The Complex Landscape Of The Levant: A Geographical And Historical Overview Of Israel, Syria, And Lebanon
The Complex Landscape of the Levant: A Geographical and Historical Overview of Israel, Syria, and Lebanon
Related Articles: The Complex Landscape of the Levant: A Geographical and Historical Overview of Israel, Syria, and Lebanon
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Complex Landscape of the Levant: A Geographical and Historical Overview of Israel, Syria, and Lebanon. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Landscape of the Levant: A Geographical and Historical Overview of Israel, Syria, and Lebanon

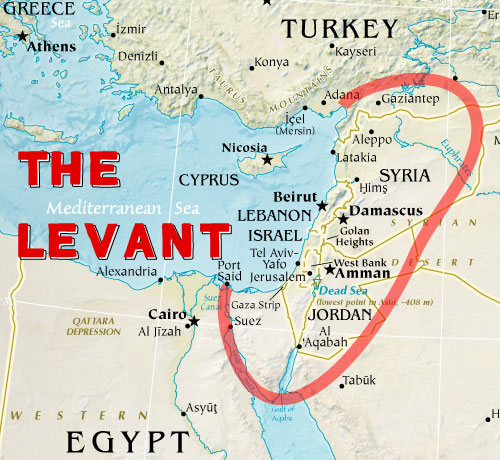
The Levant, a region encompassing the eastern Mediterranean coast and its hinterland, has witnessed a tumultuous history, shaped by its unique geography and the interplay of diverse cultures. This region, home to Israel, Syria, and