Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Earthquake Activity
Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Activity
Related Articles: Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Activity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Activity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Activity

Indonesia, an archipelago nation nestled in the heart of the "Ring of Fire," is renowned for its breathtaking beauty and rich cultural heritage. However, this natural splendor comes with a significant geological reality: Indonesia is one of the most seismically active regions on Earth. This article provides a comprehensive overview of earthquake activity in Indonesia, exploring the underlying geological factors, the impact of these events, and the vital role of preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Geological Context: The Ring of Fire and Plate Tectonics
Indonesia’s susceptibility to earthquakes stems from its location within the Pacific Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped zone encompassing the Pacific Ocean. This region is characterized by a high concentration of active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes due to the interaction of tectonic plates.
The Earth’s outer layer, the lithosphere, is composed of numerous tectonic plates that constantly move and interact. In Indonesia, the Eurasian Plate, the Australian Plate, and the Pacific Plate collide and slide past each other. These movements create immense pressure and friction, resulting in the release of energy in the form of earthquakes.
Subduction Zones and Fault Lines
The most significant geological feature contributing to Indonesia’s seismic activity is the subduction zone. Here, one tectonic plate slides beneath another, causing the denser plate to descend into the Earth’s mantle. This process generates tremendous heat and pressure, leading to the formation of magma that eventually rises to the surface, creating volcanoes.
Indonesia is home to several major subduction zones, including the Sunda Trench, where the Indo-Australian Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate, and the Banda Sea, where the Australian Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate. The collision of these plates along these zones generates numerous fault lines, which act as pathways for the release of seismic energy.
Earthquake Frequency and Intensity
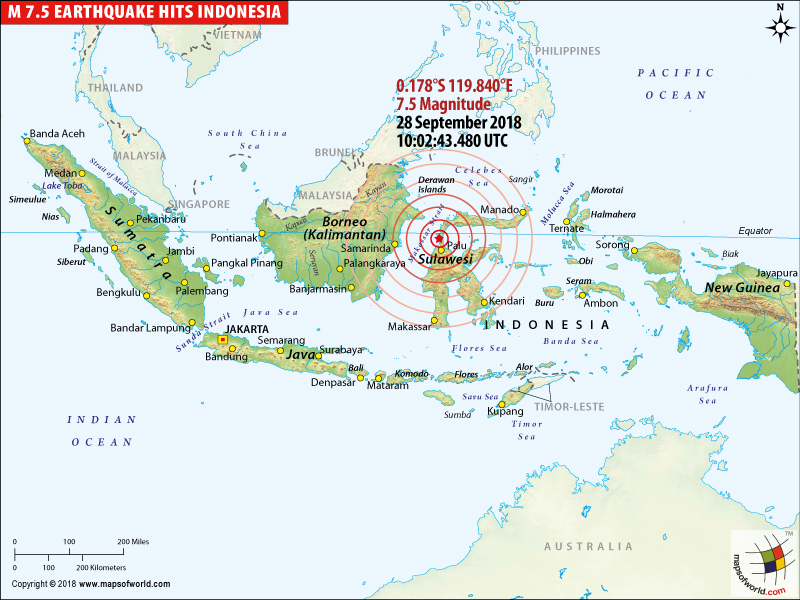
Indonesia experiences a high frequency of earthquakes, ranging from minor tremors barely noticeable to powerful events that cause widespread damage. The country’s history is marked by devastating earthquakes, including the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, triggered by a massive earthquake off the coast of Sumatra, and the 2018 Palu earthquake and tsunami.
