The Kingdom Of Saul: A Geographical Overview Of Israel’s Early Monarchy
The Kingdom of Saul: A Geographical Overview of Israel’s Early Monarchy
Related Articles: The Kingdom of Saul: A Geographical Overview of Israel’s Early Monarchy
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Kingdom of Saul: A Geographical Overview of Israel’s Early Monarchy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Kingdom of Saul: A Geographical Overview of Israel’s Early Monarchy
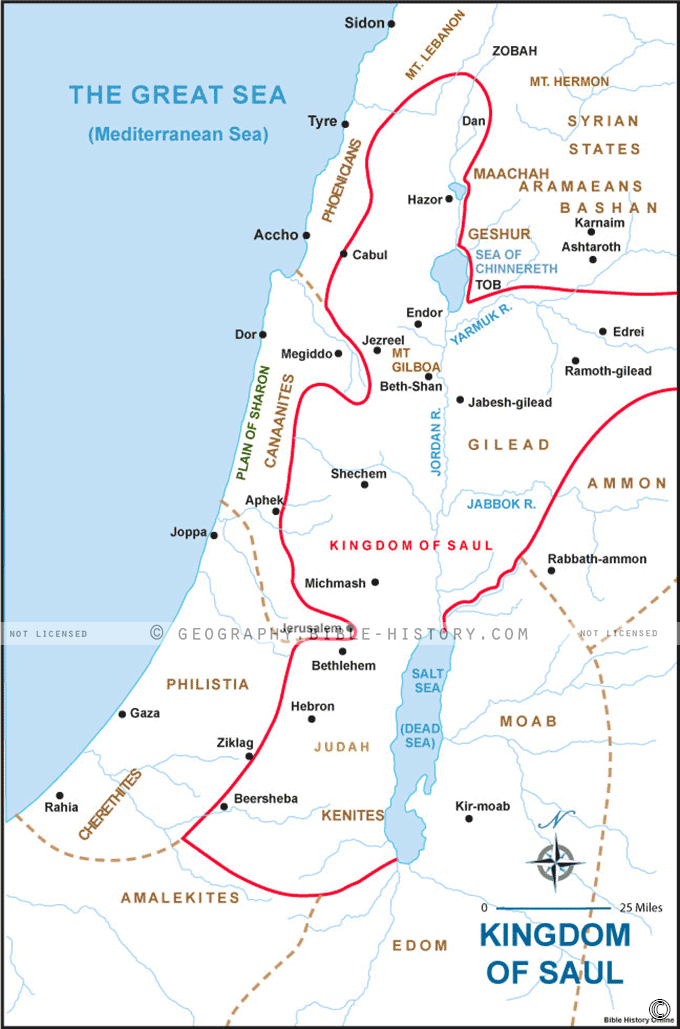
The reign of King Saul, the first monarch of Israel, marks a pivotal moment in the nation’s history. It witnessed the transition from a loosely-organized tribal confederation to a unified kingdom, laying the foundation for future Israelite expansion and political