The Geopolitical Landscape Of Israel And Its Neighbors: A Comprehensive Overview
The Geopolitical Landscape of Israel and its Neighbors: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Geopolitical Landscape of Israel and its Neighbors: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Geopolitical Landscape of Israel and its Neighbors: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geopolitical Landscape of Israel and its Neighbors: A Comprehensive Overview

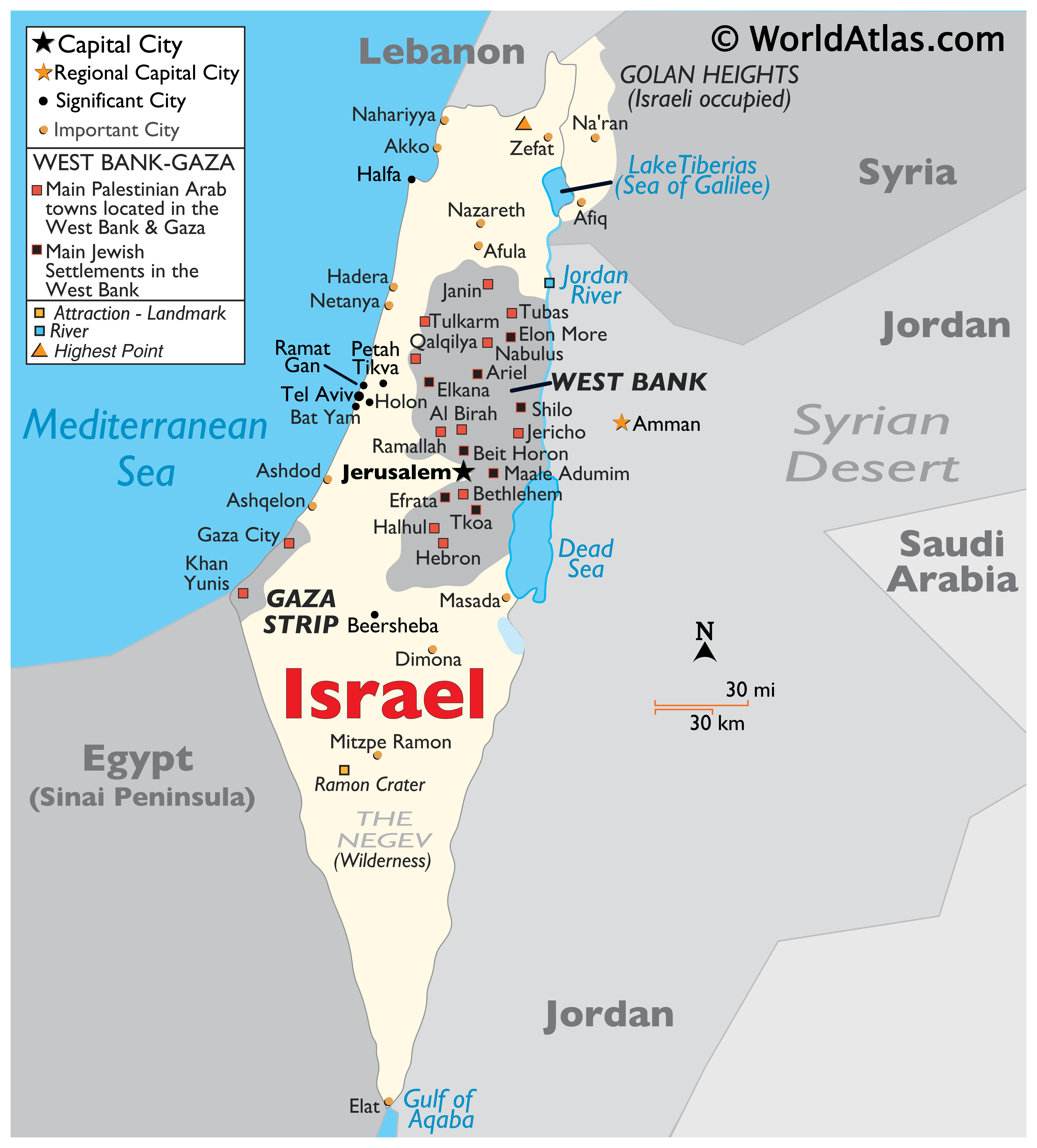
The land of Israel and its surrounding territories are a complex tapestry of history, culture, and geopolitics. This region, nestled at the crossroads of three continents, has witnessed empires rise and fall, witnessed religious and cultural movements, and remains a focal point of international attention. Understanding the map of Israel and its neighbors is crucial to grasping the intricate dynamics that shape the region’s present and future.
