The Power Of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights Through Geographic Information Systems
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights Through Geographic Information Systems
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights Through Geographic Information Systems
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights Through Geographic Information Systems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights Through Geographic Information Systems

Geographic information systems (GIS), often referred to as "geospatial analysis," have become indispensable tools for understanding and managing our world. GIS combines data from various sources, including maps, satellite imagery, and sensor networks, with advanced analytical capabilities to reveal spatial patterns, relationships, and trends. This powerful technology has revolutionized numerous fields, from environmental management and urban planning to healthcare and disaster response.
Understanding the Foundations of GIS
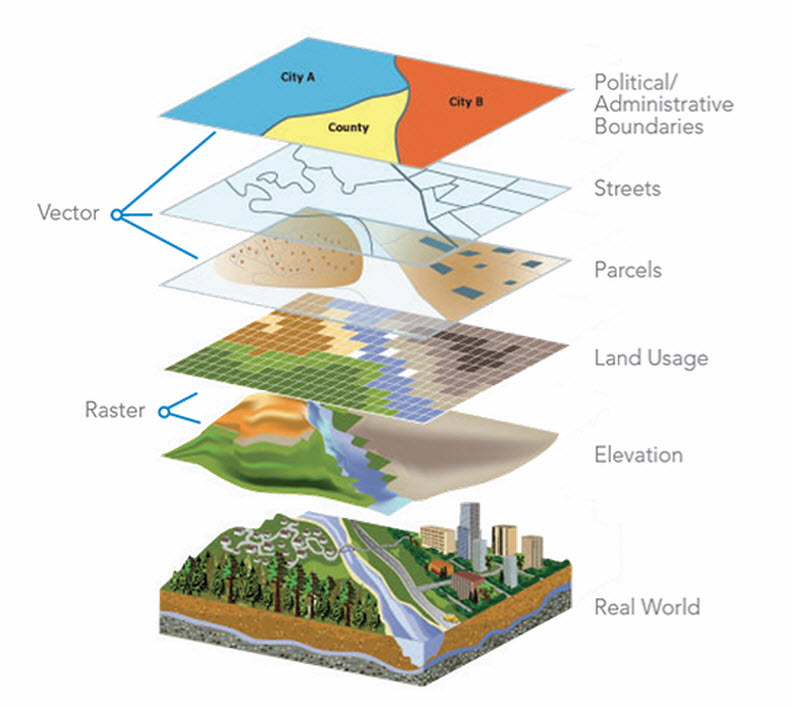
At the core of GIS lies the concept of georeferenced data. This data, linked to specific geographic locations, forms the foundation for spatial analysis. GIS software allows users to visualize, analyze, and manipulate this data to gain insights into complex spatial relationships.
Key Components of a GIS
- Hardware: Powerful computers, specialized graphics cards, and high-resolution displays are essential for handling the large datasets and complex computations involved in GIS.
- Software: GIS software provides the tools for data management, analysis, visualization, and output generation. Popular examples include ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo.
-
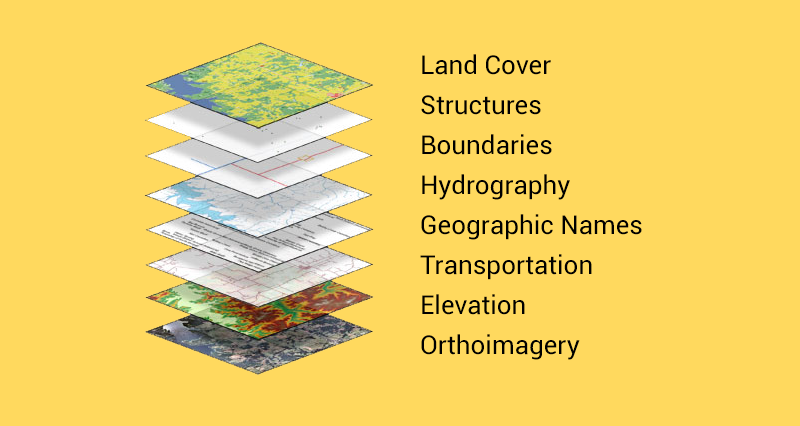
Data: The lifeblood of GIS, data can come from various sources, including:
- Geospatial data: Maps, satellite imagery, aerial photographs, topographic data, and digital elevation models.
- Attribute data: Information associated with geographic locations, such as population demographics, land use, environmental conditions, and infrastructure details.
- People: GIS professionals, ranging from data analysts and cartographers to geographers and planners, are crucial for interpreting results, designing solutions, and communicating findings.
The Advantages of Utilizing GIS
GIS offers a range of benefits, making it an invaluable tool in various sectors:
- Improved Decision Making: By providing a comprehensive spatial context, GIS enables informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
- Enhanced Visualization: GIS allows for the creation of interactive maps, charts, and dashboards that clearly communicate complex spatial relationships and trends.
- Efficient Resource Management: GIS helps optimize resource allocation by identifying patterns of resource use, predicting demand, and prioritizing areas for intervention.
