Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview

India, a vast and diverse nation, boasts a unique geographic landscape that has shaped its history, culture, and economy. This article provides a comprehensive overview of India’s geographical features, exploring its diverse terrain, climate, and natural resources, highlighting the impact of these factors on the nation’s development.
India’s Geographical Boundaries and Location
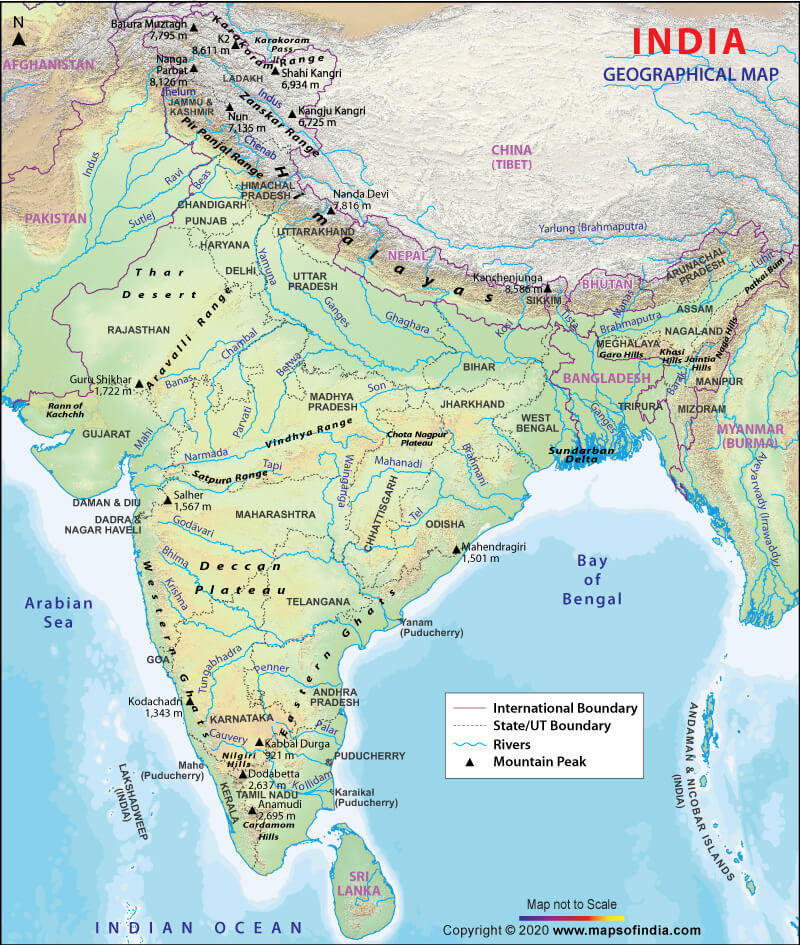
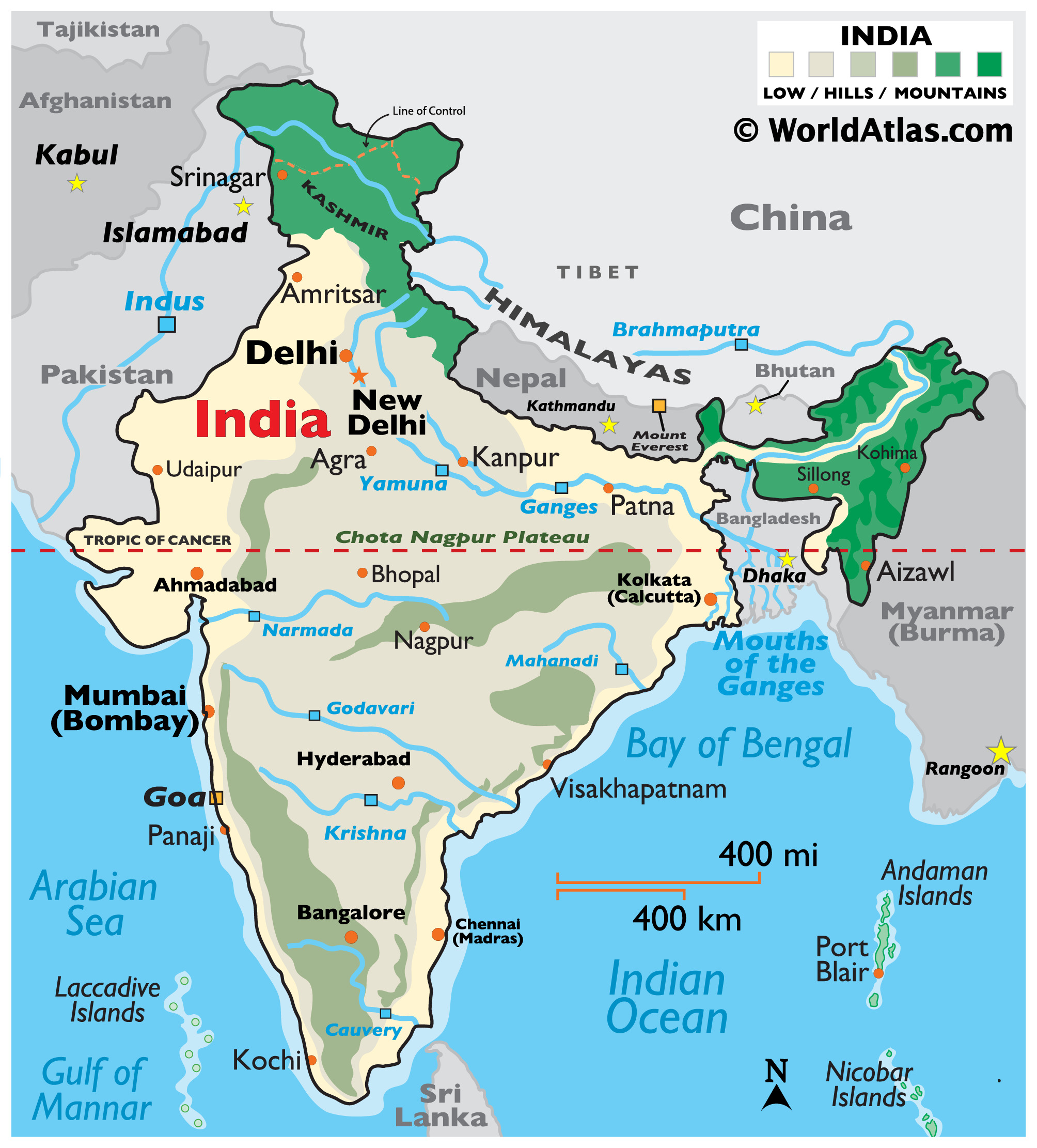
India, located in South Asia, is a subcontinent encompassing a vast expanse of land. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the south, the Arabian Sea to the west, and the Bay of Bengal to the east. Its