Understanding Indonesia’s Geography: A Vital Component Of UPSC Preparation
Understanding Indonesia’s Geography: A Vital Component of UPSC Preparation
Related Articles: Understanding Indonesia’s Geography: A Vital Component of UPSC Preparation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Indonesia’s Geography: A Vital Component of UPSC Preparation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Indonesia’s Geography: A Vital Component of UPSC Preparation
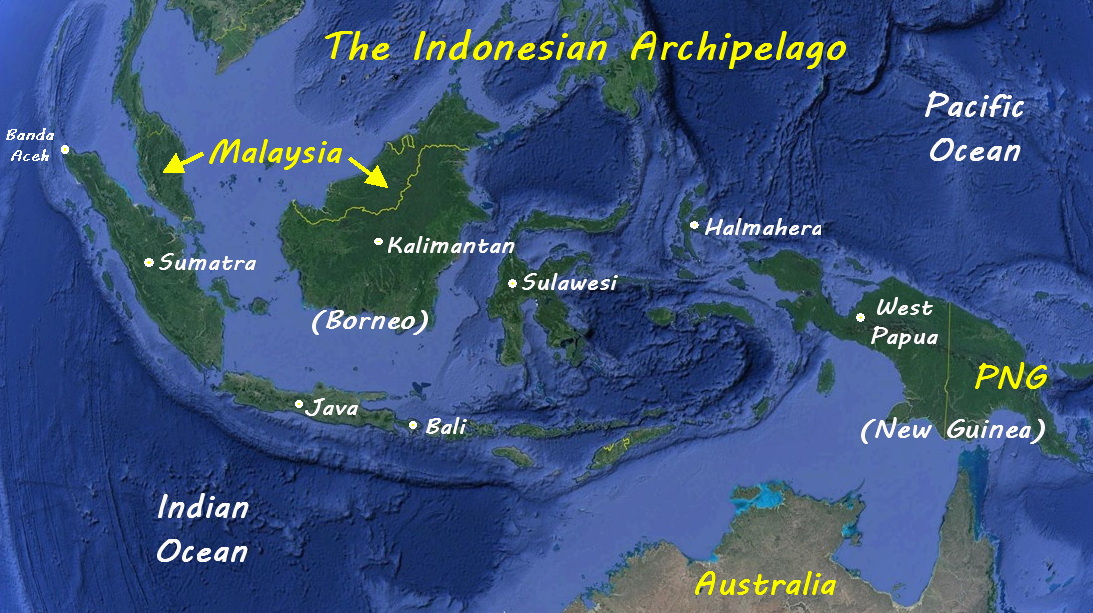
Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago nation, holds significant geopolitical and economic weight. Its strategic location, diverse geography, and rich cultural heritage make it a crucial subject of study for the UPSC Civil Services Examination. A thorough understanding of Indonesia’s map is essential for comprehending the country’s internal dynamics, regional relations, and global implications. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of Indonesia’s geography, its significance in the UPSC context, and how it can be effectively studied for the examination.
