The Indiana House District Map: A Framework For Representation
The Indiana House District Map: A Framework for Representation
Related Articles: The Indiana House District Map: A Framework for Representation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Indiana House District Map: A Framework for Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indiana House District Map: A Framework for Representation
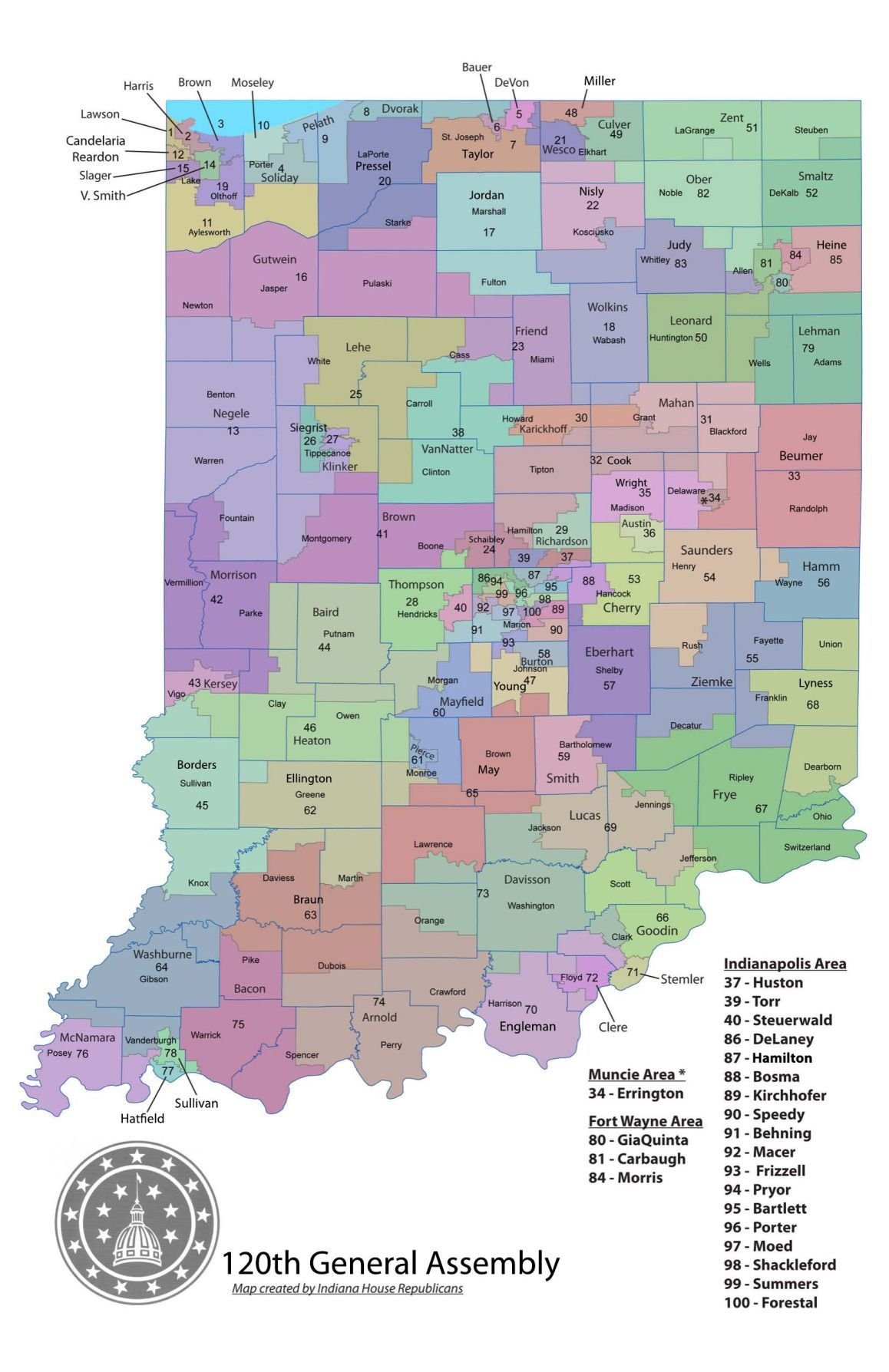
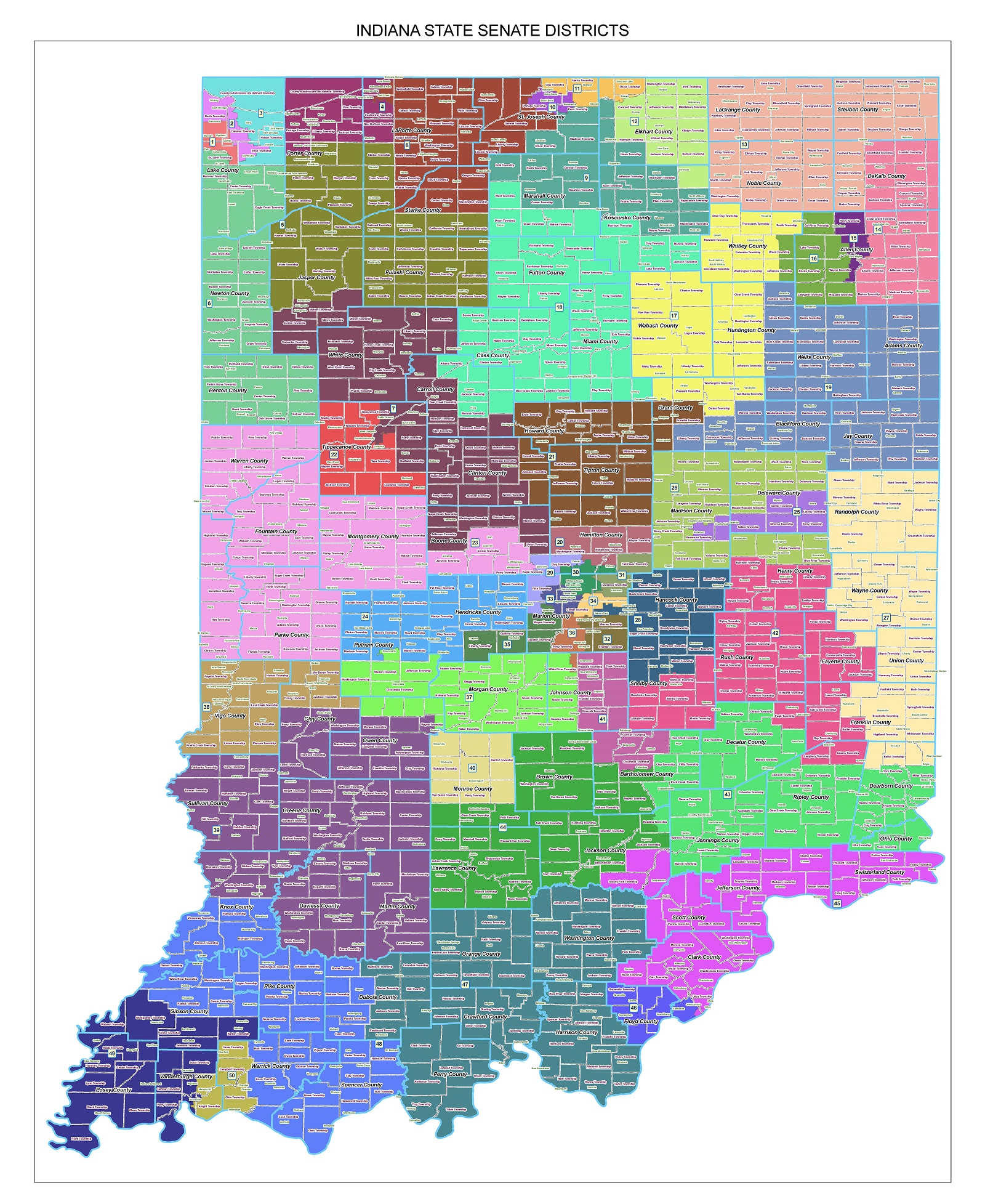
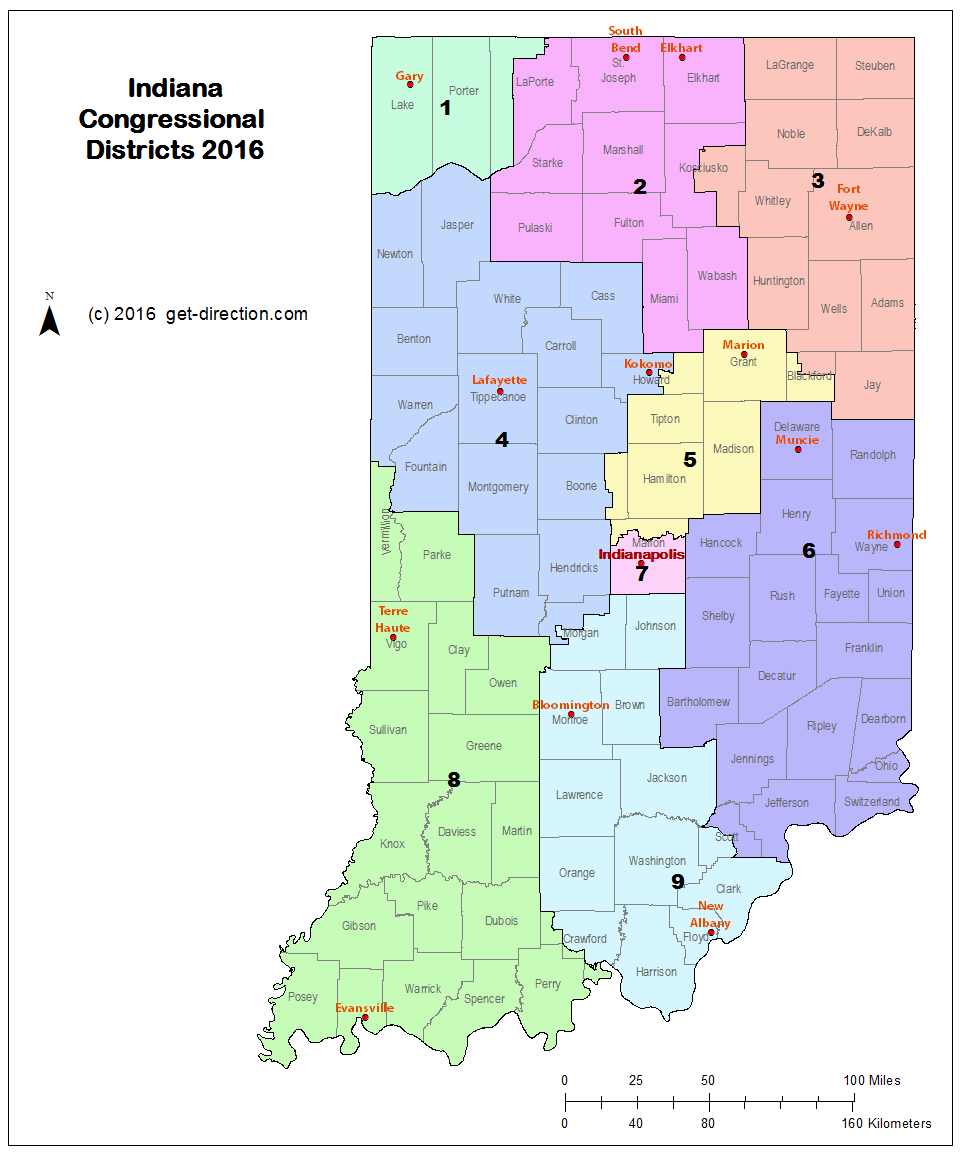
The Indiana House District Map serves as a fundamental element in the state’s political landscape, outlining the geographic boundaries that define the constituencies represented by members of the Indiana House of Representatives. This map, subject to periodic redrawing after each decennial census, plays a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of legislative elections and the overall balance of political power in the state. Understanding the intricacies of the map and its implications is essential for navigating the complexities of Indiana’s political system.
Historical Context and Evolution
The Indiana House District Map has undergone significant transformations throughout its history, reflecting shifts in population distribution, political ideologies, and legal challenges. The process of redistricting, mandated by the Constitution, aims to ensure that each district contains roughly the same number of residents, guaranteeing equal representation for all citizens. However, the map’s evolution has often been intertwined with partisan maneuvering, leading to debates about gerrymandering, where district boundaries are manipulated to favor a particular political party.