Geographical Overview:
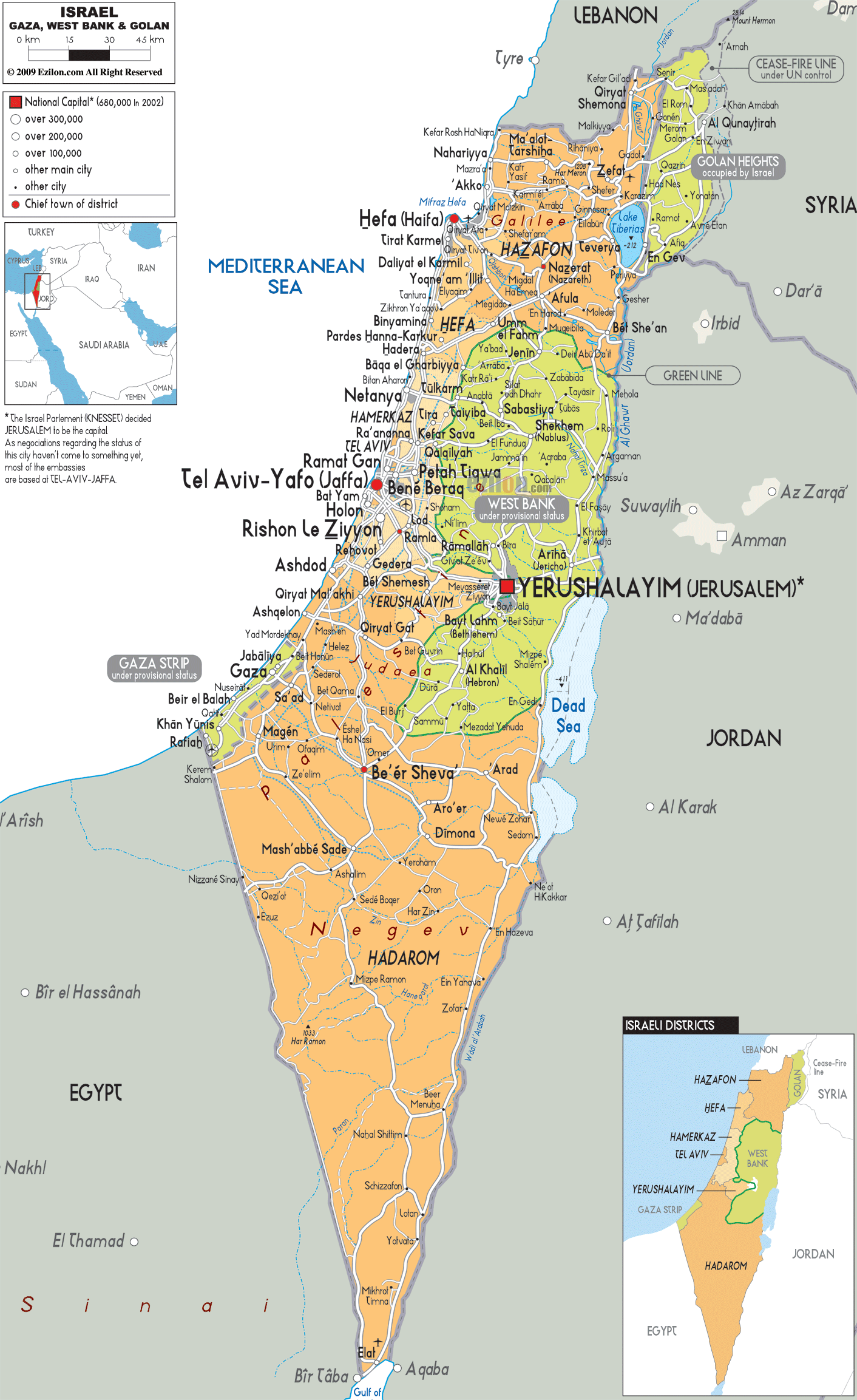
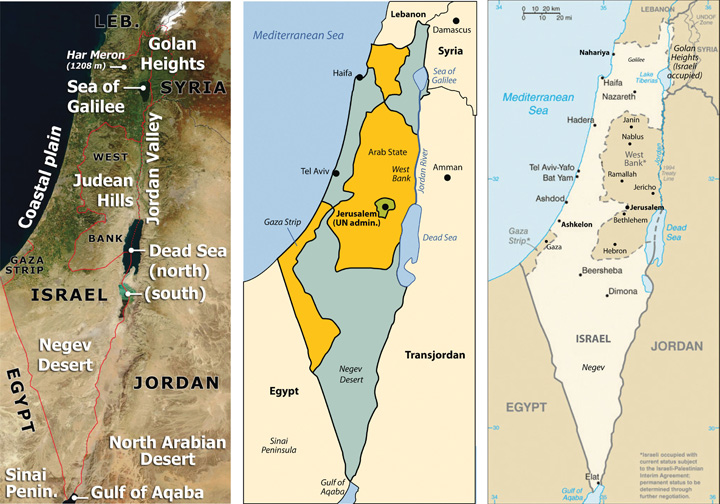
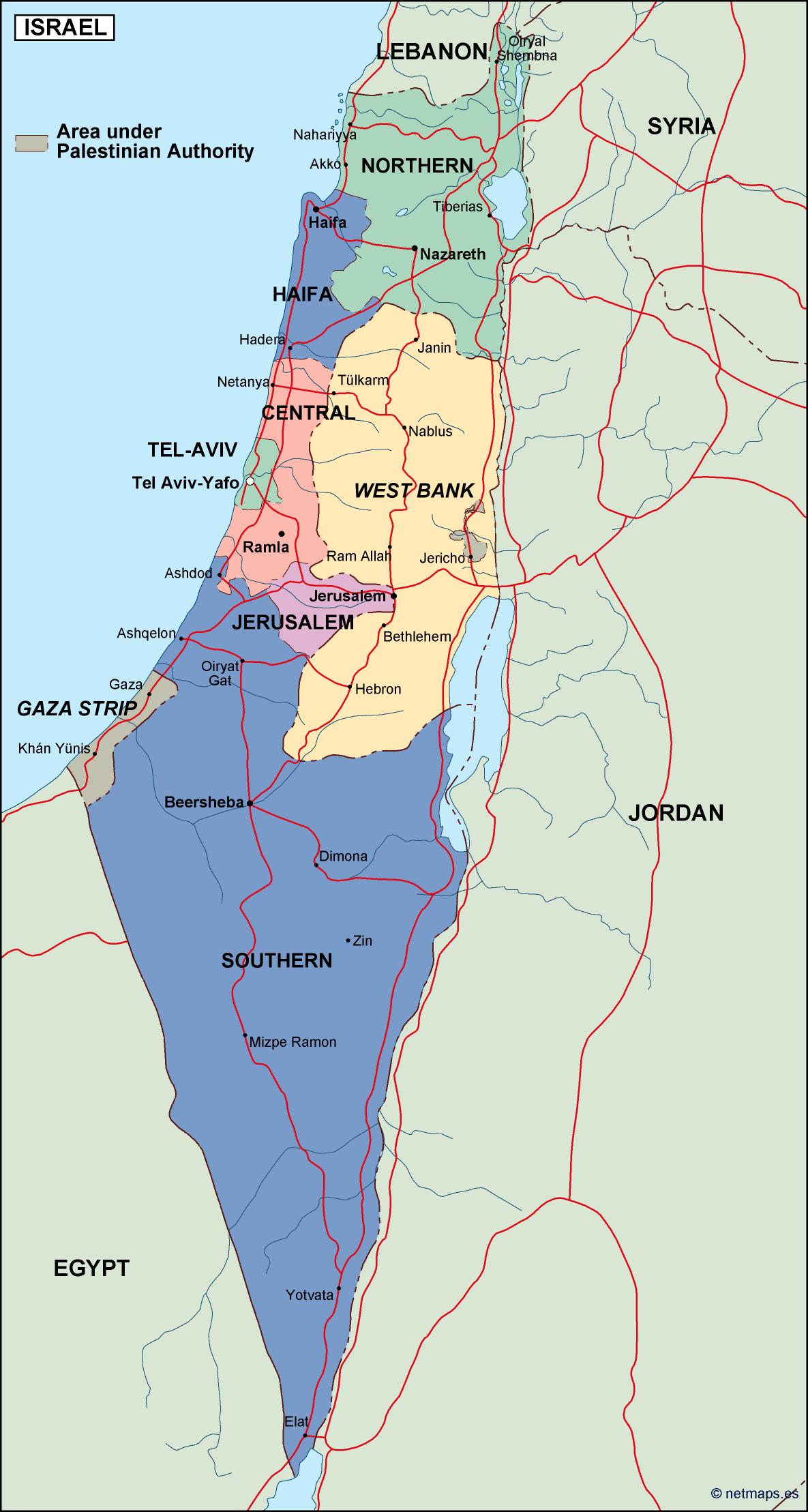
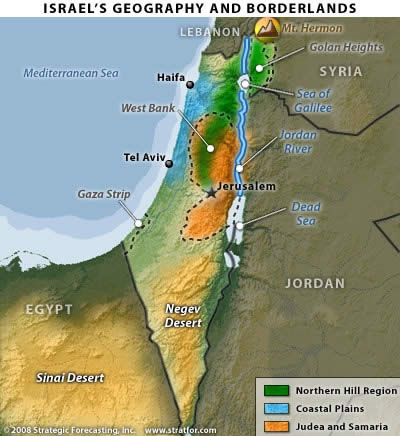
Israel occupies a relatively small landmass, approximately 25,000 square kilometers, situated on the eastern Mediterranean coast. Its borders are defined by Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the southwest, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. The West Bank, a territory claimed by both Israel and Palestine, lies to the east of Israel, while the Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory governed by Hamas, borders the Mediterranean coast.