1. Geographical Features and Significance:
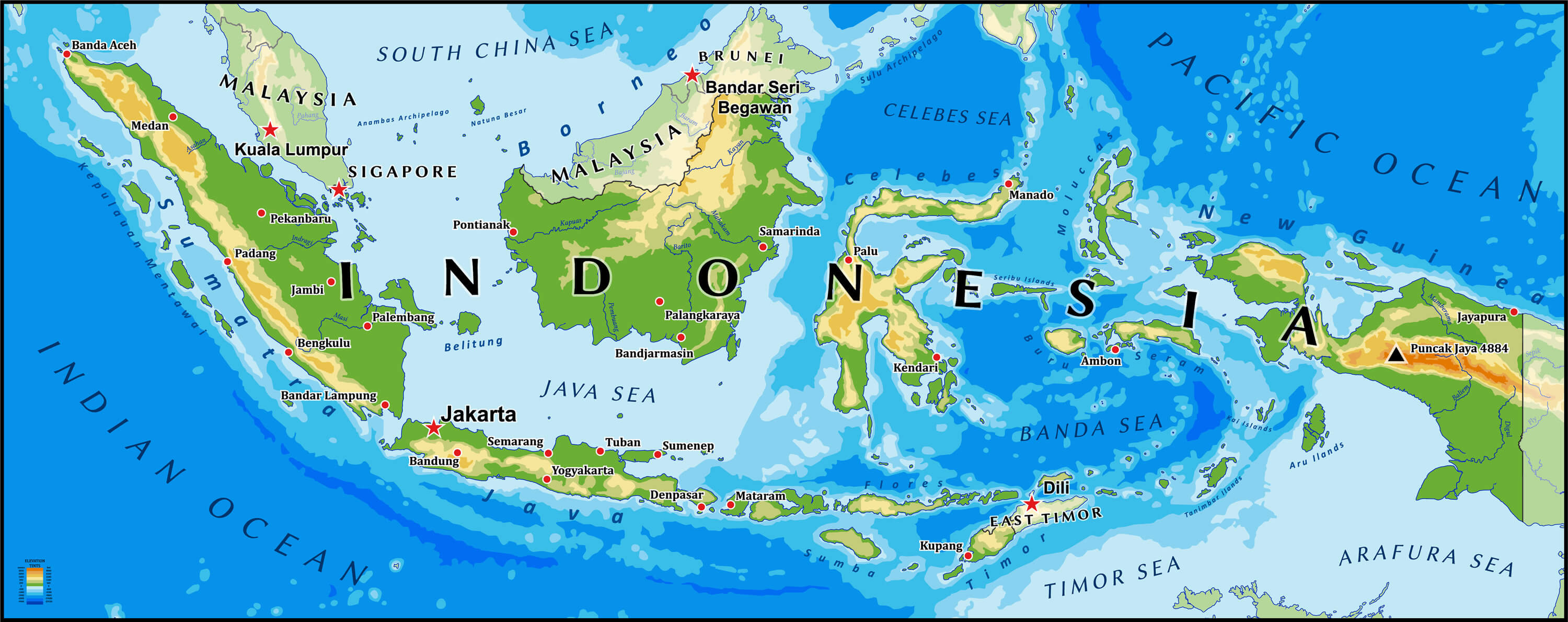
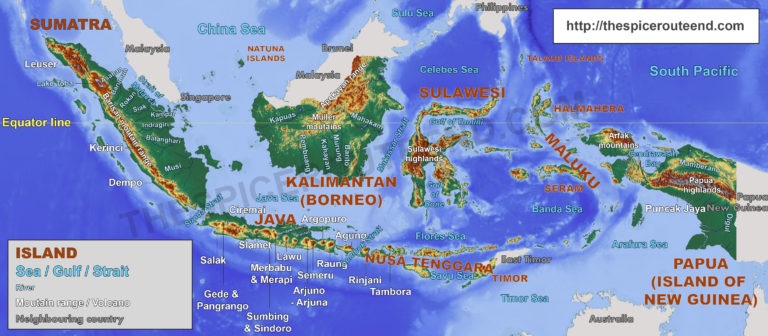
Indonesia is a sprawling archipelago comprising over 17,000 islands, of which approximately 6,000 are inhabited. It stretches across the equator, straddling Southeast Asia and Oceania. The country’s diverse geography is characterized by:
- Volcanic Mountains: Indonesia lies along the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity. This geological feature has shaped the country’s landscape, creating fertile volcanic soils and contributing to its rich biodiversity. Mount Merapi, Mount Krakatoa, and Mount Bromo are among the most prominent volcanoes.
- Island Chains: The Indonesian archipelago is divided into several island chains, each with its unique characteristics. Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan (Borneo), Sulawesi, and Papua are the largest islands. These islands are separated by straits and seas, forming intricate waterways and impacting trade routes.
- Tropical Climate: Indonesia experiences a tropical monsoon climate, characterized by high humidity, abundant rainfall, and distinct wet and dry seasons. This climate supports a diverse flora and fauna, including rainforests, mangrove swamps, and coral reefs.
