The Archipelago Of Japan: A Geographic Overview Of Four Main Islands
The Archipelago of Japan: A Geographic Overview of Four Main Islands
Related Articles: The Archipelago of Japan: A Geographic Overview of Four Main Islands
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Archipelago of Japan: A Geographic Overview of Four Main Islands. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Archipelago of Japan: A Geographic Overview of Four Main Islands
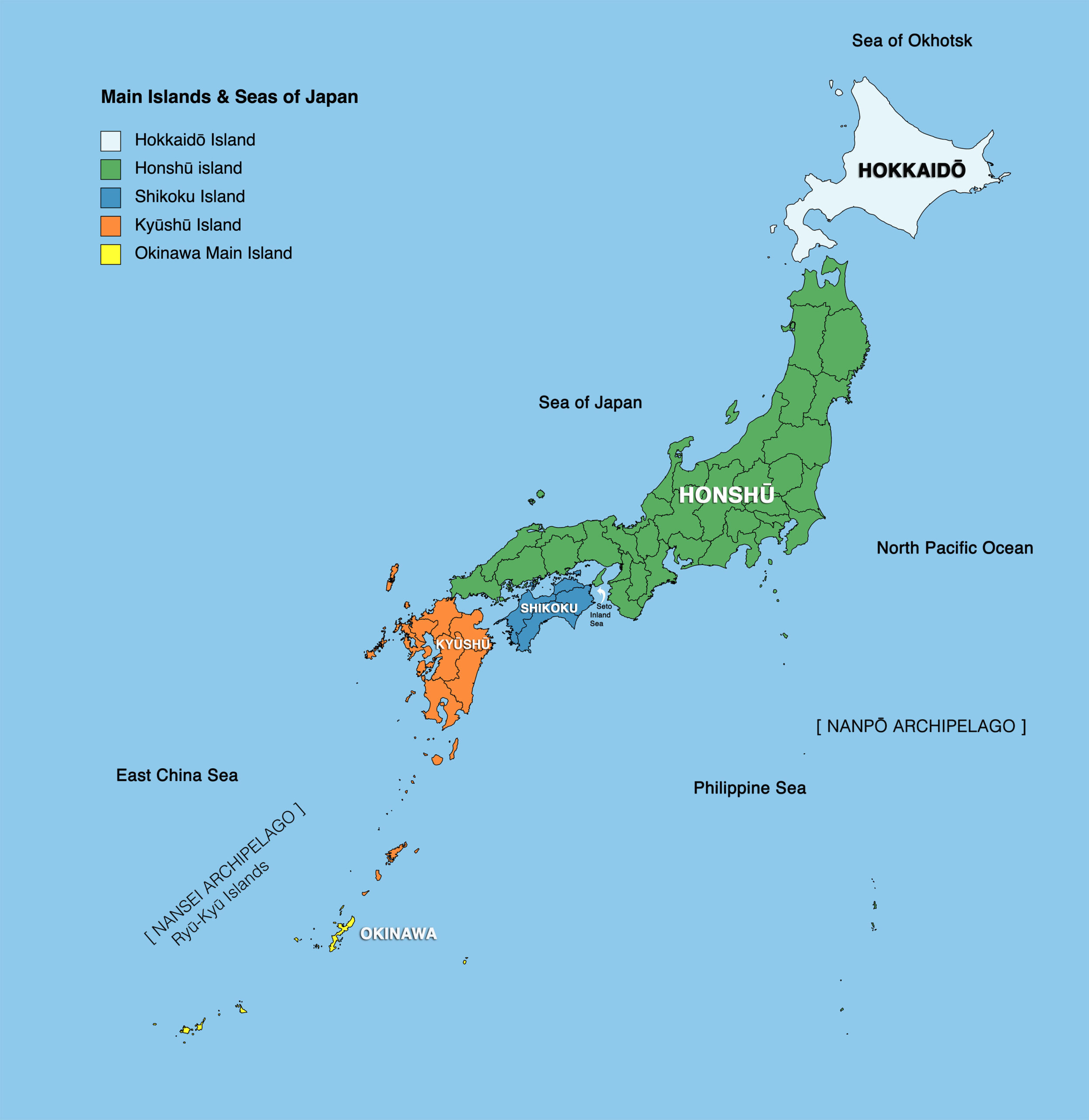
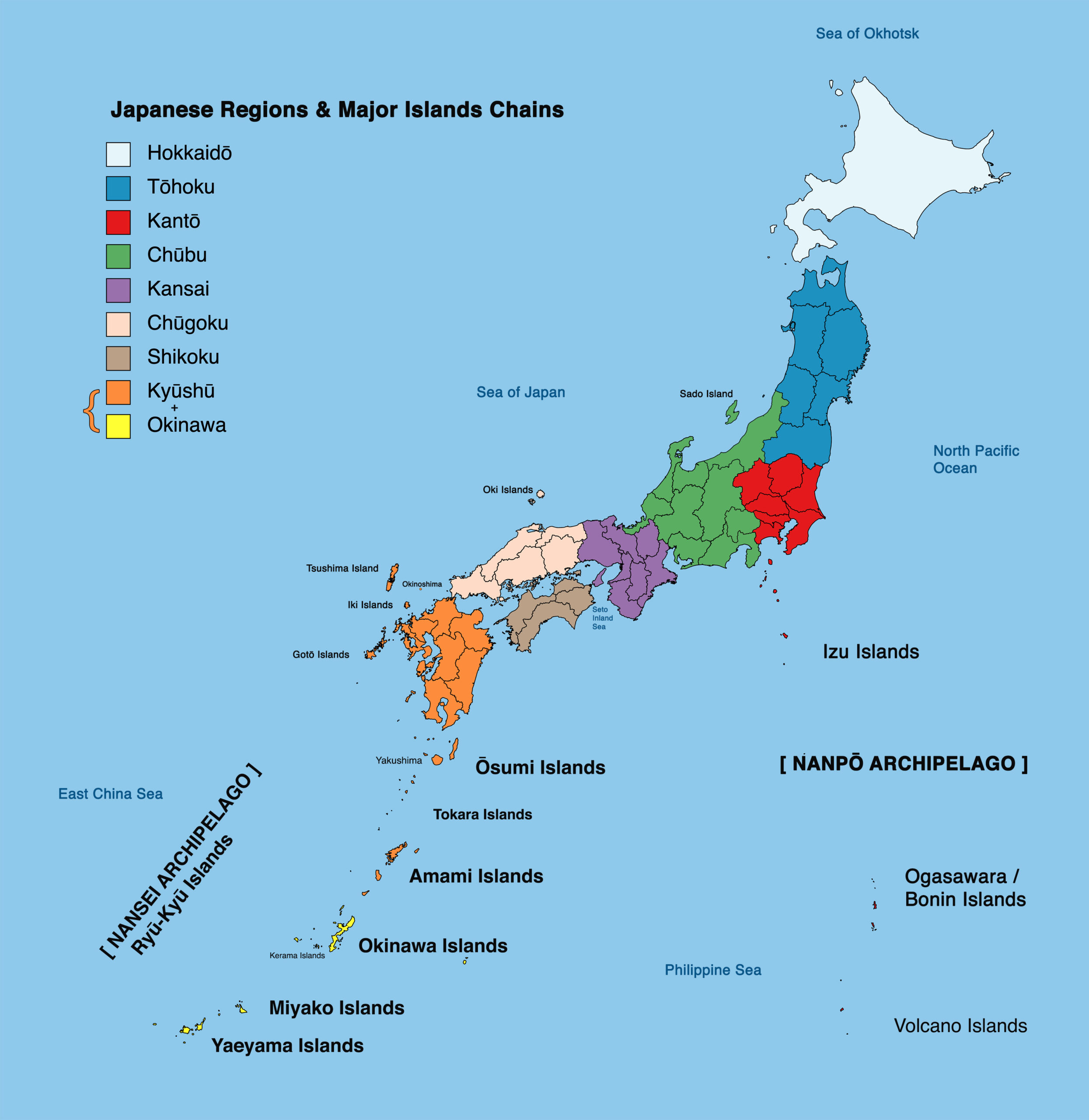
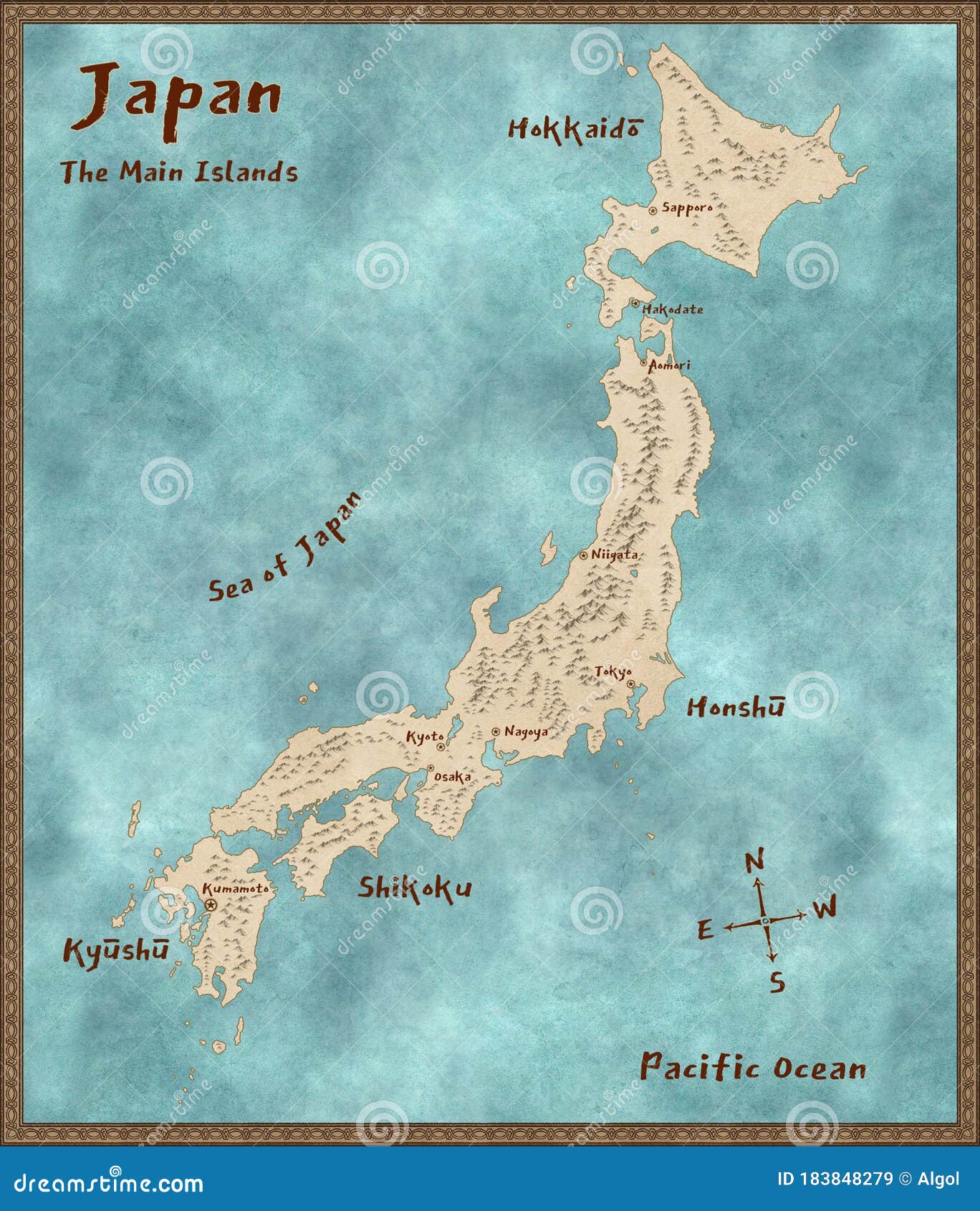
The Japanese archipelago, a string of over 6,800 islands stretching across the northwest Pacific Ocean, is a nation renowned for its rich culture, technological advancements, and breathtaking natural beauty. While the archipelago boasts numerous islands, four stand out as the most prominent: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. These four main islands, collectively forming the core of Japan’s landmass, are not only geographically diverse but also culturally and historically significant.
