The Pillars Of Email Communication: IMAP And SMTP Explained
The Pillars of Email Communication: IMAP and SMTP Explained
Related Articles: The Pillars of Email Communication: IMAP and SMTP Explained
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Pillars of Email Communication: IMAP and SMTP Explained. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Pillars of Email Communication: IMAP and SMTP Explained
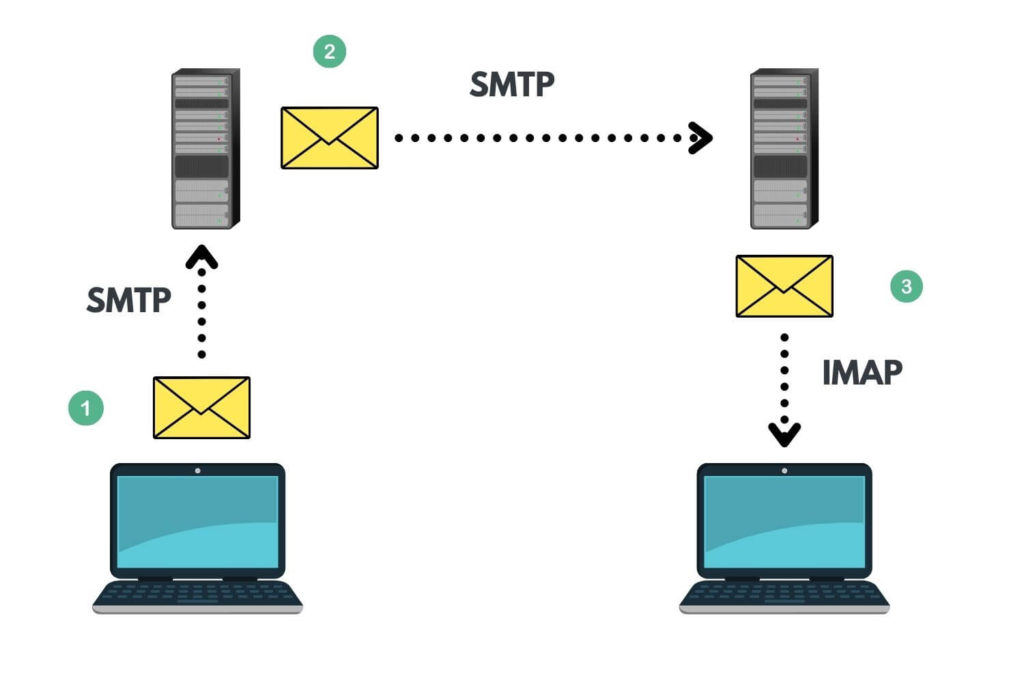
In the digital age, email has become an indispensable tool for communication, facilitating personal interactions, business transactions, and information dissemination. Behind the seamless experience of sending and receiving emails lie two fundamental protocols: Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). These protocols work in tandem to ensure emails reach their intended recipients reliably and efficiently.
IMAP: Managing Your Inbox
IMAP serves as the cornerstone of email management, enabling users to access and manipulate their emails from any device. It operates as a client-server protocol, allowing users to connect to their email server and perform various actions, including:
- Retrieving emails: IMAP downloads emails to the user’s device, allowing for offline access.
- Organizing emails: Users can create folders, move emails between folders, and apply labels to categorize messages.
- Syncing email changes: Any modifications made to emails, such as marking them as read or deleting them, are synchronized across all connected devices.
- Searching emails: IMAP allows for powerful search functionalities, enabling users to quickly locate specific messages based on keywords, sender, or date.
Key Features of IMAP:
- Offline Access: IMAP allows users to access their emails even without an internet connection. This is particularly useful for mobile users or individuals who frequently travel.
- Multiple Device Synchronization: Changes made to emails on one device are reflected on all connected devices, ensuring consistency across platforms.
- Powerful Search Capabilities: IMAP supports advanced search filters, enabling users to efficiently find specific emails within their inbox.
- Flexibility and Control: IMAP provides users with granular control over their email organization and access, allowing for customization to suit individual needs.
