The Indonesian Political Landscape: A Map Of Diversity And Decentralization
The Indonesian Political Landscape: A Map of Diversity and Decentralization
Related Articles: The Indonesian Political Landscape: A Map of Diversity and Decentralization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Indonesian Political Landscape: A Map of Diversity and Decentralization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indonesian Political Landscape: A Map of Diversity and Decentralization
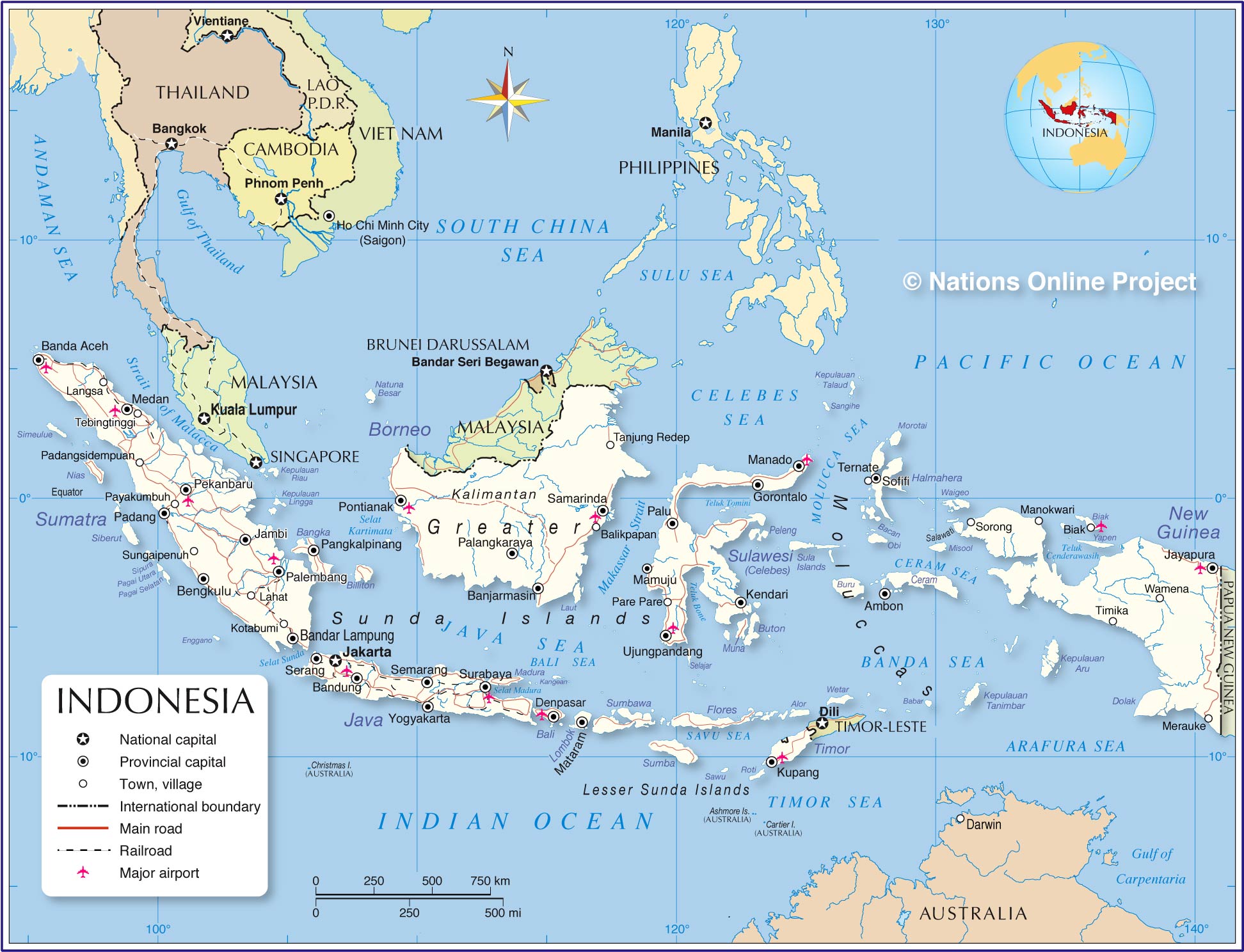
The Indonesian political map is a complex and dynamic entity, reflecting the nation’s rich history, diverse geography, and evolving political landscape. Understanding its intricacies is crucial for comprehending the country’s political processes, its social fabric, and its potential for future development. This article delves into the key features of the Indonesian political map, highlighting its historical evolution, its current structure, and its implications for governance and national identity.
A Nation Forged from Islands: The Historical Context
Indonesia’s political map is a direct consequence of its unique geographical configuration. Composed of over 17,000 islands, stretching across a vast expanse of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, Indonesia has always been a land of diverse cultures, languages, and traditions. This diversity, while enriching, has also presented challenges in forging a unified national identity and building a cohesive political structure.
Prior to independence, Indonesia was a patchwork of colonial territories under Dutch rule. The Dutch East India Company (VOC) established trading posts and gradually extended its influence over various islands, leading to a fragmented administrative system. This legacy of colonial rule left a lasting imprint on the Indonesian political map, with distinct regional identities and varying levels of economic development persisting even after independence.
The Birth of a Nation: The 1945 Constitution and Early Decentralization
The 1945 Constitution, adopted upon Indonesia’s independence, laid the foundation for a unitary state with a strong central government. However, the constitution also recognized the importance of regional autonomy, granting provinces a degree of self-governance. This early attempt at decentralization aimed to address the concerns of diverse regional populations and foster a sense of national unity.
The first decades after independence were characterized by political instability and authoritarian rule. The centralized system, while ensuring national security, often failed to effectively address the needs of local communities. This led to growing calls for greater decentralization and a more responsive political system.
The Rise of Decentralization: The 1999 Special Autonomy Law and Beyond
The 1999 Special Autonomy Law, enacted following the fall of Suharto’s regime, marked a significant shift in Indonesia’s political landscape. This law granted greater autonomy to certain provinces, particularly those with distinct cultural identities and historical grievances. Papua, Aceh, and Yogyakarta were among the regions that benefited from this legislation, receiving greater control over their resources, education, and cultural affairs.
This move towards decentralization aimed to address long-standing regional grievances, empower local communities, and promote economic development at the grassroots level. It also aimed to foster a more inclusive political system by granting greater representation to diverse regional interests.
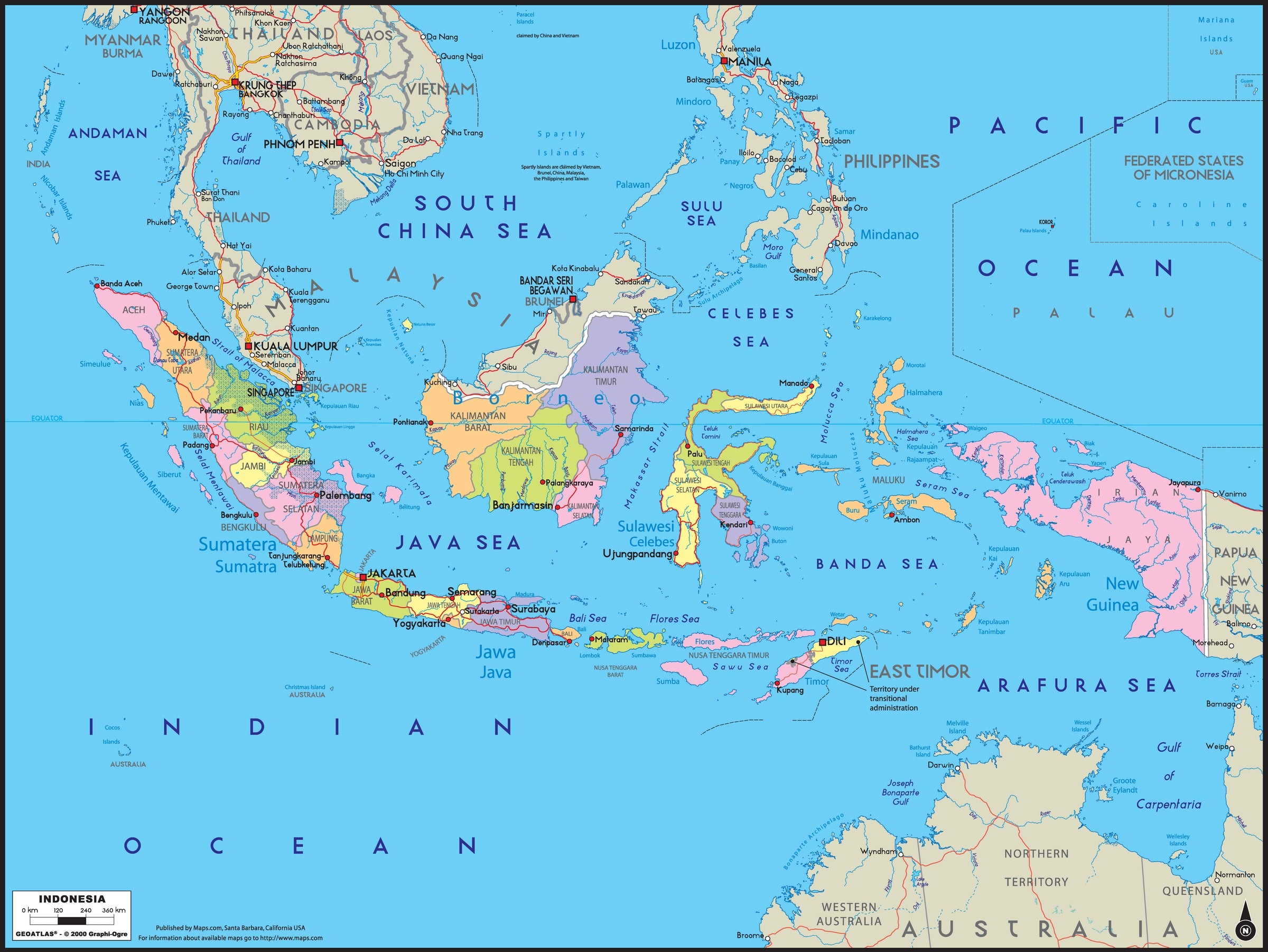
The Current Political Map: A Multi-Layered Structure
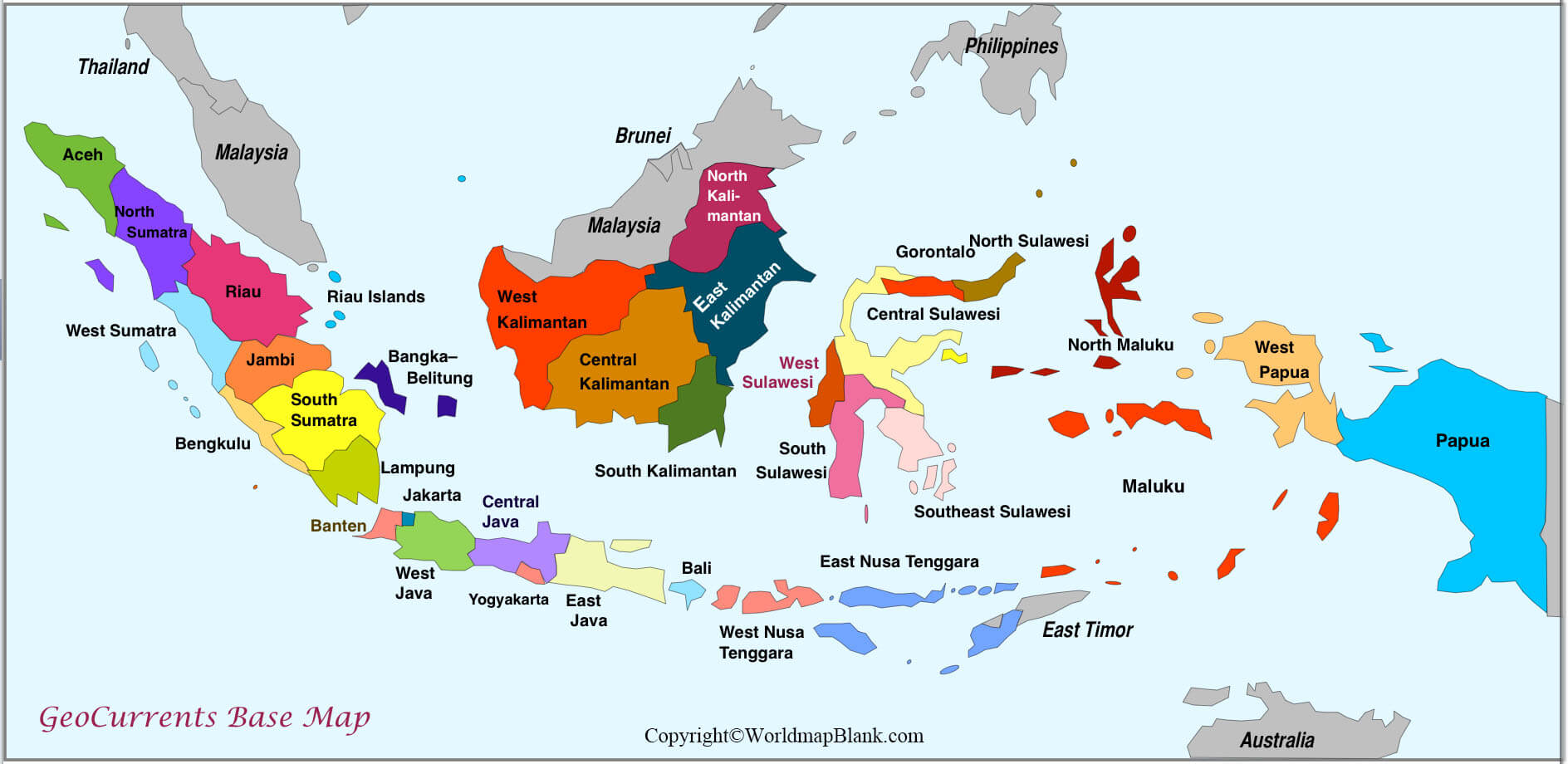
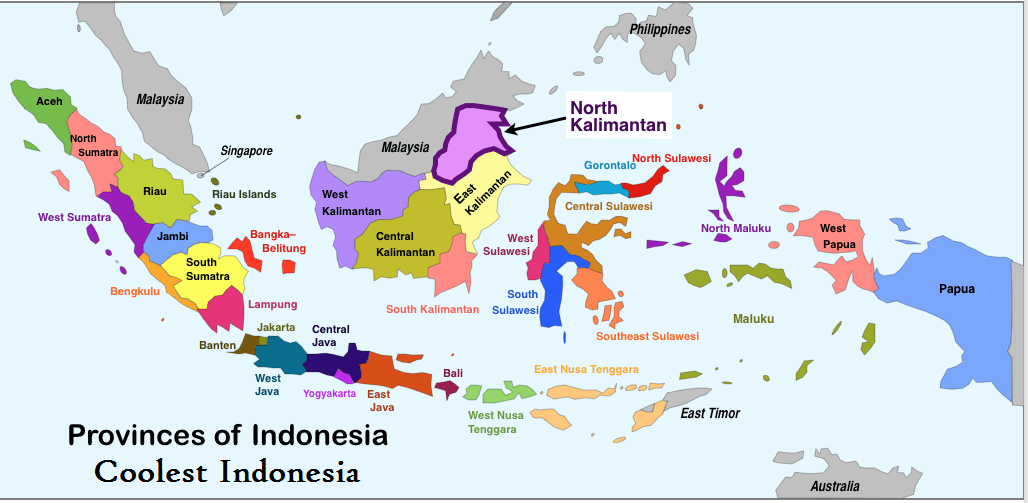
Today, the Indonesian political map is characterized by a multi-layered structure, reflecting the delicate balance between national unity and regional autonomy. The country is divided into 34 provinces, each with its own elected governor, legislature, and administrative apparatus. Provinces are further subdivided into districts (kabupaten) and cities (kota), each with their own elected leaders.
