The Intersection Of FMAP And Medicaid Expansion: A Comprehensive Analysis
The Intersection of FMAP and Medicaid Expansion: A Comprehensive Analysis
Related Articles: The Intersection of FMAP and Medicaid Expansion: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Intersection of FMAP and Medicaid Expansion: A Comprehensive Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Intersection of FMAP and Medicaid Expansion: A Comprehensive Analysis
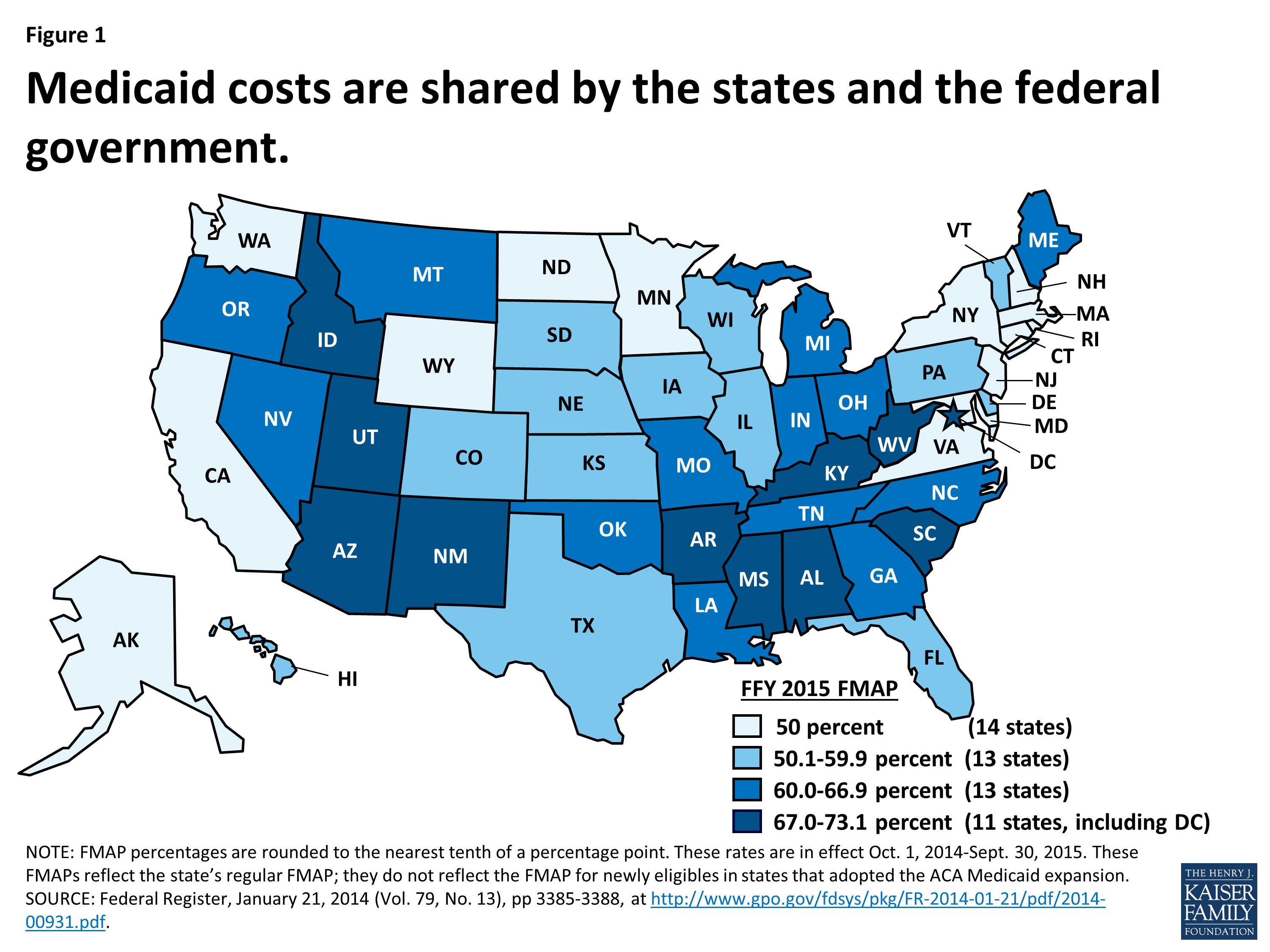
The intricate relationship between the Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) and Medicaid expansion has been a subject of ongoing debate and analysis within the healthcare policy landscape. This article delves into the complexities of these two crucial elements, examining their individual roles and the profound impact their interaction has on the American healthcare system.
