The Indiana District Map: A Framework For Representation And Governance
The Indiana District Map: A Framework for Representation and Governance
Related Articles: The Indiana District Map: A Framework for Representation and Governance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Indiana District Map: A Framework for Representation and Governance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indiana District Map: A Framework for Representation and Governance

The Indiana district map, a complex and ever-evolving framework, serves as the foundation for the state’s political landscape. This map delineates the boundaries of congressional, state legislative, and local electoral districts, determining the composition of elected bodies and influencing the allocation of resources. Understanding the Indiana district map is crucial for comprehending the state’s political dynamics, the distribution of power, and the representation of its diverse population.
The Evolution of the Indiana District Map:
The Indiana district map has undergone significant transformations throughout its history, reflecting shifts in population, political ideologies, and legal challenges. The map’s evolution is intertwined with the principles of fair representation and the pursuit of equal representation for all citizens.
Early Maps and the Rise of Gerrymandering:
Early district maps in Indiana, like those in many other states, were often drawn with little regard for population balance or fairness. The practice of "gerrymandering," named after Massachusetts Governor Elbridge Gerry, emerged as a strategy to manipulate district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group. This practice, often characterized by oddly shaped districts, aimed to concentrate opposing voters in a few districts while spreading out the party’s own voters across multiple districts, thereby maximizing their electoral advantage.
The Era of Reform and the "One Person, One Vote" Principle:
The 1960s marked a turning point in the evolution of district maps across the United States, including Indiana. The landmark Supreme Court case, Reynolds v. Sims (1964), established the "one person, one vote" principle, requiring states to draw districts with roughly equal populations. This decision aimed to ensure that each voter’s voice carried equal weight in elections, regardless of their location or the district’s size.
The Impact of Technology and Data Analysis:
The advent of sophisticated computer technology and data analysis tools has profoundly impacted the process of drawing district maps. Political strategists now employ advanced algorithms to analyze voter demographics, past election results, and other data points to create maps that maximize their party’s electoral advantage. This has led to increasingly complex and intricate district boundaries, making it more challenging to ensure fair and equal representation.
The Role of Independent Commissions and Redistricting Reform:
Recognizing the potential for abuse and the growing concerns about gerrymandering, several states have implemented reforms aimed at creating more independent and transparent redistricting processes. Some states have established independent commissions, composed of non-partisan experts, to oversee the drawing of district maps. These commissions are often tasked with adhering to specific criteria, such as population equality, adherence to geographic boundaries, and the preservation of communities of interest.
The Indiana District Map Today:
The current Indiana district map is a product of the 2020 decennial census, which revealed shifts in population distribution across the state. The redistricting process, overseen by the Indiana General Assembly, involved drawing new boundaries for congressional, state legislative, and local electoral districts. This process sparked controversy and debate, with accusations of partisan gerrymandering and attempts to dilute the voting power of certain groups.
The Impact of the Indiana District Map on Representation:
The Indiana district map has a profound impact on the composition of elected bodies and the representation of diverse communities. It influences the political ideologies of elected officials, the allocation of resources, and the ability of different groups to participate in the political process.