Lebanon, presents a complex tapestry of political, religious, and social identities, making it a focal point of international attention and concern. Understanding the intricate relationships between these nations requires delving into their shared history, geographical features, and the enduring challenges that continue to shape their present and future.
A Geography of Contrasts:
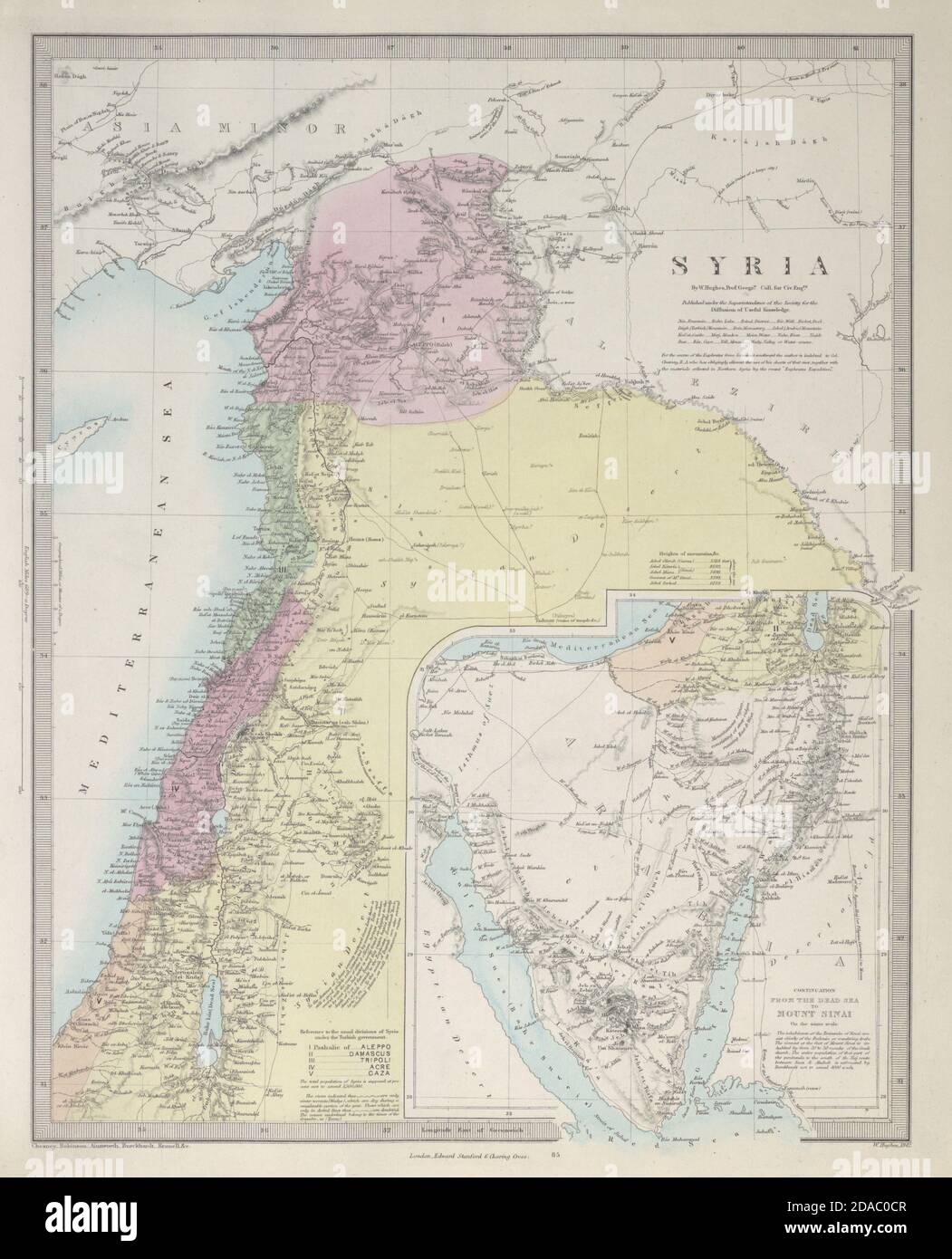
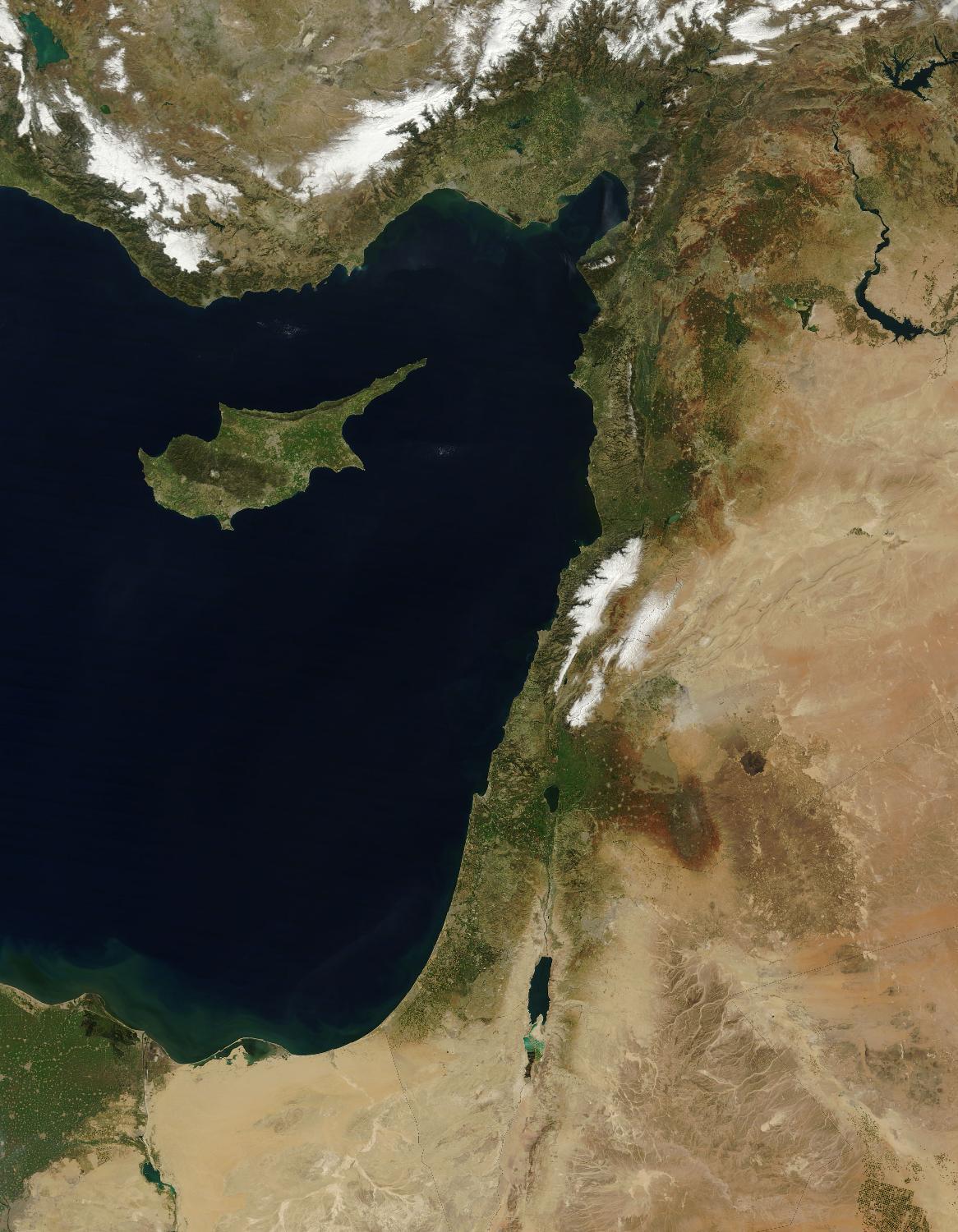
The Levant’s physical landscape is as diverse as its history. The region stretches from the fertile plains of the coastal strip, where ancient civilizations flourished, to the rugged mountains of Lebanon, a source of timber and refuge for communities seeking independence. The Jordan River, a vital lifeline, flows through the region, carving its path through the arid landscape, ultimately reaching the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth.
