The Geographic Significance Of Japan: A Nation Defined By Location
The Geographic Significance of Japan: A Nation Defined by Location
Related Articles: The Geographic Significance of Japan: A Nation Defined by Location
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Geographic Significance of Japan: A Nation Defined by Location. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geographic Significance of Japan: A Nation Defined by Location
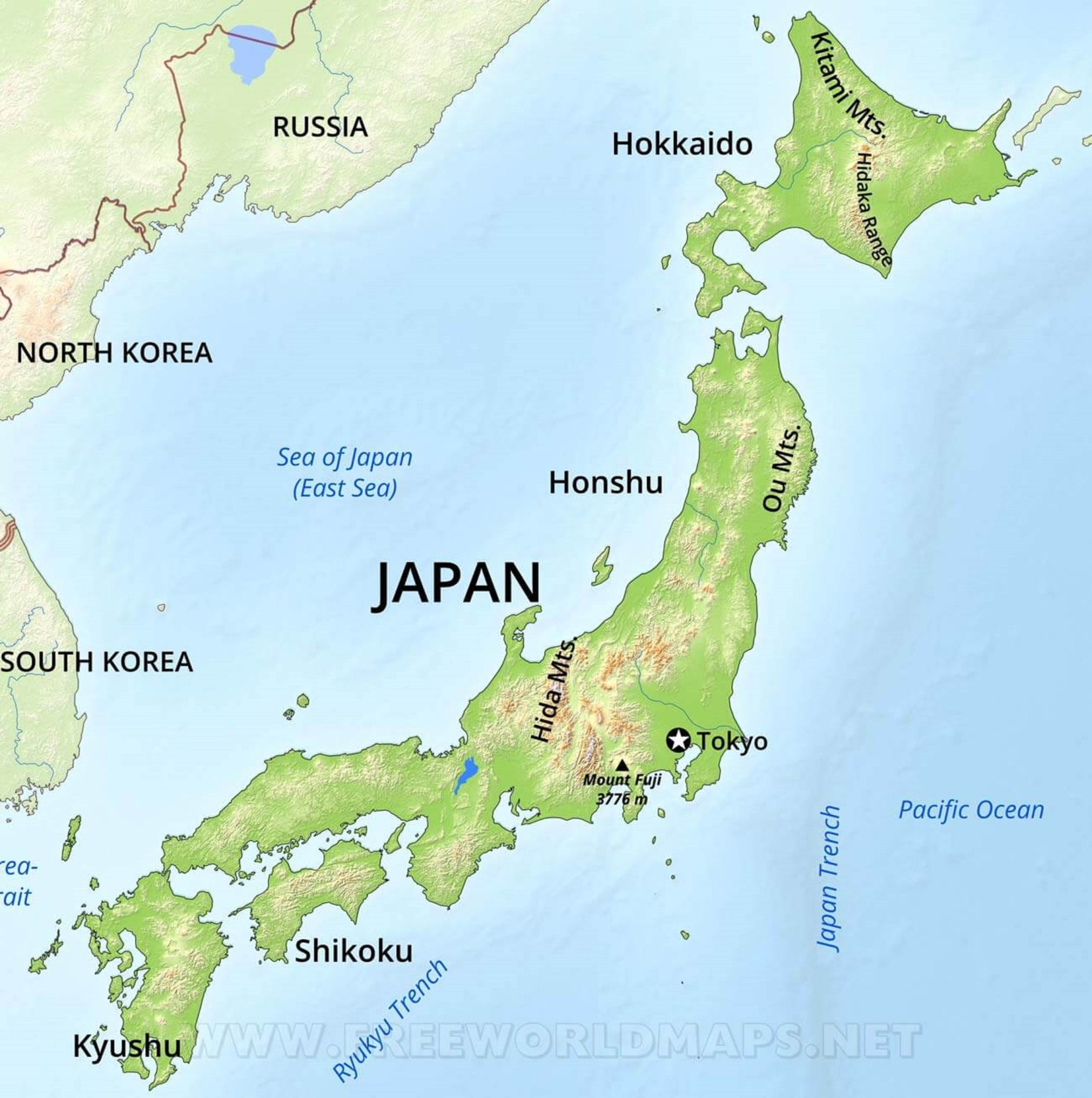
Japan, an archipelago nation nestled in the northwest Pacific Ocean, is a vibrant tapestry of culture, history, and innovation. Its location, however, is not merely a geographic fact; it is a defining characteristic that has profoundly shaped its development, its culture, and its place in the world.