- Effective Problem Solving: GIS supports the identification and analysis of spatial problems, facilitating the development of targeted solutions.
- Increased Collaboration: GIS fosters collaboration among stakeholders by providing a common platform for data sharing, visualization, and analysis.
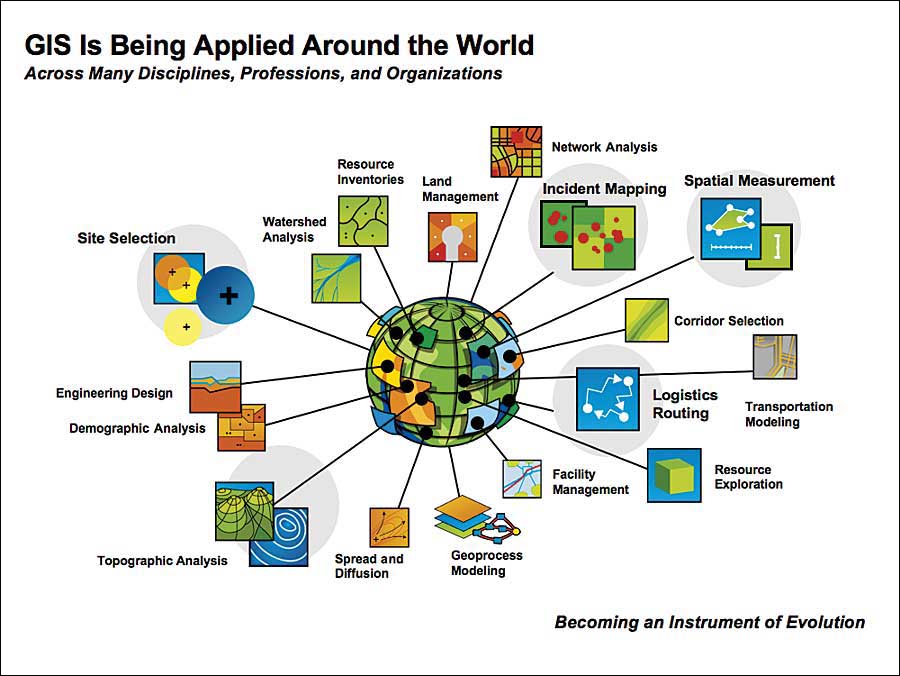
Applications of GIS Across Diverse Fields
The versatility of GIS has led to its widespread adoption in a variety of sectors:
-
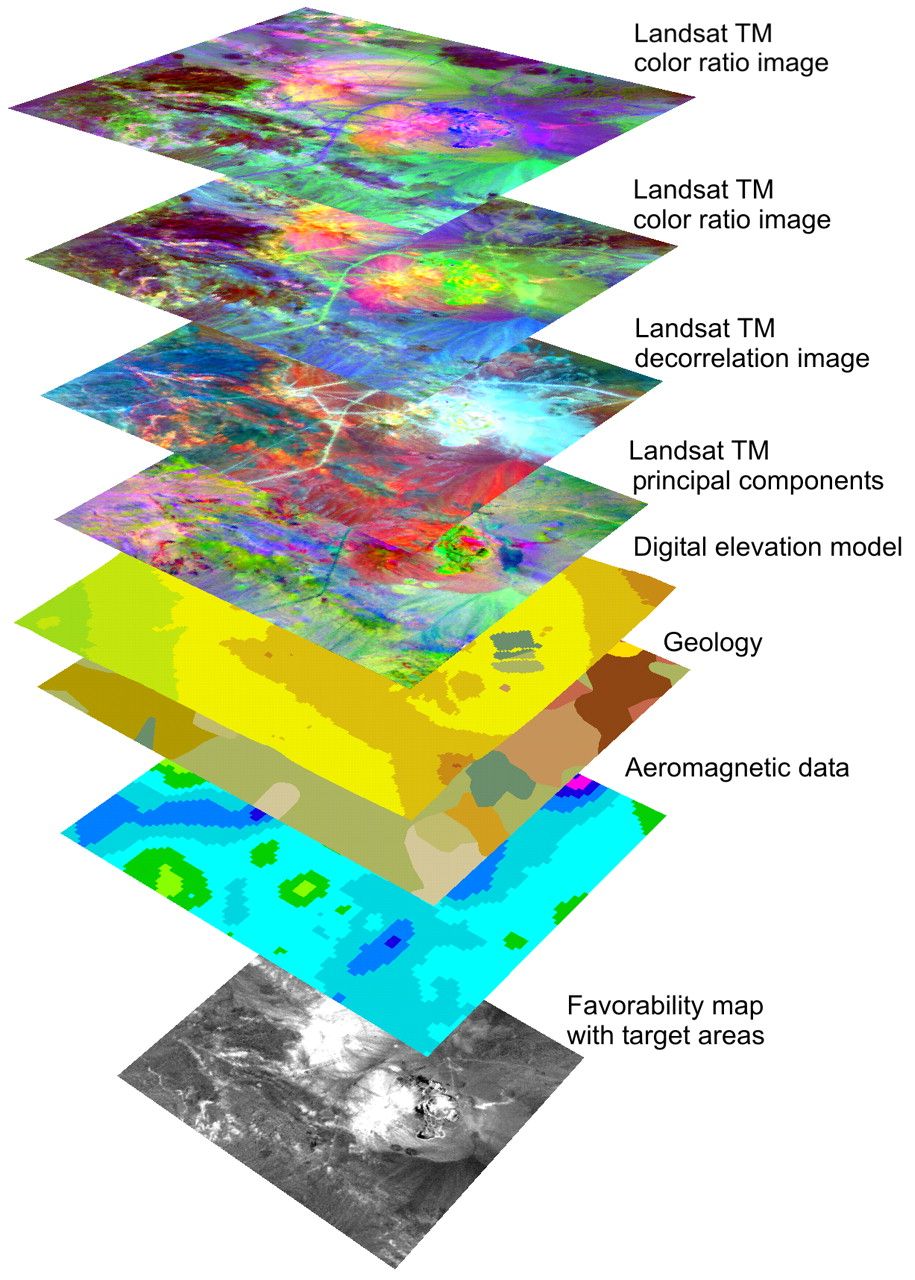
Environmental Management: GIS plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing environmental resources, including:
- Habitat mapping and conservation: Identifying and protecting critical habitats for endangered species.
