The Geography Of Israel: A Complex And Contested Landscape
The Geography of Israel: A Complex and Contested Landscape
Related Articles: The Geography of Israel: A Complex and Contested Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Geography of Israel: A Complex and Contested Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geography of Israel: A Complex and Contested Landscape

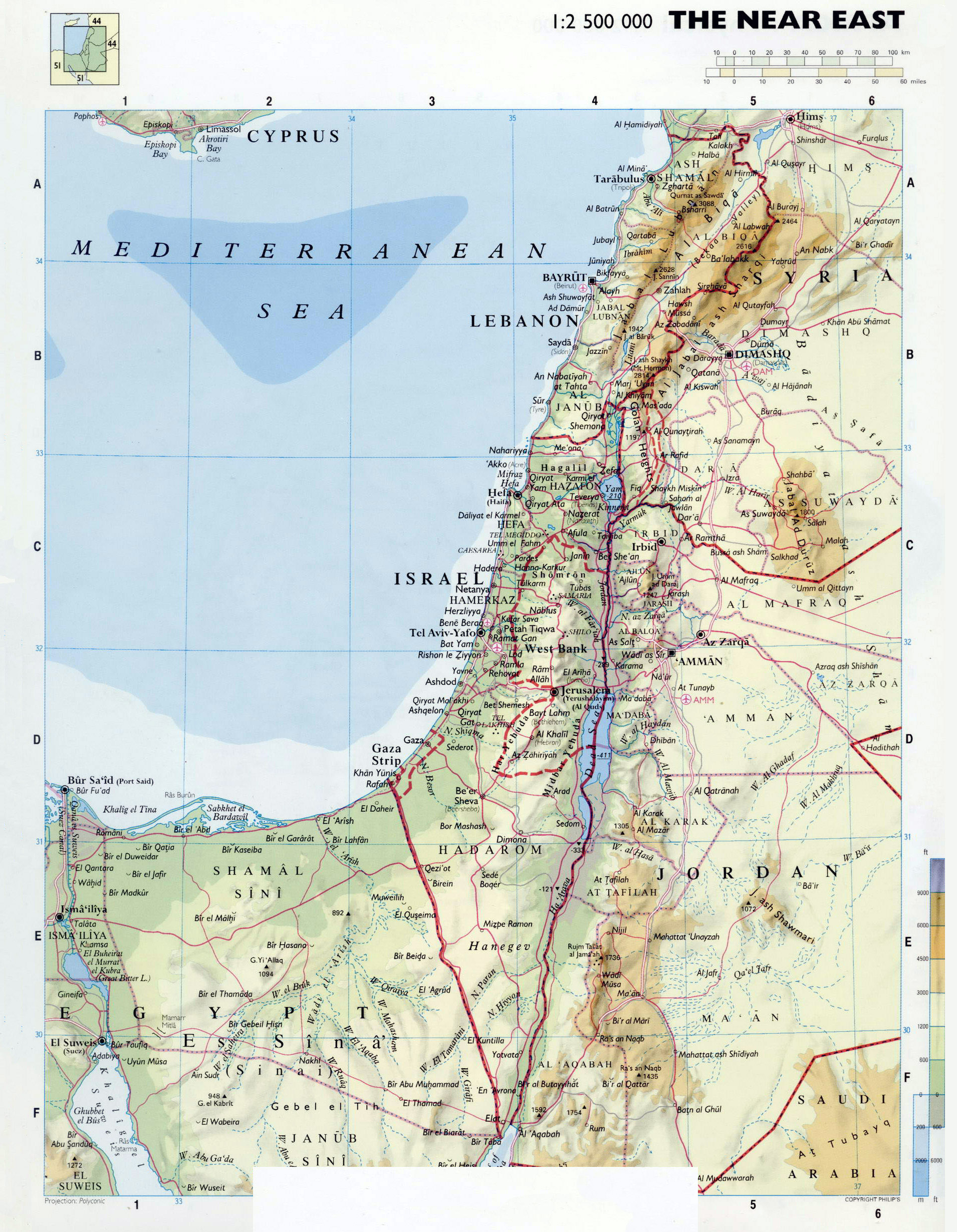
Israel, a nation situated in the Middle East, occupies a geographically and historically significant region. Its landmass, roughly the size of New Jersey, encompasses a diverse array of landscapes, from the arid Negev Desert in the south to the fertile coastal plains along the Mediterranean Sea. This diverse terrain has shaped Israel’s history, culture, and ongoing political complexities.
A Land of Contrasts:
Israel’s geography is characterized by stark contrasts:
- The Coastal Plain: This fertile region, stretching along the Mediterranean coastline, is home to major cities like Tel Aviv and Haifa. It is a hub of economic activity, agriculture, and tourism.
- The Central Highlands: This hilly region, rising from the coastal plain, is the heartland of Israel, containing Jerusalem, the country’s capital, and the city of Tel Aviv. It is a densely populated area with a mix of urban and rural landscapes.
- The Jordan Rift Valley: This geological depression, running along the eastern border of Israel, is home to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, and the Jordan River, a vital source of water. The valley is also a significant historical and religious site.
- The Negev Desert: Covering over half of Israel’s landmass, the Negev Desert is a harsh, arid environment with limited human settlements. It is a region of ecological significance and holds potential for renewable energy development.
