The Power Of Bulk Operations: Exploring Java Map’s PutAll Method
The Power of Bulk Operations: Exploring Java Map’s putAll Method
Related Articles: The Power of Bulk Operations: Exploring Java Map’s putAll Method
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Bulk Operations: Exploring Java Map’s putAll Method. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Bulk Operations: Exploring Java Map’s putAll Method
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Bulk Operations: Exploring Java Map’s putAll Method
- 3.1 Understanding the putAll Method: A Foundation for Efficient Bulk Operations
- 3.2 Beyond Basic Usage: Exploring the Benefits and Applications
- 3.3 Addressing Common Concerns: A Guide to Effective putAll Usage
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Inquiries
- 3.5 Tips for Effective putAll Usage: Optimizing Performance and Code Clarity
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of putAll for Efficient Map Manipulation
- 4 Closure
The Power of Bulk Operations: Exploring Java Map’s putAll Method

In the realm of Java programming, maps are indispensable data structures that facilitate efficient storage and retrieval of key-value pairs. While individual insertions and updates are common operations, scenarios often arise where bulk manipulation of map contents becomes necessary. This is where the putAll method shines, offering a powerful and convenient mechanism to populate or merge maps with existing data.
Understanding the putAll Method: A Foundation for Efficient Bulk Operations
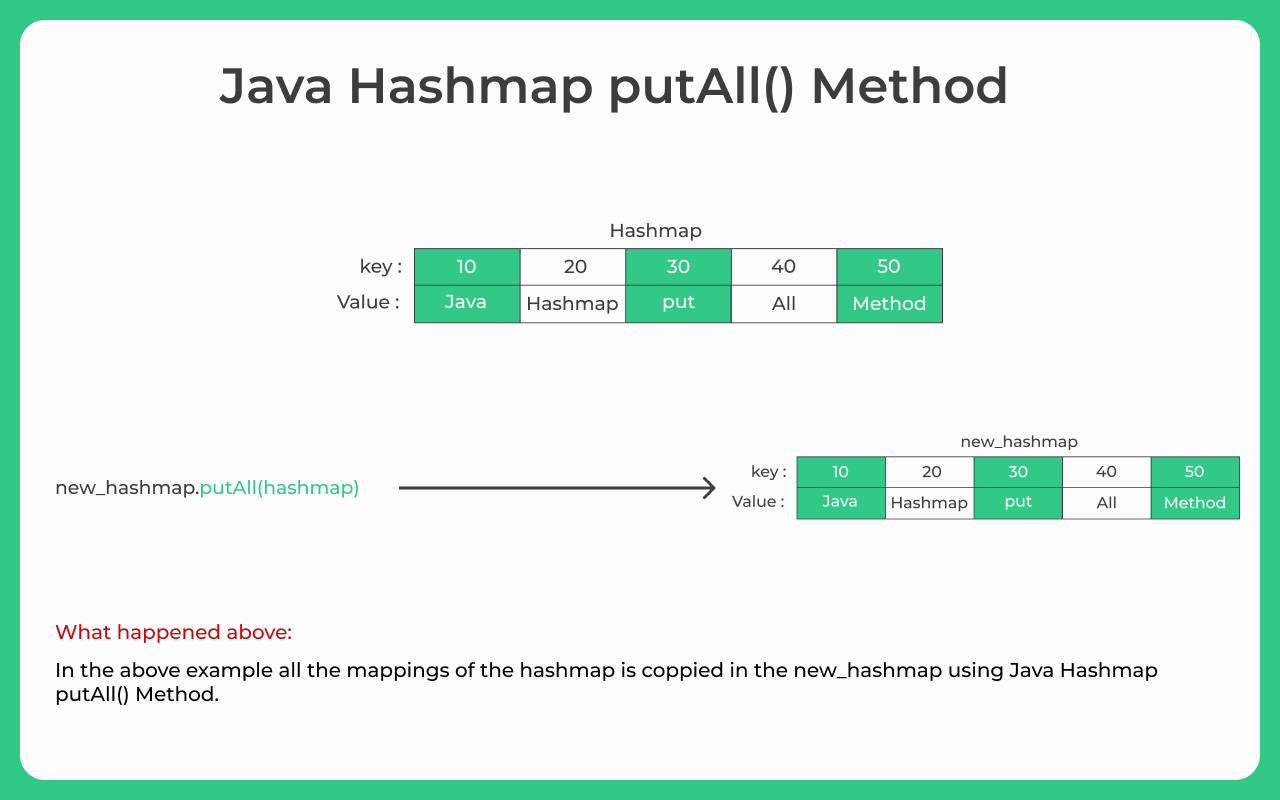
The putAll method is a fundamental operation in Java’s Map interface, designed to streamline the process of adding multiple key-value pairs to a map from another map. Its essence lies in its ability to copy all entries from a source map into the target map, effectively merging data in a single, efficient step.