- Pollution monitoring and control: Tracking air and water pollution sources and evaluating mitigation strategies.
- Climate change analysis: Assessing the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and developing adaptation plans.
-
Urban Planning: GIS is essential for sustainable urban development, enabling:
- Land use planning: Optimizing land use for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.
- Infrastructure development: Planning and managing transportation networks, utilities, and public services.
- Urban renewal: Identifying areas for revitalization and guiding urban redevelopment projects.
-
Healthcare: GIS supports public health initiatives by:
- Disease surveillance and outbreak response: Tracking disease outbreaks, identifying high-risk areas, and implementing targeted interventions.
- Healthcare facility planning: Optimizing the location and distribution of healthcare facilities to ensure equitable access.
- Health risk assessment: Identifying and mitigating environmental and social factors that contribute to health disparities.
-
Disaster Management: GIS is crucial for disaster preparedness, response, and recovery:
- Risk assessment and mitigation: Identifying areas vulnerable to natural disasters and implementing preventative measures.
- Emergency response: Coordinating rescue efforts, managing evacuation routes, and providing real-time information during disasters.
- Post-disaster recovery: Assessing damage, planning reconstruction efforts, and coordinating relief aid distribution.
-
Business and Industry: GIS provides valuable insights for businesses and industries, enabling:
- Market analysis: Identifying potential customer bases, optimizing distribution networks, and understanding market trends.
- Site selection: Finding optimal locations for new facilities, stores, or offices based on factors like accessibility, demographics, and competition.
- Logistics and transportation: Optimizing delivery routes, managing inventory, and tracking shipments.
FAQs about GIS
1. What are the key differences between GIS and GPS?
While both involve spatial data, GIS focuses on analyzing and manipulating geospatial data to extract insights, while GPS is a technology for determining precise locations on Earth. GIS uses GPS data as a source of information, but its capabilities extend far beyond simple location tracking.
2. What are the challenges associated with using GIS?
GIS involves complex data management, analysis, and visualization, which can pose challenges for users:
- Data acquisition and quality: Obtaining accurate, complete, and up-to-date data can be difficult and expensive.
- Data processing and analysis: GIS requires specialized skills and knowledge for data manipulation, analysis, and interpretation.
- Software complexity: GIS software can be complex and require significant training to master.
- Security and privacy: Managing sensitive geospatial data requires robust security measures to protect privacy and prevent unauthorized access.
3. How can I learn more about GIS?
There are numerous resources available for learning about GIS:
- Online courses: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer comprehensive GIS courses.
- University programs: Many universities offer undergraduate and graduate degrees in GIS, geography, and related fields.
- Professional organizations: Organizations like the GIS Association (GIS-A) and the Association of American Geographers (AAG) provide training and networking opportunities.
- GIS software documentation: Most GIS software vendors offer extensive documentation, tutorials, and support resources.
Tips for Effective GIS Implementation
- Define clear objectives: Clearly define the goals and desired outcomes of your GIS project before embarking on data collection and analysis.
- Focus on data quality: Ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of your data to avoid misleading results.
- Choose the right software: Select GIS software that meets the specific needs of your project and the skills of your team.
- Collaborate with experts: Seek guidance from GIS professionals to ensure effective data management, analysis, and interpretation.
- Communicate findings effectively: Present GIS results in a clear and concise manner, using visualizations and narratives that are accessible to a wider audience.
Conclusion
GIS has emerged as a transformative technology, enabling us to understand and manage our world in unprecedented ways. By integrating data from various sources and applying advanced analytical techniques, GIS empowers us to make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and build a more sustainable future. As technology continues to evolve, GIS will play an increasingly vital role in addressing global challenges and shaping a better tomorrow.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Analysis: Unveiling Insights Through Geographic Information Systems. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!