A Ring of Fire Nation:
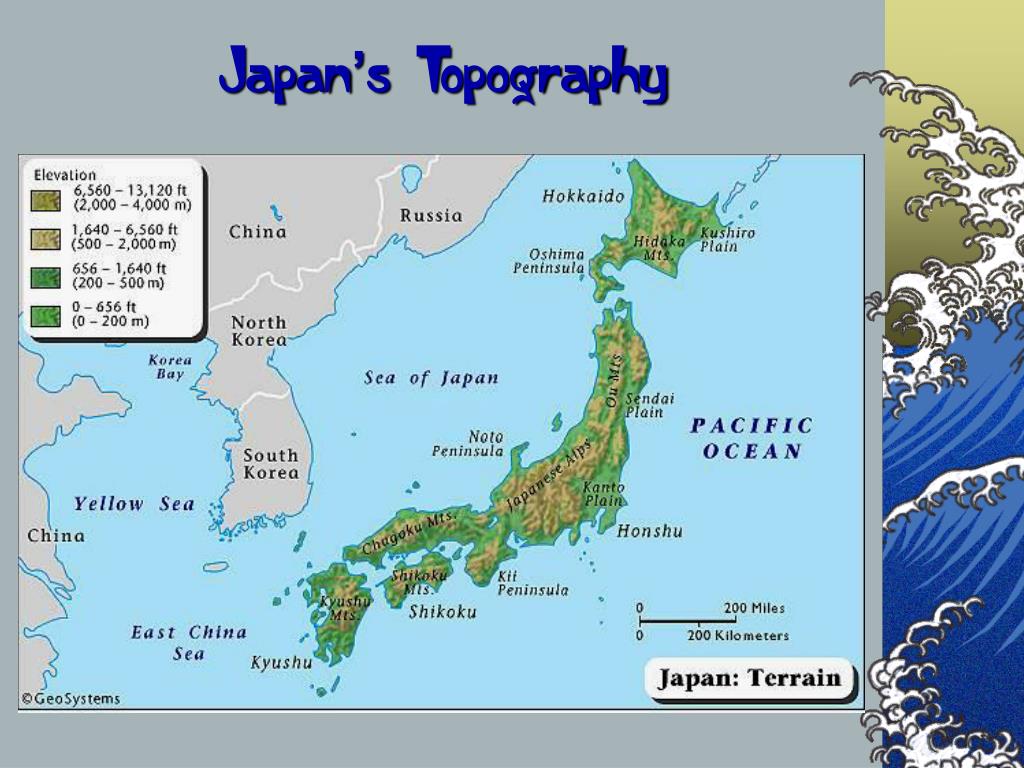
Japan’s position on the Earth’s surface is a crucial factor in understanding its unique features. It sits along the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity. This geological reality has brought both challenges and opportunities. While Japan experiences frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, these forces have also shaped its mountainous landscape, providing abundant natural resources like geothermal energy and fertile volcanic soil.