- Rich Biodiversity: Indonesia’s unique geography and climate have fostered a vast array of biodiversity. It is home to a significant portion of the world’s plant and animal species, including orangutans, komodo dragons, and numerous endemic species.
2. Strategic Location and Geopolitical Importance:
Indonesia’s strategic location at the crossroads of major shipping routes and trade networks makes it a vital player in regional and global affairs. The country’s proximity to key economic and political powers, including China, India, and Australia, enhances its strategic significance.
- Maritime Crossroads: Indonesia controls vital shipping lanes in the Malacca Strait, a key passage for oil and gas shipments from the Middle East to East Asia. This strategic waterway makes Indonesia a significant player in global maritime trade.
- Regional Hub: Indonesia’s location in Southeast Asia positions it as a regional hub for trade, investment, and cultural exchange. The country plays a crucial role in regional organizations like ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) and the East Asia Summit.
- Global Power Dynamics: Indonesia’s strategic location and growing economic influence make it a significant player in global power dynamics. The country is increasingly engaging with major powers like the United States, China, and Japan, seeking to balance its relationships and protect its national interests.
3. Economic and Social Significance:
Indonesia is a rapidly developing economy with vast natural resources, a growing population, and a vibrant cultural heritage. Understanding its economic and social landscape is crucial for comprehending its domestic and international policies.
- Natural Resources: Indonesia possesses abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, tin, copper, and nickel. These resources contribute significantly to the country’s economy and are crucial for its industrial development.
- Agriculture and Manufacturing: Agriculture remains a significant sector in Indonesia, employing a large portion of the workforce. The country is a major producer of palm oil, rubber, coffee, and rice. Manufacturing is also growing, with industries like automotive, electronics, and textiles gaining prominence.
- Tourism and Culture: Indonesia’s diverse culture, beautiful beaches, and rich historical heritage attract a significant number of tourists. Tourism is a growing industry, contributing to the economy and promoting cultural exchange.
4. Challenges and Opportunities:
Indonesia faces various challenges, including:
- Natural Disasters: The country’s volcanic activity, earthquakes, and tsunamis pose significant risks to its population and infrastructure.
- Environmental Degradation: Deforestation, pollution, and climate change are major environmental challenges that threaten Indonesia’s biodiversity and natural resources.
- Political and Social Stability: Indonesia has a history of political instability, and ethnic and religious tensions can sometimes erupt.
- Economic Inequality: The country’s economic growth has not been evenly distributed, leading to significant income disparities and poverty.
Despite these challenges, Indonesia also enjoys several opportunities:
- Growing Economy: Indonesia’s economy is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by its abundant natural resources, growing middle class, and increasing investment.
- Demographic Dividend: The country has a young and growing population, which can be a source of economic dynamism and innovation.
- Regional Leadership: Indonesia is emerging as a regional leader in Southeast Asia, playing a key role in shaping regional cooperation and promoting economic integration.
5. Studying Indonesia for UPSC:
To effectively study Indonesia for the UPSC Civil Services Examination, consider the following:
- Focus on Key Geographical Features: Understand the major islands, mountain ranges, rivers, and straits. Analyze how these features impact the country’s economy, transportation, and social development.
- Examine Regional Relations: Analyze Indonesia’s relationships with its neighboring countries, particularly within ASEAN. Explore the challenges and opportunities presented by these relationships.
- Analyze Domestic Politics: Study the country’s political system, key political parties, and recent political developments. Understand the dynamics of power and the influence of various interest groups.
- Explore Economic Policies: Analyze Indonesia’s economic policies, including its trade agreements, investment strategies, and development priorities. Understand the challenges and opportunities facing the country’s economic growth.
- Pay Attention to Current Events: Stay updated on current events in Indonesia, including political developments, economic trends, and social issues. This will help you understand the country’s evolving dynamics and its impact on regional and global affairs.
6. FAQs:
Q1: What are the major islands of Indonesia?
A: The major islands of Indonesia are Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan (Borneo), Sulawesi, and Papua.
