The Shifting Landscape Of Africa: Understanding Population Density And Its Implications
The Shifting Landscape of Africa: Understanding Population Density and its Implications
Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape of Africa: Understanding Population Density and its Implications
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Landscape of Africa: Understanding Population Density and its Implications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Landscape of Africa: Understanding Population Density and its Implications

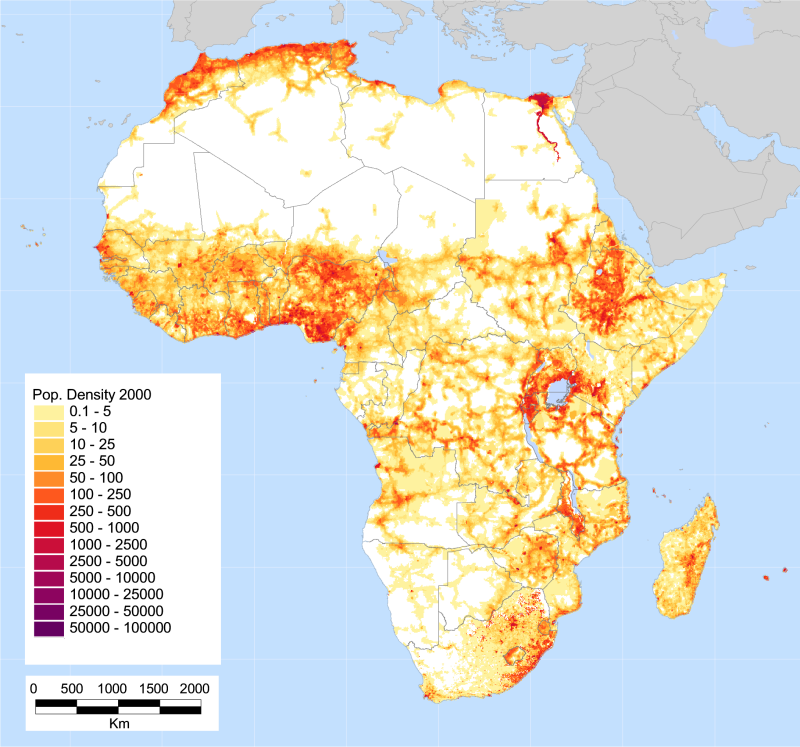
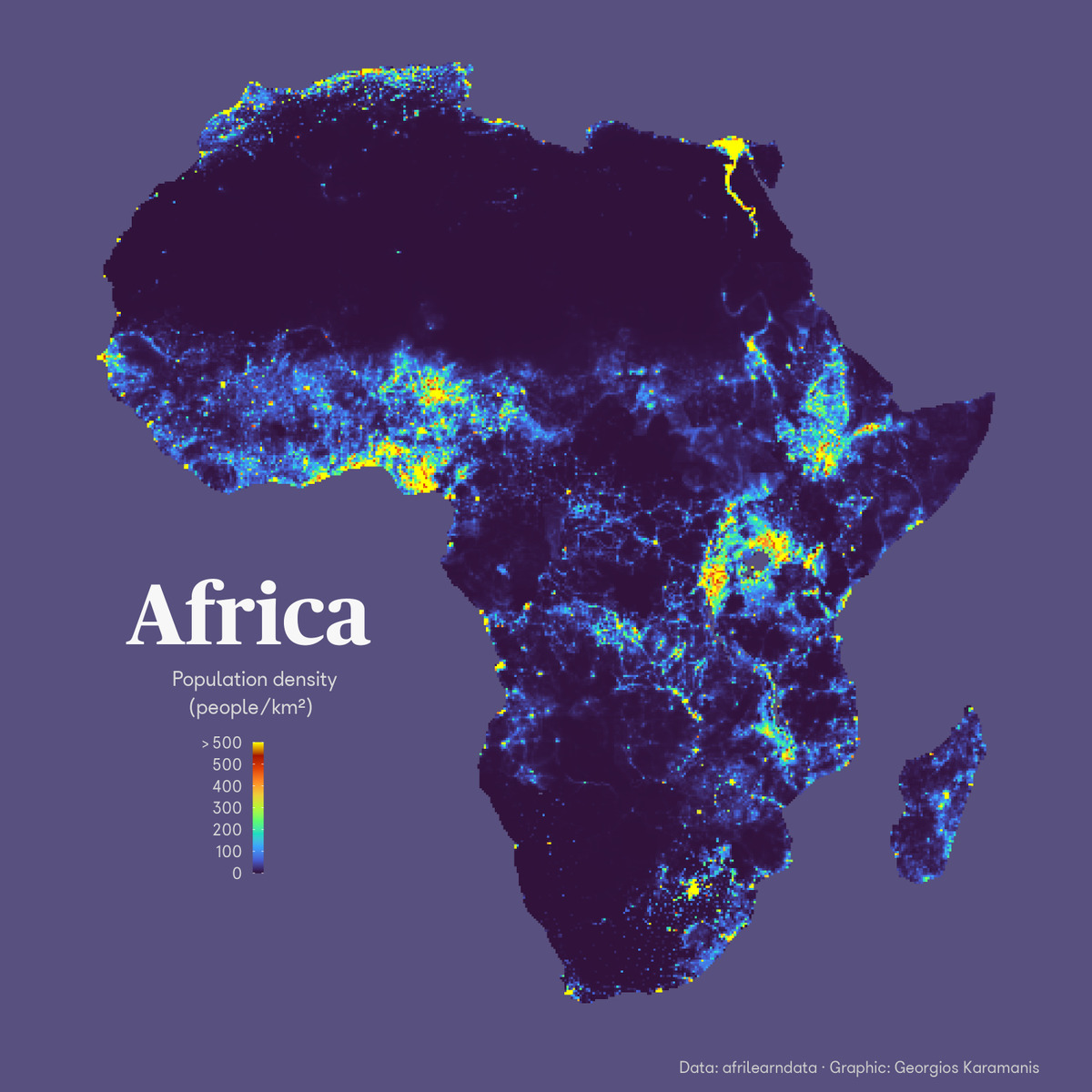