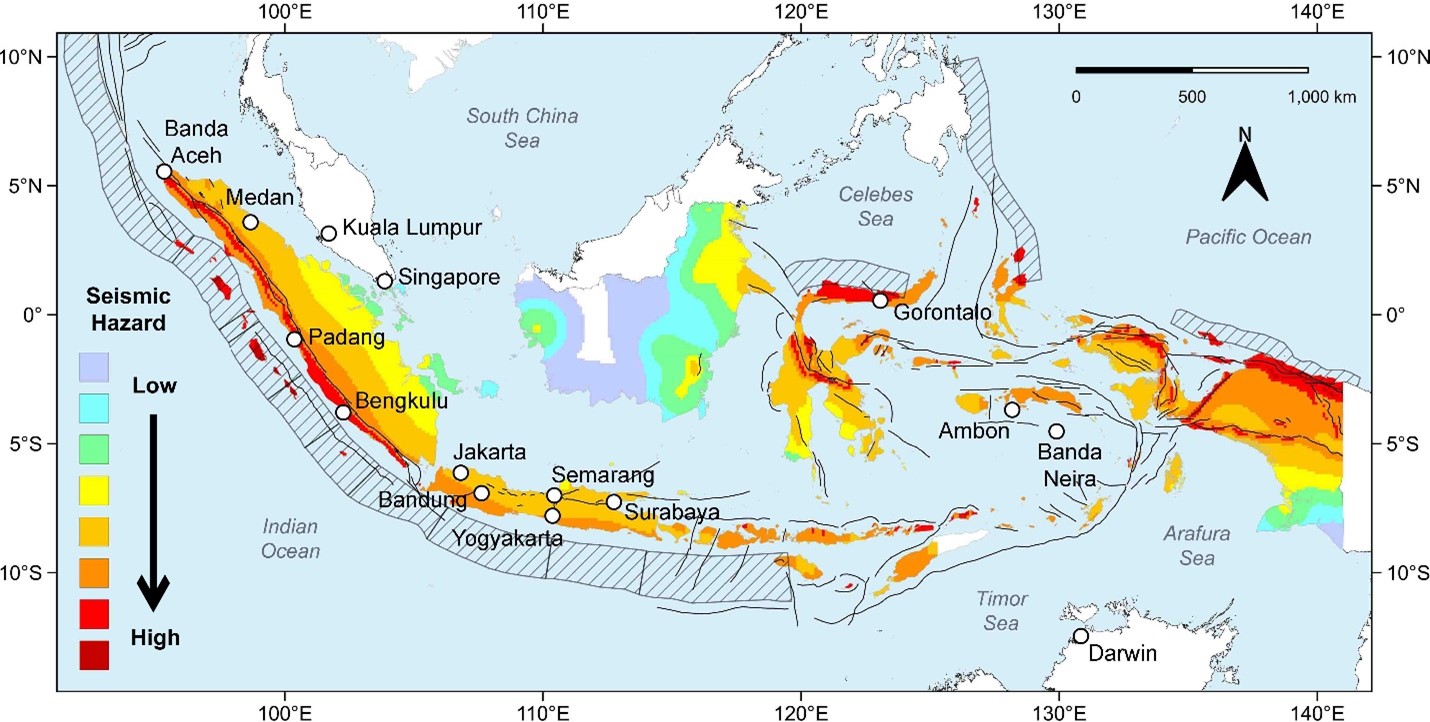
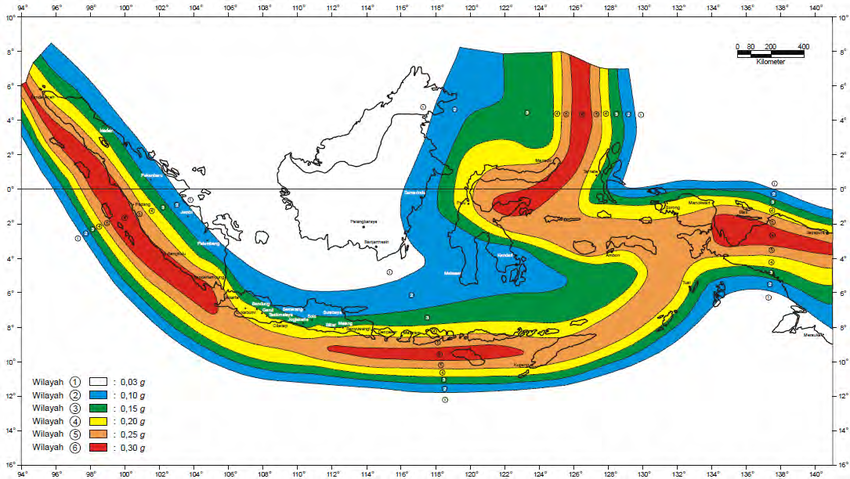
Seismic Hazard Mapping: A Tool for Preparedness
Understanding the spatial distribution of earthquake risk is crucial for effective disaster preparedness. Seismic hazard maps, which depict the likelihood of earthquake occurrence and their potential intensity, play a vital role in informing disaster mitigation strategies. These maps are developed by analyzing historical earthquake data, geological information, and modeling techniques.