FMAP: The Federal Share of Medicaid Costs
FMAP represents the percentage of Medicaid costs borne by the federal government, with the remaining portion being covered by individual states. This percentage varies based on a state’s per capita income, with lower-income states receiving a higher FMAP. The FMAP serves as a critical financial lifeline for states, enabling them to provide essential healthcare services to low-income individuals and families.
Medicaid Expansion: Expanding Coverage and Access
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced the option for states to expand Medicaid eligibility to individuals with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level. This expansion significantly broadened the program’s reach, bringing millions of previously uninsured Americans into the fold and creating a more robust safety net for vulnerable populations.
The Symbiotic Relationship: How FMAP and Medicaid Expansion Intertwine
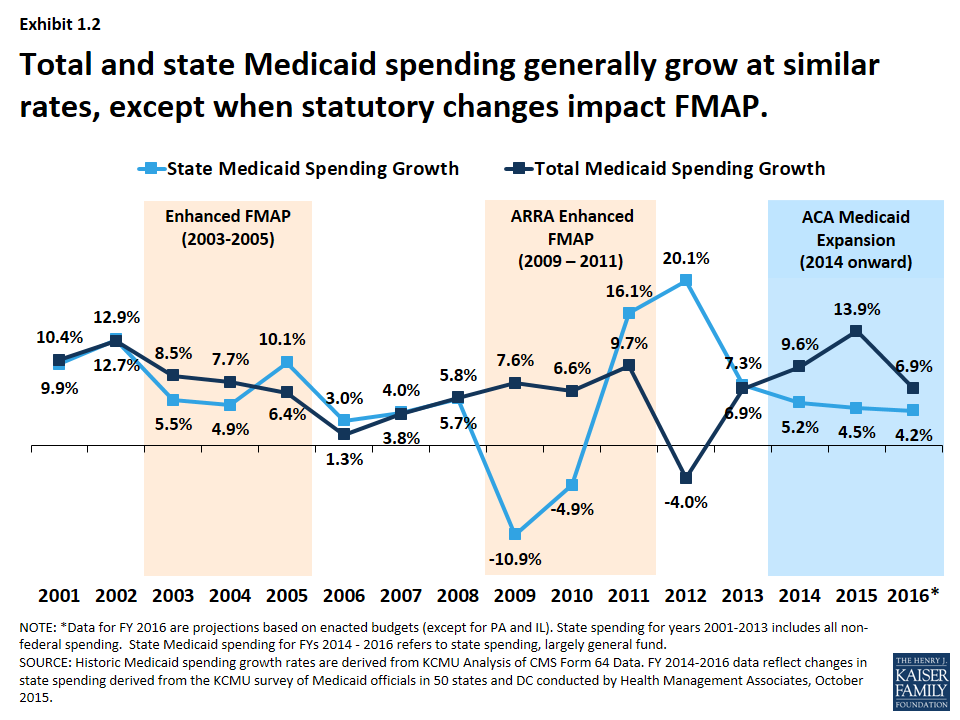
The relationship between FMAP and Medicaid expansion is symbiotic. Medicaid expansion, by increasing the number of individuals eligible for coverage, leads to higher overall Medicaid expenditures. Conversely, the higher FMAP offered for expansion populations incentivizes states to adopt the expansion, as the federal government shoulders a larger portion of the financial burden.
Analyzing the Benefits and Challenges:
Benefits:
- Increased Coverage and Access: Medicaid expansion has demonstrably reduced the number of uninsured Americans, particularly in states that have opted to participate. This expanded coverage translates into improved access to healthcare services, leading to better health outcomes and reduced financial strain for individuals and families.