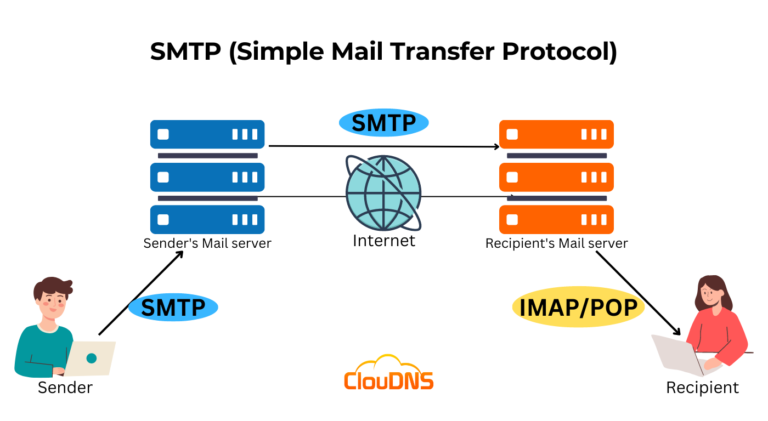
SMTP: Delivering Your Messages
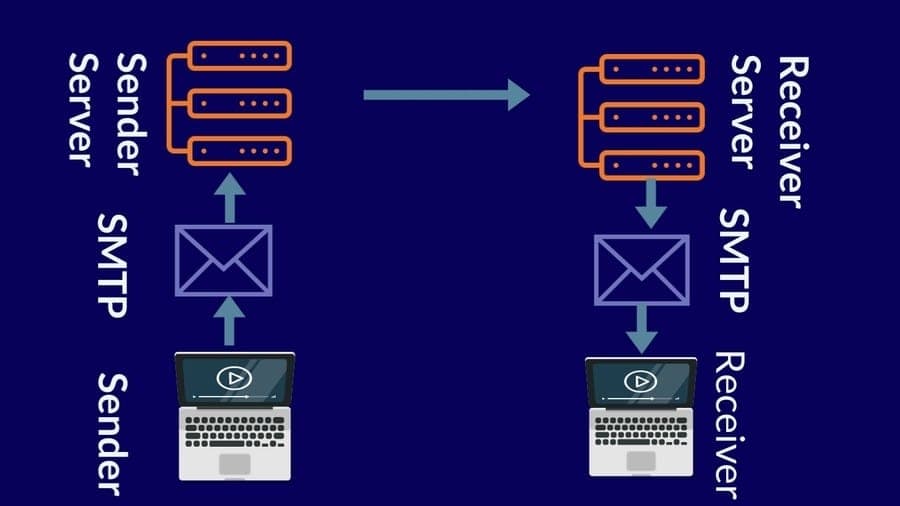
SMTP acts as the email delivery system, responsible for transmitting emails from the sender’s email client to the recipient’s email server. It operates as a server-to-server protocol, ensuring that emails are routed and delivered reliably.
The SMTP Process:
- Message Composition: The sender composes an email using their email client.
- Connection Establishment: The email client establishes a connection with the sender’s SMTP server.
- Message Transmission: The email client sends the email message to the SMTP server.
- Recipient Lookup: The SMTP server determines the recipient’s email server based on their email address.
- Message Delivery: The SMTP server forwards the email to the recipient’s server.
- Message Reception: The recipient’s server receives the email and stores it in their inbox.
Key Features of SMTP:
- Reliable Delivery: SMTP ensures that emails are delivered to the recipient’s server with minimal delays or errors.
- Secure Transmission: Modern SMTP implementations utilize encryption protocols like TLS/SSL to protect email content during transmission.
- Universal Compatibility: SMTP is a widely adopted standard, ensuring compatibility between different email clients and servers.
- Email Queueing: SMTP servers can temporarily store emails in a queue if the recipient’s server is unavailable, ensuring that emails are delivered when possible.