Impact of Earthquakes on Indonesia
Earthquakes in Indonesia have far-reaching consequences, affecting various aspects of life and infrastructure. The primary impacts include:
- Ground Shaking: The most immediate and direct impact of an earthquake is ground shaking, which can cause significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and other structures.
- Tsunamis: Earthquakes occurring beneath the ocean floor can displace vast amounts of water, generating massive waves known as tsunamis. These waves can travel long distances at high speeds, causing widespread destruction upon reaching coastal areas.
- Landslides: Earthquakes can trigger landslides, especially in mountainous regions with unstable slopes. These landslides can bury homes, roads, and other infrastructure, causing significant damage and loss of life.
- Liquefaction: In areas with loose, saturated soils, earthquakes can cause liquefaction, where the ground behaves like a liquid. This phenomenon can lead to building collapses, infrastructure damage, and widespread disruption.
- Economic Disruption: Earthquakes can cause significant economic disruption, impacting industries, transportation, and tourism. The cost of rebuilding damaged infrastructure and restoring essential services can be substantial.
- Social and Psychological Impacts: Earthquakes can have a profound impact on the mental and emotional well-being of individuals and communities. The loss of loved ones, homes, and livelihoods can lead to trauma, anxiety, and displacement.
Disaster Preparedness and Mitigation
Given the high seismic risk, Indonesia has implemented various strategies to mitigate the impact of earthquakes. These strategies include:
- Building Codes: Stringent building codes are enforced to ensure that new structures are designed and built to withstand earthquake forces.
- Early Warning Systems: Early warning systems are being developed and deployed to provide timely alerts of impending earthquakes and tsunamis.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Public awareness campaigns educate citizens on earthquake preparedness, including evacuation procedures, safe practices during earthquakes, and the importance of having emergency kits.
- Disaster Response Teams: Well-trained disaster response teams are prepared to provide immediate assistance in the aftermath of earthquakes, including search and rescue operations, medical aid, and shelter provision.
- Infrastructure Strengthening: Existing infrastructure, including bridges, roads, and buildings, are being strengthened and retrofitted to enhance their resilience to earthquakes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Indonesia?
A: Indonesia experiences hundreds of earthquakes every year, ranging from minor tremors to powerful events. The frequency and intensity of earthquakes vary depending on the location and the activity of tectonic plates.
Q: What are the most earthquake-prone regions in Indonesia?
A: The most earthquake-prone regions in Indonesia include Sumatra, Java, Bali, Lombok, and Sulawesi. These regions are located along major subduction zones and fault lines.
Q: How can I prepare for an earthquake?
A: Preparing for an earthquake involves several steps:
- Secure heavy objects that could fall during an earthquake.
- Identify safe places to take cover during an earthquake, such as under sturdy furniture or in doorways.
- Develop an emergency plan with your family, including evacuation routes and meeting points.
- Prepare an emergency kit containing essential supplies, such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a flashlight.
Q: What should I do during an earthquake?
A: If you are indoors during an earthquake, drop, cover, and hold on. Find a sturdy piece of furniture to take cover under or stand in a doorway. If you are outdoors, move away from buildings, trees, and power lines.
Q: What should I do after an earthquake?
A: After an earthquake, check for injuries and provide first aid if needed. Be aware of potential aftershocks. Listen to local authorities for instructions and follow evacuation orders.
Tips for Staying Safe During Earthquakes
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about earthquake preparedness and safety measures by following official sources such as the Indonesian Agency for Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysics (BMKG).
- Participate in Drills: Participate in earthquake drills to practice evacuation procedures and familiarize yourself with safety measures.
- Secure Your Home: Secure heavy objects and furniture that could fall during an earthquake.
- Have an Emergency Kit: Prepare an emergency kit containing essential supplies, such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a flashlight.
- Be Prepared to Evacuate: Know your evacuation routes and have a designated meeting point for your family.
Conclusion
Indonesia’s position within the Ring of Fire makes it a region of significant seismic activity. Understanding the geological context, the frequency and intensity of earthquakes, and the potential impacts is essential for effective disaster preparedness. By implementing robust mitigation strategies, raising public awareness, and fostering a culture of preparedness, Indonesia can minimize the devastating effects of earthquakes and build a more resilient future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Activity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!