Q2: What is the significance of the Malacca Strait?
A: The Malacca Strait is a vital shipping lane connecting the Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean. It is a key passage for oil and gas shipments from the Middle East to East Asia, making Indonesia a significant player in global maritime trade.
Q3: What are the major challenges facing Indonesia?
A: Indonesia faces various challenges, including natural disasters, environmental degradation, political and social instability, and economic inequality.
Q4: What are the opportunities for Indonesia’s economic growth?
A: Indonesia has several opportunities for economic growth, including its abundant natural resources, growing middle class, increasing investment, and demographic dividend.
Q5: Why is Indonesia important for UPSC preparation?
A: Indonesia’s strategic location, diverse geography, and significant economic and political influence make it a crucial subject of study for the UPSC Civil Services Examination. Understanding Indonesia’s dynamics is essential for comprehending regional and global affairs.
7. Tips for Studying Indonesia for UPSC:
- Use a comprehensive atlas: A detailed map of Indonesia will help you visualize the country’s geography, its islands, major cities, and key geographical features.
- Read relevant articles and reports: Stay updated on current events in Indonesia through news articles, reports from think tanks, and academic journals.
- Analyze past UPSC papers: Examine previous UPSC papers to understand the types of questions asked about Indonesia and the depth of knowledge expected.
- Practice map-based questions: Familiarize yourself with map-based questions that test your knowledge of geographical features, locations, and their significance.
- Develop a strong understanding of regional and global connections: Analyze how Indonesia’s geography and policies impact regional and global affairs, particularly in Southeast Asia and the Indo-Pacific region.