Key Features and Principles
The Indiana House District Map adheres to several key principles:
- Equal Population: Districts are designed to contain roughly the same number of residents, ensuring that each representative represents an equal number of constituents. This principle is based on the concept of "one person, one vote," enshrined in the Fourteenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution.
- Contiguity: District boundaries must be contiguous, meaning that all parts of a district must be connected and not separated by other districts. This principle helps to maintain the integrity of representation and prevent the fragmentation of communities.
- Compactness: Districts should be geographically compact, minimizing the distance between residents and their representative. This principle promotes efficient representation and facilitates communication between constituents and their elected officials.
- Respect for Communities of Interest: The map strives to avoid dividing communities with shared interests or identities, such as cities, towns, or neighborhoods. This principle promotes cohesive representation and ensures that the voices of diverse communities are heard.
The Redistricting Process
The process of redrawing the Indiana House District Map is a complex and politically charged one. It typically involves the following steps:
- Data Collection and Analysis: The Indiana Redistricting Commission gathers data from the decennial census and other sources to analyze population changes and demographic trends.
- Public Input and Hearings: The commission holds public hearings and solicits input from citizens, community organizations, and political parties, allowing for diverse perspectives on the proposed map.
- Map Development and Review: The commission develops and reviews various map proposals, considering factors such as population equality, contiguity, compactness, and communities of interest.
- Legislative Approval: The proposed map is submitted to the Indiana General Assembly for approval. This process can involve further debate and amendments before the final map is adopted.
Implications of the Map
The Indiana House District Map has significant implications for the state’s political landscape:
- Electoral Outcomes: The map can influence the outcome of legislative elections by creating districts that favor one party over another. Gerrymandering can create safe seats for incumbents or make it difficult for challengers to win.
- Representation: The map determines which communities are represented by which legislators, potentially impacting the priorities and policies addressed by the state legislature.
- Political Power: The map can shift the balance of power between political parties, influencing the composition of the legislature and the ability of different factions to advance their agendas.
Challenges and Controversies
The Indiana House District Map has been the subject of numerous legal challenges and political controversies:
- Gerrymandering: The manipulation of district boundaries for partisan advantage has been a recurring issue, leading to accusations of unfair elections and diminished representation.
- Racial and Ethnic Gerrymandering: The map has been challenged for creating districts that dilute the voting power of minority communities, violating the Voting Rights Act.
- Transparency and Public Participation: The redistricting process has faced criticism for a lack of transparency and limited opportunities for public participation.
FAQs
Q: How often is the Indiana House District Map redrawn?
A: The map is redrawn every ten years, following the completion of the decennial census.
Q: Who is responsible for drawing the Indiana House District Map?
A: The Indiana Redistricting Commission, a bipartisan body composed of five members, is responsible for drawing the map.
Q: What are the criteria used to draw the Indiana House District Map?
A: The map must adhere to several criteria, including equal population, contiguity, compactness, and respect for communities of interest.
Q: How can I get involved in the redistricting process?
A: You can participate in public hearings held by the Indiana Redistricting Commission, submit written testimony, or contact your elected officials to express your views on the proposed map.
Tips
- Stay informed: Follow the redistricting process closely and stay informed about the proposed map and its potential implications.
- Engage in public discourse: Participate in public hearings and share your opinions with the Redistricting Commission and your elected officials.
- Support organizations advocating for fair redistricting: Many organizations work to promote fair and transparent redistricting processes. Consider supporting these groups.
Conclusion
The Indiana House District Map is a crucial instrument in shaping the state’s political landscape. Its impact extends beyond the boundaries of legislative elections, influencing the representation of diverse communities, the balance of political power, and the priorities of the state government. Understanding the map’s intricacies and the challenges it presents is essential for informed political engagement and ensuring that the voices of all Hoosiers are heard in the halls of government. As the map continues to evolve, it remains a focal point for ongoing debate and scrutiny, highlighting the importance of fair and transparent redistricting practices in safeguarding democratic principles and ensuring equitable representation for all.

