The Foundation Of Email: A Deep Dive Into IMAP And POP3 Protocols
The Foundation of Email: A Deep Dive into IMAP and POP3 Protocols
Related Articles: The Foundation of Email: A Deep Dive into IMAP and POP3 Protocols
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Foundation of Email: A Deep Dive into IMAP and POP3 Protocols. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Foundation of Email: A Deep Dive into IMAP and POP3 Protocols

In the digital age, email has become an indispensable tool for communication, facilitating everything from personal correspondence to business transactions. Behind the seamless experience of sending and receiving emails lies a complex infrastructure, with protocols like IMAP and POP3 playing a crucial role in managing and accessing email data. This article delves into the intricacies of these two protocols, exploring their functionalities, differences, and the advantages they offer to users.
Understanding the Email Landscape: A Journey Through Protocols
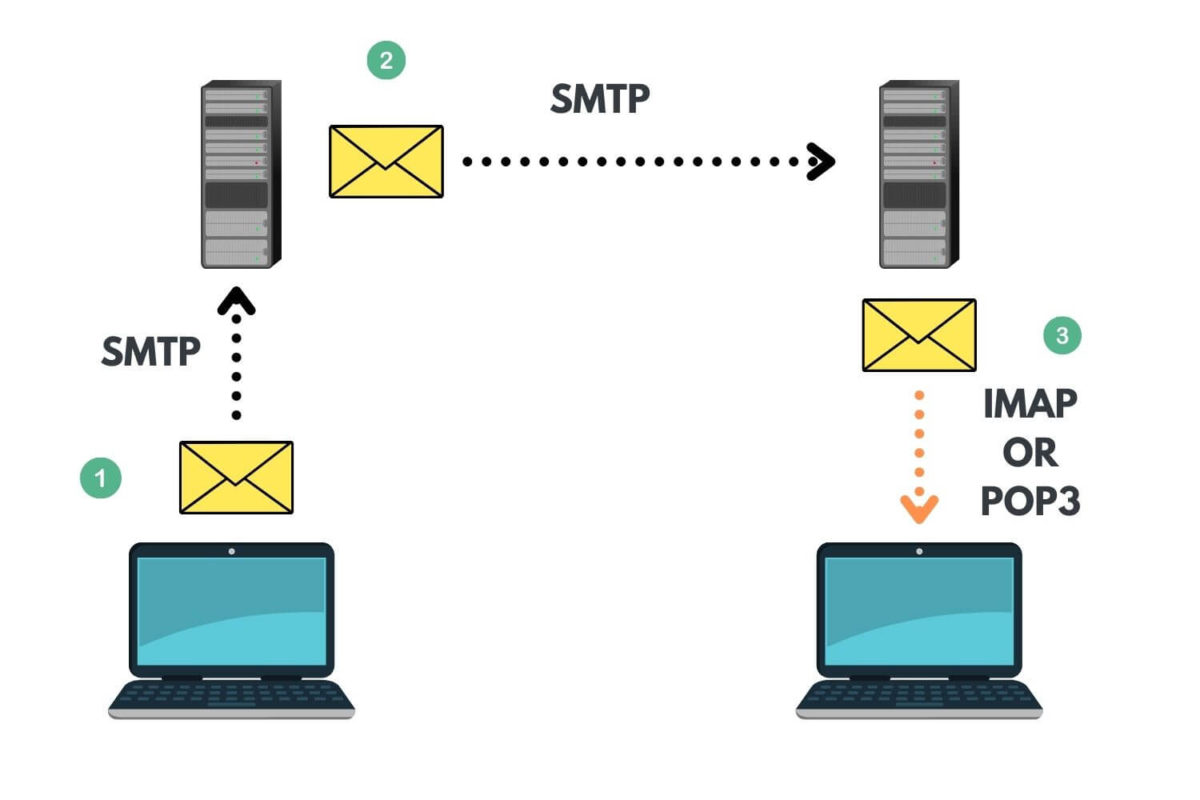
Imagine email as a vast network of interconnected systems. Each email client, whether it’s on your desktop, mobile device, or web browser, needs a way to connect to the email server where your messages are stored. This connection is established through specific protocols, with IMAP and POP3 being two of the most widely used.