- Economic Boost: Medicaid expansion has been linked to positive economic effects, including job creation in the healthcare sector and increased economic activity. The infusion of federal funds into state economies contributes to overall economic growth.
- Improved Public Health: By providing access to preventive care and treatment, Medicaid expansion has contributed to improvements in public health, leading to reductions in chronic diseases and preventable health conditions.
- Reduced Uncompensated Care: The expansion of Medicaid coverage has led to a decrease in uncompensated care for hospitals and healthcare providers, as more individuals have access to insurance coverage.
Challenges:
- State Budget Constraints: While the federal government provides significant financial assistance, states still bear a portion of the cost of Medicaid expansion. This can create budgetary challenges for states with limited financial resources, particularly during periods of economic downturn.
- Administrative Complexity: Implementing and managing Medicaid expansion can be complex, requiring significant administrative infrastructure and resources. States need to navigate the complexities of eligibility verification, enrollment processes, and ongoing program administration.
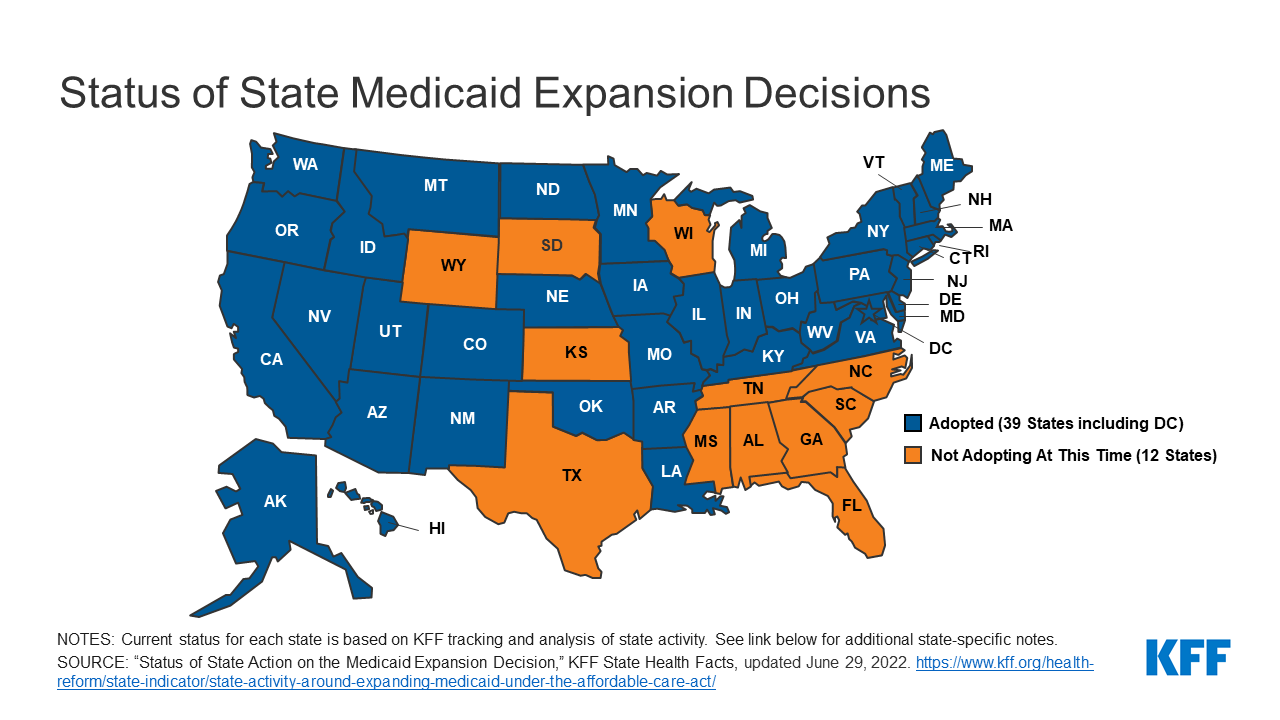
- Political Polarization: Medicaid expansion has become a highly politicized issue, with some states resisting expansion due to ideological objections or concerns about fiscal sustainability. This political polarization can hinder progress in expanding coverage and creating a more equitable healthcare system.