Key Characteristics of putAll:
-
Merging: The
putAllmethod gracefully handles situations where keys from the source map already exist in the target map. The existing values associated with those keys are overwritten by the values from the source map. -
Efficiency: By performing bulk operations,
putAlloptimizes performance, particularly when dealing with large datasets. It avoids the overhead of individual insertion operations, leading to faster execution times. -
Flexibility: The
putAllmethod is versatile, accommodating both maps of the same type and maps with different types, as long as the source map’s keys are compatible with the target map.
Syntax:
targetMap.putAll(sourceMap);Where:
-
targetMap: TheMapobject that will receive the entries from the source map. -
sourceMap: TheMapobject containing the entries to be added to the target map.
Example:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PutAllExample
public static void main(String[] args)
Map<String, Integer> sourceMap = new HashMap<>();
sourceMap.put("Apple", 1);
sourceMap.put("Banana", 2);
sourceMap.put("Cherry", 3);
Map<String, Integer> targetMap = new HashMap<>();
targetMap.put("Grape", 4);
targetMap.put("Orange", 5);
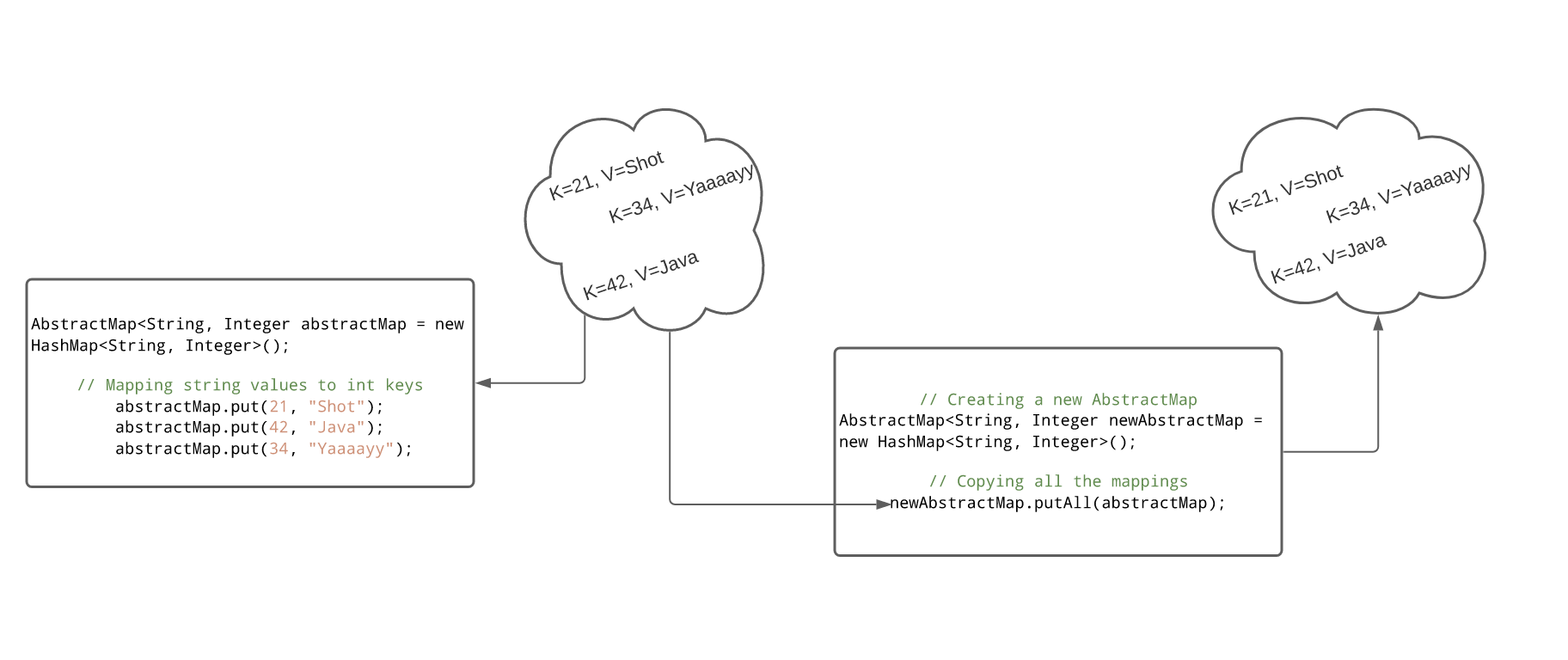
targetMap.putAll(sourceMap);
System.out.println("Target Map: " + targetMap);
This example demonstrates the putAll method in action. The sourceMap contains three key-value pairs, while the targetMap has two. After calling putAll, the targetMap now includes all the entries from both maps, with the values for "Apple", "Banana", and "Cherry" overwriting any existing values in the targetMap.