Hokkaido: The Northern Frontier
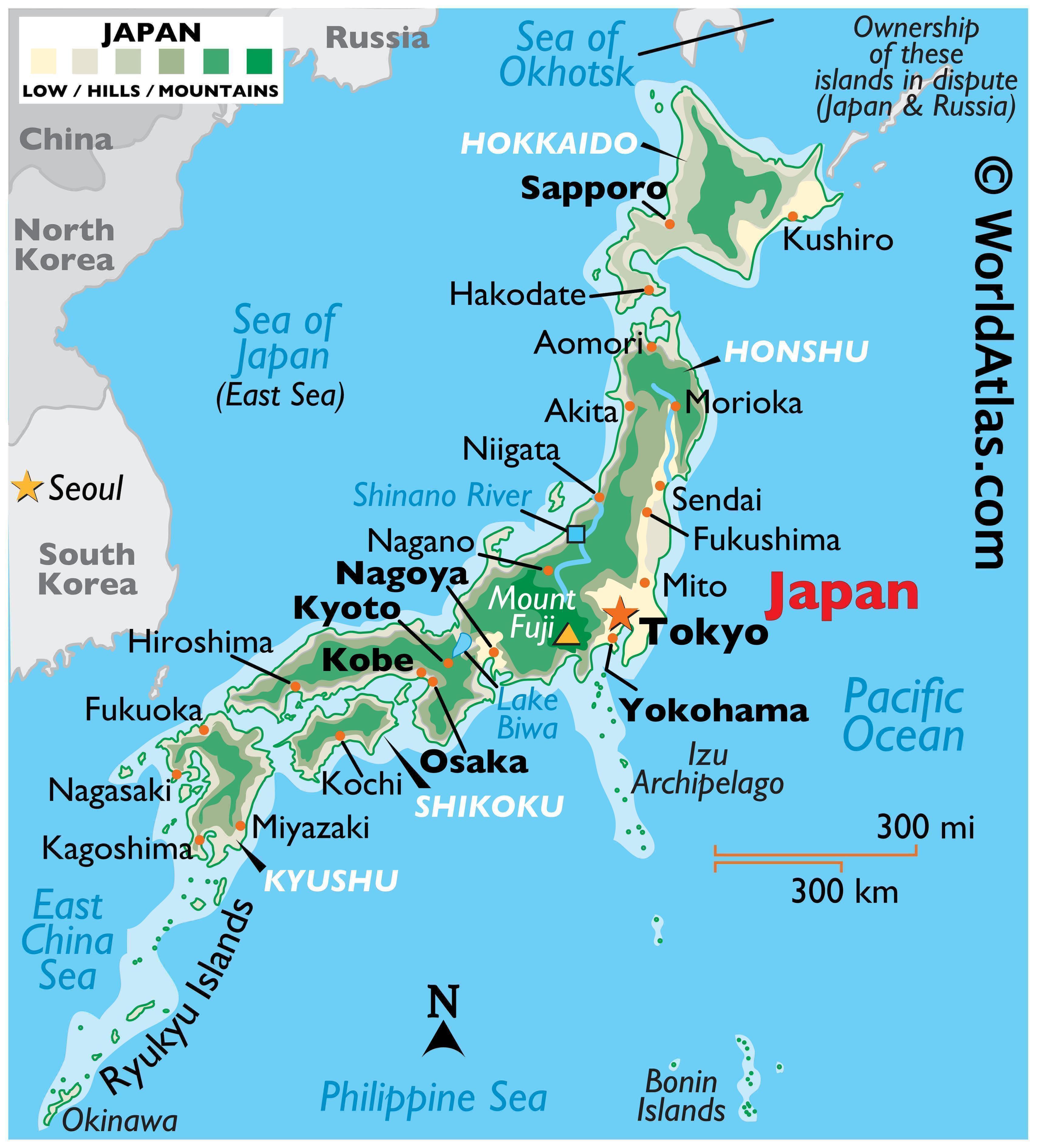
Hokkaido, the second-largest island, sits north of Honshu, separated by the Tsugaru Strait. Its rugged landscape, characterized by vast forests, volcanic mountains, and fertile plains, provides a stark contrast to the more densely populated southern islands. Mount Asahi, a dormant volcano, stands as its highest peak, while the Shiretoko Peninsula, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is known for its pristine wilderness and diverse wildlife.
Hokkaido’s geography influences its climate, resulting in long, cold winters and short, cool summers. This unique environment has fostered a distinctive culture and economy. The island is a major producer of agricultural products, particularly dairy and seafood, and attracts tourists with its natural beauty, ski resorts, and hot springs.
Honshu: The Heart of Japan
Honshu, the largest and most populous island, is the heart of Japan, both geographically and culturally. It houses the capital city, Tokyo, and major urban centers like Osaka, Kyoto, and Nagoya. The island is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, ranging from the snow-capped peaks of the Japanese Alps to the lush plains of the Kanto region.