Island Nation, Global Power:
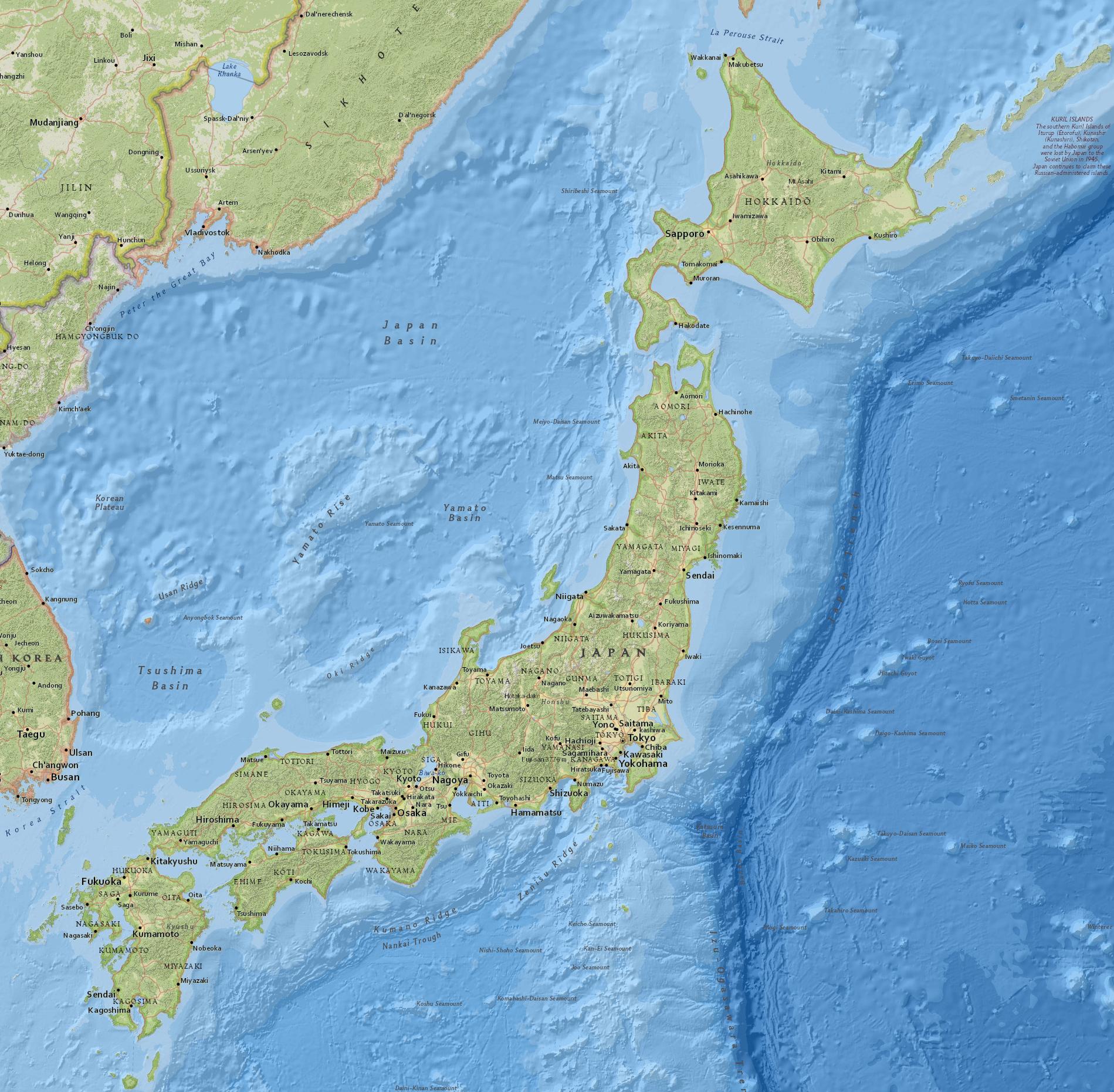
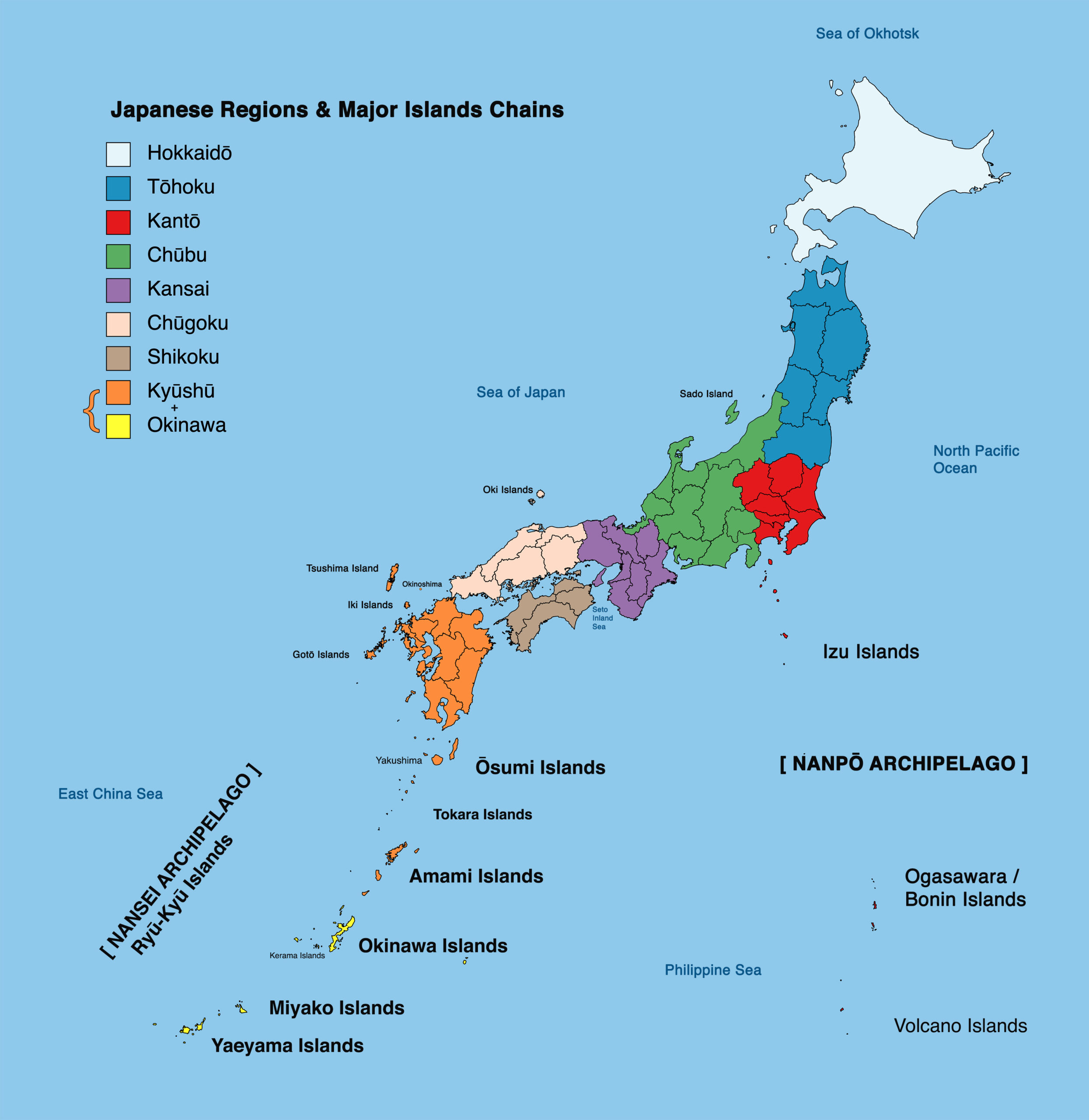
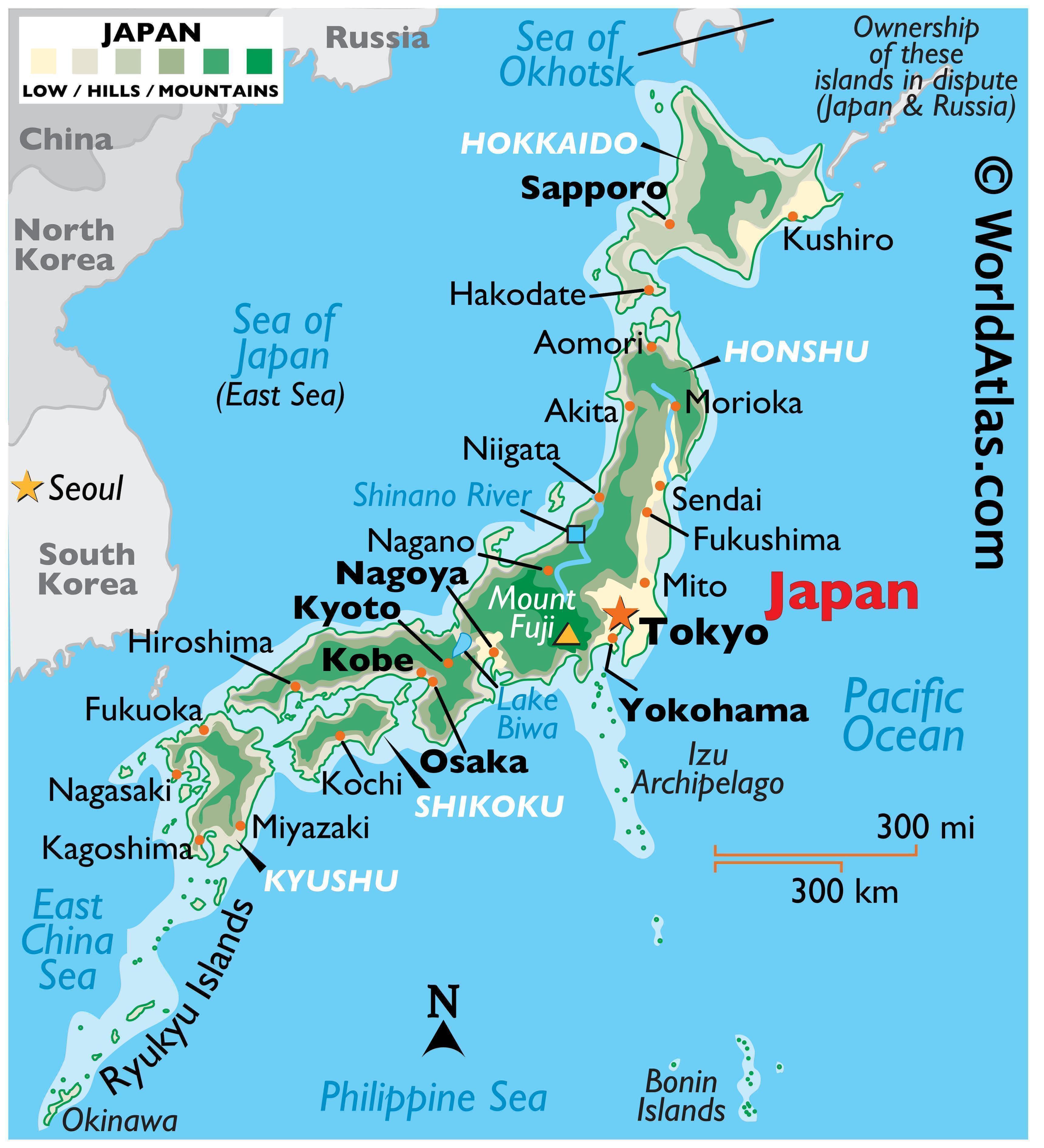
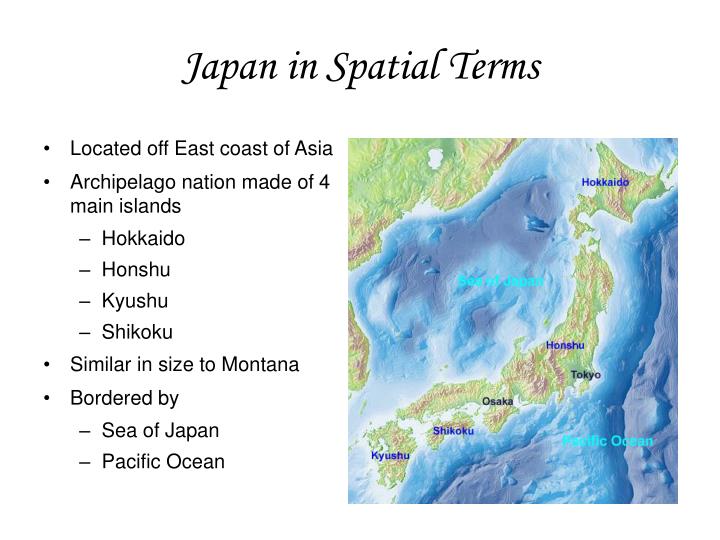