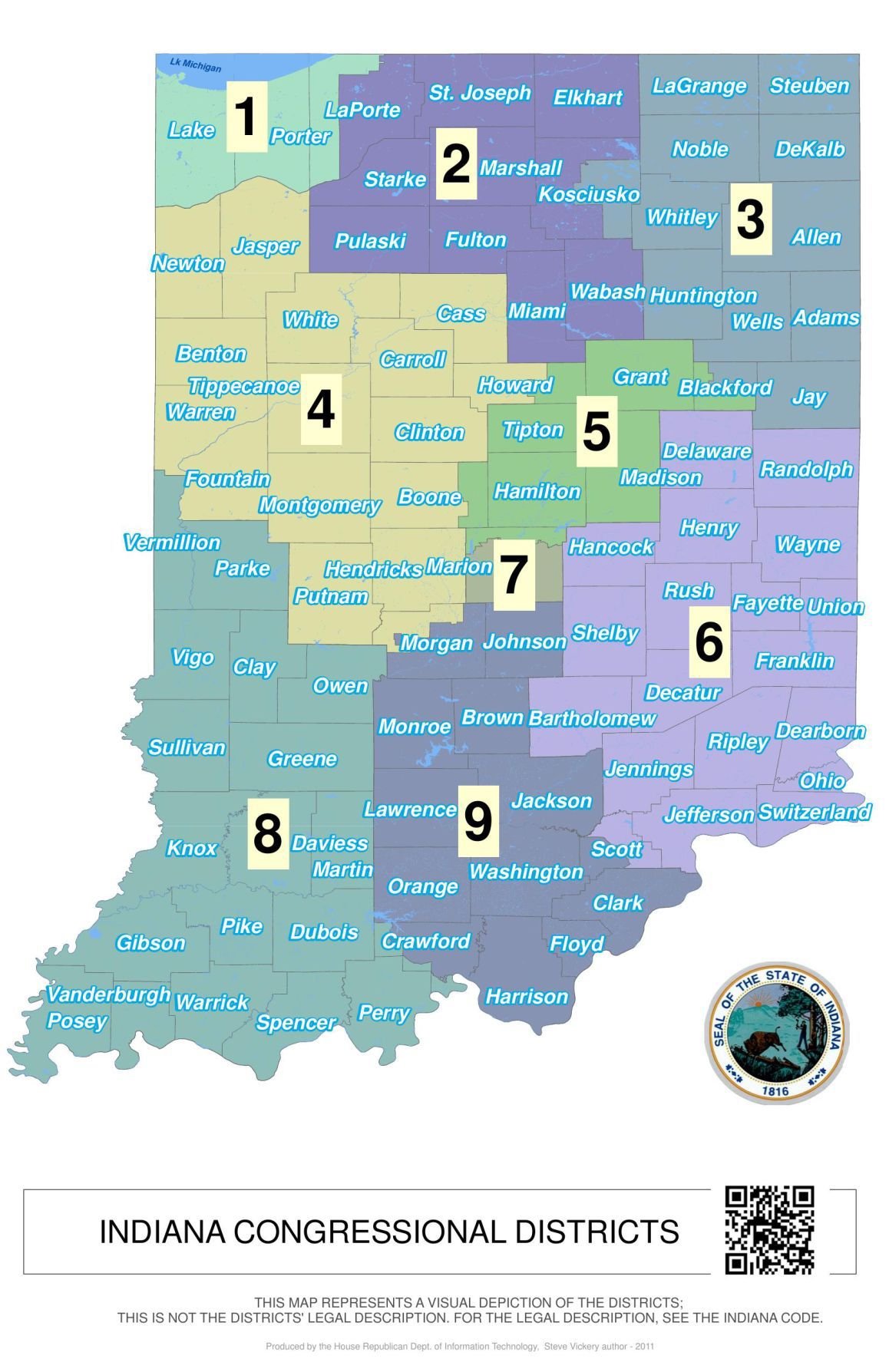
Congressional Districts:
Indiana is allocated nine congressional districts, each represented by a member of the U.S. House of Representatives. The district boundaries determine the political makeup of each congressional delegation, influencing the state’s voice in national legislation and policy.