This decentralized structure allows for local communities to have a greater say in their governance, facilitating the delivery of public services and promoting economic development at the regional level. However, the system also presents challenges in coordinating policies across different levels of government and ensuring consistent standards of governance.
The Importance of the Indonesian Political Map
The Indonesian political map is not merely a geographical representation; it is a living document reflecting the nation’s political and social realities. It highlights the country’s diversity, its complex history, and its ongoing quest for a balance between unity and autonomy. Understanding the nuances of this map is crucial for:
- Effective Governance: Decentralization allows for more responsive governance, tailoring policies to specific regional needs and fostering greater local participation in decision-making.
- Economic Development: Regional autonomy empowers local communities to leverage their resources and develop their economies, contributing to national economic growth.
- National Unity: By acknowledging and accommodating regional identities, the decentralized system fosters a sense of belonging and strengthens national unity.
- Political Stability: A more inclusive political system, reflecting the diversity of the Indonesian people, can contribute to political stability and reduce the potential for separatist movements.
Challenges and Opportunities
While decentralization has brought significant benefits, it also presents challenges. These include:
- Uneven Development: The uneven distribution of resources and infrastructure across different regions can lead to disparities in economic development and social welfare.
- Corruption: Decentralization can increase opportunities for corruption, particularly if local governments lack strong oversight and accountability mechanisms.
- Inter-regional Conflicts: The competition for resources and political power can sometimes lead to inter-regional conflicts, undermining national unity.
Despite these challenges, the Indonesian political map offers significant opportunities for progress. By strengthening governance at all levels, promoting equitable development, and fostering inter-regional cooperation, Indonesia can unlock its full potential and create a more prosperous and inclusive future for its diverse population.
FAQs about the Indonesian Political Map:
Q: How has the Indonesian political map evolved over time?
A: The Indonesian political map has undergone significant transformations since independence. From a centralized system with limited regional autonomy, the country has transitioned to a decentralized model with greater power devolved to provinces. This evolution reflects the changing political landscape, the desire for greater regional representation, and the need for more responsive governance.
Q: What are the key features of the current Indonesian political map?
A: The current map is characterized by a multi-layered structure, with 34 provinces, each having its own elected governor, legislature, and administrative apparatus. Provinces are further divided into districts and cities, each with its own elected leaders. This decentralized system allows for local communities to have a greater say in their governance.
Q: What are the benefits of decentralization in Indonesia?
A: Decentralization has brought numerous benefits, including more responsive governance, increased local participation in decision-making, and greater empowerment of regional communities. It has also facilitated economic development at the grassroots level and contributed to national unity by acknowledging and accommodating regional identities.
Q: What are the challenges associated with decentralization in Indonesia?
A: Decentralization has also presented challenges, such as uneven development across regions, increased opportunities for corruption, and potential inter-regional conflicts. Addressing these challenges requires strengthening governance at all levels, promoting equitable development, and fostering inter-regional cooperation.
Q: What is the future of the Indonesian political map?
A: The future of the Indonesian political map will likely involve further refinements to the decentralized system, aiming to address the existing challenges and enhance the benefits. This may include strengthening local governance, promoting inter-regional collaboration, and ensuring equitable distribution of resources and opportunities.
Tips for Understanding the Indonesian Political Map:
- Consider the historical context: Understanding the colonial legacy and the evolution of decentralization is crucial for comprehending the current political map.
- Focus on regional identities: Recognize the diverse cultural, linguistic, and historical identities of different regions, as these influence political dynamics.
- Analyze the role of local governments: Understand the powers and responsibilities of provincial, district, and city governments, and how they interact with the central government.
- Explore the challenges and opportunities: Recognize the challenges associated with decentralization, but also acknowledge the potential for progress through effective governance, equitable development, and inter-regional cooperation.
Conclusion
The Indonesian political map is a testament to the country’s complex history, its diverse geography, and its ongoing journey towards a more inclusive and responsive political system. By understanding the nuances of this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities facing the nation. The future of Indonesia will be shaped by its ability to harness the benefits of decentralization while addressing its challenges, ensuring a future of prosperity and unity for all its people.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indonesian Political Landscape: A Map of Diversity and Decentralization. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!