse topography creates a mosaic of habitats, supporting a rich biodiversity. The Blue Mountains, with their high elevation and cool climate, harbor unique flora and fauna, including endangered species like the Jamaican Blackbird. The Cockpit Country’s intricate karst system provides refuge for endemic species like the Jamaican Boa and the Jamaican Iguana. Coastal plains and mangrove swamps support diverse marine ecosystems, vital for fishing and coastal protection.
3. Influencing Human Settlement and Development: The topography of Jamaica has shaped human settlement patterns throughout history. Coastal plains, with their fertile soils and access to transportation routes, have traditionally attracted human settlements and agricultural activity. The mountainous regions, while challenging to inhabit, have offered refuge and opportunities for resource extraction, particularly in areas with rich mineral deposits.
4. Guiding Infrastructure Development: The topographical map provides crucial information for infrastructure development, from road construction and transportation networks to the siting of energy facilities and communication towers. Understanding the terrain, elevation changes, and potential hazards like landslides is essential for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of infrastructure projects.
5. Unveiling the Island’s Cultural Heritage: Jamaica’s topography has deeply influenced its cultural heritage. The mountainous regions, often considered sacred spaces, have been imbued with spiritual significance and are associated with traditional beliefs and practices. The Cockpit Country, with its unique landscape and cultural significance, has been a source of inspiration for Jamaican folklore and music.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Jamaica’s Topography
1. What is the highest point in Jamaica?
The highest point in Jamaica is Blue Mountain Peak, reaching 2,256 meters above sea level.
2. What is the significance of the Cockpit Country?
The Cockpit Country is a unique karst landscape with significant ecological and cultural importance. It is home to endemic species and is a source of inspiration for Jamaican folklore.
3. How does Jamaica’s topography influence its climate?
The Blue Mountain range acts as a natural barrier, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates across the island.
4. What are the main challenges posed by Jamaica’s topography?
Jamaica’s rugged terrain can present challenges for transportation, infrastructure development, and access to certain areas, especially in the Cockpit Country.
5. What are the opportunities presented by Jamaica’s topography?
Jamaica’s diverse topography offers opportunities for tourism, agriculture, and renewable energy development, particularly in areas with abundant water resources and scenic beauty.
Tips for Understanding and Using Jamaica’s Topographical Map
-
Familiarize yourself with the different topographic features: Understand the meaning of contour lines, elevation points, and symbols representing different landforms.
-
Study the distribution of resources: Analyze the location of rivers, forests, and mineral deposits to understand their relationship to the topography.
-
Consider the impact of topography on human activities: Analyze how the terrain influences agriculture, transportation, and settlement patterns.
-
Use the map to plan outdoor activities: Utilize the map to identify hiking trails, scenic viewpoints, and areas suitable for different outdoor activities.
-
Stay updated on topographic data: Regularly consult updated maps and resources to ensure you have the most accurate information.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Landscape and Resilience
Jamaica’s topographical map is more than just a visual representation of the island’s surface; it is a window into its complex history, diverse ecosystem, and cultural identity. By understanding the intricate interplay of elevation, landforms, and natural resources, we gain a deeper appreciation for the island’s unique characteristics, its resilience in the face of environmental challenges, and its potential for sustainable development. As we continue to explore and learn from this fascinating landscape, we can strive to protect its biodiversity, manage its resources wisely, and ensure that Jamaica’s future remains intertwined with the legacy of its remarkable topography.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Jamaica’s Topographical Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!