The Land Of Israel And Judah: A Historical And Geographical Overview
The Land of Israel and Judah: A Historical and Geographical Overview
Related Articles: The Land of Israel and Judah: A Historical and Geographical Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Land of Israel and Judah: A Historical and Geographical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Land of Israel and Judah: A Historical and Geographical Overview

The land known as Israel and Judah, a region encompassing the modern-day State of Israel and parts of the West Bank, holds profound significance in both historical and religious contexts. Understanding the historical geography of this area requires navigating a complex tapestry of empires, religions, and cultural influences that have shaped the region for millennia.
Ancient Origins and Early Kingdoms:
The region’s history can be traced back to the Bronze Age, with the emergence of Canaanite city-states like Jericho and Megiddo. The arrival of the Israelites, as described in the Hebrew Bible, led to the establishment of the Kingdom of Israel in the 11th century BCE. This kingdom, initially united under King Saul, later split into two separate entities: the Kingdom of Israel in the north and the Kingdom of Judah in the south.
The Kingdom of Judah, centered around Jerusalem, played a pivotal role in Jewish history. Under King David, Jerusalem became the capital and a central place of worship. The subsequent reign of King Solomon witnessed a period of prosperity and the construction of the First Temple, a monumental structure that solidified Jerusalem’s religious significance.
The Babylonian Exile and the Return:
The Babylonian conquest of Judah in the 6th century BCE marked a turning point. The destruction of Jerusalem, the sacking of the Temple, and the exile of the Jewish population to Babylon significantly altered the political and religious landscape. This period of exile, however, also fostered a sense of unity and strengthened the Jewish identity.
The return from exile under Persian rule in the 6th century BCE saw the rebuilding of the Temple and the re-establishment of Jerusalem as a center of Jewish life. This period also witnessed the emergence of the Second Temple, a significant symbol of Jewish faith and cultural revival.
Roman Rule and the Diaspora:
The Roman conquest of Judea in 63 BCE ushered in a new era. The region was incorporated into the Roman province of Judea, and tensions between the Jewish population and Roman authorities escalated, culminating in the Great Revolt of 66-73 CE. The destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE marked a profound turning point, scattering the Jewish population across the Roman Empire and leading to the development of the Jewish Diaspora.
Medieval and Modern Times:
The region subsequently witnessed various rulers, including the Byzantines, the Arabs, the Crusaders, and the Ottoman Empire. The land of Israel and Judah remained a focal point for religious communities, with Jerusalem holding particular significance for Jews, Christians, and Muslims.
The late 19th century witnessed the rise of Zionism, a movement advocating for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine. The Balfour Declaration of 1917, which pledged support for the creation of a Jewish national home in Palestine, further fueled the Zionist movement.
The State of Israel and the Ongoing Conflict:
The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 was a defining moment in the region’s history. However, the declaration of the state was met with opposition from neighboring Arab states, leading to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. This conflict, coupled with the ongoing Palestinian-Israeli conflict, continues to shape the political and social landscape of the region.