dominance. Understanding the geographical boundaries of Saul’s kingdom is essential for comprehending the political, social, and religious dynamics of this crucial period.
Mapping the Kingdom:
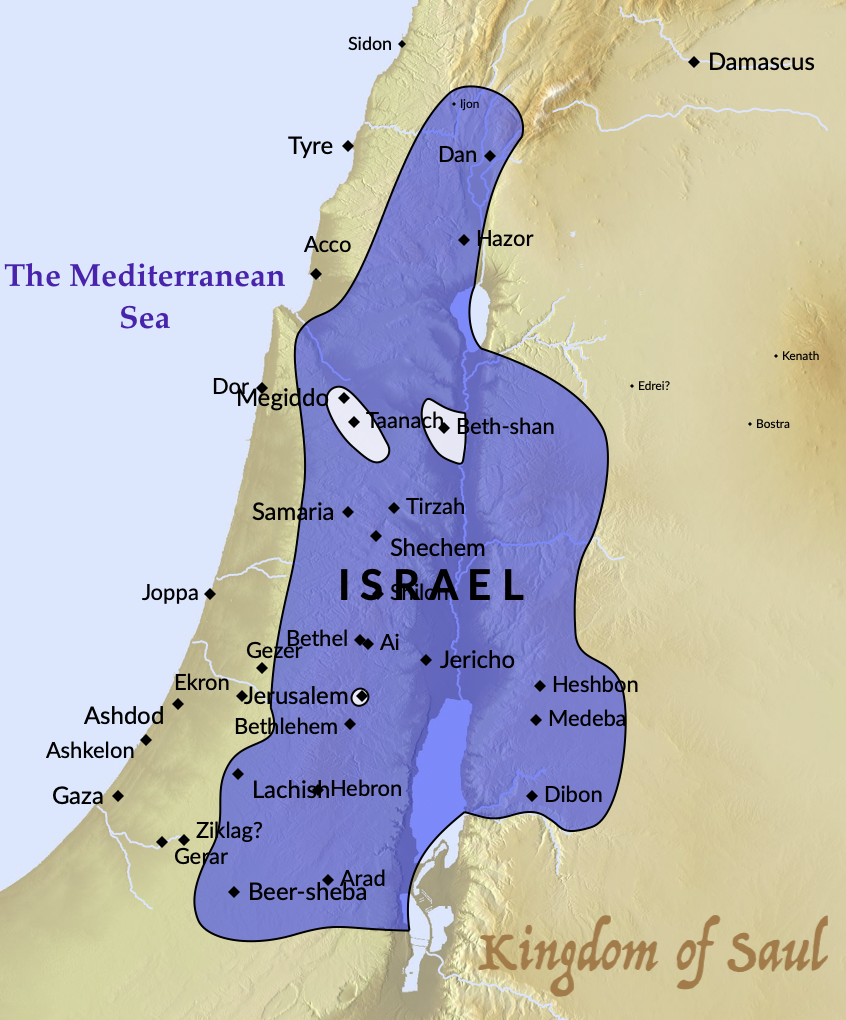
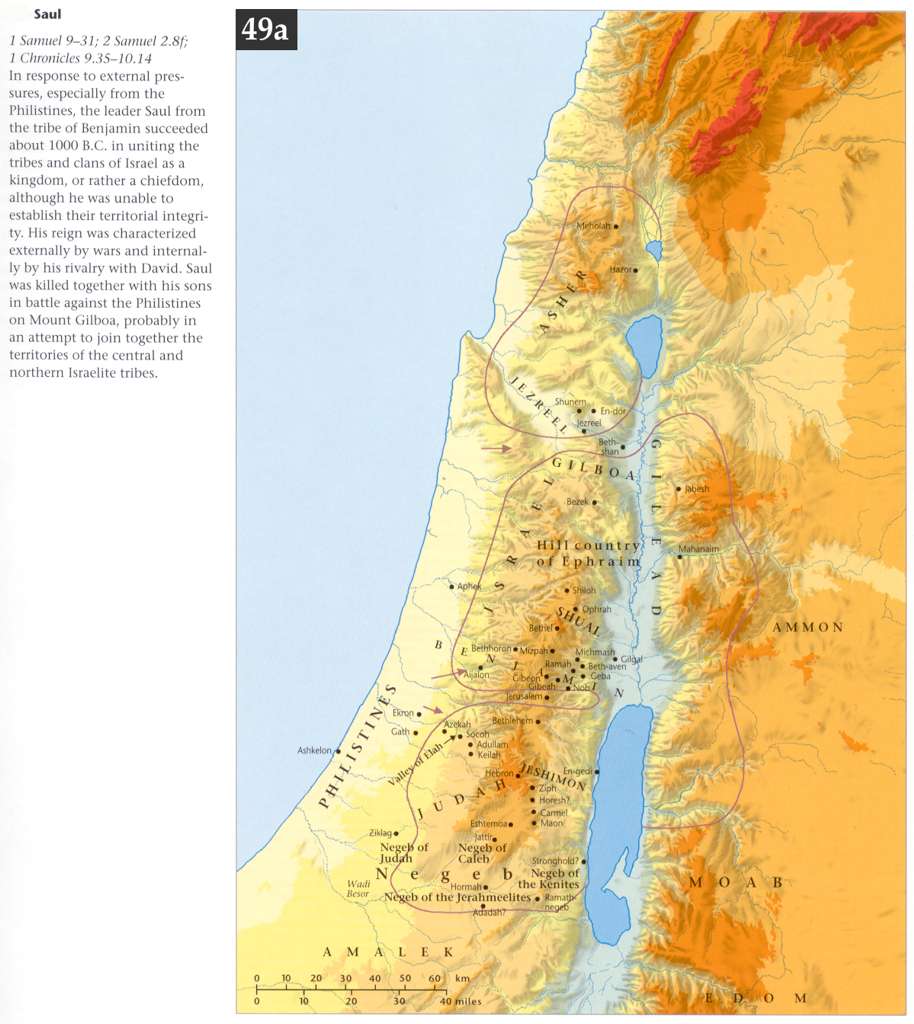
The precise boundaries of Saul’s kingdom are not definitively established in the biblical text. However, based on archaeological evidence and scriptural accounts, a plausible map emerges, outlining the key regions under his control:
- The Heartland: Saul’s base of power lay in the central highlands of Israel, encompassing the territory of the tribes of Benjamin and Ephraim. This region, known as the "hill country," offered strategic advantages, providing natural defenses and access to key trade routes.