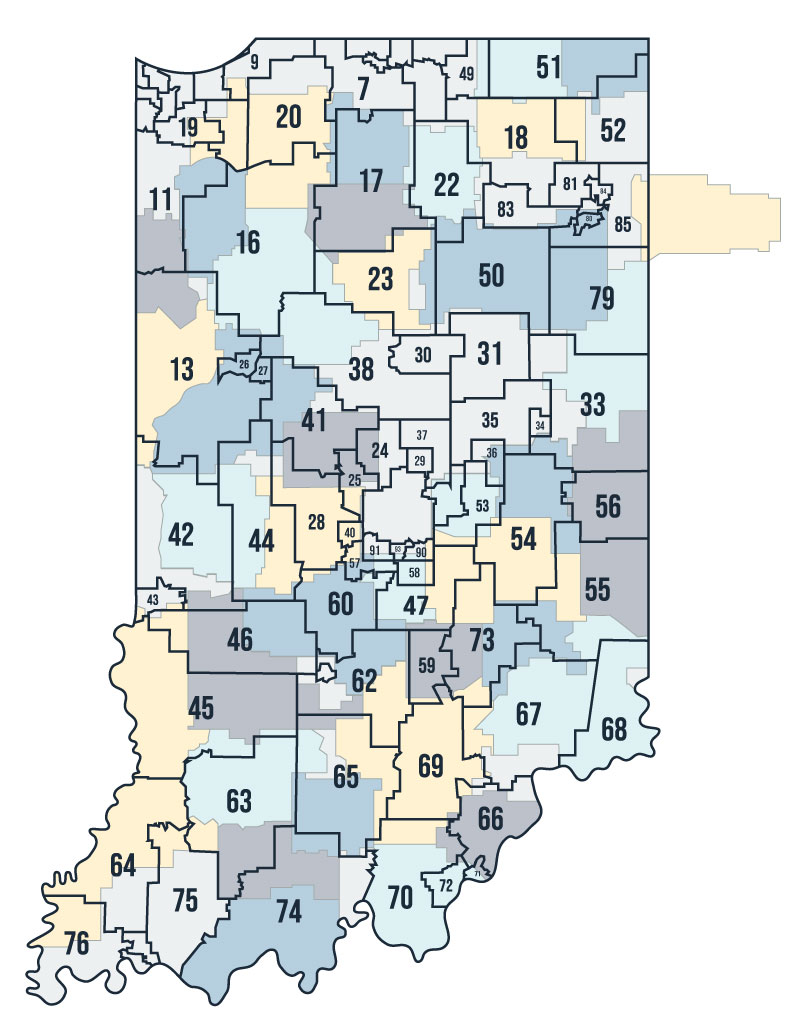
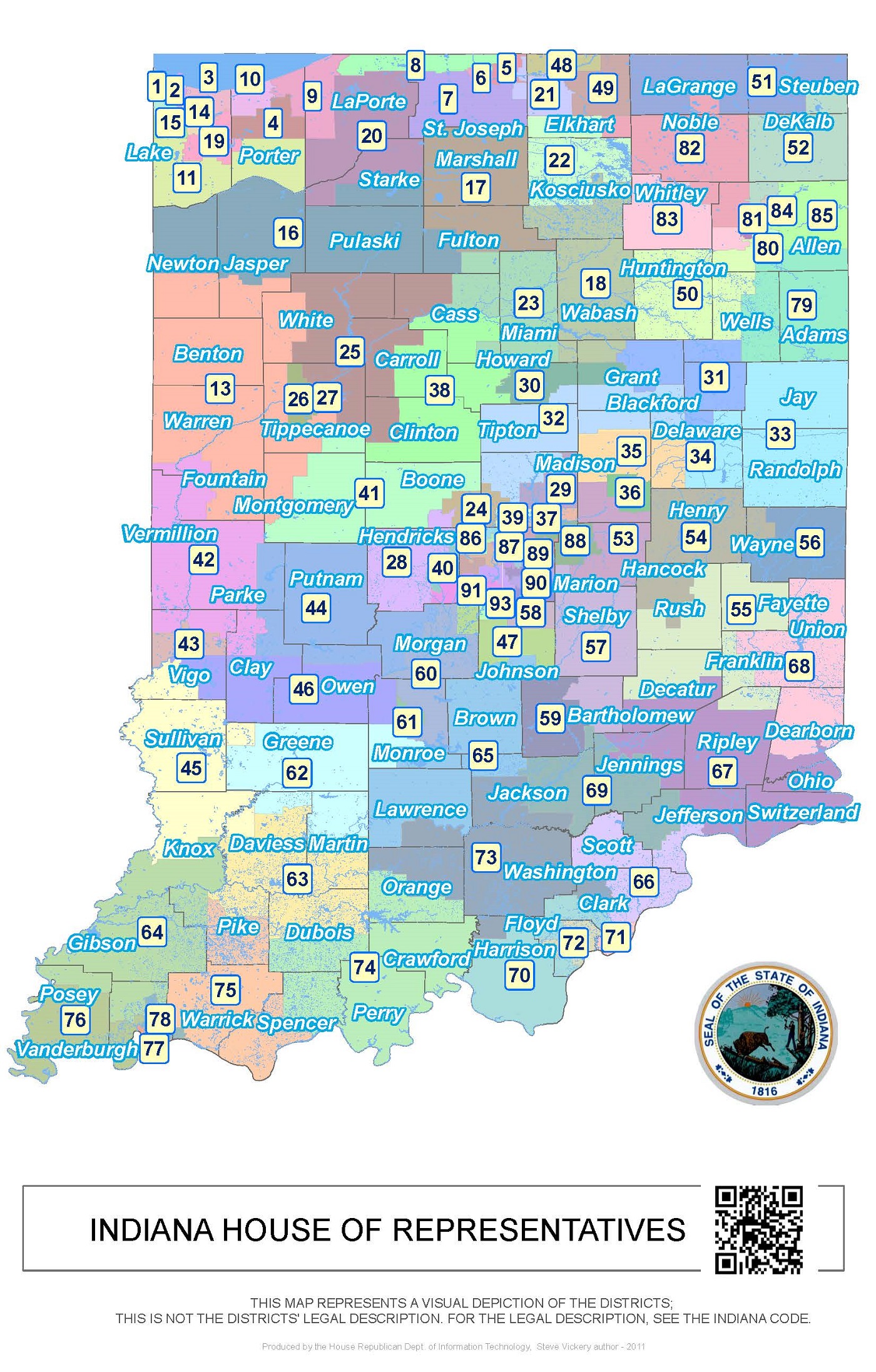
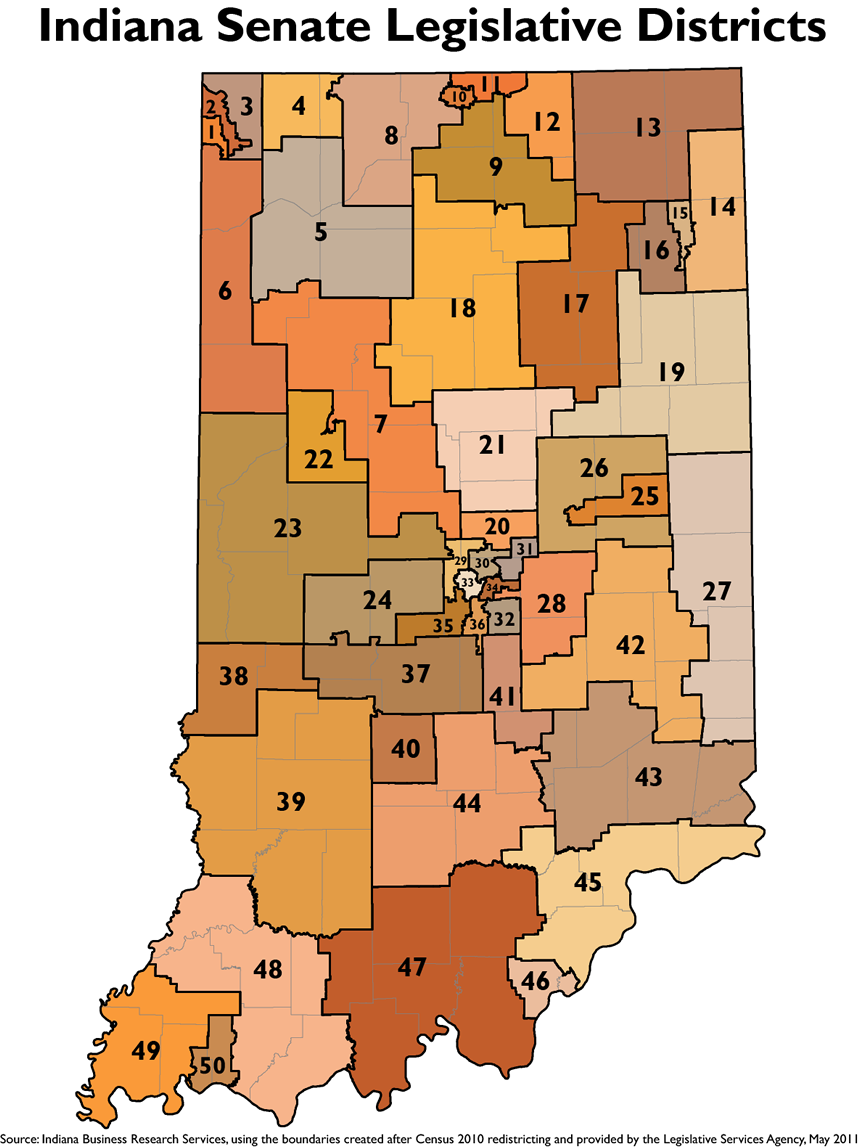
State Legislative Districts:
The Indiana General Assembly, composed of the House of Representatives and the Senate, is divided into 100 state legislative districts. These districts determine the representation of different communities and regions within the state legislature, influencing the passage of state laws and the allocation of state resources.
Local Electoral Districts:
The Indiana district map also extends to the local level, defining the boundaries of city councils, county boards, and school boards. These districts influence the representation of different neighborhoods and communities within local governments, impacting local policies and service delivery.
The Importance of Fair and Equal Representation:
The Indiana district map is a critical component of a functioning democracy. It ensures that all citizens have an equal opportunity to participate in the political process and that their voices are heard in government. Fair and equal representation is essential for maintaining a healthy and responsive government, promoting civic engagement, and fostering trust in democratic institutions.