Israel: Situated on the southeastern Mediterranean coast, Israel is a relatively small country, encompassing diverse landscapes. The fertile coastal plain, known as the "Sharon," contrasts sharply with the arid Negev Desert in the south, and the mountainous regions of Galilee and Judea in the north and center. Israel’s geographical position has historically made it a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, while also rendering it vulnerable to external influences.
Syria: Bordering Israel to the north and east, Syria is a larger and geographically varied nation. Its landscape encompasses the fertile Golan Heights, the arid Syrian Desert, and the fertile plains of the Euphrates River. The country’s strategic location, situated between the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Peninsula, has played a significant role in shaping its history and its political landscape.
Lebanon: Located on the Mediterranean coast, Lebanon is a relatively small country with a diverse geography. Its mountainous terrain, dominated by the Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon ranges, offers breathtaking scenery and provides a natural barrier against invaders. The country’s fertile coastal plain has traditionally been a center of trade and agriculture, while the mountainous regions have served as a refuge for diverse communities.
A History of Intertwined Destinies:
The history of the Levant is marked by the rise and fall of empires, the constant ebb and flow of cultural exchange, and the enduring influence of religion. The region has witnessed the flourishing of ancient civilizations, from the Phoenicians and the Greeks to the Romans and the Ottomans.
The shared history of Israel, Syria, and Lebanon is particularly complex. The region was historically part of the Roman province of Syria Palaestina, with a significant Jewish population. Following the collapse of the Roman Empire, the region fell under the rule of the Byzantine Empire, and later, the Islamic caliphates. The Ottoman Empire ruled the region for centuries, shaping its political and social structures.
The emergence of Zionism in the late 19th century, advocating for a Jewish homeland in Palestine, ignited a complex and often violent conflict with the region’s Arab population. The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 triggered a series of wars between Israel and its Arab neighbors, including Syria and Lebanon, resulting in territorial disputes and ongoing tensions.
Challenges and Opportunities in the 21st Century:
The Levant continues to face a myriad of challenges in the 21st century, including:
- Political Instability: The region has been plagued by political instability and armed conflict, fueled by internal divisions, regional rivalries, and the complex geopolitical landscape. The Syrian Civil War, which began in 2011, has had a devastating impact on the region, displacing millions of refugees and contributing to the rise of extremist groups. Lebanon has also faced political instability and sectarian violence, exacerbated by the influx of Syrian refugees.
- Economic Challenges: The Levant’s economies face significant challenges, including high unemployment, poverty, and limited access to resources. The ongoing conflicts have further exacerbated economic difficulties, disrupting trade, infrastructure, and investment.
- Environmental Issues: The region faces a number of environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and pollution. The increasing demand for water resources, coupled with the effects of climate change, has created significant tensions.
Despite these challenges, the Levant also holds potential for cooperation and progress. The region possesses a rich cultural heritage, a strategic location, and a young, dynamic population. Addressing the challenges and seizing the opportunities will require regional cooperation, political dialogue, and a focus on sustainable development.
FAQs
Q: What are the major religions practiced in the Levant?
A: The Levant is home to a diverse range of religious communities, including Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and various other faiths. The region has been a center of religious activity for centuries, with Jerusalem holding particular significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
Q: What are the main languages spoken in the Levant?
A: The primary languages spoken in the Levant include Arabic, Hebrew, and French. Arabic is the official language of Syria and Lebanon, while Hebrew is the official language of Israel. French is widely spoken in Lebanon due to its historical ties to France.
Q: What are the main sources of conflict in the Levant?
A: The Levant is a region marked by historical tensions, fueled by competing claims to territory, religious differences, and political ideologies. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the Syrian Civil War, and the sectarian divisions in Lebanon are among the major sources of conflict in the region.
Q: What are the potential for cooperation and development in the Levant?
A: Despite the challenges, the Levant offers potential for cooperation and development. The region possesses a rich cultural heritage, a strategic location, and a young, dynamic population. Economic cooperation, cultural exchange, and joint initiatives to address environmental challenges could contribute to regional stability and prosperity.
Tips
- Stay Informed: It is crucial to stay informed about the latest developments in the Levant, through reliable news sources and academic research.
- Engage in Dialogue: Engage in open and respectful dialogue about the region’s challenges and opportunities, fostering understanding and promoting constructive solutions.
- Support Humanitarian Efforts: Support humanitarian organizations working to provide relief and assistance to those affected by conflict and displacement in the Levant.
- Promote Cultural Exchange: Encourage cultural exchange programs and initiatives that foster understanding and bridge divides between communities in the region.
Conclusion
The Levant, encompassing Israel, Syria, and Lebanon, remains a region of immense complexity and enduring challenges. Its history, geography, and cultural diversity have shaped its present and continue to influence its future. While the region faces significant obstacles, including political instability, economic hardship, and environmental challenges, it also holds potential for cooperation and progress. By promoting dialogue, fostering understanding, and supporting sustainable development, the Levant can begin to navigate its challenges and build a more peaceful and prosperous future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Landscape of the Levant: A Geographical and Historical Overview of Israel, Syria, and Lebanon. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!