FAQs on FMAP and Medicaid Expansion:
Q: What is the current FMAP rate for Medicaid expansion populations?
A: The current FMAP rate for expansion populations is 90%, meaning the federal government covers 90% of the cost, while states cover the remaining 10%.
Q: How do states benefit from the increased FMAP for expansion populations?
A: The higher FMAP makes Medicaid expansion more financially attractive for states, as the federal government assumes a larger share of the cost, reducing the financial burden on state budgets.
Q: What are the eligibility criteria for Medicaid expansion?
A: Individuals with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level are eligible for Medicaid expansion. This includes adults without dependent children who were previously ineligible for Medicaid.
Q: What are the consequences of not expanding Medicaid?
A: States that have not expanded Medicaid face higher rates of uninsurance, poorer health outcomes, and a greater strain on their healthcare systems. They also miss out on the economic and public health benefits associated with expansion.
Q: How has Medicaid expansion impacted the healthcare system?
A: Medicaid expansion has led to increased access to healthcare, reduced uncompensated care, and improved public health outcomes. It has also contributed to job creation and economic growth in the healthcare sector.
Tips for Understanding FMAP and Medicaid Expansion:
- Consult official government resources: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) website provides comprehensive information on FMAP and Medicaid expansion, including program guidelines, eligibility criteria, and funding details.
- Engage with advocacy groups: Organizations dedicated to healthcare policy and advocacy, such as the Kaiser Family Foundation and the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, offer insightful analysis and research on FMAP and Medicaid expansion.