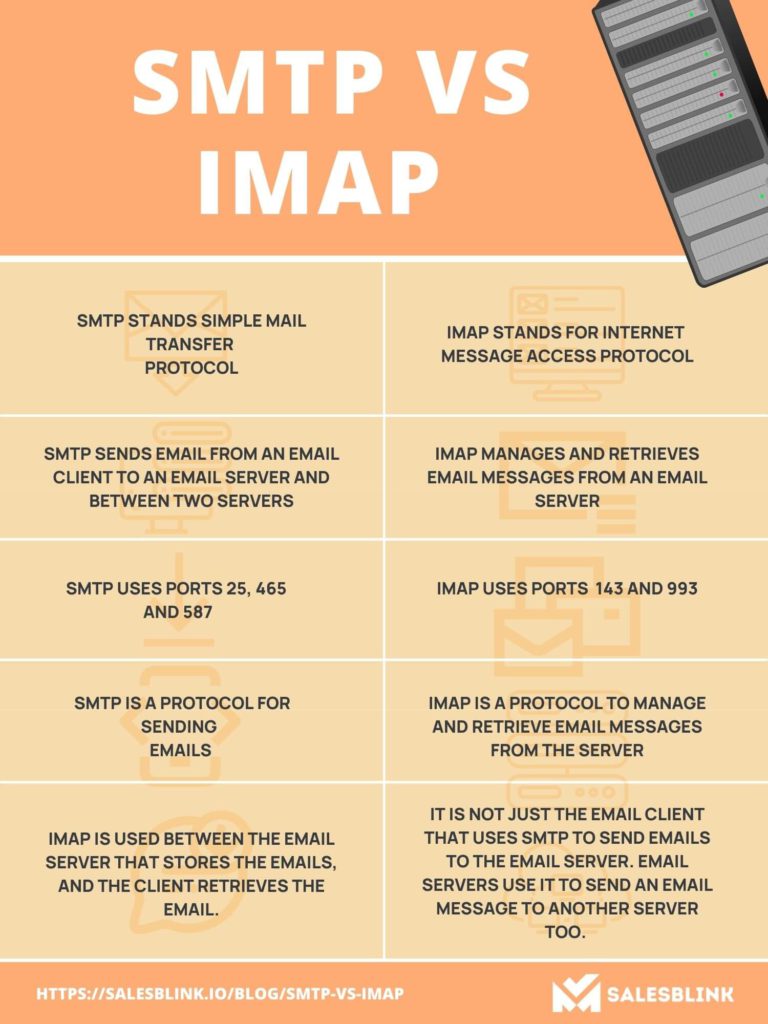
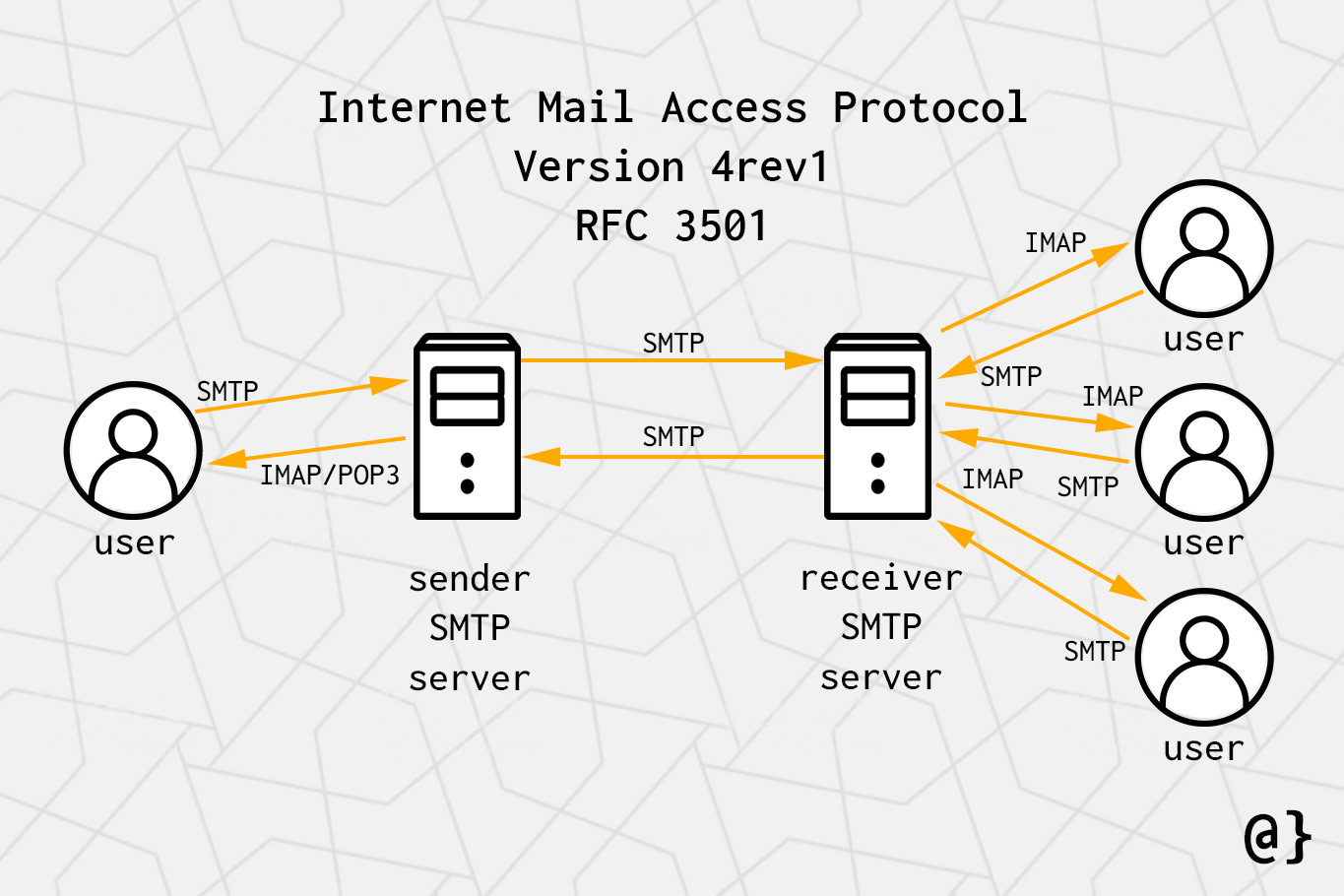
The Synergy of IMAP and SMTP
IMAP and SMTP complement each other seamlessly, working together to provide a complete email experience. While IMAP manages the user’s email inbox, SMTP ensures the reliable delivery of messages.
- IMAP enables users to access and manage their emails, while SMTP delivers those emails to their intended recipients.
- IMAP allows users to organize and categorize emails, while SMTP ensures that these organized emails are delivered correctly.
- IMAP provides users with flexibility and control over their email experience, while SMTP provides the underlying infrastructure for email delivery.
Understanding the Importance of IMAP and SMTP
IMAP and SMTP play a crucial role in the modern digital landscape, underpinning email communication across various platforms and devices. Their importance stems from the following factors:
- Global Communication: Email remains a fundamental tool for communication, connecting individuals and businesses across geographical boundaries. IMAP and SMTP facilitate this global communication by ensuring reliable email delivery.
- Business Operations: Email is essential for business operations, enabling communication with clients, partners, and employees. IMAP and SMTP ensure that business emails are delivered promptly and securely.
- Information Dissemination: Email serves as a primary channel for disseminating information, whether it’s news updates, marketing materials, or official announcements. IMAP and SMTP ensure the efficient and widespread distribution of information.
- Security and Privacy: IMAP and SMTP, especially when implemented with encryption protocols, protect email content from unauthorized access, safeguarding sensitive information.