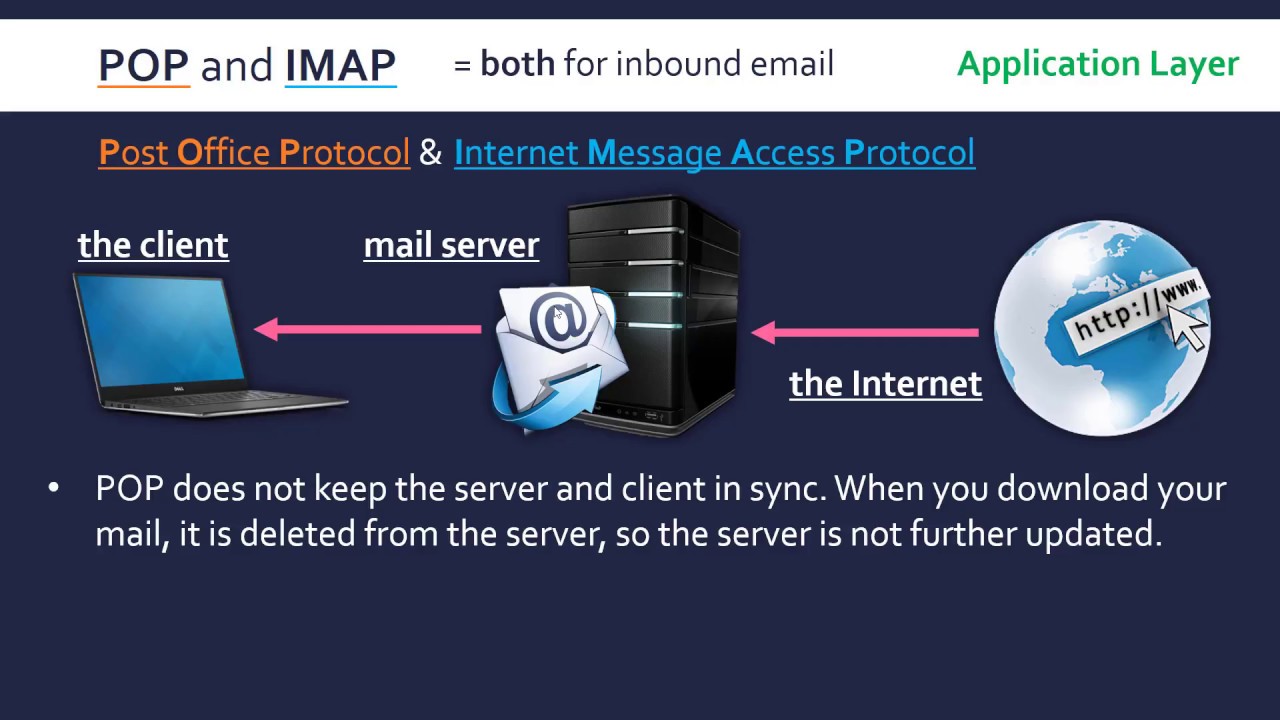
POP3: The Traditional Approach to Email Retrieval
POP3, or Post Office Protocol version 3, is a relatively old protocol designed for retrieving emails from a server to a client. It operates on a simple principle: emails are downloaded from the server to the client’s local machine and then deleted from the server. This approach offers the advantage of offline access to emails, as they are stored locally.
Key Characteristics of POP3:
- Offline Access: POP3 allows users to access emails even without an internet connection, as the messages are downloaded and stored locally.
- Limited Functionality: POP3 focuses solely on retrieving and deleting emails, offering minimal features for managing or organizing messages.
- Server-Based Deletion: Once emails are downloaded, they are typically deleted from the server, making them inaccessible from other devices.
IMAP: A More Sophisticated Approach to Email Management
IMAP, or Internet Message Access Protocol, offers a more advanced and flexible approach to email management. Unlike POP3, IMAP does not download emails to the client’s local machine. Instead, it provides a two-way communication channel between the client and the server, allowing for real-time synchronization of emails.
Key Characteristics of IMAP:
- Real-time Synchronization: IMAP keeps email folders and messages synchronized across all devices connected to the account. Changes made on one device are reflected on others.
- Multiple Client Access: Multiple devices can access the same email account simultaneously, as emails remain on the server.
- Enhanced Functionality: IMAP offers a wide range of features for managing emails, including folder creation, message filtering, and search capabilities.
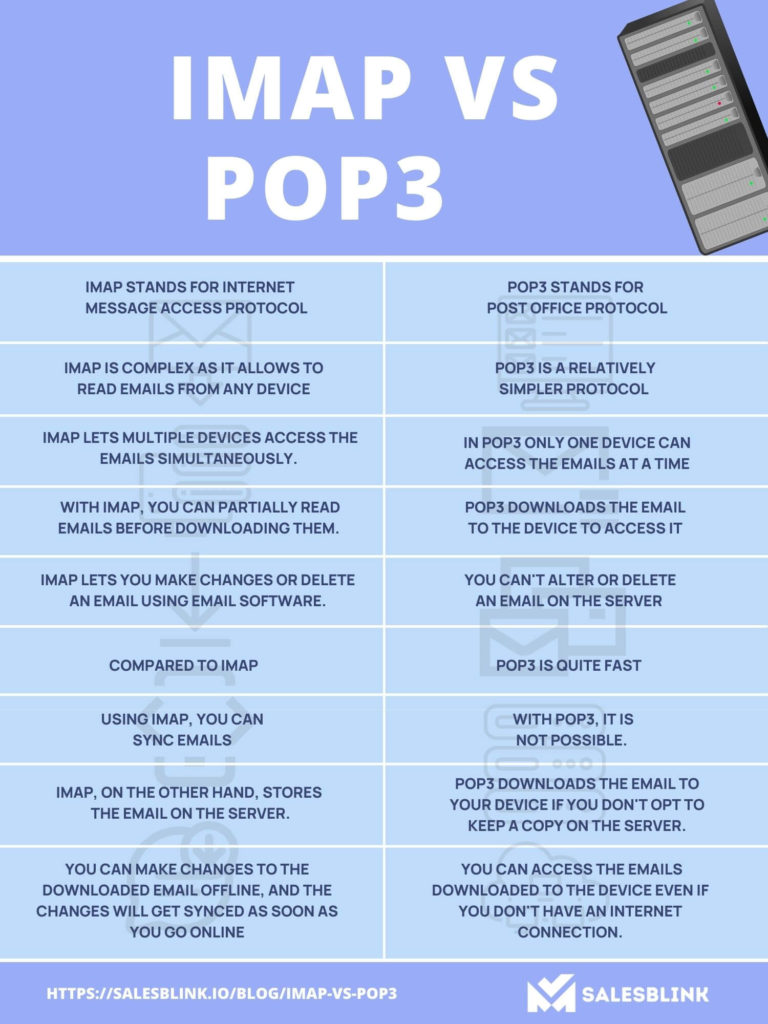
Comparing IMAP and POP3: A Table of Key Differences
| Feature | POP3 | IMAP |
|---|---|---|
| Email Storage | Downloaded to client’s local machine | Remains on the server |
| Synchronization | No synchronization | Real-time synchronization across devices |
| Offline Access | Yes | Limited offline access (depends on client) |
| Multiple Client Access | No | Yes |
| Functionality | Basic: Retrieve and delete emails | Advanced: Folder management, search, etc. |
The Advantages of IMAP: Why it’s the Preferred Choice
While POP3 offers the simplicity of offline access, IMAP emerges as the preferred protocol for its numerous advantages:
- Centralized Data: Emails are stored centrally on the server, ensuring data consistency across all devices.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Multiple users can access and manage the same email account simultaneously, facilitating seamless collaboration.
- Improved Organization: Advanced features like folder creation, message filtering, and search capabilities enhance email organization and management.
- Increased Flexibility: IMAP allows users to access emails from any device with an internet connection, promoting greater flexibility.
FAQs about IMAP and POP3: Addressing Common Questions
1. Which Protocol Should I Choose?
For most users, IMAP is the recommended choice due to its enhanced functionality, real-time synchronization, and flexibility. However, if offline access is a primary concern and minimal email management is required, POP3 might be a suitable option.
2. Can I Switch Protocols After Setting Up My Account?
Yes, most email providers allow users to switch between IMAP and POP3 protocols within their account settings.
3. What Happens to My Emails When I Switch Protocols?
Switching protocols typically does not affect existing emails. However, it’s recommended to back up important emails before making any changes.
4. Can I Use Both IMAP and POP3 Simultaneously?
Some email providers allow users to configure both IMAP and POP3 access simultaneously. However, this can lead to inconsistencies and is not recommended for most users.
5. What are the Best Practices for Email Security?
- Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication for your email account.
- Be cautious of suspicious emails and avoid clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Keep your email client and operating system updated with the latest security patches.
Tips for Optimizing Email Management with IMAP
- Create Folders: Organize your emails into folders based on categories, such as work, personal, or specific projects.
- Use Filters: Set up filters to automatically sort incoming emails into specific folders based on sender, subject, or keywords.
- Enable Search: Utilize the search function to quickly find specific emails within your inbox.
- Utilize Labels: Assign labels to emails to categorize them further and facilitate easy retrieval.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Email Protocols
Understanding IMAP and POP3 protocols is essential for navigating the world of email effectively. While POP3 offers a basic approach to email retrieval, IMAP provides a more robust and versatile platform for managing and accessing emails. By choosing the appropriate protocol and utilizing its features, users can optimize their email experience, enhancing productivity and streamlining communication. As technology continues to evolve, understanding these fundamental protocols remains crucial for ensuring seamless and secure email communication in the digital age.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Foundation of Email: A Deep Dive into IMAP and POP3 Protocols. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!