The Shifting Sands Of Power: A Comprehensive Look At Kingdoms Surrounding Ancient Israel
The Shifting Sands of Power: A Comprehensive Look at Kingdoms Surrounding Ancient Israel
Related Articles: The Shifting Sands of Power: A Comprehensive Look at Kingdoms Surrounding Ancient Israel
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Sands of Power: A Comprehensive Look at Kingdoms Surrounding Ancient Israel. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Sands of Power: A Comprehensive Look at Kingdoms Surrounding Ancient Israel

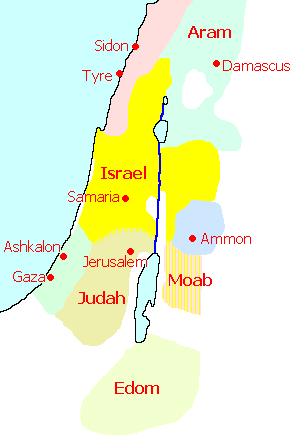
The ancient world was a tapestry of shifting alliances, territorial disputes, and fluctuating power dynamics. Understanding the kingdoms surrounding ancient Israel provides a crucial lens through which to interpret its history, culture, and religious development. This article delves into the complex geopolitical landscape surrounding Israel, highlighting the prominent kingdoms and their influence on the region.
The Early Kingdoms: A Mosaic of Power
The period before the rise of the Israelite monarchy witnessed a diverse array of kingdoms and empires vying for control of the Levant.
1. The Egyptians: From the Old Kingdom onwards, Egypt exerted significant influence on the region. The pharaohs, with their powerful military and economic strength, established a presence in Canaan, often using it as a buffer zone against other empires. Their influence is evident in Egyptian artifacts found throughout the region, indicating cultural exchange and trade.
2. The Amorites: These Semitic tribes, originating from the Arabian peninsula, established powerful city-states in the Levant during the Early Bronze Age. Notable Amorite kingdoms included Mari, Ebla, and the Amorite dynasty of Babylon. Their influence extended over much of Mesopotamia and Syria, posing a significant challenge to Egyptian dominance.
3. The Hittites: Emerging from Anatolia, the Hittites rose to prominence in the Late Bronze Age, becoming a major power in the Levant. Their empire, centered in Anatolia, stretched as far south as Syria, challenging Egyptian control. The Hittites, known for their formidable military prowess and sophisticated ironworking technology, left a lasting impact on the region.
4. The Canaanite City-States: Scattered throughout Canaan, these city-states, like Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos, were centers of trade and cultural innovation. Their religious practices, often characterized by polytheism and the worship of fertility deities, influenced early Israelite religious beliefs.
The Rise of Israel: A New Player in the Game
The establishment of the Israelite monarchy under King Saul marked a significant shift in the power dynamics of the region.
5. The Kingdom of Israel (Northern Kingdom): The Northern Kingdom, established by Jeroboam I after the division of Solomon’s kingdom, maintained a complex relationship with its neighbors. It faced constant threats from the powerful Aramean kingdoms to the north, particularly Damascus, which sought to expand its influence into Israel.
6. The Kingdom of Judah (Southern Kingdom): The Southern Kingdom, centered in Jerusalem, faced threats from both its northern neighbor and the growing power of the Assyrian Empire. Its strategic location and religious significance made it a coveted prize for empires seeking to expand their dominion.
The Rise and Fall of Empires: A New Order
The rise of powerful empires like Assyria, Babylonia, and Persia dramatically reshaped the political landscape of the Levant.
7. The Assyrian Empire: Known for its military might and ruthless tactics, the Assyrians conquered much of the Near East, including the Northern Kingdom of Israel in 722 BCE. Their influence extended across Mesopotamia, Syria, and Egypt, marking a period of instability and upheaval for the kingdoms of Israel and Judah.