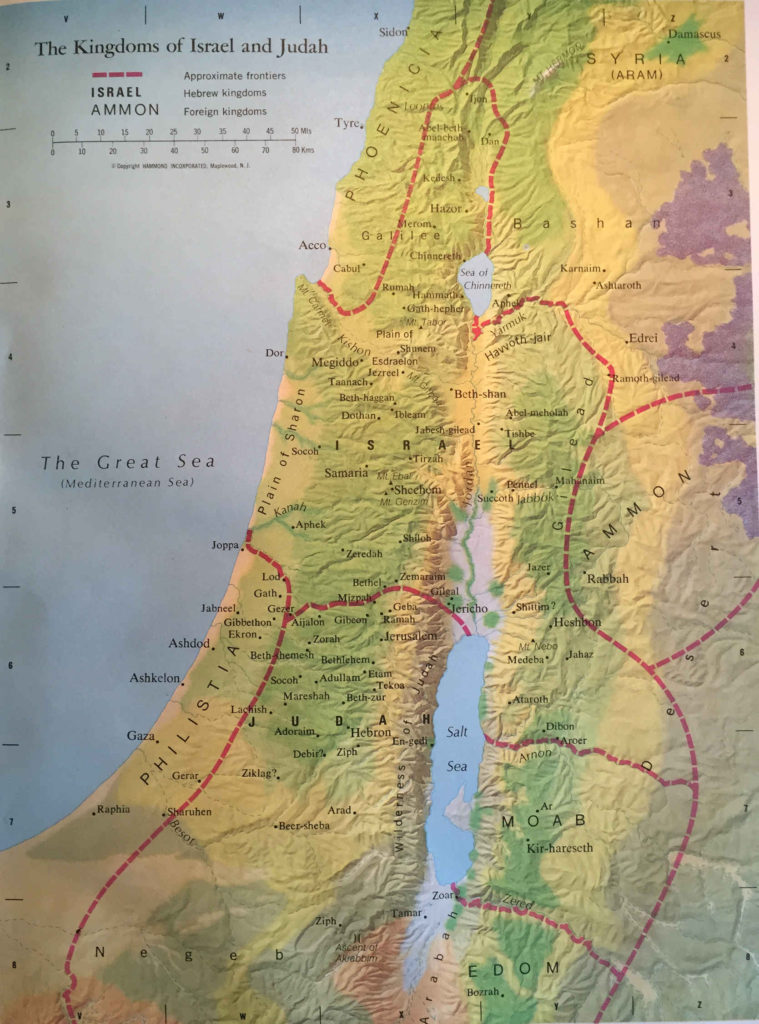
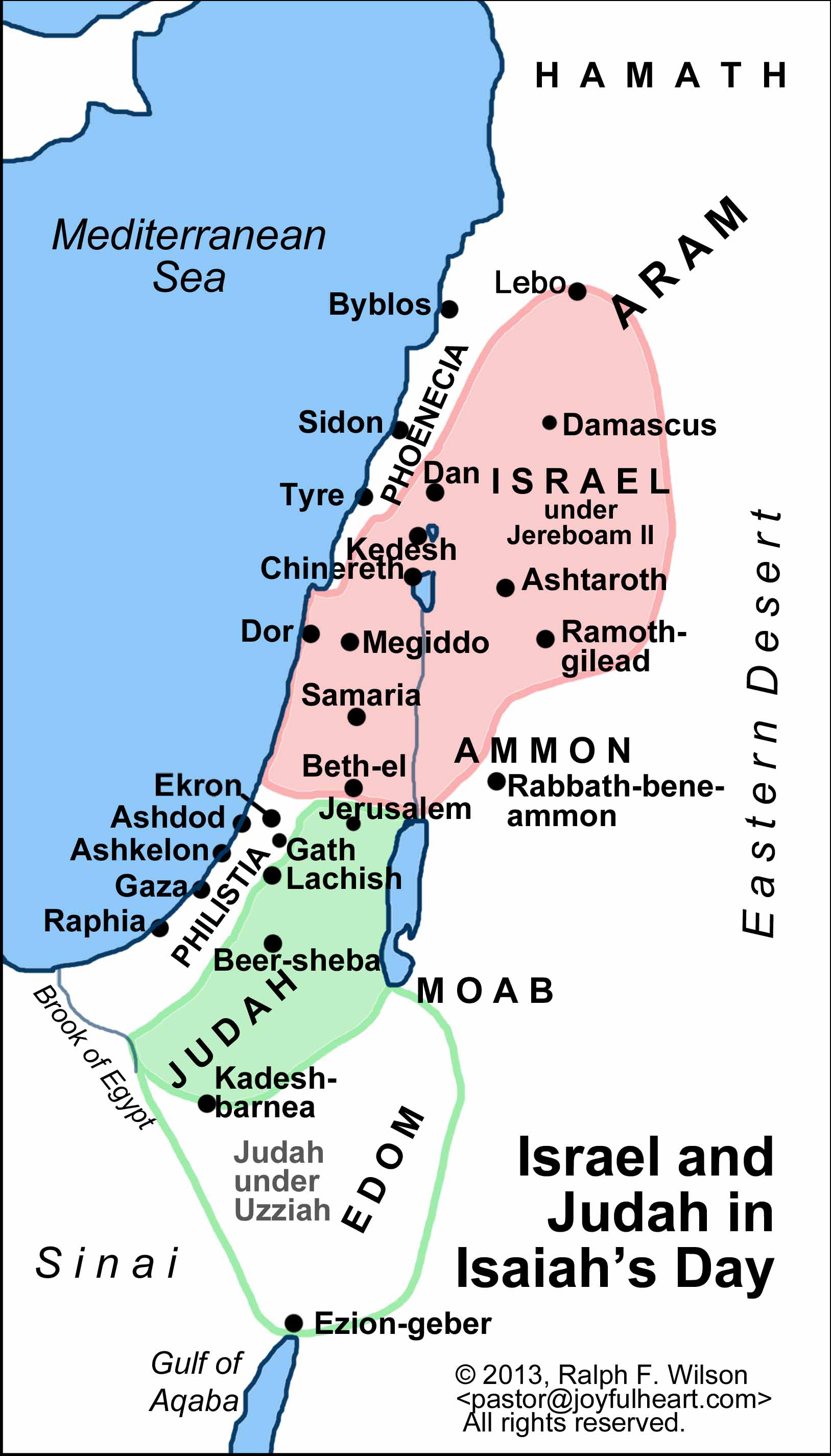
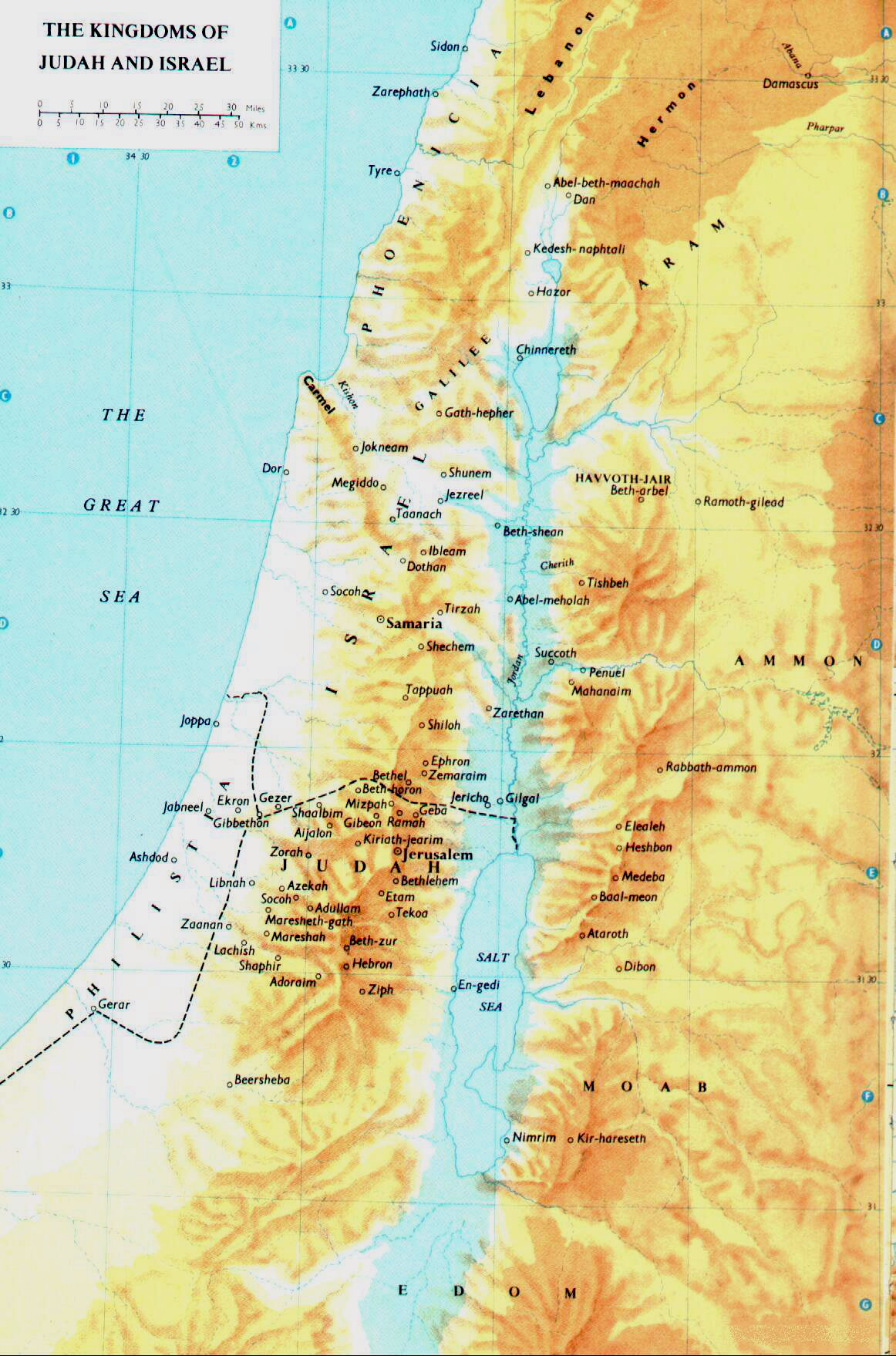
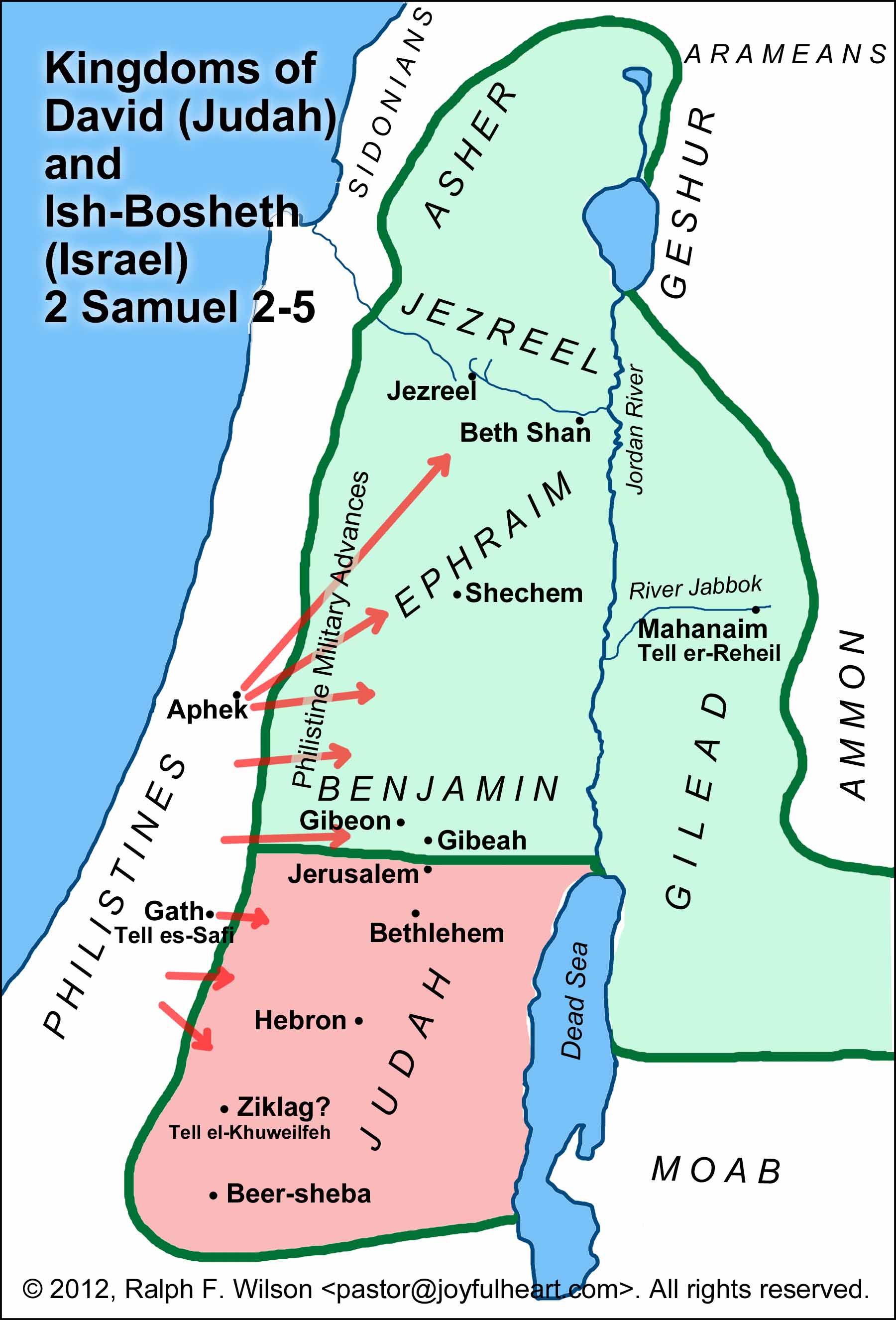
Maps of Israel and Judah: A Visual Representation of History:
Maps play a crucial role in understanding the history of Israel and Judah. They provide a visual representation of the geographical boundaries, political divisions, and cultural influences that shaped the region.
Key Features of Maps of Israel and Judah:
- Historical Boundaries: Maps can depict the boundaries of ancient kingdoms, empires, and provinces that have governed the region throughout history.
- Religious Sites: Maps can highlight the location of significant religious sites, such as Jerusalem, the Temple Mount, and other holy places.
