The Complex Geography Of Israel, The West Bank, And Gaza: A Detailed Examination
The Complex Geography of Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza: A Detailed Examination
Related Articles: The Complex Geography of Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza: A Detailed Examination
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Complex Geography of Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza: A Detailed Examination. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Geography of Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza: A Detailed Examination
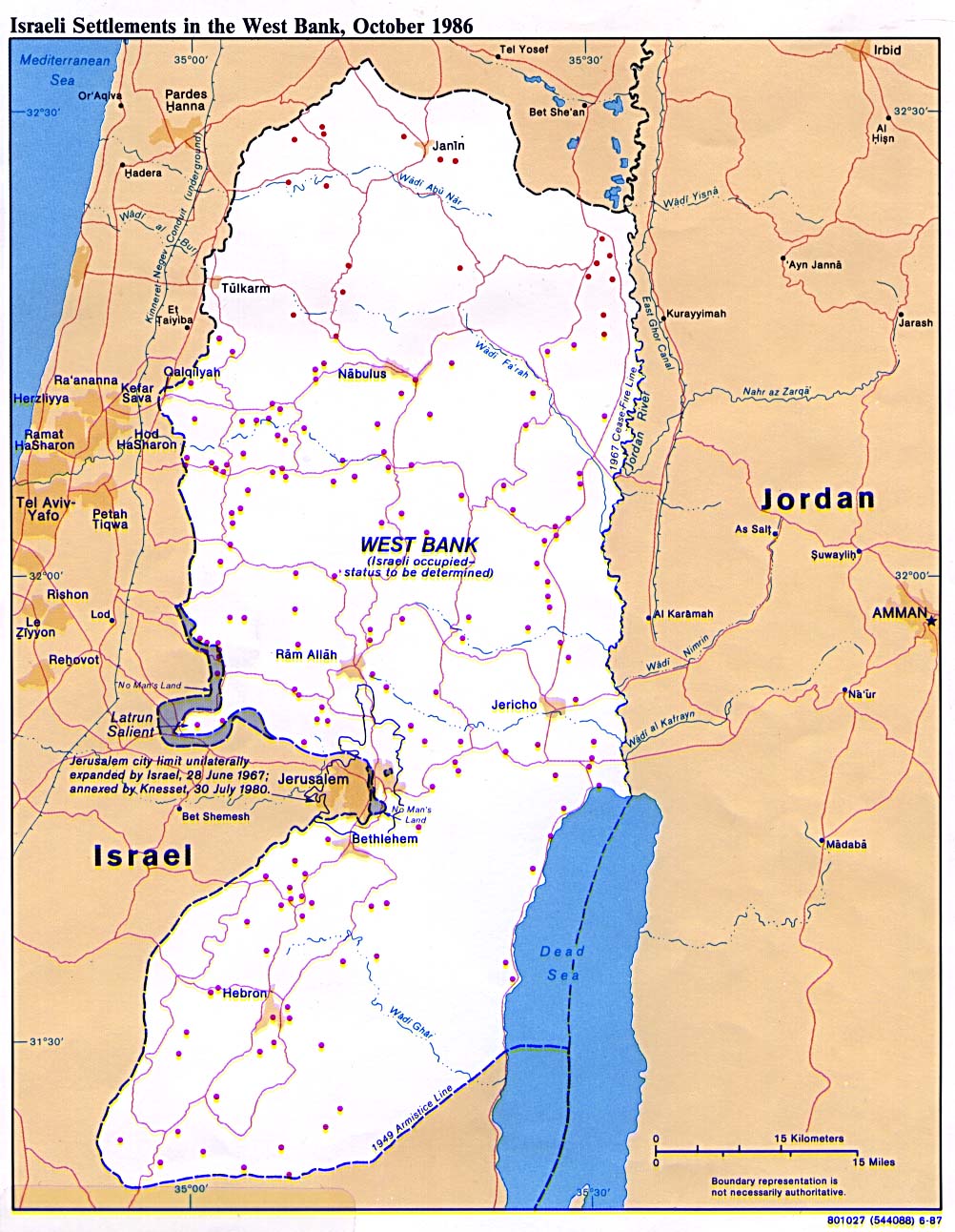
The region encompassing Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza presents a geographically and politically complex landscape. Understanding the intricate interplay of these territories is crucial for comprehending the ongoing conflicts and the challenges to achieving peace in the region. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the area, delving into its historical context, geographical features, and the current political realities.