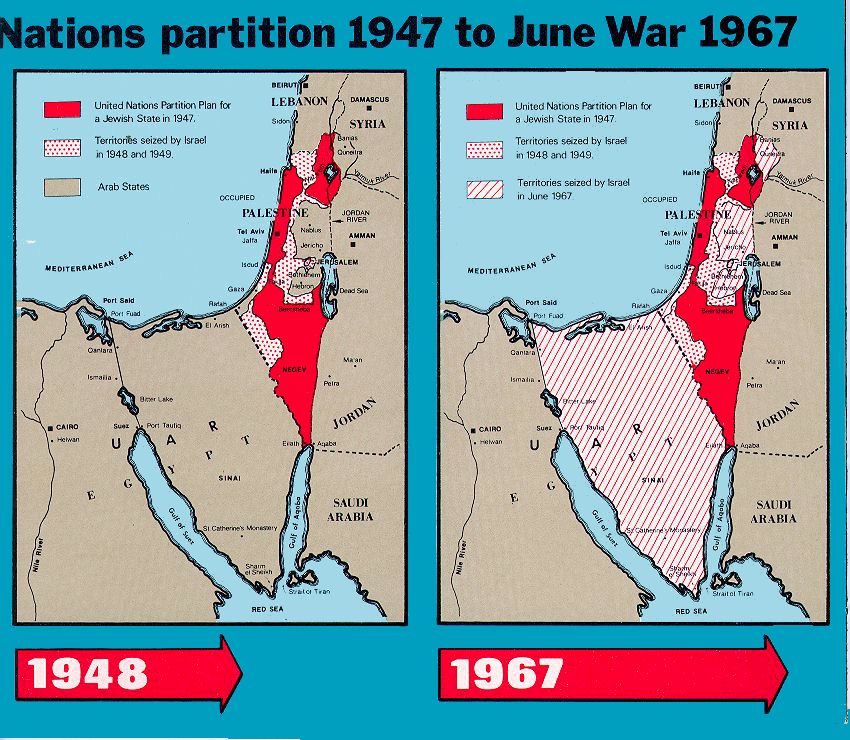
- The Golan Heights: A strategically important plateau overlooking the Jordan Valley, the Golan Heights were captured by Israel from Syria in 1967. Its status remains a contentious issue in the Israeli-Syrian conflict.
Historical and Political Significance:
Israel’s geography has profound implications for its history and present-day political landscape:
- Ancient Civilizations: The land has been inhabited for millennia, serving as a crossroads for ancient civilizations like the Canaanites, Israelites, Romans, and Ottomans. This rich history is evident in the numerous archaeological sites scattered across the country.
- Religious Importance: Israel is a holy land for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, attracting pilgrims and tourists from around the world. Jerusalem, in particular, holds immense religious significance for all three faiths, making it a contested city with deep historical and political ties.
- Water Scarcity: Israel faces a constant challenge of water scarcity due to its arid climate and limited freshwater resources. This scarcity has led to the development of innovative water management technologies and has played a significant role in the country’s political relations with its neighbors.
- Border Disputes: Israel’s borders have been subject to ongoing disputes and conflicts since its establishment in 1948. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, in particular, revolves around competing claims to land and resources, further complicating the country’s political landscape.
The Impact of Geography on Israeli Society:
Israel’s geography has shaped its society in numerous ways:
- Urban Development: The coastal plain and the central highlands have witnessed rapid urbanization, leading to the development of major cities like Tel Aviv, Jerusalem, and Haifa. These cities are hubs of economic activity, cultural development, and technological innovation.
- Agricultural Innovation: Despite its arid climate, Israel has developed sophisticated agricultural technologies, including drip irrigation and desalination, to maximize water use and produce a diverse range of crops.
- Military Strategy: Israel’s geography has influenced its military strategy, particularly in terms of defense against potential threats from neighboring countries. The country’s mountainous terrain and strategic location have been key factors in its military successes.
- Environmental Challenges: Israel faces significant environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and pollution. The country has implemented various initiatives to address these issues, but they remain a pressing concern.
FAQs on Israel’s Geography:
Q: What is the highest point in Israel?
A: Mount Meron, located in the Upper Galilee, is the highest point in Israel, reaching an elevation of 1,208 meters (3,963 feet).
Q: What is the largest city in Israel?
A: Jerusalem is the largest city in Israel, with a population of over 900,000 people. However, Tel Aviv is the country’s commercial and cultural center, with a population of over 450,000.
Q: What is the status of the Golan Heights?
A: The Golan Heights remain a contested territory, with Israel claiming it as part of its sovereign territory while Syria demands its return. The international community largely considers the Golan Heights as occupied Syrian territory.
Q: How does Israel address its water scarcity problem?
A: Israel has developed advanced water management technologies, including drip irrigation, desalination, and wastewater recycling, to conserve water and meet its growing demand.
Q: What are the main environmental challenges facing Israel?
A: Israel faces challenges related to water scarcity, desertification, air pollution, and the disposal of waste. The country is actively working on mitigating these issues through environmental regulations, renewable energy initiatives, and sustainable development practices.
Tips for Understanding Israel’s Geography:
- Explore Maps: Utilize online maps and geographical resources to gain a better understanding of Israel’s diverse landscapes and key geographical features.
- Read Travel Guides: Travel guides often provide insightful information about the country’s geography, including historical sites, cultural landmarks, and natural attractions.
- Watch Documentaries: Documentaries focusing on Israel’s geography, history, and environmental challenges can offer a deeper understanding of the country’s complex landscape.
- Engage in Discussions: Engage in discussions with people who have visited or lived in Israel to gain firsthand perspectives on the country’s geography and its impact on daily life.
Conclusion:
Israel’s geography plays a crucial role in shaping its history, culture, politics, and daily life. The country’s diverse landscapes, from the fertile coastal plain to the arid Negev Desert, have presented both opportunities and challenges. Understanding Israel’s geographical context is essential for appreciating its rich history, its complex political realities, and its ongoing efforts to overcome environmental challenges. By engaging with the country’s geography, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of life in this fascinating and often contested region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geography of Israel: A Complex and Contested Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!