Africa, the second-largest continent by both land area and population, presents a complex and dynamic demographic landscape. Understanding the distribution of its population across the vast continent is crucial for effective policy-making, resource management, and addressing pressing challenges like urbanization, food security, and environmental sustainability. Population density, a key indicator of population distribution, provides valuable insights into the spatial patterns of human settlement and their associated socio-economic and environmental implications.
A Diverse Tapestry of Population Density
Africa’s population density varies significantly across its diverse regions, reflecting a multitude of factors including geographical features, climate, economic opportunities, and historical events.
Densely Populated Zones:
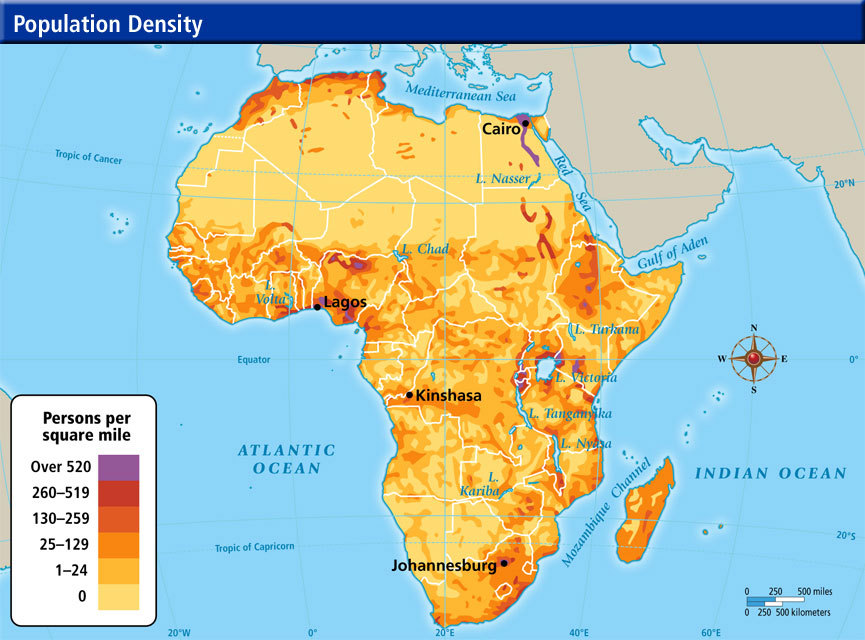
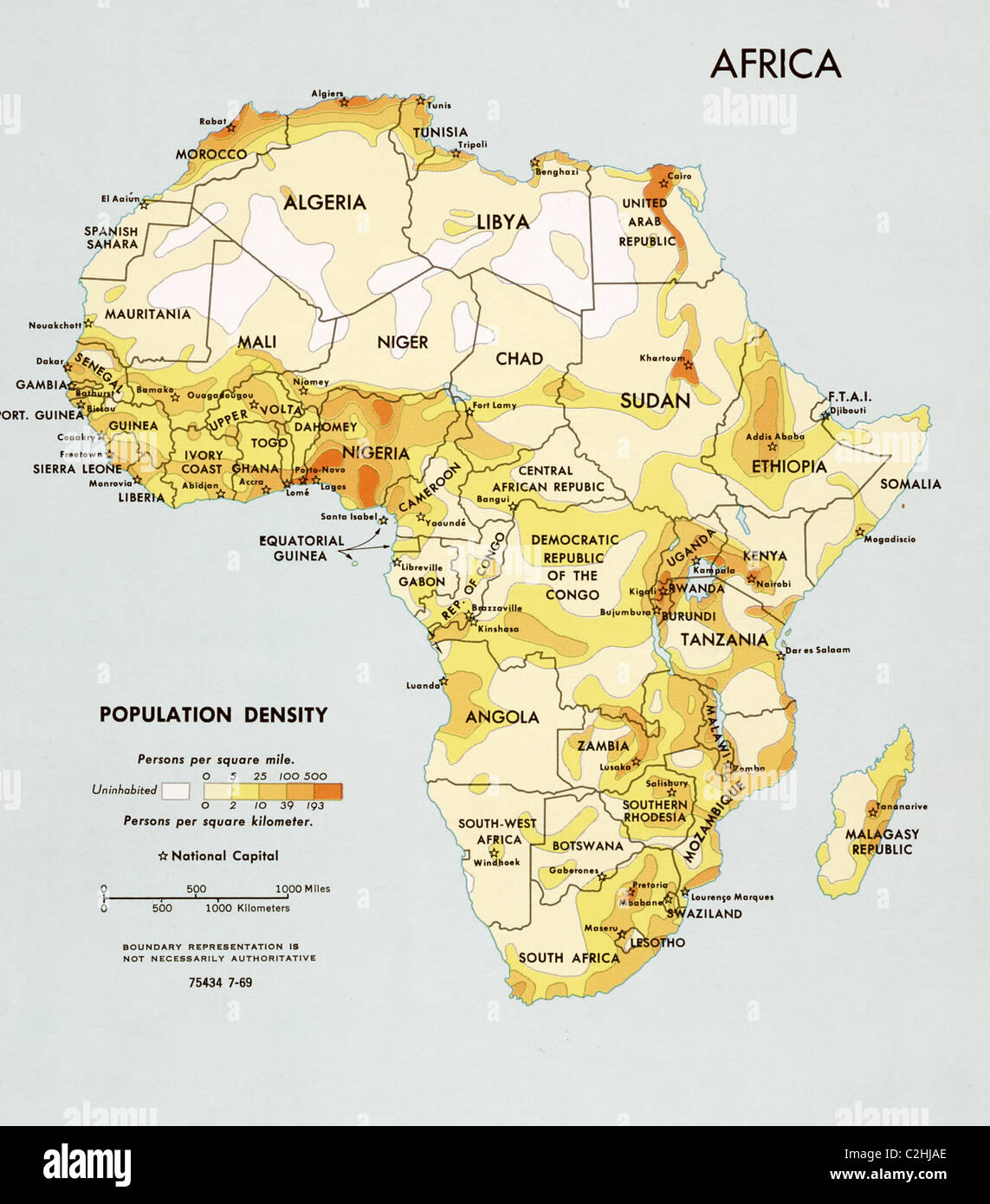
- The Nile Valley: This fertile strip along the Nile River in Egypt and Sudan boasts a high population density, supported by rich agricultural land and historical civilizations.
- Coastal Regions: Coastal areas in West Africa, particularly Nigeria, Ghana, and Côte d’Ivoire, exhibit high population density due to their access to trade routes, economic opportunities, and fertile land.
- Urban Centers: Major cities across Africa, including Lagos, Cairo, Johannesburg, and Kinshasa, attract significant populations, contributing to high population density in their surrounding areas.
