The Archipelago Of Indonesia: A Geographic Tapestry Of Diversity
The Archipelago of Indonesia: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity
Related Articles: The Archipelago of Indonesia: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Archipelago of Indonesia: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Archipelago of Indonesia: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity

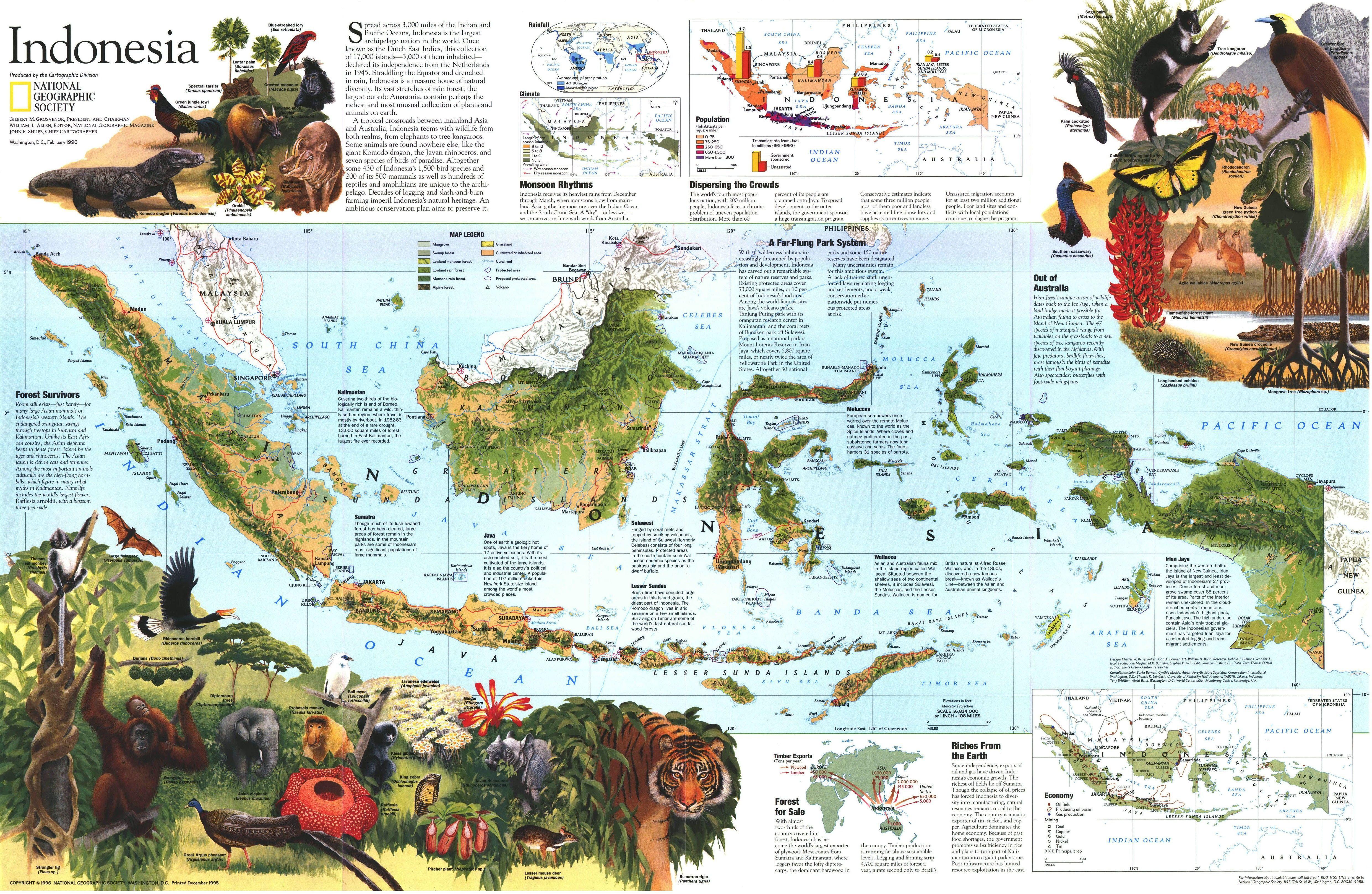
Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago nation, is a breathtaking tapestry of over 17,000 islands, of which approximately 6,000 are inhabited. This vast expanse, stretching across the equator and nestled between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, is a testament to the dynamic forces of plate tectonics and the relentless power of nature. Understanding the intricate geography of Indonesia, its diverse islands, and their unique characteristics is crucial for appreciating the country’s rich cultural heritage, ecological significance, and economic potential.
A Geographic Overview: The Archipelago’s Formation and Structure
The Indonesian archipelago’s formation is a captivating story of geological processes. Millions of years ago, the collision of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian tectonic plates resulted in the emergence of volcanic mountains and the creation of numerous islands. This dynamic geological activity continues to shape the landscape, with active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes being integral parts of the Indonesian experience.
The archipelago can be broadly divided into three major regions:
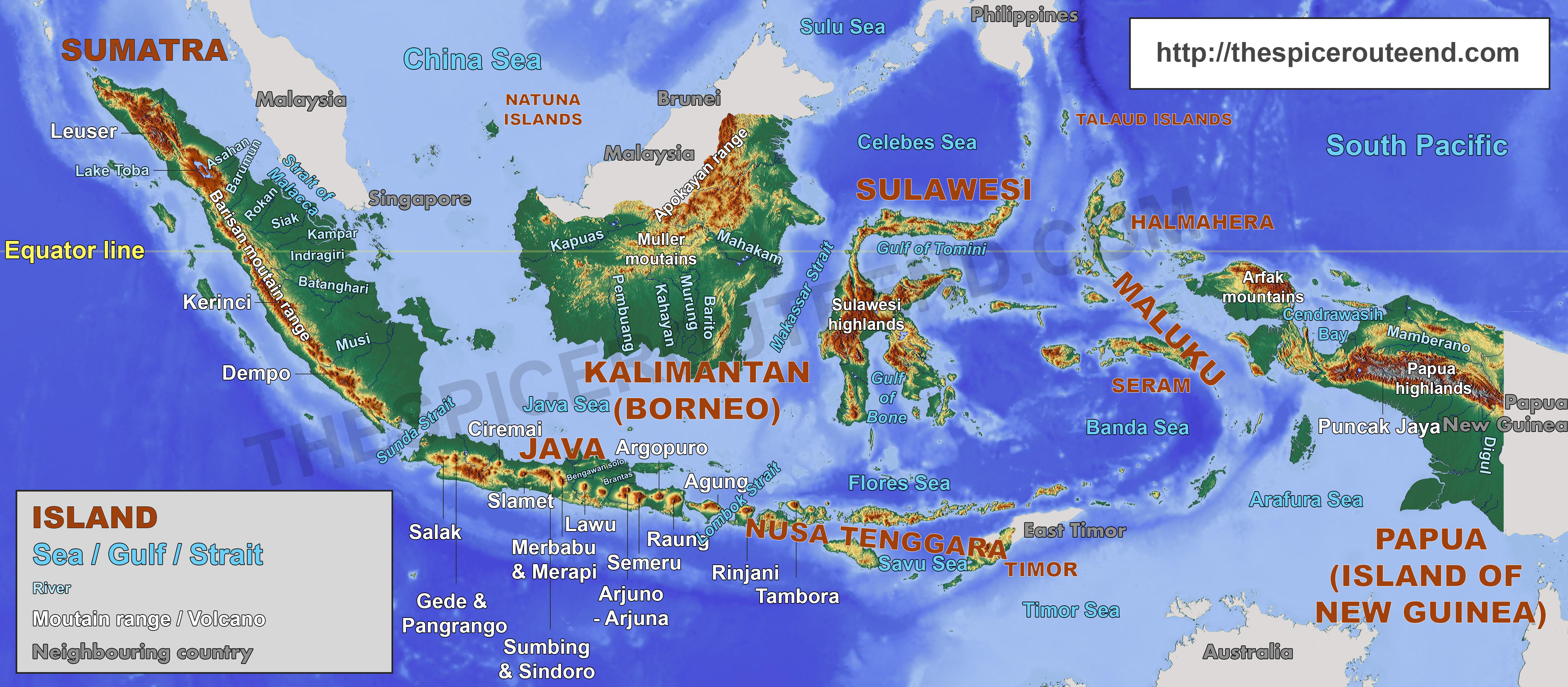
- Sumatra: The westernmost island, characterized by its long, narrow shape and a mountainous backbone. It is home to dense rainforests, active volcanoes, and rich biodiversity.
- Java: The most populous island, with a high concentration of people and urban centers. It is known for its fertile volcanic soil, rich cultural heritage, and historic sites.
- The Lesser Sunda Islands: A chain of islands extending eastwards from Java, featuring diverse landscapes ranging from volcanic peaks to coral reefs. This region is known for its stunning beaches, unique wildlife, and traditional cultures.
Beyond the Major Islands: The Vastness of Indonesia’s Geography
While Sumatra, Java, and the Lesser Sunda Islands are prominent, they represent only a fraction of Indonesia’s immense geographic expanse. The country also encompasses:
- Kalimantan (Borneo): The third largest island in the world, shared with Malaysia and Brunei. It is renowned for its vast rainforests, rich biodiversity, and untapped natural resources.
- Sulawesi: A unique island shaped like a K, known for its rugged mountains, diverse ecosystems, and rich cultural traditions.
- Irian Jaya (New Guinea): The second largest island in the world, shared with Papua New Guinea. It boasts a breathtaking landscape of mountains, rainforests, and pristine coastal areas, harboring incredible biodiversity.
The Importance of Understanding the Archipelago’s Geography
Comprehending the geography of Indonesia’s islands is vital for several reasons:
- Resource Management: The archipelago’s diverse islands house a wealth of natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, timber, and fisheries. Understanding the distribution and potential of these resources is crucial for sustainable development and responsible resource management.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: Indonesia is prone to natural disasters, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and floods. Knowing the specific vulnerabilities of each island and its surrounding areas is essential for effective disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Indonesia’s islands harbor a remarkable array of flora and fauna, many of which are endemic and endangered. Understanding the unique ecosystems and biodiversity hotspots is vital for conservation efforts and sustainable development.
- Cultural Understanding: The diverse islands of Indonesia boast a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions. Understanding the geographic distribution of these cultural groups is essential for promoting cultural appreciation, preserving heritage, and fostering national unity.
- Economic Development: The archipelago’s diverse islands offer opportunities for economic development in various sectors, such as tourism, agriculture, fisheries, and mining. Understanding the specific characteristics and potential of each island is crucial for targeted development strategies.
FAQs: Exploring the Archipelago’s Geography
1. What are the largest islands in Indonesia?
The five largest islands in Indonesia are:
- Kalimantan (Borneo)
- Irian Jaya (New Guinea)
- Sumatra
- Sulawesi
- Java
2. What are the main geographical features of Indonesia?
Indonesia is characterized by its volcanic mountains, active volcanoes, fertile soil, dense rainforests, extensive coastlines, and diverse marine ecosystems.
3. How many islands are there in Indonesia?
Indonesia has over 17,000 islands, of which approximately 6,000 are inhabited.
4. What are the major mountain ranges in Indonesia?
The major mountain ranges in Indonesia include:
- The Barisan Mountains in Sumatra
- The Sunda Mountains in Java
- The Jayawijaya Mountains in Irian Jaya (New Guinea)
5. What are some of the major volcanoes in Indonesia?
Indonesia has over 120 active volcanoes, including:
- Mount Merapi in Java
- Mount Bromo in Java
- Mount Tambora in Sumbawa
- Mount Krakatoa in Sunda Strait
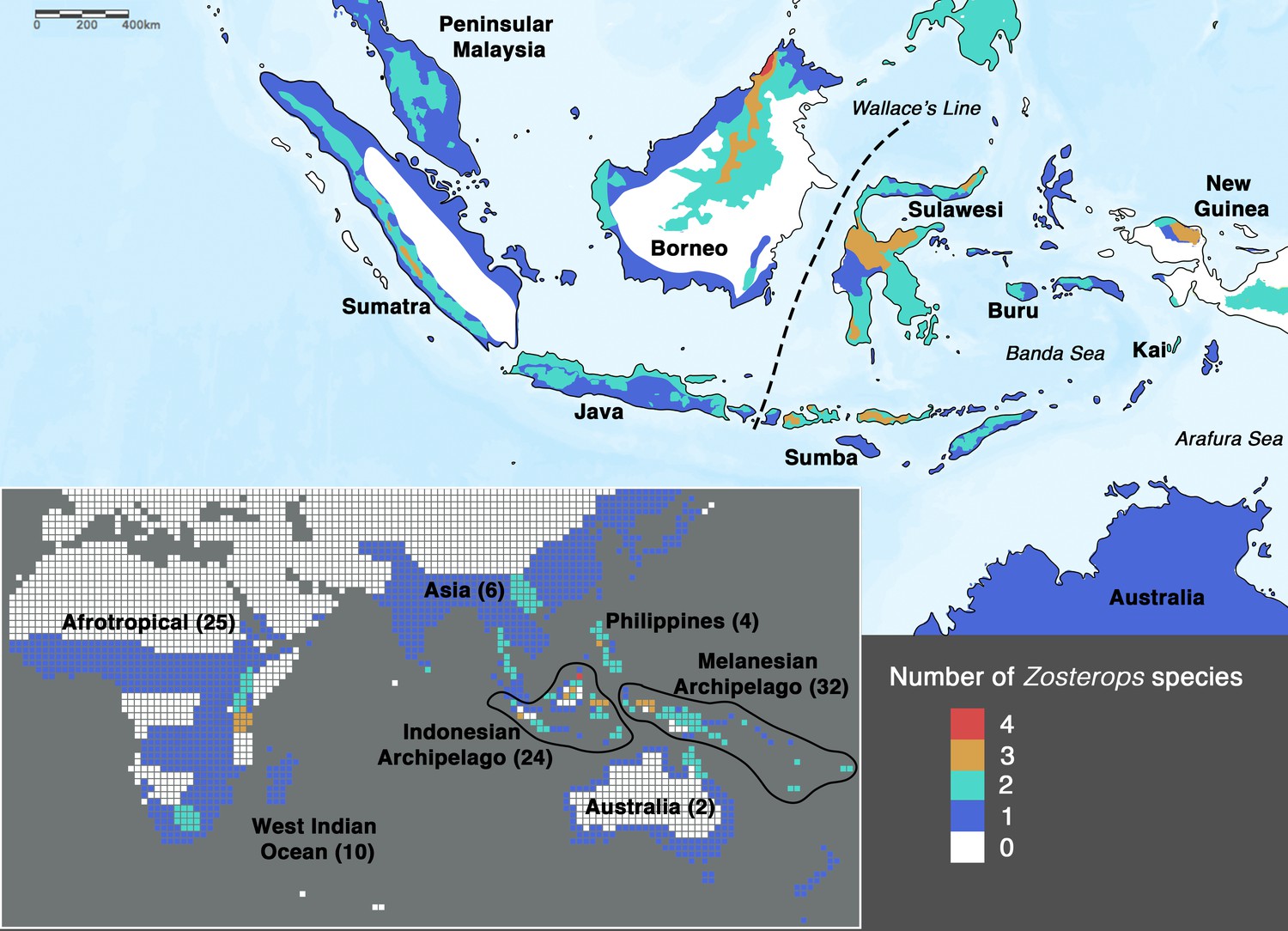
6. What is the significance of the Wallace Line?
The Wallace Line is an imaginary line separating the Asian and Australian biogeographic realms. It runs between Borneo and Sulawesi, highlighting the distinct fauna and flora found on either side.
7. How do the islands of Indonesia differ in terms of their natural resources?
Indonesia’s islands vary significantly in their natural resources. Sumatra is rich in oil and gas, while Java has fertile volcanic soil suitable for agriculture. Kalimantan is known for its timber and mineral resources, while Irian Jaya (New Guinea) boasts abundant biodiversity and potential for tourism.
8. What are some of the challenges faced by Indonesia in managing its islands?
Indonesia faces challenges in managing its islands, including:
- Environmental degradation: Deforestation, pollution, and overfishing are significant environmental challenges.
- Natural disasters: Indonesia is highly vulnerable to natural disasters, requiring effective disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Infrastructure development: Developing infrastructure across the vast archipelago is a significant challenge.
- Economic disparities: Economic development varies significantly between islands, creating disparities and challenges in achieving equitable growth.
Tips for Navigating the Archipelago’s Geography
- Utilize online maps and resources: Explore interactive maps and websites that provide detailed information about Indonesia’s islands.
- Read travel guides and books: Gain insights into the unique features, culture, and attractions of each island.
- Learn about the history and geology of the archipelago: Understand the forces that shaped the islands and their unique characteristics.
- Engage with local communities: Interact with locals to learn about their experiences and perspectives on their island.
- