The Kingdom Of David: A Map Of Power And Expansion
The Kingdom of David: A Map of Power and Expansion
Related Articles: The Kingdom of David: A Map of Power and Expansion
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Kingdom of David: A Map of Power and Expansion. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Kingdom of David: A Map of Power and Expansion
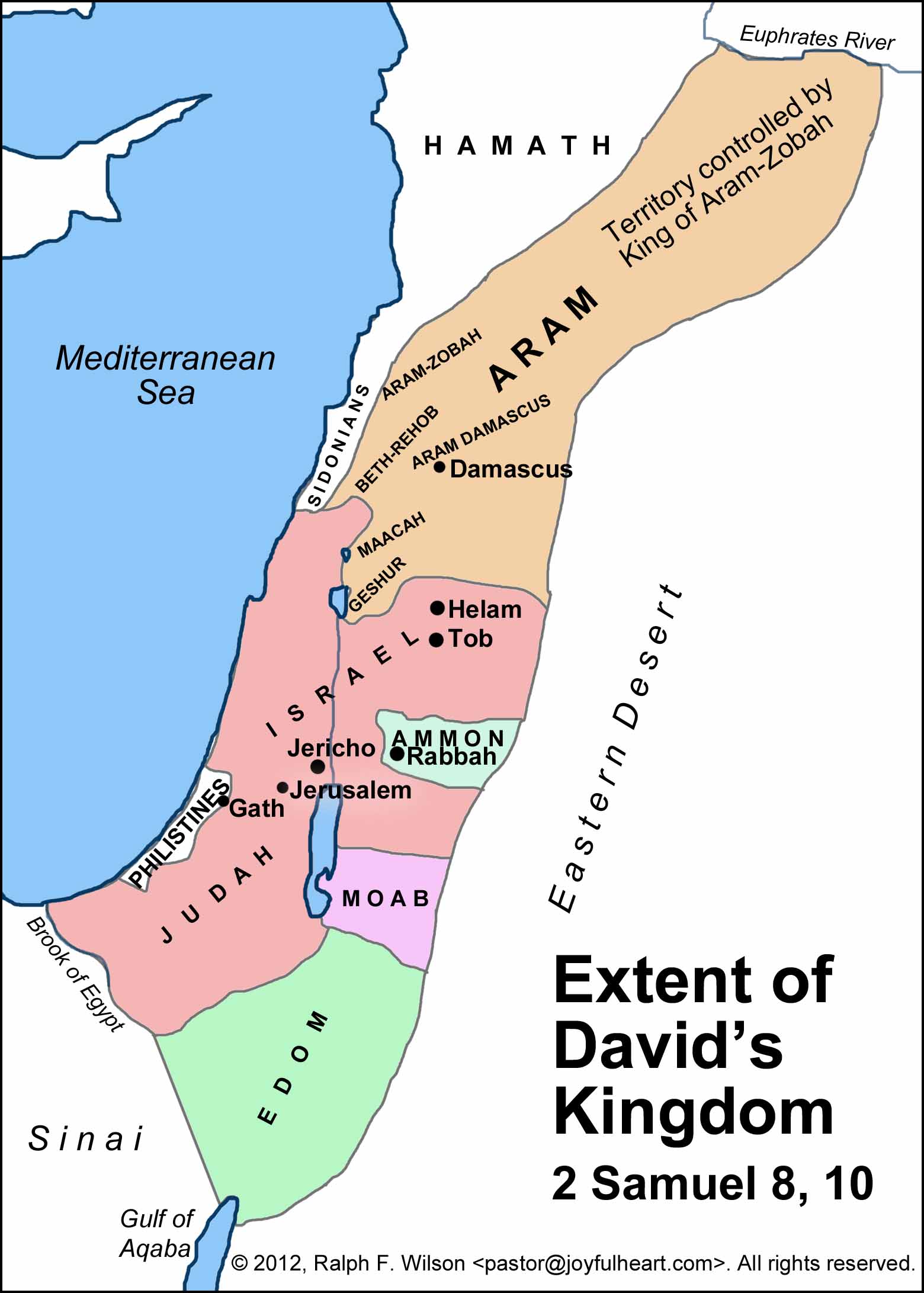
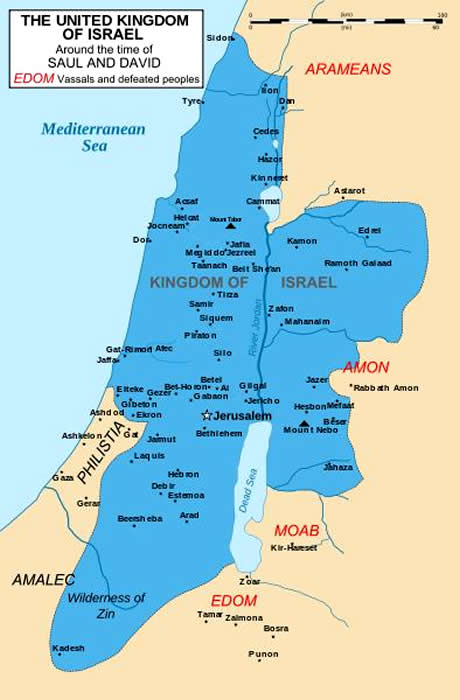
The reign of King David, a pivotal figure in biblical history, marked a significant turning point for the Israelites. His military prowess and political acumen transformed a loose confederation of tribes into a unified kingdom, expanding its territory and establishing a lasting legacy. Understanding the map of Israel under King David provides crucial insights into the political, social, and religious landscape of the ancient Near East.
The Boundaries of David’s Kingdom:
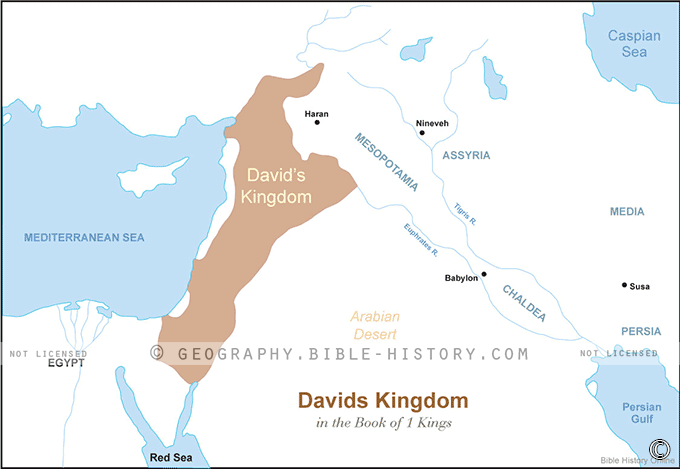
While the precise borders of David’s kingdom remain a subject of scholarly debate, historical accounts and archaeological evidence offer a compelling picture. The kingdom stretched from the Mediterranean Sea in the west to the Jordan River in the east, encompassing a vast expanse of land that included:
- The Southern Levant: This region, encompassing modern-day Israel and parts of Jordan, formed the core of David’s kingdom. It included the cities of Jerusalem, Hebron, Bethlehem, and Jericho, all of which held significant religious and political importance.
- The Philistine Coastal Plain: This fertile region, historically inhabited by the Philistines, was conquered by David, extending the kingdom’s influence towards the Mediterranean Sea. Major Philistine cities like Gath, Ashkelon, and Gaza fell under David’s control.
- The Transjordan: David’s kingdom also encompassed the eastern bank of the Jordan River, including the regions of Gilead and Moab. This expansion secured vital trade routes and provided access to valuable resources.
The Significance of Jerusalem:
David’s capture of Jerusalem from the Jebusites marked a watershed moment in the history of Israel. This strategic city, situated on a hilltop overlooking the surrounding valleys, offered a commanding position and became the political and religious center of the united kingdom. David established his palace in Jerusalem, making it the capital of his kingdom, and also brought the Ark of the Covenant, a sacred symbol of the Israelites’ faith, to the city.
