Transforming Data With JavaScript’s Map Function: A Comprehensive Guide
Transforming Data with JavaScript’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Transforming Data with JavaScript’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Transforming Data with JavaScript’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Transforming Data with JavaScript’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Transforming Data with JavaScript’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of map
- 3.2 Illustrative Examples: Unveiling the Power of map
- 3.3 Advantages of Using map
- 3.4 Understanding the map Function’s Behavior
- 3.5 FAQs on JavaScript’s map Function
- 3.6 Tips for Using map Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Transforming Data with JavaScript’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide

The JavaScript map function is a powerful tool that enables developers to efficiently transform arrays of data. It allows for the application of a specific function to each element of an array, generating a new array with the modified elements. This process of transformation is fundamental in various programming scenarios, from manipulating data structures to enhancing code readability and efficiency.
Understanding the Essence of map
At its core, the map function iterates through each element of an array, executing a provided function on each element. This function, often referred to as the "callback function," defines the transformation logic. The result of applying the callback function to each element is then added to a new array, which is ultimately returned by the map function.
The syntax of the map function is straightforward:
const newArray = array.map(callbackFunction);Here, array represents the original array, callbackFunction is the function that defines the transformation logic, and newArray is the resulting array containing the transformed elements.
Illustrative Examples: Unveiling the Power of map
To solidify the understanding of the map function’s capabilities, let’s explore some practical examples:
1. Doubling Array Elements:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const doubledNumbers = numbers.map(number => number * 2);
console.log(doubledNumbers); // Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]In this example, the map function iterates through each element in the numbers array. For each element, the callback function (number => number * 2) multiplies the element by 2. The resulting values are then stored in the doubledNumbers array.
2. Converting Strings to Uppercase:
const names = ["john", "jane", "peter"];
const uppercaseNames = names.map(name => name.toUpperCase());
console.log(uppercaseNames); // Output: ["JOHN", "JANE", "PETER"]Here, the map function transforms each string in the names array to uppercase by applying the toUpperCase() method within the callback function.
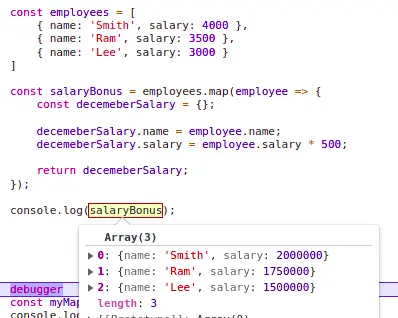
3. Extracting Specific Properties from an Array of Objects:
const users = [
name: "Alice", age: 25 ,
name: "Bob", age: 30 ,
name: "Charlie", age: 28
];
const userNames = users.map(user => user.name);
console.log(userNames); // Output: ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]This example demonstrates extracting a specific property (name) from each object within the users array using the map function. The callback function accesses the name property of each object and adds it to the userNames array.
Advantages of Using map
The map function offers several advantages over traditional loop-based approaches:
-
Conciseness:
mapprovides a concise and expressive way to transform arrays, making code more readable and maintainable. -
Immutability:
mapdoes not modify the original array; it creates a new array with the transformed elements, promoting data integrity and preventing unintended side effects. -
Reusability: The callback function used with
mapcan be easily reused for different arrays, fostering code modularity and reducing redundancy. -
Functional Programming:
mapaligns with functional programming principles, emphasizing pure functions that operate on data without modifying the original source.
Understanding the map Function’s Behavior
It is crucial to understand that the map function always returns a new array, even if the callback function returns the original element without modification. This behavior ensures that the original array remains untouched, adhering to the principle of immutability.
Furthermore, the map function preserves the order of elements in the original array. The transformed elements in the new array will appear in the same order as they were in the original array.
FAQs on JavaScript’s map Function
1. Can the map function modify the original array?
No, the map function always creates a new array containing the transformed elements. The original array remains unchanged.
2. What happens if the callback function returns undefined?
If the callback function returns undefined for a specific element, the resulting array will contain undefined at the corresponding index.
3. Can I use multiple callback functions with map?
No, the map function only accepts one callback function at a time. However, you can chain multiple map calls to achieve sequential transformations.
4. Is it possible to use map with nested arrays?
Yes, you can use map with nested arrays. The callback function can access elements within nested arrays and perform transformations accordingly.
5. Can I use map with other array methods like filter or reduce?
Yes, you can combine map with other array methods to perform complex data manipulations. For instance, you can use map to transform elements and then apply filter to select only the desired elements.
Tips for Using map Effectively
-
Use
mapfor transformations that apply to every element in an array. If you need to perform a specific operation on only certain elements, consider usingfilteror a conditional statement within the callback function. -
Ensure the callback function returns a value for each element. If the callback function returns
undefined, the resulting array will containundefinedat the corresponding index. - Consider using arrow functions for concise callback definitions. Arrow functions provide a more compact syntax for defining callback functions.
- Utilize
mapwith other array methods likefilterandreduceto perform complex data manipulations.
Conclusion
The JavaScript map function is a versatile and efficient tool for transforming arrays of data. Its ability to apply a specific function to each element, creating a new array with the modified elements, makes it an indispensable part of modern JavaScript development. By understanding the principles and advantages of using map, developers can enhance code readability, maintainability, and efficiency while effectively manipulating data structures.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Transforming Data with JavaScript’s map Function: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!