- Stay informed about state-level developments: Each state has its own unique implementation of Medicaid expansion, with varying eligibility criteria and program details. Keeping track of state-level developments is essential for understanding the impact of FMAP and Medicaid expansion at the local level.
Conclusion:
The interplay between FMAP and Medicaid expansion has profound implications for the American healthcare system. While the expansion has undoubtedly improved access to care and yielded positive health and economic outcomes, it also presents challenges for states in terms of financial sustainability and administrative complexity. As the debate surrounding healthcare policy continues, understanding the intricacies of FMAP and Medicaid expansion is crucial for shaping a more equitable and accessible healthcare system for all Americans.

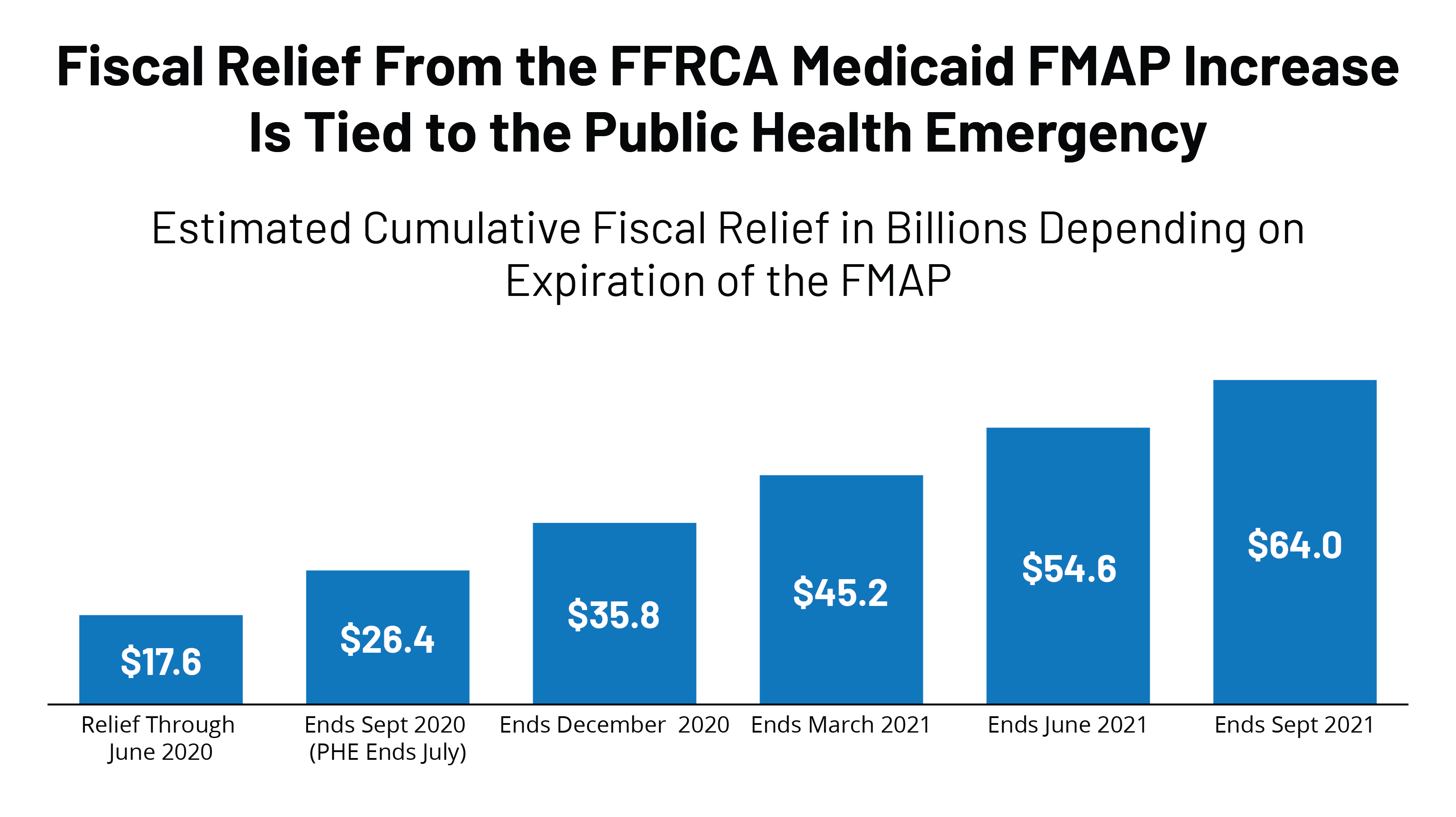
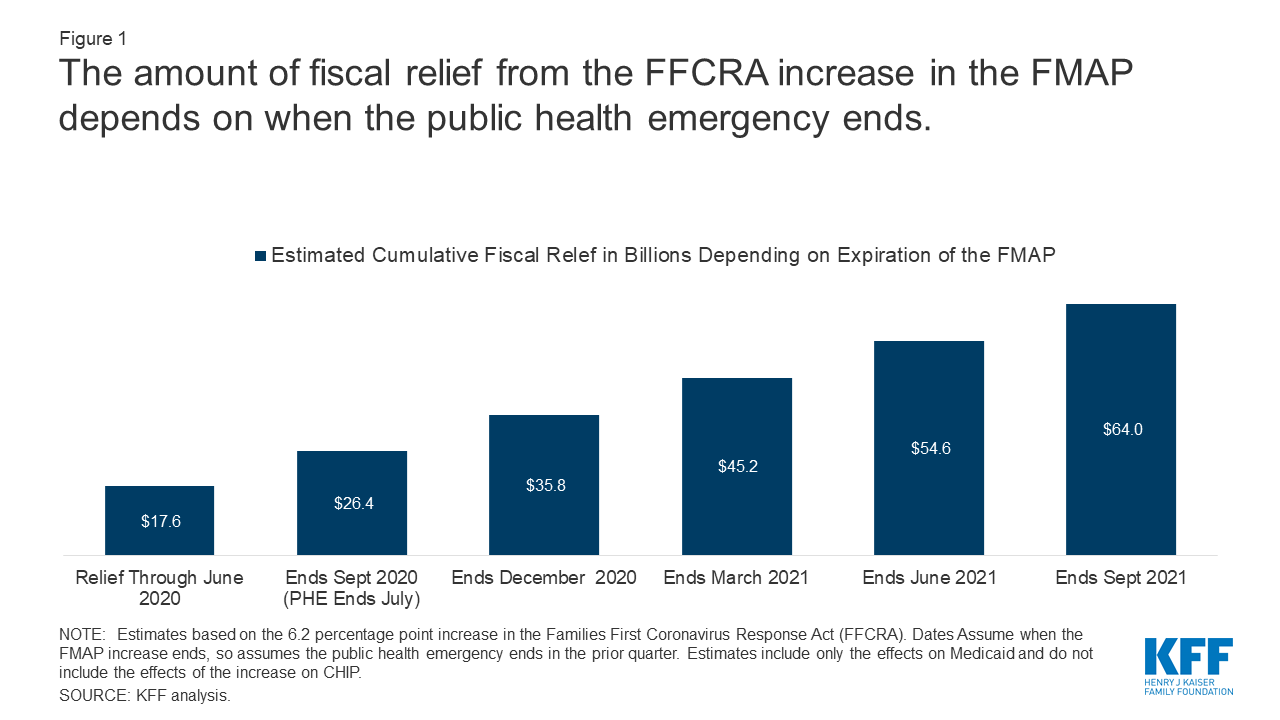
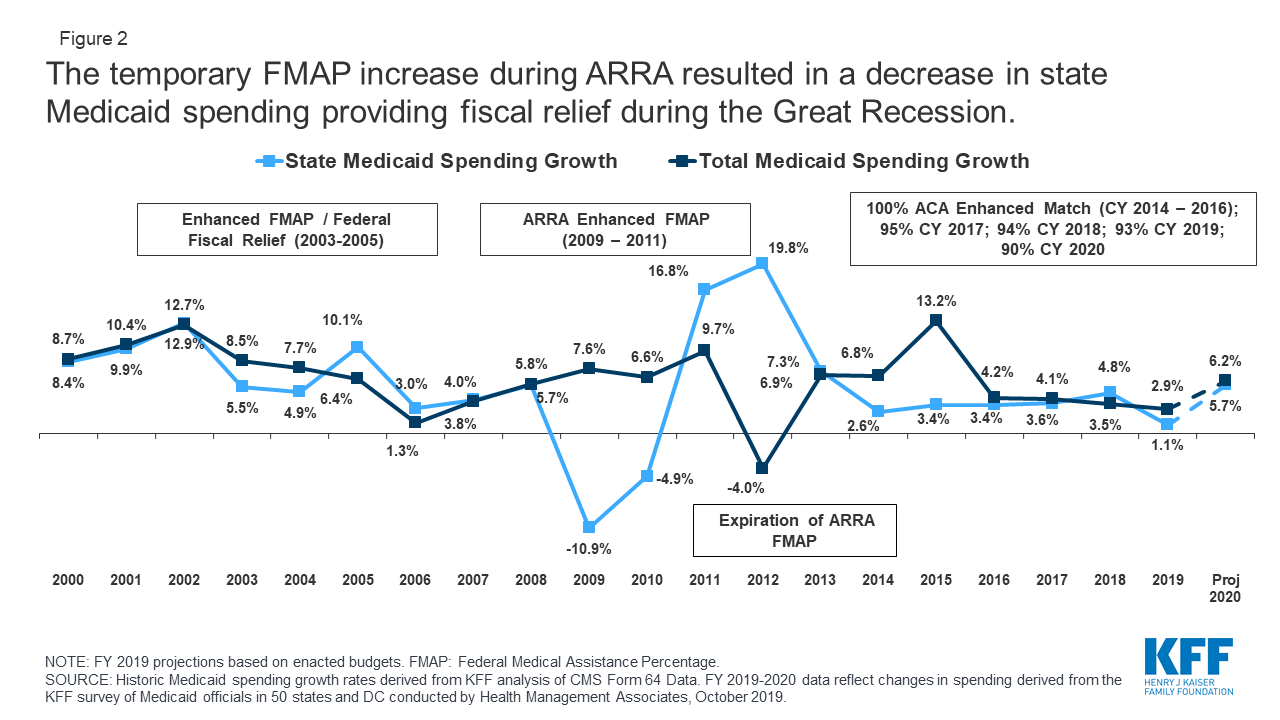


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Intersection of FMAP and Medicaid Expansion: A Comprehensive Analysis. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!