Sparsely Populated Zones:
- Deserts: The Sahara Desert in North Africa and the Namib and Kalahari deserts in southern Africa are sparsely populated due to extreme aridity and limited resources.
- Tropical Rainforests: Dense rainforests in Central Africa, while rich in biodiversity, present challenges for human habitation due to difficult terrain and limited arable land.
- Mountainous Regions: The Atlas Mountains in North Africa and the Ethiopian Highlands are sparsely populated due to their challenging terrain and harsh climates.
Understanding the Factors Influencing Population Density
Several factors contribute to the varying population density across Africa:
- Climate: Areas with favorable climates, such as fertile valleys and coastal regions, tend to have higher population density. Conversely, arid deserts and mountainous regions with harsh climates often have lower population density.
- Water Availability: Access to water is crucial for human settlements and agriculture. Regions with abundant water resources, like the Nile Valley, typically have higher population density.
- Soil Fertility: Areas with fertile soils suitable for agriculture, such as the coastal regions of West Africa, attract higher population densities.
- Economic Opportunities: Urban centers and areas with diverse economic opportunities, including mining, manufacturing, and tourism, tend to have higher population densities due to job prospects.
- Historical Influences: Past settlements, trade routes, and colonial legacies have significantly shaped current population distribution patterns.
The Implications of Population Density
Understanding population density is essential for addressing a range of challenges and opportunities across Africa:
- Urbanization: As populations grow and migrate to urban centers, understanding population density is crucial for planning sustainable cities with adequate infrastructure, housing, and services.
- Resource Management: High population densities can strain resources, leading to challenges in managing water, food, and energy. Understanding population distribution can inform resource allocation and conservation efforts.
- Environmental Sustainability: Population density can impact environmental sustainability through deforestation, pollution, and land degradation. Understanding population distribution allows for targeted conservation and sustainable development initiatives.
- Health and Education: High population densities can strain healthcare and educational systems. Understanding population distribution can inform the allocation of resources and the development of targeted interventions.
- Economic Development: Population density can influence economic development by impacting access to markets, labor, and infrastructure. Understanding population distribution can inform economic policies and investments.
FAQs
Q: What are the most densely populated countries in Africa?
A: The most densely populated countries in Africa are:
- Rwanda: With a population density of approximately 500 people per square kilometer.
- Burundi: With a population density of approximately 450 people per square kilometer.
- Egypt: With a population density of approximately 100 people per square kilometer, largely concentrated along the Nile Valley.
Q: How has population density changed in Africa over time?
A: Africa has experienced significant population growth in recent decades, leading to an overall increase in population density. However, the rate of change varies across regions, with some areas experiencing rapid urbanization and others experiencing slower growth.
Q: What are the potential consequences of high population density in Africa?
A: High population density can lead to challenges such as:
- Urban sprawl: Rapid urbanization can lead to uncontrolled growth and inadequate infrastructure.
- Resource depletion: High population density can strain resources, leading to water scarcity, food shortages, and environmental degradation.
- Social tensions: High population density can lead to social tensions, particularly in areas with limited resources and opportunities.
Q: What are the potential benefits of low population density in Africa?
A: Low population density can offer advantages such as:
- Preservation of natural resources: Sparsely populated areas can help preserve biodiversity and natural ecosystems.
- Sustainable development: Low population density can facilitate sustainable development practices, such as ecotourism and agroforestry.
- Improved quality of life: Low population density can lead to a higher quality of life with less crowding, pollution, and competition for resources.
Tips
- Use accurate and up-to-date data: Population density data can be found from sources such as the World Bank, the United Nations, and national statistical agencies.
- Consider spatial patterns: Population density maps should be analyzed in conjunction with other geographic data, such as climate, topography, and infrastructure.
- Recognize the limitations of population density: Population density is a useful indicator, but it is not a perfect measure of population distribution. It is important to consider other factors, such as population growth, migration patterns, and socio-economic conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding population density in Africa is crucial for addressing a range of challenges and opportunities. By analyzing population distribution patterns and the factors that influence them, policymakers, researchers, and communities can develop effective strategies for sustainable development, resource management, and promoting a brighter future for the continent. While the challenges of population growth and urbanization are significant, Africa’s diverse demographic landscape also presents opportunities for innovation, economic growth, and a more equitable and sustainable future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Landscape of Africa: Understanding Population Density and its Implications. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!