FAQs about IMAP and SMTP
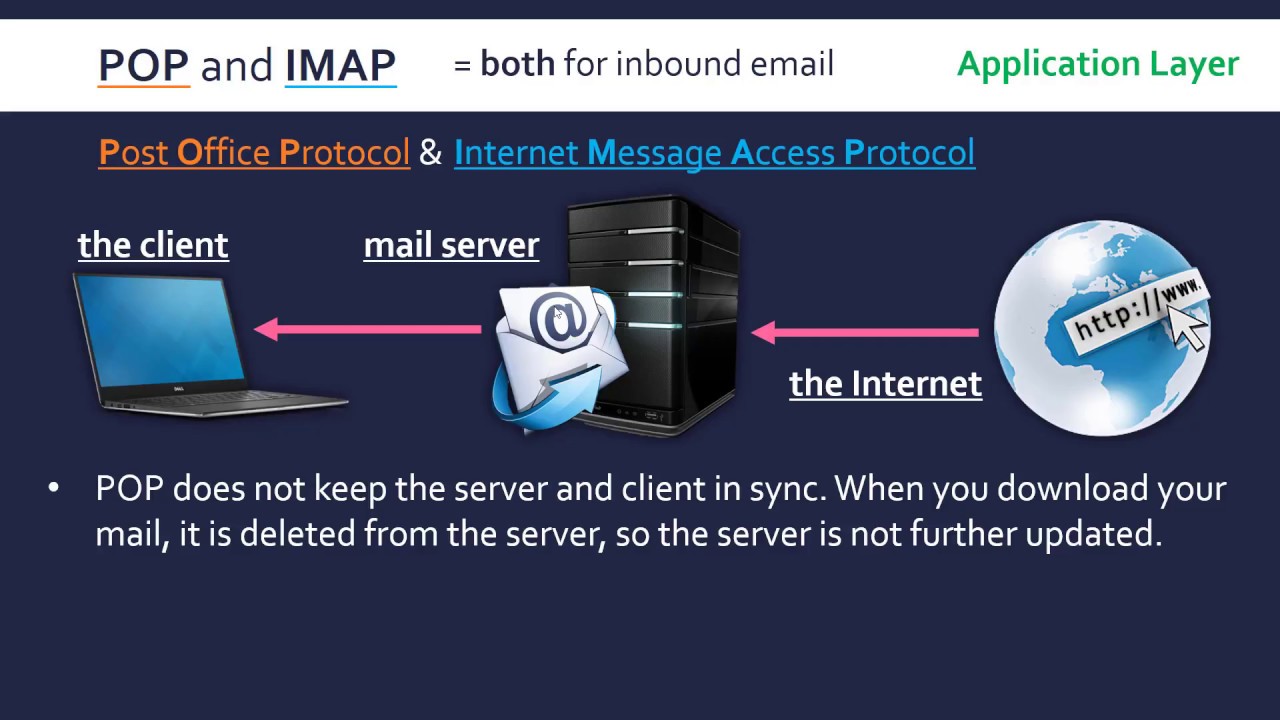
1. What is the difference between IMAP and POP3?
IMAP and POP3 are both email protocols that enable users to access their emails. However, they differ in their approach to email management:
- IMAP downloads emails to the user’s device but keeps a copy on the server, allowing access from multiple devices.
- POP3 downloads emails to the user’s device and deletes them from the server, making them inaccessible from other devices.
2. How secure are IMAP and SMTP?
IMAP and SMTP are inherently secure protocols. However, their security depends on the implementation and encryption protocols used. Modern implementations typically employ TLS/SSL encryption to protect email content during transmission.
3. Can I use IMAP and SMTP with different email providers?
Yes, IMAP and SMTP are widely supported by various email providers, ensuring compatibility across platforms. Users can configure their email clients to connect to different email servers using IMAP and SMTP.
4. What are the advantages of using IMAP over POP3?
IMAP offers several advantages over POP3, including:
- Offline access to emails: IMAP allows users to access their emails even without an internet connection.
- Multiple device synchronization: IMAP keeps emails synchronized across all connected devices.
- Powerful search capabilities: IMAP supports advanced search filters for efficient email retrieval.
5. How do I configure IMAP and SMTP in my email client?
The configuration process for IMAP and SMTP varies depending on the email client. However, most clients provide clear instructions and settings for configuring these protocols.
Tips for Using IMAP and SMTP
- Use a secure email client: Choose an email client that supports encryption protocols like TLS/SSL to protect your email communication.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your email account, preventing unauthorized access.
- Be cautious of phishing emails: Avoid clicking on links or opening attachments from suspicious emails, as they may contain malware.
- Regularly update your email client and operating system: Updates often include security patches that protect against vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords: Create complex passwords that are difficult to guess and avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
Conclusion
IMAP and SMTP are the fundamental protocols that underpin email communication, enabling the reliable and efficient delivery of messages across the globe. They provide users with powerful tools for managing their emails, ensuring accessibility, organization, and security. As email continues to play a vital role in our digital lives, understanding these protocols and their importance is essential for navigating the complexities of modern communication.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Pillars of Email Communication: IMAP and SMTP Explained. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!