A Historical Overview:
The land encompassing modern-day Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza has witnessed a rich and turbulent history. Throughout centuries, it has been the cradle of major civilizations, including the ancient Israelites, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans. The region’s strategic location, bridging continents and serving as a crossroads of trade routes, has contributed to its historical significance.
The modern history of the region is heavily intertwined with the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. The creation of Israel, following the British withdrawal from Palestine, led to the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians and the outbreak of the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. This war resulted in the division of the land, with Israel controlling a significant portion, while the West Bank and Gaza were occupied by Jordan and Egypt, respectively.
The 1967 Six-Day War saw Israel capture the West Bank, Gaza, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights from Jordan, Egypt, and Syria. This expansion of Israeli control further complicated the already complex political landscape.
The Geographical Landscape:
The region is characterized by diverse geographical features, influencing its history, demographics, and political dynamics.
-
Israel: Situated along the eastern Mediterranean coast, Israel encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, from the coastal plains and fertile valleys to the rugged mountains of the Negev Desert. Its strategic location has historically made it a crossroads of civilizations and a center of trade.
-
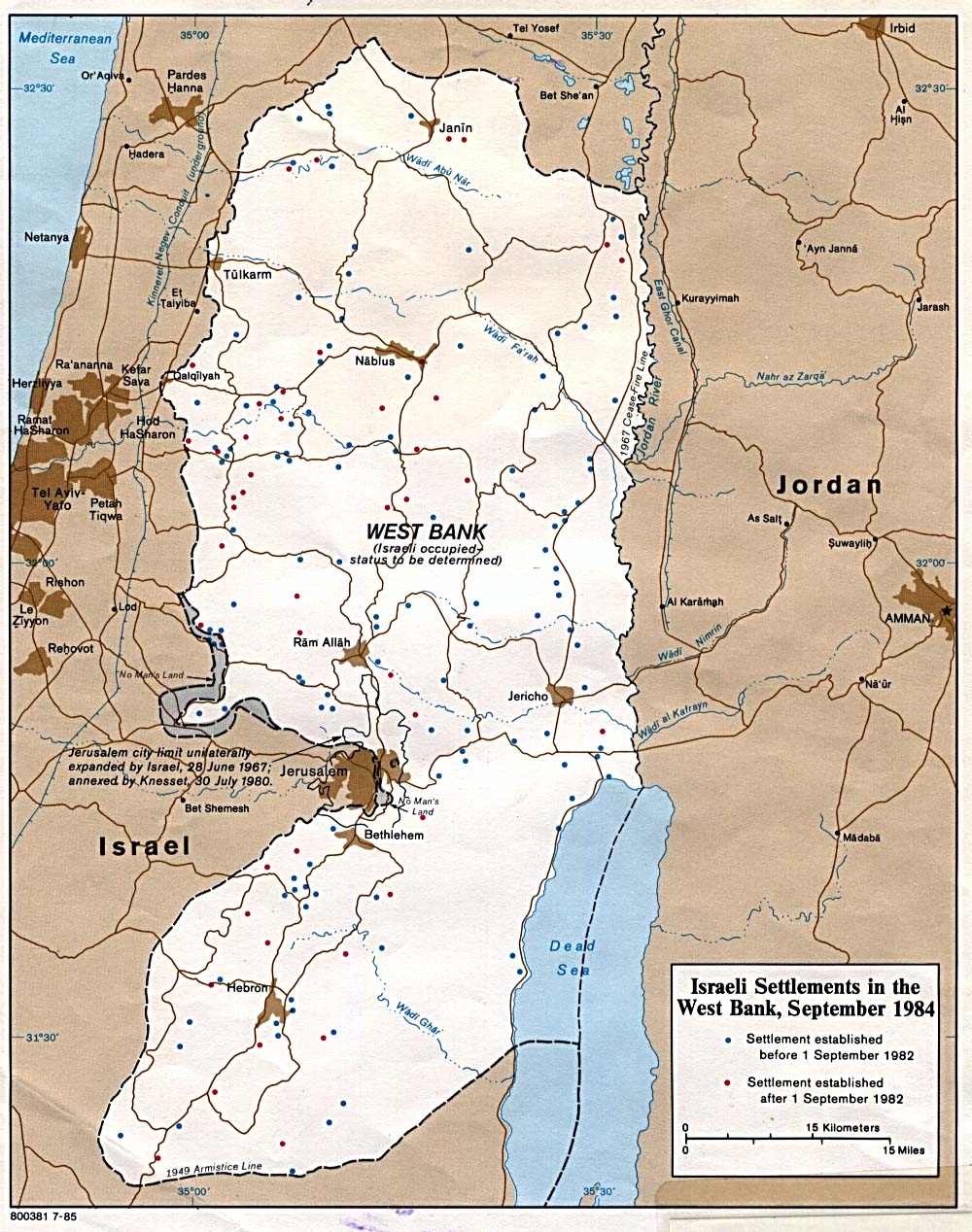
The West Bank: Located on the western side of the Jordan River, the West Bank is a mountainous region with fertile valleys and limited access to water resources. Its proximity to Jerusalem and its historical significance to both Israelis and Palestinians make it a focal point of conflict.