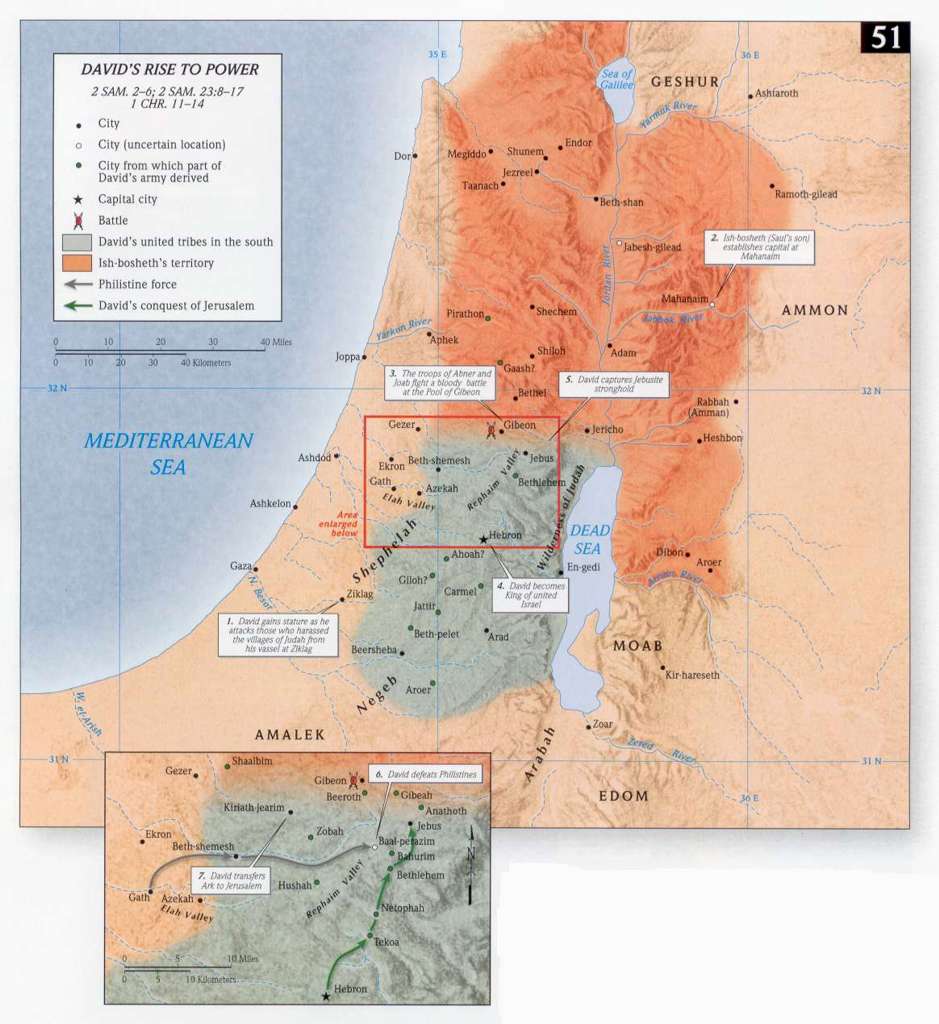
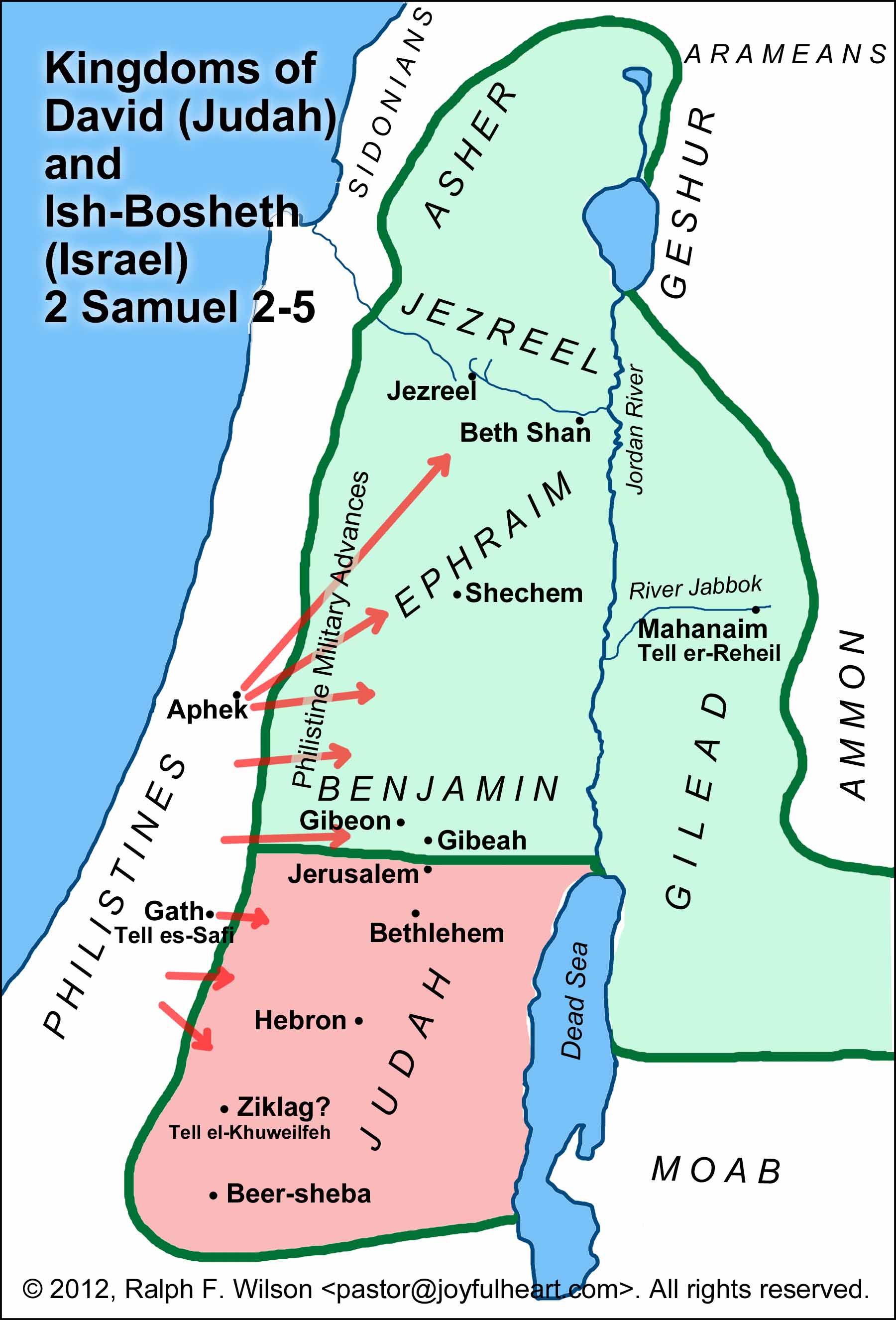
The Rise of a Unified Israel:
Before David’s reign, the Israelites were divided into twelve tribes, often operating independently. David’s conquests and administrative reforms unified these tribes under a single monarch, creating a powerful and cohesive nation. This unification had profound consequences:
- Military Strength: A unified army under David’s leadership enabled the Israelites to defend their territory against external threats and expand their influence in the region.
- Economic Prosperity: A unified kingdom facilitated trade and economic growth, fostering a sense of shared prosperity among the Israelites.
- Cultural Identity: The establishment of a central government and the shared experience of conquest fostered a stronger sense of national identity and shared purpose among the Israelites.
The Legacy of David’s Kingdom:
David’s reign laid the foundation for the future glory of the Israelite kingdom. His son, Solomon, continued his father’s work, expanding the kingdom’s wealth and influence. The establishment of a unified kingdom under David, centered in Jerusalem, had a lasting impact on the history of the Israelites, shaping their political, social, and religious development for centuries to come.
FAQs on the Map of Israel under King David:
Q: What sources are used to reconstruct the map of Israel under King David?
A: The reconstruction of the map relies on a combination of sources:
- Biblical accounts: The books of Samuel and Kings provide detailed narratives of David’s conquests and the extent of his kingdom.
- Archaeological evidence: Excavations at sites like Jerusalem, Hebron, and other cities within David’s kingdom offer physical evidence of the kingdom’s extent and its administrative structure.
- Historical records: Ancient Egyptian and Assyrian texts sometimes mention the Israelites and their kings, providing additional insights into the political landscape of the region.
Q: What are the challenges in accurately reconstructing the map?
A: Reconstructing the map of David’s kingdom presents several challenges:
- Biblical accounts: While detailed, biblical accounts often focus on key events and may not provide precise geographical information.
- Archaeological evidence: Interpreting archaeological evidence can be challenging, and the dating of artifacts can be subject to debate.
- Historical records: Ancient historical records are often incomplete or fragmented, requiring careful analysis and interpretation.
Q: How does the map of Israel under King David relate to the modern-day political situation in the region?
A: The map of Israel under King David is relevant to modern-day politics as it highlights the historical claims to the land by both Israelis and Palestinians. Both groups draw on biblical narratives and archaeological evidence to support their claims, making the region a complex and contested space.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Israel under King David:
- Focus on key cities: Jerusalem, Hebron, and Bethlehem are crucial cities that offer insights into the political and religious significance of the kingdom.
- Consider the geographical context: The map’s location within the ancient Near East helps to understand the kingdom’s strategic importance and its interactions with neighboring empires.
- Explore historical accounts: Reading accounts of David’s reign in the Bible and other historical sources can provide a richer understanding of the kingdom’s development and its impact on the region.
- Engage with archaeological evidence: Learning about archaeological discoveries at key sites within the kingdom can offer a tangible connection to the past.
Conclusion:
The map of Israel under King David provides a valuable window into a pivotal period in Israelite history. It illustrates the rise of a unified kingdom, the strategic importance of Jerusalem, and the lasting impact of David’s conquests on the political and religious landscape of the ancient Near East. While the precise boundaries of the kingdom remain debated, the map offers a compelling picture of David’s achievements and the legacy he left behind, shaping the destiny of the Israelites and the region for centuries to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Kingdom of David: A Map of Power and Expansion. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!