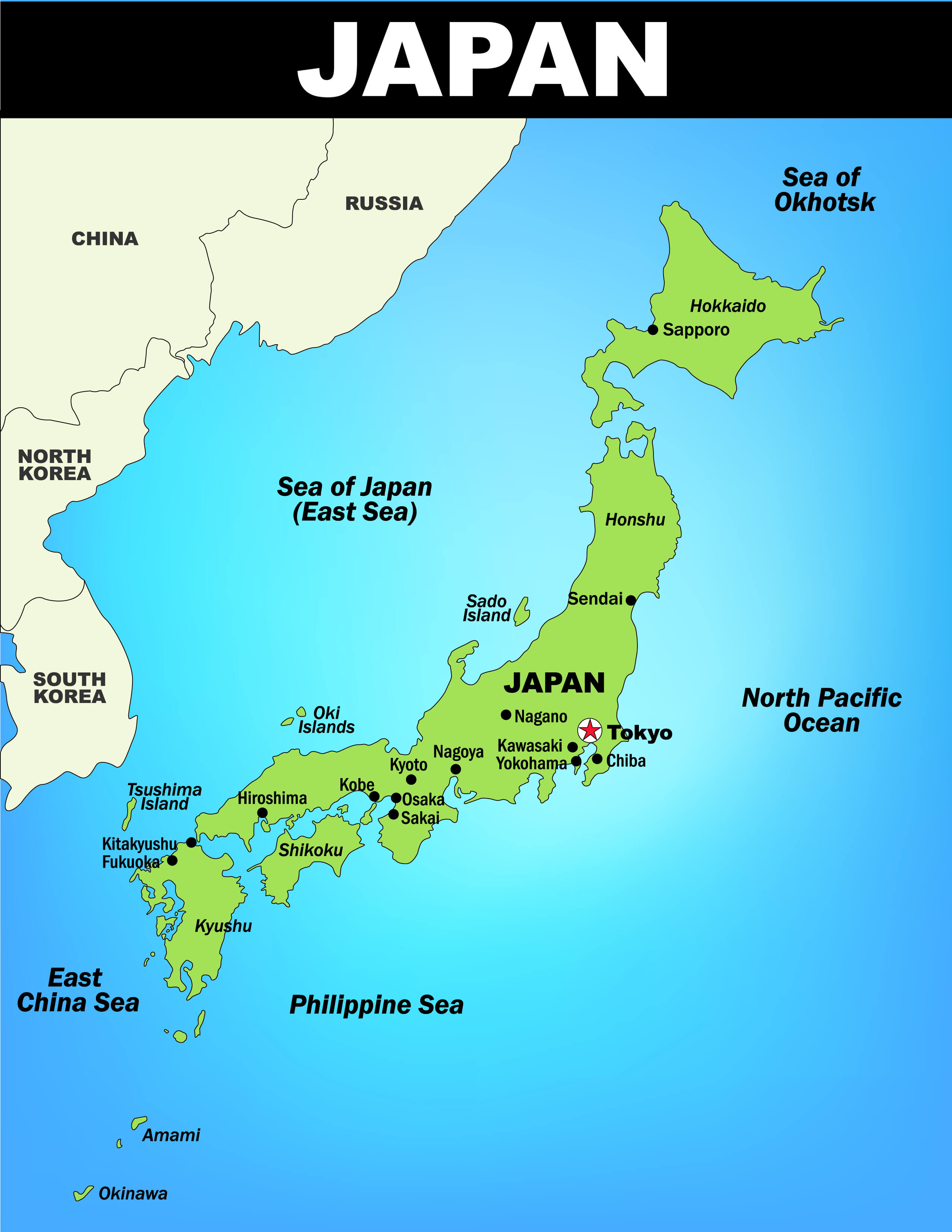
The Japanese archipelago, comprising four main islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu) and thousands of smaller islands, has fostered a strong sense of national identity and unity. Its island status has also contributed to a unique cultural development, relatively isolated from mainland Asia, yet open to global influences. Japan’s geographical location, strategically situated between mainland Asia and the Pacific Ocean, has made it a vital trading hub and a significant player in international affairs.
A Crossroads of Cultures:
Japan’s location at the crossroads of East Asia has facilitated cultural exchanges and influenced its artistic, culinary, and philosophical traditions. Over centuries, Japan has absorbed and adapted influences from China, Korea, and other neighboring countries, creating a distinctive cultural blend. Its geographical proximity to major economic and cultural centers in East Asia also underscores its importance as a regional leader.
The Importance of Geography in Japanese History:
Japan’s location has been a crucial factor in its history, influencing its interactions with other nations and its internal development. Its island status provided a degree of natural protection, allowing for the development of a unique culture and political system. However, its proximity to powerful neighbors, such as China and Korea, also led to periods of conflict and cultural exchange.
Navigating the Challenges:
While Japan’s location offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges. The country’s vulnerability to natural disasters, particularly earthquakes and tsunamis, necessitates robust disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies. The mountainous terrain also poses challenges to infrastructure development and transportation.
The Future of Japan: A Location of Opportunity:
Despite these challenges, Japan’s location remains a source of strength and opportunity. Its strategic location in the Pacific Ocean, coupled with its advanced technological capabilities, positions it as a crucial player in global trade and diplomacy. Its cultural richness and innovative spirit continue to attract international attention, making it a dynamic and influential nation on the world stage.
FAQs:
Q: What is the precise geographical location of Japan?
A: Japan is located in the northwest Pacific Ocean, east of the Asian mainland. It is situated between latitudes 30° and 45° north and longitudes 128° and 146° east.
Q: What are the major islands of Japan?
A: The four main islands of Japan are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu.
Q: How does Japan’s location impact its economy?
A: Japan’s location has made it a vital trading hub, connecting East Asia with other regions. Its strategic position also allows for efficient access to global markets.
Q: What are the main challenges posed by Japan’s location?
A: Japan’s location presents challenges related to natural disasters, particularly earthquakes and tsunamis. The mountainous terrain also poses obstacles to infrastructure development and transportation.
Tips:
- Utilize maps and online resources: Explore interactive maps and online resources to gain a deeper understanding of Japan’s geographic features and location.
- Learn about Japanese history and culture: Understanding the historical and cultural context of Japan will help you appreciate the influence of its location on its development.
- Follow news and current events: Stay informed about Japan’s role in international affairs and its responses to global challenges.
Conclusion:
Japan’s location is not merely a geographical fact; it is a defining characteristic that has shaped its history, culture, and global influence. Its position on the Pacific Ring of Fire, its island status, and its strategic location at the crossroads of East Asia have all contributed to its unique identity and its role as a significant player in the international arena. Understanding the geographic context of Japan is crucial to appreciating its complexities and its potential for continued growth and development.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geographic Significance of Japan: A Nation Defined by Location. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!