-
Gaza: Situated on the Mediterranean coast, Gaza is a small and densely populated strip of land. It is separated from the West Bank by Israel and Egypt, with limited access to the sea. Gaza’s economic dependence on external aid and its vulnerability to political instability contribute to its challenges.
Political Realities and the Ongoing Conflict:
The region’s political landscape is marked by ongoing conflict and unresolved issues. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, stemming from competing claims to the same land, has been a source of instability for decades.
-
The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The core of the conflict lies in the competing claims to the same land. Palestinians seek an independent state in the West Bank and Gaza, while Israelis claim the land as part of their historical homeland. The conflict is further complicated by the issue of Jerusalem, considered holy by both Jews and Muslims.
-
Settlements: The establishment of Israeli settlements in the West Bank, considered illegal under international law, exacerbates tensions and complicates peace negotiations. These settlements, often located on Palestinian land, are seen as a barrier to a two-state solution.
-
Gaza Blockade: The Israeli blockade of Gaza, imposed in 2007 following the Hamas takeover, has significantly impacted the lives of Gazans. The blockade restricts movement of people and goods, hindering economic development and creating humanitarian crises.
International Perspectives and Peace Efforts:
The international community has played a significant role in attempting to resolve the conflict. The United Nations has passed numerous resolutions calling for a two-state solution, while various peace initiatives have been proposed and implemented.
-
The Two-State Solution: The two-state solution, widely recognized as the most viable path to peace, envisions the establishment of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel. However, achieving this solution has proven challenging, with both sides facing internal divisions and mistrust.
-
International Pressure: The international community continues to exert pressure on both Israel and Palestine to engage in meaningful negotiations and reach a peaceful resolution. However, the lack of trust and the complex political realities on the ground pose significant obstacles.
The Importance of Understanding the Region:
Comprehending the complex geography, history, and political realities of Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza is crucial for understanding the ongoing conflict and its global implications.
-
International Security: The conflict has significant implications for regional and global security. The instability in the region can escalate into wider conflicts, affecting international relations and global peace.
-
Humanitarian Concerns: The conflict has a devastating impact on the lives of millions of people. The displacement of Palestinians, the restrictions on movement, and the ongoing violence have created a humanitarian crisis demanding international attention.
-
Economic Development: The conflict hinders economic development and prosperity in the region. The lack of stability and the ongoing violence deter investment and hinder the creation of jobs and opportunities.
FAQs on Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza:
Q: What is the difference between Israel and Palestine?
A: Israel is a recognized state, while Palestine is a territory under dispute. The Palestinian territories include the West Bank, Gaza, and East Jerusalem, which are claimed by both Palestinians and Israelis.
Q: What is the significance of Jerusalem?
A: Jerusalem is a holy city for Jews, Christians, and Muslims, making it a focal point of conflict and a source of religious tension.
Q: What is the role of the United Nations in the conflict?
A: The United Nations has played a significant role in attempting to resolve the conflict, passing numerous resolutions and establishing peacekeeping forces. However, its efforts have been hampered by the lack of consensus and the complexity of the issues.
Q: What is the future of the region?