- Expansion to the North: Saul’s campaigns against the Philistines, Ammonites, and Moabites resulted in the extension of his authority northward. He likely controlled portions of the Jezreel Valley, a fertile agricultural plain that was strategically vital for access to the Mediterranean coast.
- Limited Control in the South: While Saul’s influence extended to the southern regions of Judah, his control over these areas was not as secure. The tribe of Judah, under the leadership of David, maintained a degree of independence, leading to a complex power dynamic within the nascent kingdom.
- The Western Frontier: Saul’s kingdom encompassed the western coastal plain, including the important city of Joppa (modern-day Jaffa), providing access to maritime trade and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Eastern Limits: Saul’s influence likely extended eastward into the Transjordan, encompassing portions of the territory of the tribes of Reuben, Gad, and Manasseh. This expansion provided access to vital grazing lands and trade routes.
The Importance of Geography:
The geographical configuration of Saul’s kingdom played a crucial role in its development and stability.
- Strategic Advantages: The central highlands provided a secure base of operations, while the fertile Jezreel Valley and the coastal plain offered economic prosperity and access to vital resources.
- Challenges of Unity: The fragmented nature of the Israelite tribes, coupled with the presence of powerful enemies like the Philistines, presented significant challenges to consolidating a unified kingdom.
- Vulnerability to External Threats: While the highlands offered natural defenses, the lack of a strong navy left Saul vulnerable to attacks from the sea. The eastern frontier also remained exposed to raids by nomadic tribes.
The Legacy of Saul’s Kingdom:
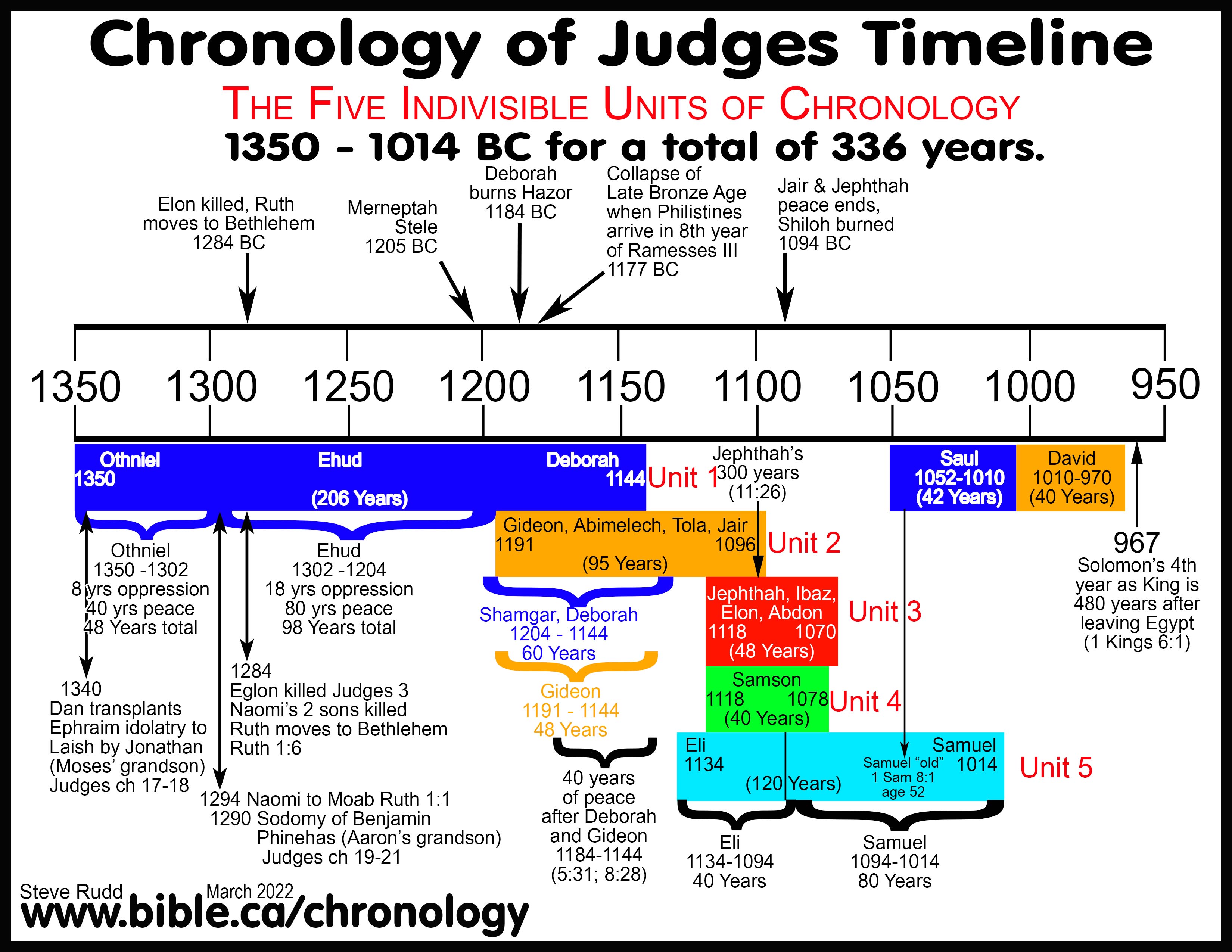
Saul’s reign, despite its turbulent nature, laid the groundwork for the future development of the Israelite monarchy. He established a centralized authority, consolidated the tribes, and expanded Israel’s territorial influence. However, his inability to fully unify the nation and his failure to secure victory against the Philistines ultimately led to his downfall.
