Understanding The Seismic Landscape Of Japan: A Comprehensive Look At Earthquake Risk
Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Look at Earthquake Risk
Related Articles: Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Look at Earthquake Risk
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Look at Earthquake Risk. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Look at Earthquake Risk

Japan, an archipelago nation situated on the Pacific Ring of Fire, is renowned for its seismic activity. This geological reality necessitates a deep understanding of earthquake risk, a task made easier by the development of detailed earthquake hazard maps. While a specific "2024 Japan quake map" does not exist, comprehensive earthquake hazard maps are continuously updated and refined by experts, providing invaluable insights into the potential for seismic events in the coming years. This article delves into the importance of these maps, explaining their creation, interpretation, and application in mitigating earthquake risk in Japan.
Understanding Earthquake Hazard Maps:
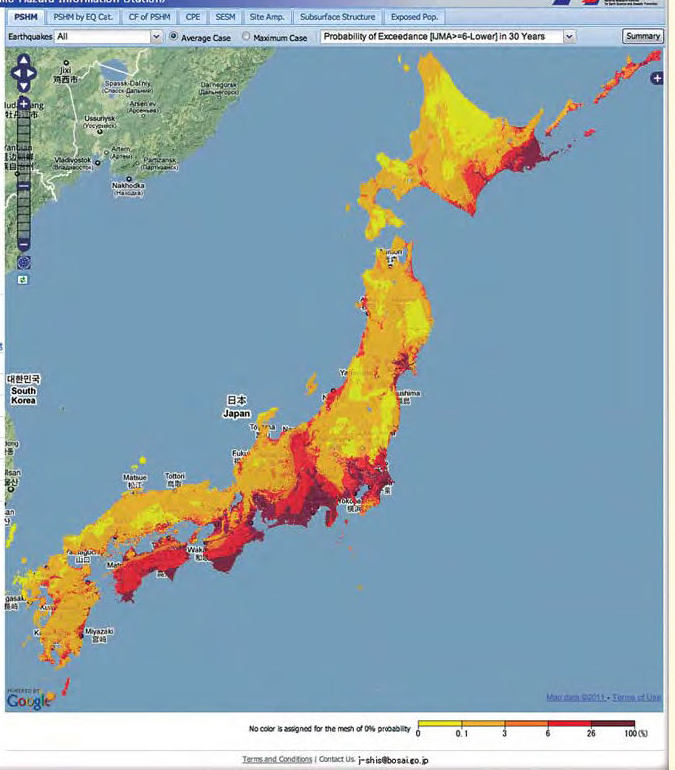
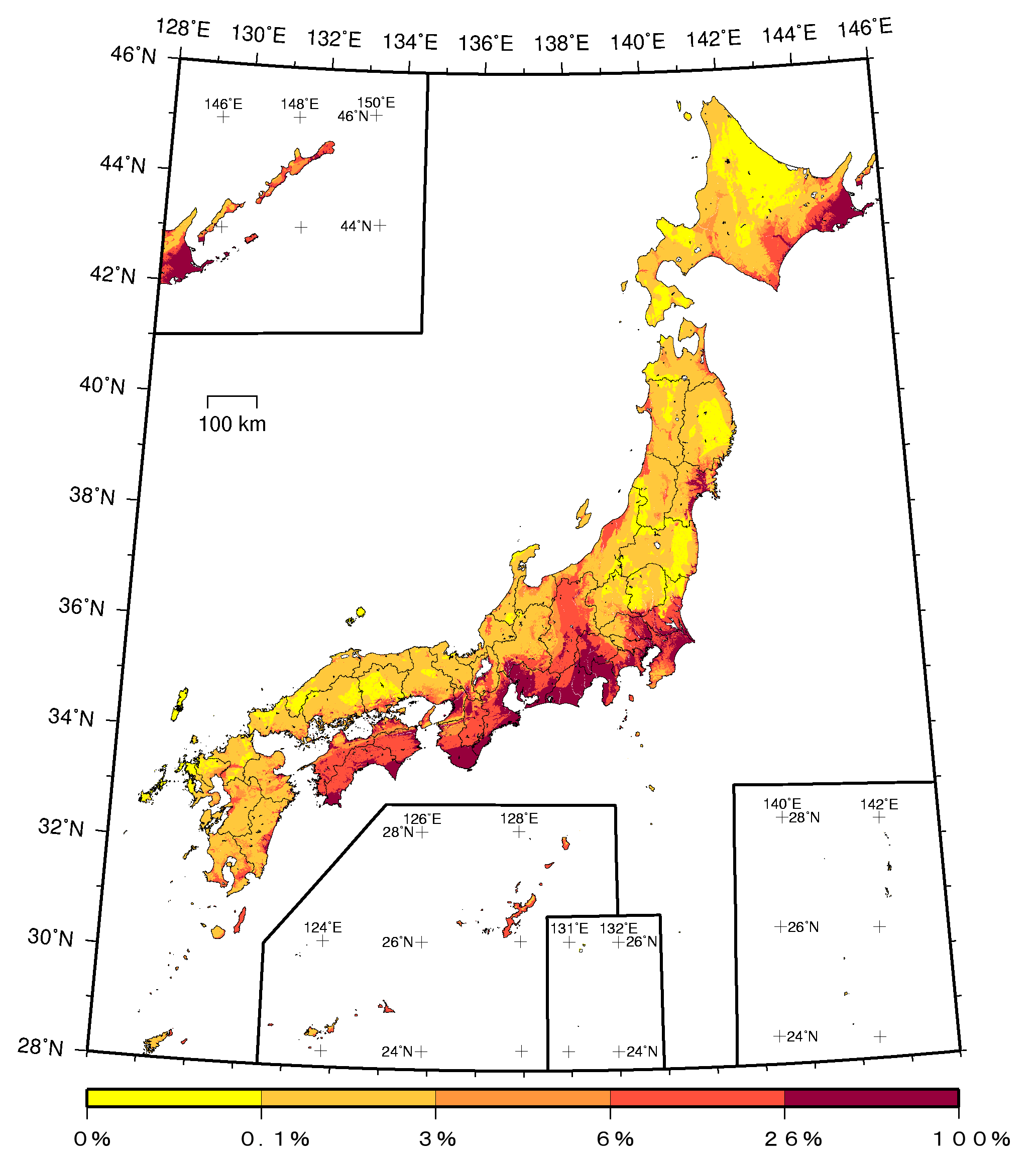
Earthquake hazard maps are not predictions of future earthquakes; rather, they represent probabilistic assessments of seismic risk. They depict areas with varying levels of potential ground shaking, based on historical earthquake data, geological understanding, and advanced modeling techniques. These maps are crucial for:
- Infrastructure Design and Construction: Architects and engineers use these maps to design buildings and infrastructure that can withstand potential ground motions. This includes incorporating earthquake-resistant features like flexible foundations, reinforced concrete, and seismic dampers.