A: The future of the region remains uncertain. The ongoing conflict and the lack of a negotiated solution pose significant challenges to achieving peace and stability. However, continued international pressure and the pursuit of a two-state solution offer hope for a peaceful resolution.
Tips for Understanding the Region:
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from multiple sources, including Israeli, Palestinian, and international perspectives.
- Explore the historical context: Understand the historical roots of the conflict, including the role of colonialism, displacement, and competing claims to the land.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about the latest developments in the region, including political negotiations, security incidents, and humanitarian crises.
- Support organizations working for peace: Engage with organizations promoting dialogue, reconciliation, and peaceful solutions.
Conclusion:
The complex geography of Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza, intertwined with its turbulent history and ongoing conflict, presents a multifaceted challenge to achieving peace and stability in the region. Understanding the intricate interplay of these territories is crucial for comprehending the conflict’s roots, its global implications, and the potential paths toward a peaceful resolution. While the challenges remain immense, continued international efforts, coupled with a commitment to dialogue and reconciliation, offer hope for a future where peace and prosperity prevail.
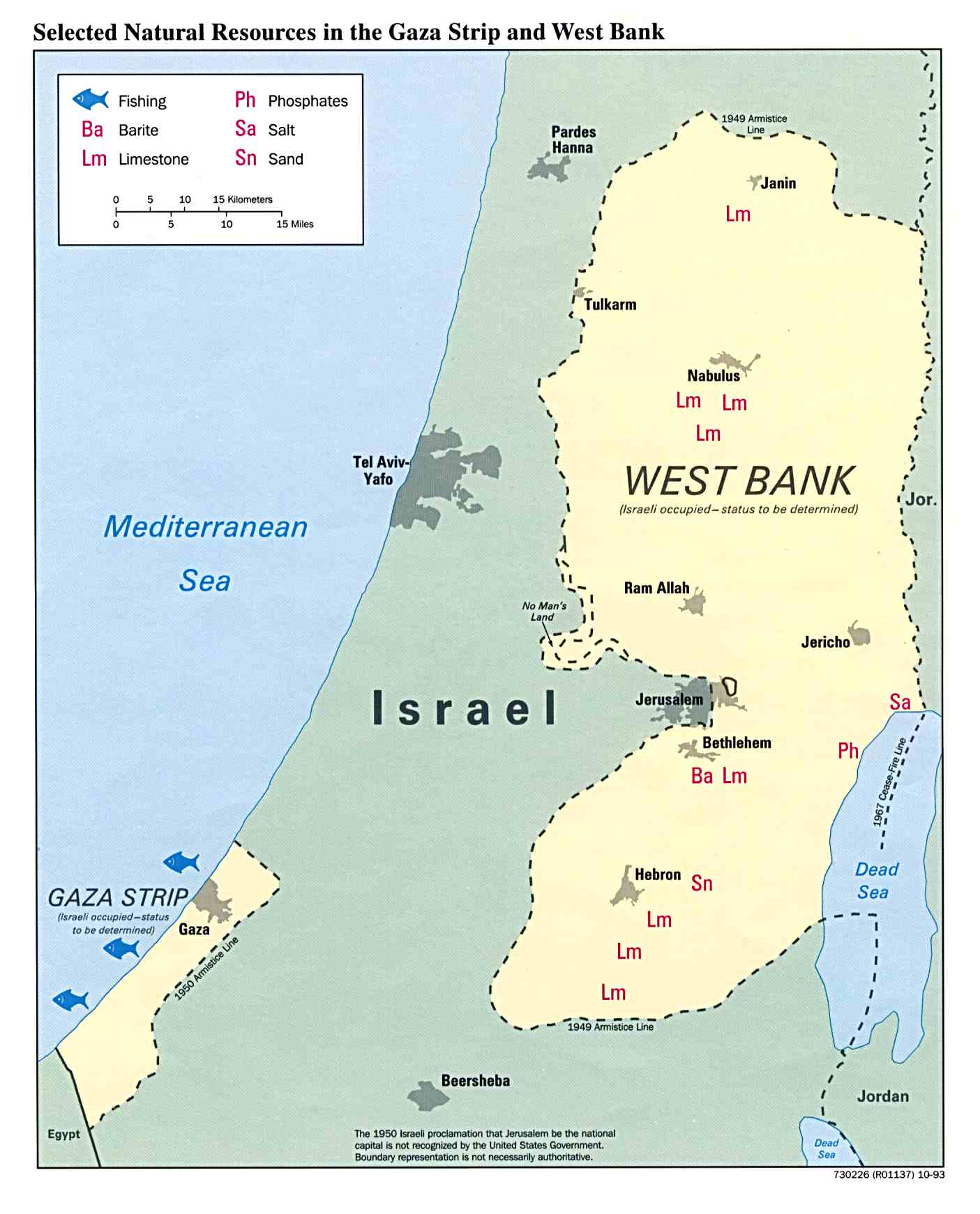
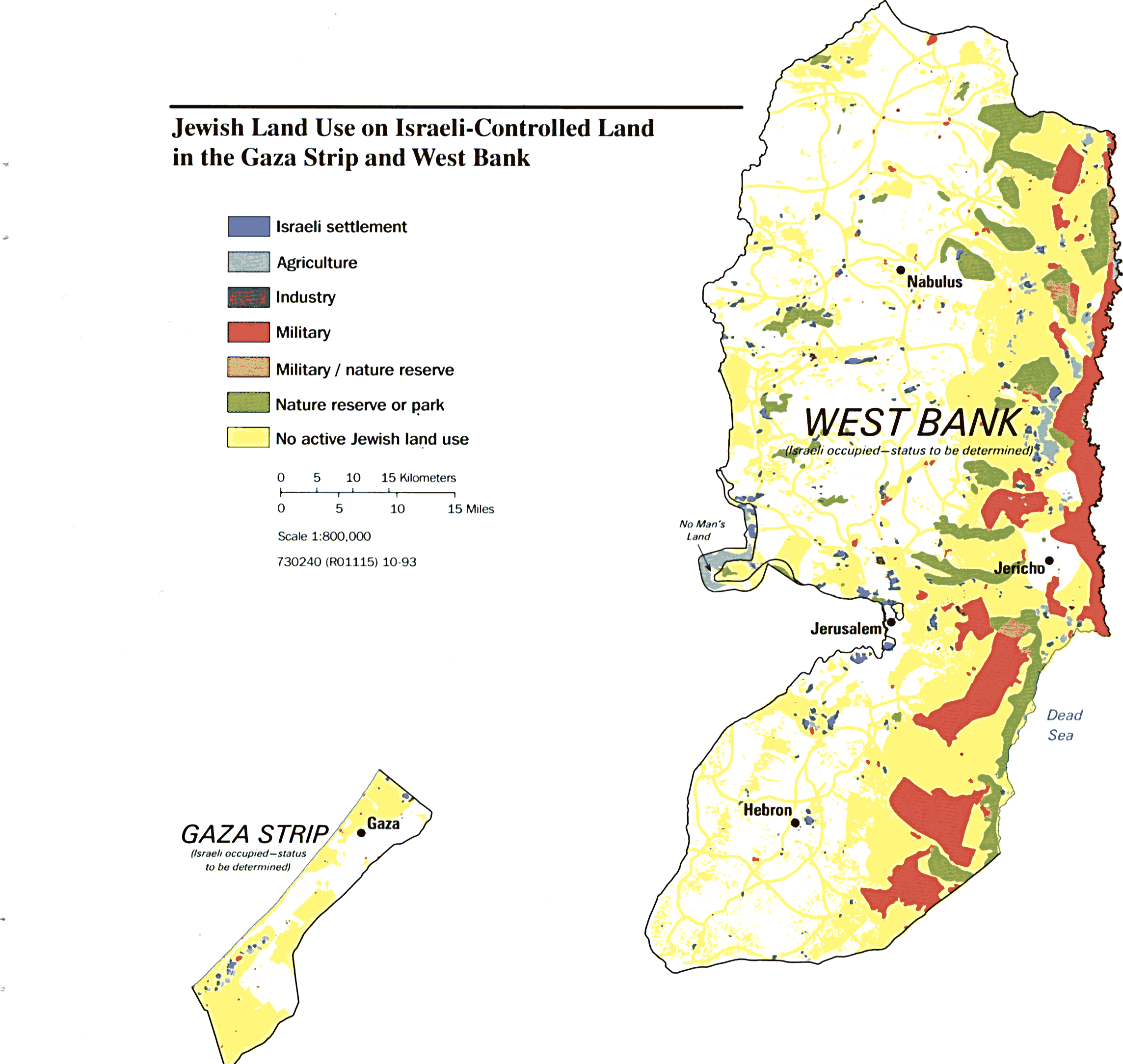

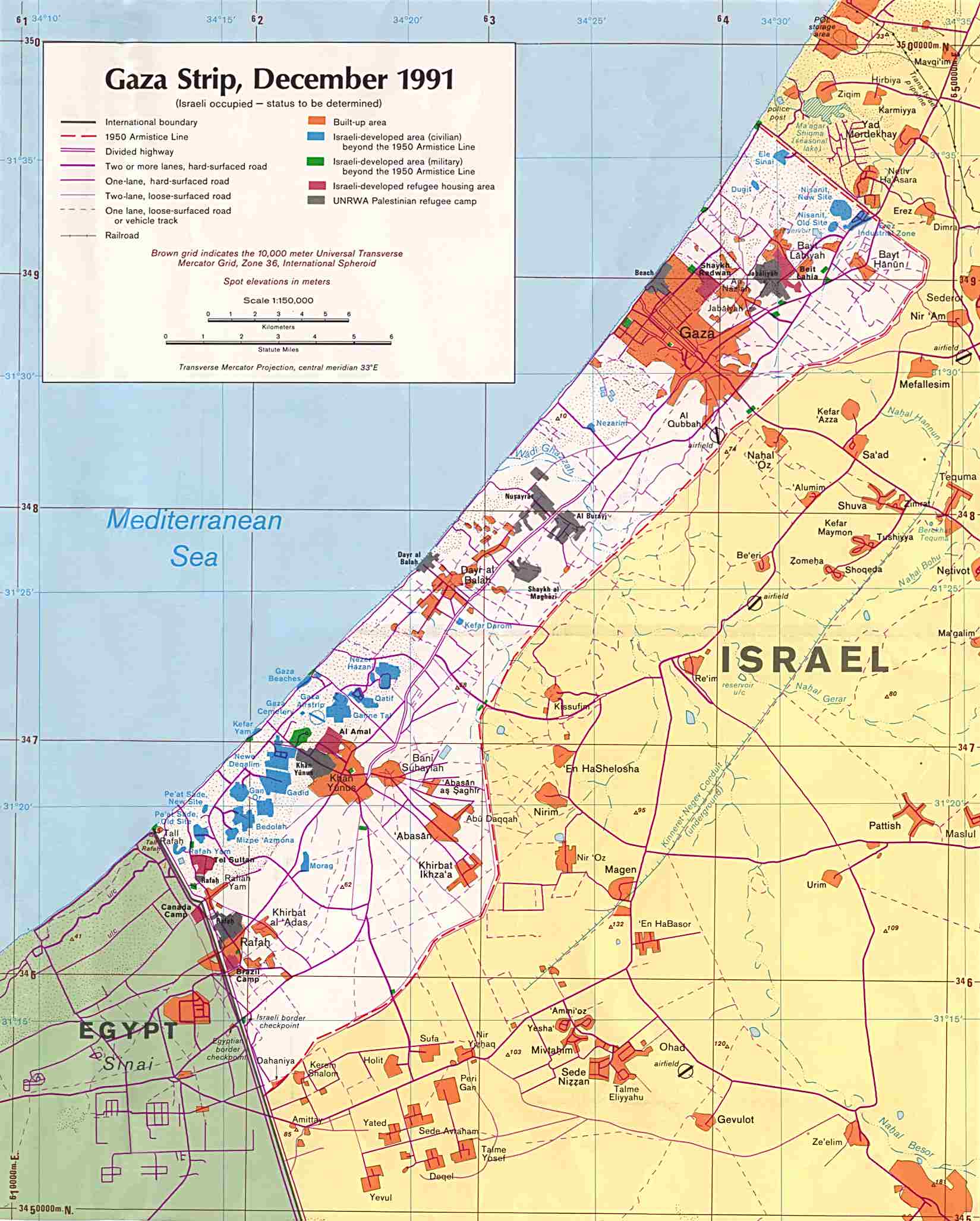


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Geography of Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza: A Detailed Examination. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!