The island’s central spine is formed by a chain of mountains, including Mount Fuji, Japan’s iconic symbol. Honshu is also home to numerous active volcanoes, like Mount Asama, a reminder of the country’s volcanic nature. Its diverse geography has led to a range of climates, from the temperate coastal areas to the colder mountainous regions.
Shikoku: The Island of Pilgrimage
Shikoku, the smallest of the four main islands, is known for its rolling hills, verdant forests, and numerous rivers. The island is deeply rooted in Buddhist tradition, with the Shikoku Pilgrimage, a 1,200-kilometer route visiting 88 temples, attracting pilgrims from across the country and beyond.
Shikoku’s coastline is dotted with picturesque inlets and harbors, contributing to its maritime history. The island is also a significant producer of agricultural products, including rice, citrus fruits, and tea.
Kyushu: The Island of Fire
Kyushu, the southernmost of the four main islands, is a land of volcanic activity and hot springs. The island is home to Mount Aso, one of the world’s largest active volcanoes, and numerous other volcanic features. Kyushu’s unique geological history has shaped its landscape, resulting in fertile plains, rugged mountains, and volcanic hot springs.
Kyushu is also known for its rich history and culture. The island was a major center of trade and politics during the feudal period, and its cities, like Fukuoka and Nagasaki, still bear the marks of its historical significance. Kyushu’s warm climate and diverse landscape make it a popular tourist destination, offering everything from volcanic landscapes to coastal beaches.
Interconnected and Diverse
These four main islands are not merely geographical entities; they are intertwined threads in the fabric of Japanese history, culture, and identity. The islands have been interconnected for centuries, with people, goods, and ideas flowing between them. This interconnectedness is reflected in the shared cultural heritage, language, and traditions found across the archipelago.
However, each island also possesses its own unique character, shaped by its geography, history, and culture. Hokkaido’s frontier spirit, Honshu’s bustling urban centers, Shikoku’s spiritual tranquility, and Kyushu’s fiery dynamism offer a glimpse into the multifaceted nature of Japan.
Importance and Benefits
Understanding the geography of the four main islands of Japan is crucial for appreciating the country’s diverse landscapes, rich culture, and economic development. The islands’ geographic features have played a significant role in shaping the country’s history, influencing its political and social structures, and contributing to its unique identity.
FAQs
Q: What is the largest island in Japan?
A: Honshu is the largest island in Japan, accounting for roughly 60% of the country’s total landmass.
Q: Which island is the capital city of Japan located on?
A: Tokyo, the capital city of Japan, is located on Honshu, the largest island.
Q: What are some of the major cities located on the four main islands?
A:
- Hokkaido: Sapporo
- Honshu: Tokyo, Osaka, Kyoto, Nagoya, Yokohama
- Shikoku: Matsuyama, Kochi
- Kyushu: Fukuoka, Nagasaki, Kumamoto
Q: What are some of the natural features found on the four main islands?
A:
- Hokkaido: Mount Asahi, Shiretoko Peninsula, Lake Toya
- Honshu: Mount Fuji, Japanese Alps, Mount Asama, Lake Biwa
- Shikoku: Ishizuchi Mountains, Shikoku Pilgrimage Route
- Kyushu: Mount Aso, Beppu Hot Springs, Sakurajima Volcano
Tips for Studying the Map
- Use a physical map: A physical map provides a more tactile and intuitive way to understand the geographic relationships between the islands.
- Focus on key features: Identify the major cities, mountain ranges, and rivers on each island.
- Compare and contrast: Analyze the similarities and differences between the islands’ landscapes, climates, and cultures.
- Use online resources: Explore interactive maps and online databases to gain a deeper understanding of the islands’ geography and demographics.
Conclusion
The four main islands of Japan – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – are not just geographical divisions but reflections of the country’s diverse landscapes, vibrant culture, and rich history. By understanding the geography of these islands, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances that define the Japanese archipelago. From the rugged beauty of Hokkaido to the bustling urban centers of Honshu, from the spiritual serenity of Shikoku to the fiery dynamism of Kyushu, each island contributes to the unique tapestry of Japan’s identity.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Archipelago of Japan: A Geographic Overview of Four Main Islands. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!