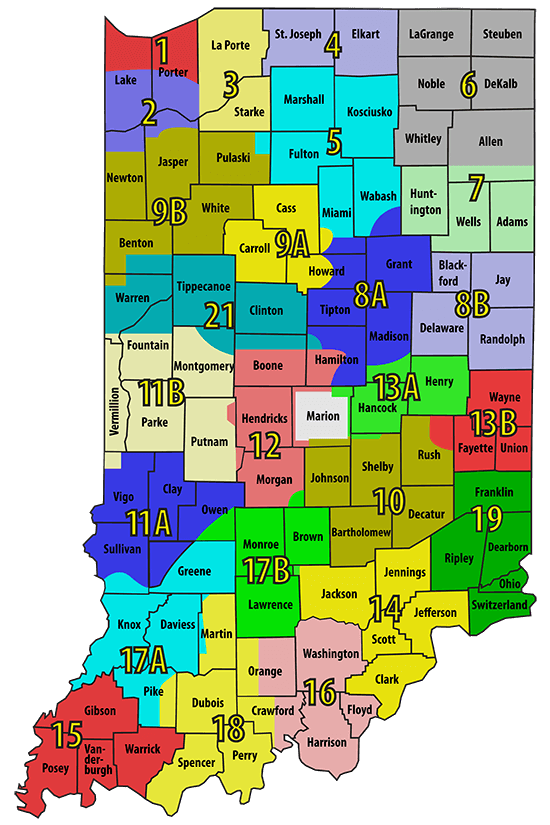
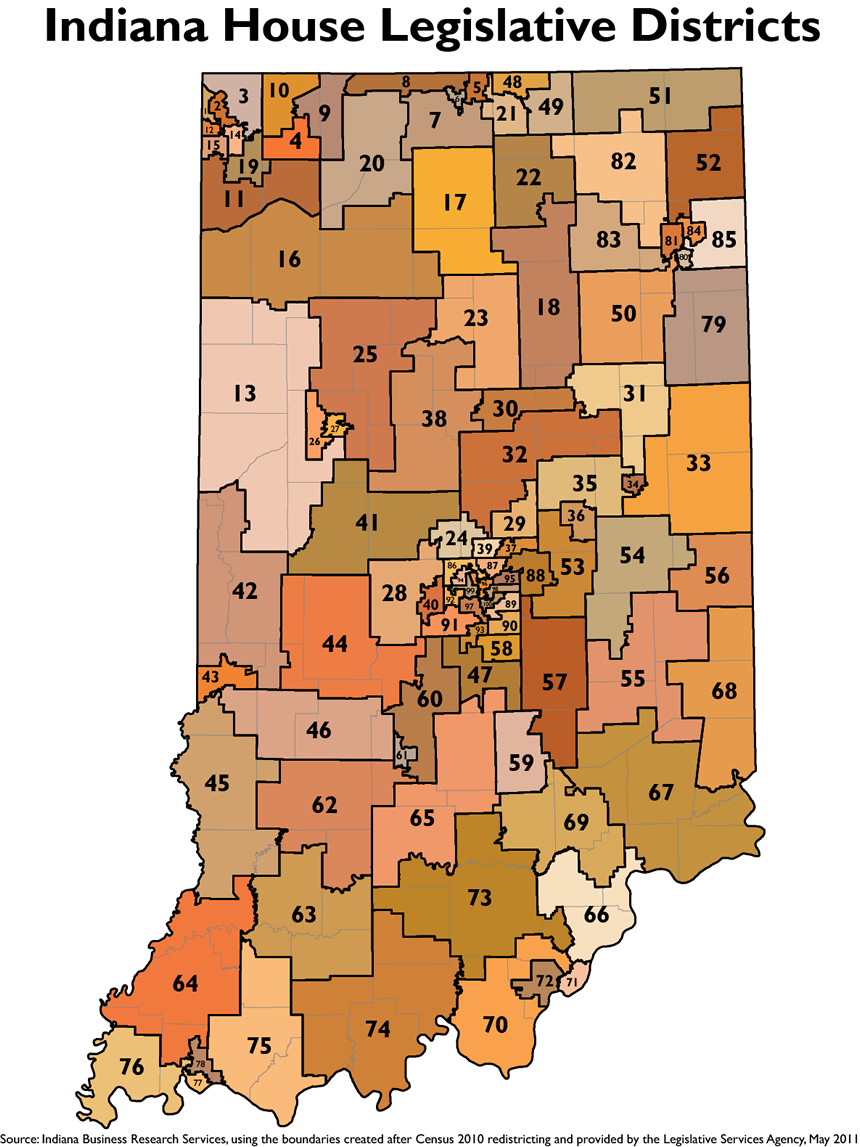
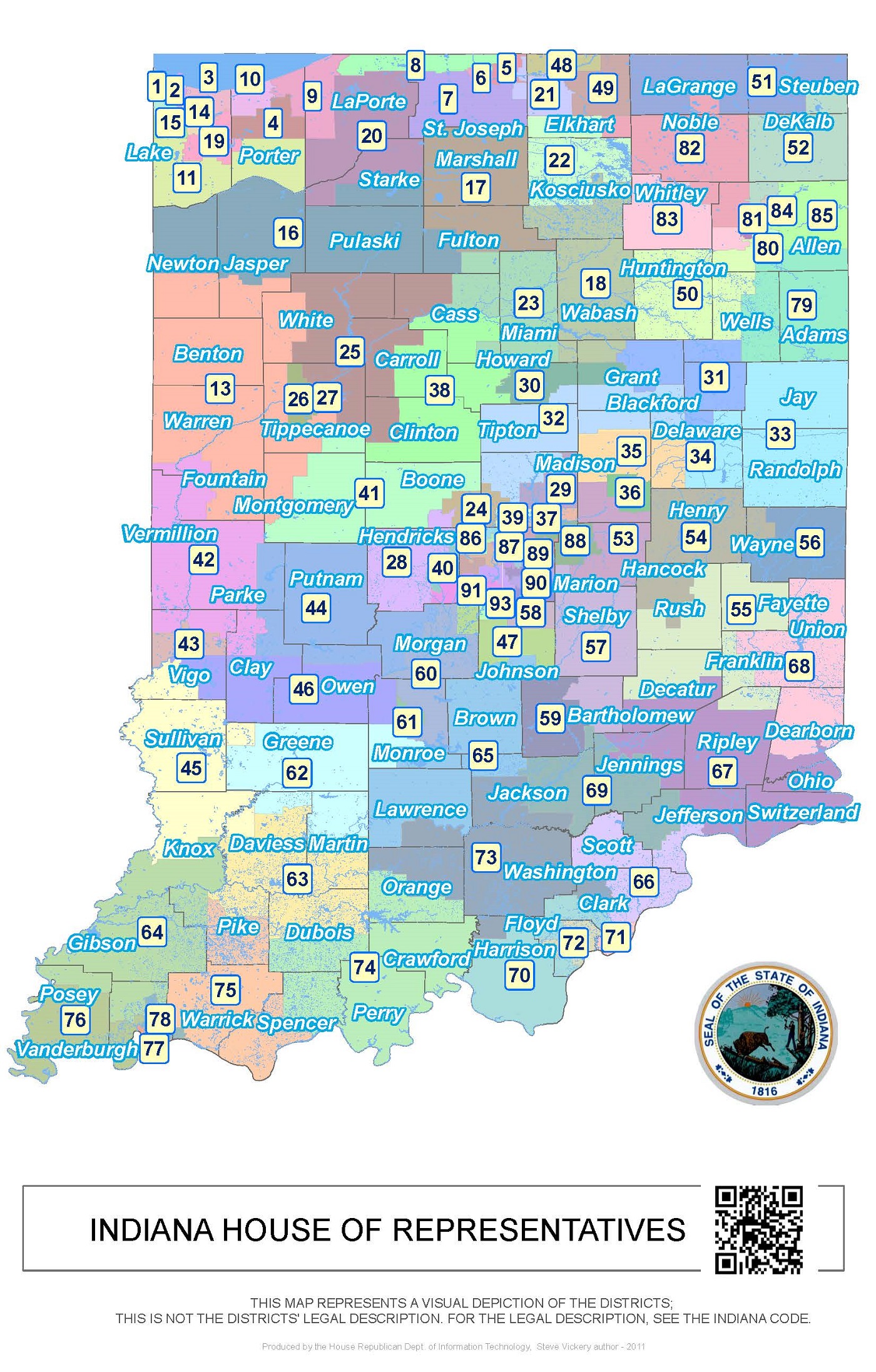


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indiana House District Map: A Framework for Representation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!