Conclusion:
Indonesia’s geography, strategic location, and economic and social significance make it a crucial subject of study for the UPSC Civil Services Examination. By understanding the country’s diverse landscape, its regional and global connections, and the challenges and opportunities it faces, candidates can gain a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics of Southeast Asia and its impact on the global stage. This knowledge is essential for formulating informed opinions and contributing to effective policymaking in the context of international relations and development.
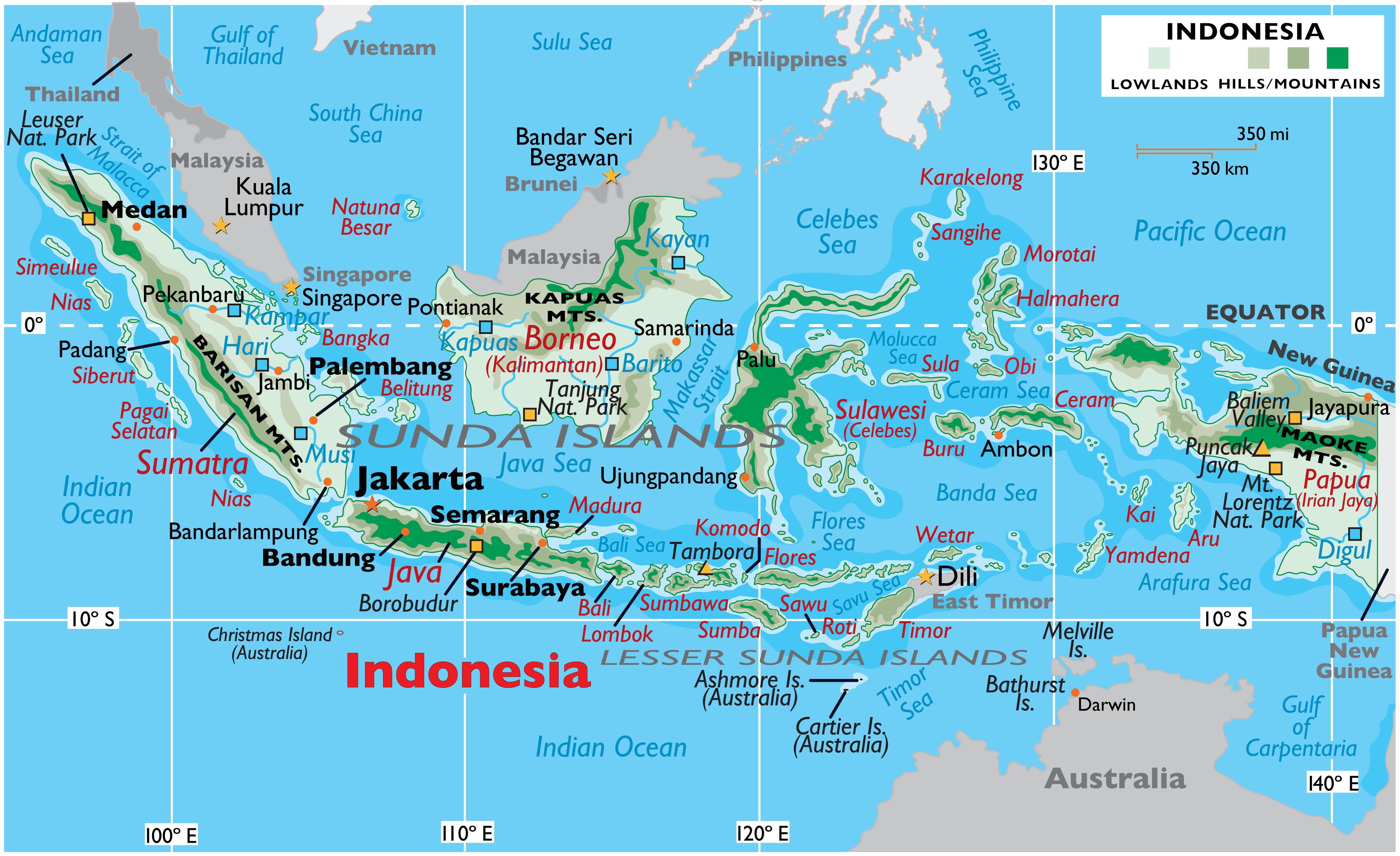
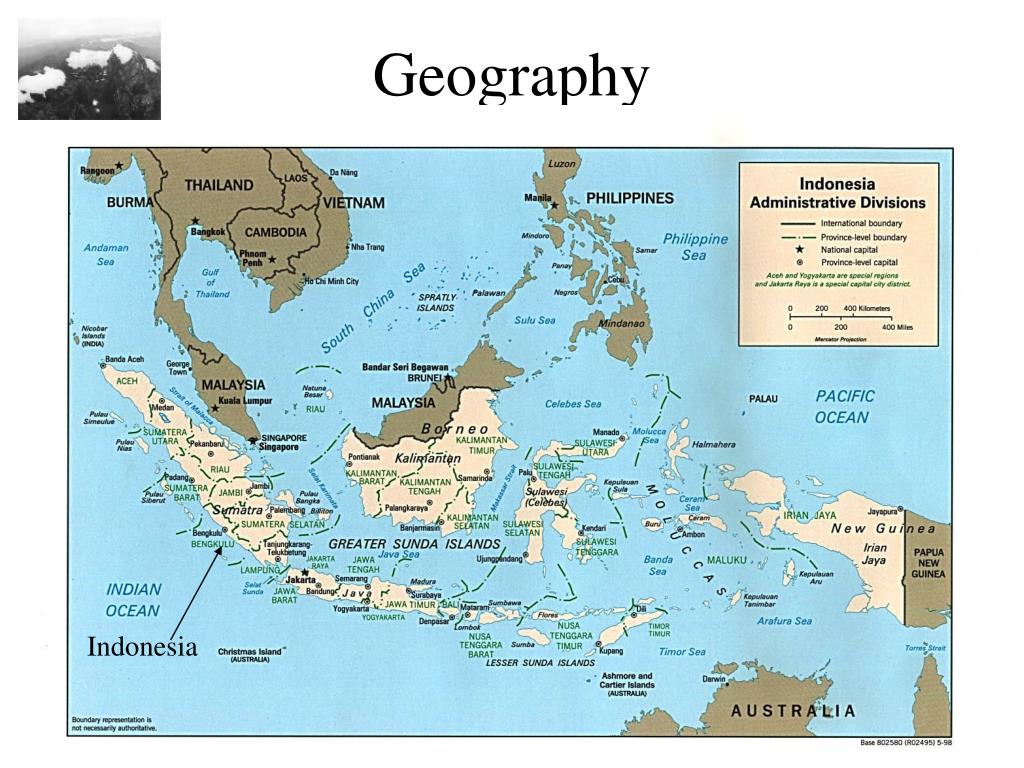
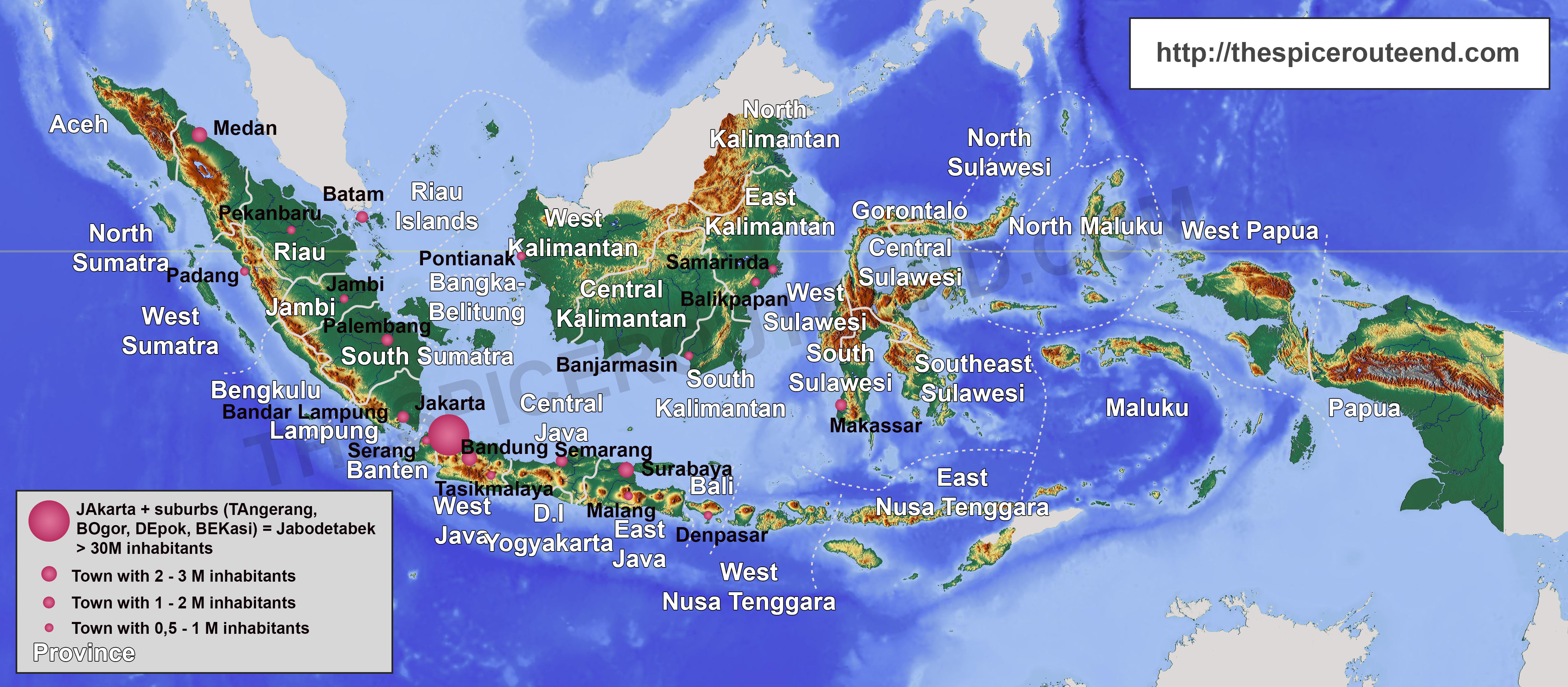



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Indonesia’s Geography: A Vital Component of UPSC Preparation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!