Beyond Basic Usage: Exploring the Benefits and Applications
The putAll method transcends basic data insertion. Its power lies in its ability to simplify and optimize various programming tasks. Here are some key benefits and applications of putAll:
1. Data Consolidation: The putAll method facilitates efficient merging of data from multiple sources into a single map. This is particularly useful in scenarios involving data aggregation, where information needs to be consolidated from different sources.
2. Data Initialization: putAll is ideal for initializing maps with pre-defined data. This can be advantageous when setting up configuration maps, look-up tables, or other data structures that require initial values.
3. Map Transformation: By selectively copying entries from a source map based on specific criteria, the putAll method can be used to transform a map, filtering or modifying its content.
4. Data Migration: In situations where data needs to be migrated from one map to another, the putAll method provides a straightforward and efficient solution.
5. Enhanced Performance: As putAll performs bulk operations, it can significantly improve performance compared to individual insertion operations, especially when working with large datasets.
Addressing Common Concerns: A Guide to Effective putAll Usage
While the putAll method offers numerous advantages, certain aspects require careful consideration to ensure optimal usage and avoid potential pitfalls.
1. Key Overwrites: Remember that the putAll method overwrites existing values associated with keys that appear in both the source and target maps. This behavior can be desirable in some cases but might lead to unintended data loss in others.
2. Type Compatibility: Ensure that the keys in the source map are compatible with the target map. If the types differ, a ClassCastException might occur.
3. Thread Safety: When using maps in multithreaded environments, consider the thread-safety implications of the putAll method. For instance, if the target map is not synchronized, concurrent modifications can lead to unexpected behavior.
4. Performance Considerations: While putAll generally offers performance benefits, its efficiency can vary depending on the implementation of the specific map type. In some cases, especially when dealing with very large maps, alternative approaches might be more efficient.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Inquiries
Q: What happens if a key exists in both the source and target maps?
A: The value associated with the key in the source map will overwrite the existing value in the target map.
Q: Is putAll thread-safe?
A: The thread-safety of putAll depends on the specific map implementation. For unsynchronized maps, concurrent modifications can lead to unpredictable results.
Q: Can putAll be used with maps of different types?
A: Yes, but the keys in the source map must be compatible with the target map. If the key types differ, a ClassCastException might occur.
Q: Is there a way to avoid overwriting existing values in the target map?
A: Yes, you can use the computeIfAbsent method to insert a value only if the key is not already present in the target map.
Q: When should I use putAll instead of individual insertion operations?
A: Use putAll when you need to add multiple key-value pairs to a map efficiently, especially when dealing with large datasets or when merging data from multiple sources.
Tips for Effective putAll Usage: Optimizing Performance and Code Clarity
1. Use putAll judiciously: Only use putAll when it offers a clear performance advantage over individual insertions.
2. Understand the behavior of key overwrites: Be aware that putAll overwrites existing values. If this behavior is not desired, consider alternative approaches like computeIfAbsent.
3. Ensure type compatibility: Verify that the keys in the source and target maps are compatible to avoid ClassCastException.
4. Consider thread-safety: In multithreaded environments, use synchronized maps or implement appropriate synchronization mechanisms to prevent data corruption.
5. Optimize for large datasets: For very large maps, explore specialized data structures or algorithms to optimize performance.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of putAll for Efficient Map Manipulation
The putAll method is a powerful tool in the Java programmer’s arsenal, providing an efficient and convenient way to perform bulk operations on maps. Its ability to merge data, initialize maps, and transform content makes it invaluable for a wide range of programming tasks. By understanding its characteristics, benefits, and potential pitfalls, developers can harness the power of putAll to enhance code efficiency, clarity, and performance.



%3B+void+clear()%3B.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Bulk Operations: Exploring Java Map’s putAll Method. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!