Challenges and Future Directions:
The Indiana district map continues to be a subject of debate and controversy. Concerns about gerrymandering, the impact of technology on redistricting, and the need for greater transparency and accountability in the process remain prominent.
Addressing Gerrymandering:
Efforts to address gerrymandering and ensure fair representation have gained momentum in recent years. Proposed reforms include:
- Independent Redistricting Commissions: Establishing independent commissions, free from political influence, to oversee the drawing of district maps.
- Criteria-Based Redistricting: Implementing clear criteria for district boundaries, such as population equality, adherence to geographic boundaries, and the preservation of communities of interest.
- Public Input and Transparency: Increasing public participation and transparency in the redistricting process, allowing for community input and ensuring that the process is open and accessible.
The Role of Technology:
The use of technology in redistricting presents both opportunities and challenges. While advanced algorithms can help to ensure population equality and minimize partisan bias, they also raise concerns about the potential for manipulation and the lack of transparency in the process. It is crucial to ensure that technology is used responsibly and ethically in redistricting, with safeguards in place to prevent abuse.
Promoting Civic Engagement:
Engaging citizens in the redistricting process is essential for ensuring that the Indiana district map reflects the needs and interests of all communities. Educating the public about redistricting, providing opportunities for input, and fostering open dialogue can help to build trust in the process and ensure that it serves the interests of all citizens.
Conclusion:
The Indiana district map is a dynamic and evolving framework that shapes the state’s political landscape. It is a complex and often controversial subject, reflecting the challenges and opportunities of ensuring fair and equal representation in a diverse and changing society. As technology advances and societal values evolve, the Indiana district map will continue to be a subject of debate and reform, reflecting the ongoing pursuit of a more inclusive and representative democracy.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indiana District Map: A Framework for Representation and Governance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!