The legacy of Saul’s kingdom, therefore, is a complex one, marked by both successes and failures. His reign laid the foundation for the later, more successful monarchies of David and Solomon, but also served as a cautionary tale about the challenges of building a stable and unified kingdom in a turbulent region.
FAQs on the Map of Israel Under King Saul:
1. What were the primary challenges faced by Saul in establishing his kingdom?
Saul faced a multitude of challenges, including:
- Tribal rivalries: The Israelite tribes were accustomed to autonomy and lacked a strong sense of national unity.
- External threats: The Philistines, Ammonites, and Moabites posed constant military threats to the nascent kingdom.
- Lack of resources: The limited resources and infrastructure of the time hampered Saul’s ability to build a strong military and administrative apparatus.
2. What were the key factors contributing to Saul’s downfall?
Saul’s downfall was a culmination of several factors:
- Disobedience to God: His disobedience to God’s commands, particularly in the case of the Amalekite war, led to the withdrawal of divine favor.
- Jealousy and paranoia: Saul’s growing jealousy and paranoia towards David, a rising military hero, led to a breakdown in trust and ultimately to a civil war.
- Military defeats: Saul’s military defeats against the Philistines, culminating in the tragic Battle of Mount Gilboa, eroded his authority and contributed to his downfall.
3. What is the significance of the map of Israel under King Saul for understanding the history of the Israelite monarchy?
The map provides a visual representation of the territorial extent of Saul’s kingdom, allowing us to understand:
- The geographical context of Saul’s reign: It highlights the challenges and opportunities presented by the terrain, resources, and neighboring nations.
- The political landscape of early Israel: It illustrates the complex power dynamics between the tribes and the emerging monarchy.
- The foundations of the Israelite monarchy: It reveals the crucial steps taken by Saul in establishing a centralized authority and expanding Israel’s territorial influence.
4. How does the map of Israel under King Saul differ from the map of the later United Monarchy under David and Solomon?
The map of the United Monarchy under David and Solomon shows a significantly larger territory, encompassing all twelve tribes of Israel and extending south to include the entire territory of Judah. This expansion was achieved through David’s military conquests and Solomon’s wise diplomacy.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Israel Under King Saul:
- Study the Biblical Text: The books of Samuel, particularly 1 Samuel, provide detailed accounts of Saul’s reign, including his military campaigns and territorial expansion.
- Consult Archaeological Evidence: Archaeological findings from the time of Saul’s reign offer valuable insights into the political, social, and economic realities of his kingdom.
- Compare the Map with Later Maps: Comparing the map of Saul’s kingdom with later maps of the United Monarchy and the Divided Kingdom helps to understand the evolution of Israel’s territorial boundaries and the impact of different political structures.
Conclusion:
The map of Israel under King Saul offers a valuable lens for understanding the early stages of the Israelite monarchy. It reveals the challenges and opportunities faced by Saul in unifying the tribes, expanding his territory, and establishing a stable kingdom. While Saul’s reign ultimately ended in tragedy, his efforts laid the groundwork for the later, more successful monarchies of David and Solomon, shaping the course of Israelite history and leaving an enduring legacy for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Kingdom of Saul: A Geographical Overview of Israel’s Early Monarchy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!