Historical Context:
The region’s history stretches back millennia, with evidence of human settlement dating back to the Neolithic period. The land has been a focal point for empires, including the Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman empires. The modern State of Israel was established in 1948 following the British Mandate for Palestine, a period marked by conflict and displacement. The ensuing Arab-Israeli wars further shaped the region’s borders and political landscape.
Key Features of the Map:
1. The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The conflict between Israel and Palestine is central to the region’s dynamics. The West Bank and Gaza Strip, home to a Palestinian population, are at the heart of this conflict. The dispute over land, resources, and political sovereignty continues to fuel tensions and instability.
2. The Golan Heights: This strategically important plateau, captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 Six-Day War, remains a point of contention. Syria claims sovereignty over the Golan Heights, while Israel maintains its control, citing security concerns and strategic importance.
3. The Jordan River: This river, flowing from the north to the south, serves as a natural border between Israel and Jordan. It also holds significant religious importance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
4. The Dead Sea: This salt lake, located at the lowest point on Earth, is shared by Israel, Jordan, and the West Bank. It faces environmental challenges due to water depletion and pollution.
5. The Mediterranean Coast: The Mediterranean Sea provides access to international trade and transportation, playing a vital role in Israel’s economy and security.
The Importance of the Map:
Understanding the map of Israel and its neighbors is essential for several reasons:
- Political Context: The map reflects the complex geopolitical realities of the region, including territorial disputes, security concerns, and regional alliances.
- Historical Understanding: The map provides a visual representation of the historical events that have shaped the region’s borders, demographics, and cultural identities.
- Economic Significance: The map highlights the region’s strategic location, its access to trade routes, and its potential for economic growth.
- International Relations: The map underscores the intricate web of international relations in the region, with major powers like the United States, Russia, and the European Union playing significant roles.
Benefits of Studying the Map:
- Enhanced Awareness: Studying the map fosters a deeper understanding of the region’s political, social, and economic complexities.
- Informed Decision-Making: Knowledge of the map allows for informed decision-making in various fields, including diplomacy, journalism, and business.
- Improved Communication: Understanding the map facilitates effective communication about the region’s challenges and opportunities.
- Increased Empathy: Studying the map promotes empathy and understanding for the diverse populations and cultures that inhabit the region.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the status of the West Bank and Gaza Strip?
The West Bank and Gaza Strip are territories claimed by both Israel and Palestine. The West Bank is currently under Israeli control, while the Gaza Strip is governed by Hamas. The status of these territories remains a major point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
2. Why is the Golan Heights so important?
The Golan Heights is strategically important due to its high elevation, which provides a commanding view of the surrounding areas. It also holds significant agricultural value and water resources.
3. What is the role of the Jordan River in the region?
The Jordan River is a vital source of water for the region and holds significant religious and cultural importance. It is also a symbol of the conflict between Israel and Palestine, as it forms a natural border between the two entities.
4. What are the environmental challenges facing the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea is facing environmental challenges due to water depletion caused by excessive water extraction for agriculture and industrial use. This has led to a decline in water levels and increased salinity, posing threats to the ecosystem and tourism industry.
5. How does the Mediterranean Sea impact the region?
The Mediterranean Sea provides access to international trade and transportation, making it vital for Israel’s economy and security. It also plays a role in tourism and fishing industries.
Tips for Studying the Map:
- Use a variety of maps: Explore different types of maps, including political, physical, and historical maps, to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Focus on key features: Pay attention to the major cities, rivers, mountains, and borders to understand the region’s geography and political landscape.
- Research historical events: Learn about the historical events that have shaped the region’s borders and demographics.
- Read news and articles: Stay informed about current events and political developments in the region.
- Engage in discussions: Discuss the region’s complexities with others to gain different perspectives and deepen your understanding.
Conclusion:
The map of Israel and its neighbors is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s intricate dynamics. It provides a visual representation of the historical events, political tensions, and cultural complexities that define the region. By studying the map and its various features, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities facing this vital part of the world. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of the region and the need for peaceful resolution of conflicts to ensure a stable and prosperous future for all its inhabitants.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geopolitical Landscape of Israel and its Neighbors: A Comprehensive Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!