- Settlements and Cities: Maps can showcase the development of settlements and cities over time, reflecting population movements and urban growth.
- Trade Routes: Maps can illustrate the key trade routes that connected the region to other parts of the world, highlighting economic and cultural exchanges.
- Modern Political Boundaries: Maps can depict the current political boundaries of Israel, the West Bank, and other neighboring countries.
Importance of Studying Maps of Israel and Judah:
- Historical Context: Maps provide a visual framework for understanding the historical context of the region, helping to contextualize events and understand the evolution of boundaries and settlements.
- Religious Significance: Maps highlight the location of religious sites, offering insights into the importance of specific locations for different faiths.
- Political Understanding: Maps can help visualize the current political landscape, including disputed territories and areas of conflict.
- Cultural Appreciation: Maps provide a visual representation of the cultural diversity of the region, showcasing the influence of different civilizations and religions.
Understanding Maps of Israel and Judah:
- Scale and Accuracy: It is crucial to consider the scale and accuracy of maps, as different maps may use varying levels of detail and may not always reflect the most up-to-date information.
- Historical Context: When studying historical maps, it is important to consider the historical context in which they were created, as maps can reflect biases or perspectives of the time.
- Multiple Perspectives: It is important to consider multiple perspectives when interpreting maps, as different groups may have different interpretations of boundaries and territories.
Conclusion:
The land of Israel and Judah is a complex and multifaceted region with a rich and often turbulent history. Maps provide a valuable tool for understanding the geographical and historical context of this region, offering insights into the evolution of boundaries, settlements, and cultural influences. By studying maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the historical and religious significance of this land, as well as the ongoing challenges and complexities that shape its present and future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Land of Israel and Judah: A Historical and Geographical Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!