- Emergency Planning and Response: Understanding potential earthquake zones allows for effective emergency preparedness. This includes developing evacuation plans, establishing designated safe zones, and ensuring the availability of essential resources.
- Land-use Planning and Development: These maps guide urban planning decisions, preventing high-risk areas from being developed for vulnerable purposes, such as residential areas or critical infrastructure.
- Public Awareness and Education: Disseminating information about earthquake hazards through maps fosters public awareness and encourages proactive measures for safety and resilience.
The Science Behind Earthquake Hazard Maps:
The creation of earthquake hazard maps involves a multi-faceted approach:
- Geological Data Collection: Detailed geological surveys are conducted to identify active fault lines, historical earthquake epicenters, and the nature of underlying bedrock.
- Seismic Monitoring Networks: Extensive networks of seismographs continuously monitor ground vibrations, providing valuable data for analyzing seismic activity and identifying potential fault zones.
- Computer Modeling: Advanced computer models are used to simulate earthquake scenarios, considering factors like fault rupture behavior, ground motion propagation, and soil amplification effects.
- Probabilistic Analysis: By combining historical data, geological knowledge, and modeling results, scientists calculate the probability of various earthquake magnitudes occurring in specific locations.
Interpreting Earthquake Hazard Maps:
Earthquake hazard maps often depict risk levels using color gradients or numerical scales. A high-risk area typically indicates a higher probability of experiencing strong ground shaking during a future earthquake. These maps are not static; they are continuously updated as new data becomes available and our understanding of earthquake processes evolves.
Benefits of Earthquake Hazard Maps:
- Enhanced Safety and Resilience: By understanding potential earthquake hazards, communities can implement measures to mitigate risk and build more resilient infrastructure, reducing the impact of future events.
- Informed Decision-Making: These maps provide a crucial basis for informed decisions regarding land-use planning, infrastructure development, and emergency preparedness, leading to safer and more sustainable communities.
- Effective Resource Allocation: Understanding areas with higher risk allows for targeted allocation of resources for earthquake preparedness, such as strengthening buildings, improving evacuation routes, and establishing emergency shelters.
- Public Education and Awareness: Disseminating information about earthquake hazards through maps fosters public awareness, encouraging individuals to take proactive steps to prepare for potential events.
FAQs on Earthquake Hazard Maps:
Q: Are these maps predictions of when and where earthquakes will occur?
A: No, earthquake hazard maps are not predictions of future earthquakes. They represent probabilistic assessments of risk based on historical data and scientific models. They indicate the likelihood of experiencing strong ground shaking in different locations.
Q: How often are these maps updated?
A: Earthquake hazard maps are continuously updated as new data becomes available and our understanding of earthquake processes evolves. This may occur annually, or more frequently in areas with significant seismic activity.
Q: What does a high-risk area on the map mean?
A: A high-risk area indicates a higher probability of experiencing strong ground shaking during a future earthquake. It does not mean that an earthquake will definitely occur there, but it highlights the need for increased preparedness.
Q: How can I find the earthquake hazard map for my area?
A: Earthquake hazard maps are typically available from government agencies responsible for disaster management, geological surveys, and seismological research. They can also be accessed online through websites dedicated to earthquake preparedness.
Tips for Utilizing Earthquake Hazard Maps:
- Familiarize yourself with the map for your area: Understand the risk levels and potential hazards in your neighborhood.
- Consult with local authorities: Learn about evacuation plans, designated safe zones, and emergency procedures.
- Strengthen your home and workplace: Implement earthquake-resistant measures, such as securing heavy objects, installing earthquake-resistant furniture, and strengthening structural elements.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Stock up on essential supplies like food, water, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
- Stay informed: Monitor news and official sources for updates and warnings about potential seismic activity.
Conclusion:
Earthquake hazard maps are essential tools for understanding and mitigating the risks associated with seismic activity in Japan. They provide a scientific framework for informed decision-making, enhancing safety, and fostering resilience in communities. By utilizing these maps and implementing appropriate preparedness measures, Japan can continue to navigate its complex seismic landscape, safeguarding lives and property, and ensuring a safer future for its citizens.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Seismic Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Look at Earthquake Risk. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!