northern border shares land with Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh. This strategic location has historically played a significant role in shaping India’s trade routes, cultural exchanges, and geopolitical dynamics.
Terrain and Topography: A Diverse Landscape
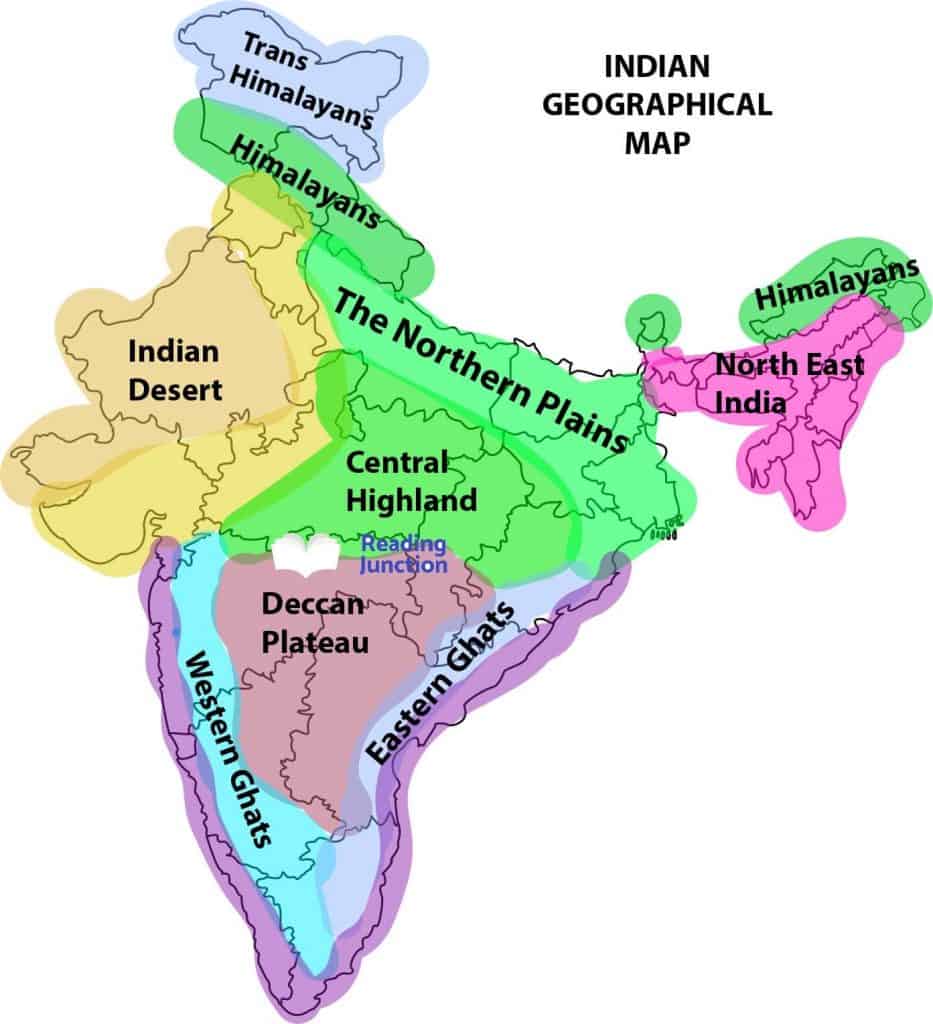
India’s topography is remarkably diverse, ranging from towering Himalayan peaks to vast plains, fertile river valleys, and coastal lowlands. The northern frontier is dominated by the mighty Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, which act as a natural barrier. The Himalayas, with their snow-capped peaks and glaciers, are a vital source of water for major river systems like the Ganges and Brahmaputra.
To the south of the Himalayas lie the Indo-Gangetic Plains, a fertile alluvial plain stretching from the Indus River in the west to the Brahmaputra in the east. This region is a major agricultural hub, supporting a significant portion of India’s population.
Central India is characterized by a plateau known as the Deccan Plateau, a large triangular landmass formed by volcanic activity. This region is home to diverse ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
India’s coastline, stretching over 7,500 kilometers, is marked by numerous bays, estuaries, and islands. The country has two major peninsulas: the Indian Peninsula and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. This extensive coastline provides access to important sea routes and harbors, contributing to India’s maritime trade and economic development.
Climate: A Complex Mosaic
India experiences a wide range of climates, influenced by its diverse topography and geographic location. The country can be broadly divided into four major climate zones:
-
Tropical Monsoon Climate: This climate prevails over most of India, characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons. The summer monsoon brings heavy rainfall, crucial for agriculture, while the winter months are relatively dry.
-
Subtropical Climate: This climate is found in the northern plains and the Deccan Plateau, with hot summers and mild winters.
-
Arid and Semi-Arid Climate: The western and northwestern parts of India experience arid and semi-arid climates, with low rainfall and high temperatures.
-
Mountain Climate: The Himalayan region experiences a cold and dry climate, with snow and freezing temperatures during the winter months.
Natural Resources: A Wealth of Assets
India is endowed with a rich array of natural resources, crucial for its economic growth and development. These resources include:
-
Mineral Resources: India is rich in mineral resources, including iron ore, manganese, bauxite, coal, and petroleum. These minerals are essential for various industries, including steel, aluminum, and energy production.
-
Forest Resources: India has vast forest cover, providing timber, fuelwood, and other forest products. Forests also play a vital role in maintaining biodiversity, regulating climate, and preventing soil erosion.
-
Water Resources: India has numerous rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Indus, and Godavari, which provide water for irrigation, drinking, and hydropower generation. The country also has substantial groundwater resources.
-
Land Resources: India’s diverse topography offers a wide range of land resources, suitable for agriculture, forestry, and other economic activities.
The Impact of Geography on India’s Development
India’s geographic features have played a profound role in shaping its history, culture, and economic development.
-
Agriculture: The fertile Indo-Gangetic Plains have historically been the backbone of India’s agriculture, providing sustenance to a vast population. The monsoon rains are crucial for agricultural production, but the country also faces challenges related to water scarcity and droughts in certain regions.
-
Industry: India’s mineral resources have fueled the growth of its industrial sector, particularly in the areas of steel, aluminum, and energy production. The country’s coastline has also played a crucial role in its maritime trade and economic development.
-
Tourism: India’s diverse landscape, rich culture, and historical monuments attract millions of tourists every year. Tourism is a significant contributor to the Indian economy.
-
Challenges: India also faces geographic challenges, including natural disasters like floods, droughts, earthquakes, and cyclones. The country’s mountainous terrain poses difficulties for infrastructure development and transportation.
Conclusion
India’s geographic landscape is a testament to its rich biodiversity, cultural diversity, and economic potential. The country’s diverse terrain, climate, and natural resources have shaped its history, culture, and economic development. While India faces geographic challenges, its unique features also offer opportunities for growth and progress. Understanding India’s geographic landscape is crucial for appreciating its complex and fascinating story.
FAQs
Q: What are the main geographical features of India?
A: India’s geographical features include the Himalayas, the Indo-Gangetic Plains, the Deccan Plateau, and a vast coastline.
Q: What is the dominant climate in India?
A: The dominant climate in India is the tropical monsoon climate, characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons.
Q: What are the major rivers in India?
A: Some of the major rivers in India include the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Indus, and Godavari.
Q: What are the key natural resources found in India?
A: India is rich in mineral resources, forest resources, water resources, and land resources.
Q: How does India’s geography impact its agriculture?
A: The fertile Indo-Gangetic Plains are a major agricultural hub, but India faces challenges related to water scarcity and droughts in certain regions.
Tips
- Utilize maps and online resources: Maps and online platforms can provide valuable insights into India’s geography and its various features.
- Explore different regions: Visiting different parts of India can offer firsthand experiences of its diverse landscapes and cultures.
- Read books and articles: There are numerous books and articles available that delve deeper into India’s geography and its impact on the country’s development.
Conclusion
India’s geography is a complex and fascinating tapestry, woven with diverse landscapes, climates, and natural resources. Understanding this geographic landscape is essential for appreciating India’s rich history, culture, and economic development. As India continues to evolve, its geography will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping its future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!