8. The Babylonian Empire: Under King Nebuchadnezzar II, the Babylonians conquered Assyria and later Judah, destroying Jerusalem in 586 BCE. The Babylonian Exile, a period of forced deportation of Judeans to Babylon, had a profound impact on Jewish identity and history.
9. The Persian Empire: The Persian Empire, under Cyrus the Great, conquered Babylon in 539 BCE, ushering in a period of relative stability and tolerance for the Jews. Cyrus allowed the exiles to return to Jerusalem and rebuild their temple, marking a significant turning point in Jewish history.
The Legacy of the Kingdoms: A Lasting Influence
The kingdoms surrounding ancient Israel left a lasting legacy on the region, influencing its culture, religion, and political landscape.
1. Cultural Exchange: The interaction between Israel and its neighbors facilitated cultural exchange, evident in the adoption of foreign customs, artistic styles, and religious practices.
2. Religious Influence: The religious beliefs and practices of the surrounding kingdoms, particularly those of the Canaanites, left an imprint on early Israelite religious development. The struggles against idolatry and the development of monotheistic beliefs can be understood in light of the religious landscape of the region.
3. Political Legacy: The constant struggle for power and territory between the kingdoms of Israel and its neighbors shaped the political landscape of the region. The lessons learned from these interactions, particularly the dangers of unchecked ambition and the importance of alliances, resonated throughout Jewish history.
FAQs: Understanding the Kingdoms Surrounding Ancient Israel
Q: What was the significance of the Canaanite city-states?
A: The Canaanite city-states were important centers of trade, culture, and religion. Their economic prosperity and sophisticated urban infrastructure made them influential players in the Levant. Their religious practices, often centered on fertility deities, influenced early Israelite religious beliefs, leading to complex interactions between the two groups.
Q: What were the key factors contributing to the rise of the Assyrian Empire?
A: The Assyrians’ rise to power was driven by several factors, including:
- Military Innovations: They developed advanced military techniques and weaponry, including the use of iron weapons and siege warfare.
- Efficient Administration: They established a centralized government with a well-organized bureaucracy, allowing for efficient resource mobilization and military campaigns.
- Ruthless Tactics: Their reputation for brutality and cruelty instilled fear in their enemies, often leading to submission without major resistance.
Q: How did the Babylonian Exile impact Jewish history?
A: The Babylonian Exile had a profound impact on Jewish history and identity. The forced deportation to Babylon resulted in:
- Development of Jewish Identity: The shared experience of exile strengthened Jewish unity and identity, fostering a sense of community and shared history.
- The Rise of Rabbinic Judaism: The exile led to the development of rabbinic Judaism, emphasizing oral tradition and the interpretation of scripture.
- The Preservation of Jewish Culture: Despite the exile, the Jews preserved their religious and cultural traditions, ensuring their survival and transmission to future generations.
Tips: Navigating the Kingdoms Surrounding Ancient Israel
1. Use a Timeline: A clear timeline of the major kingdoms and their periods of dominance helps to understand the sequence of events and the shifting power dynamics.
2. Focus on Key Relationships: Understanding the key relationships between Israel and its neighbors, particularly those involving conflict, trade, or cultural exchange, provides a deeper understanding of the region’s history.
3. Explore Primary Sources: Ancient texts, inscriptions, and archaeological evidence offer valuable insights into the daily lives, religious beliefs, and political systems of the kingdoms surrounding ancient Israel.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Influence and Complexity
The kingdoms surrounding ancient Israel offer a rich tapestry of history, culture, and religious development. Understanding their influence on the Israelite experience provides crucial context for interpreting its history, religious beliefs, and cultural identity. The constant struggle for power, the complexities of cultural exchange, and the impact of religious interactions offer valuable insights into the dynamic and ever-evolving world of the ancient Near East. By exploring the kingdoms surrounding Israel, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of relationships that shaped the history and legacy of the Jewish people.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Sands of Power: A Comprehensive Look at Kingdoms Surrounding Ancient Israel. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!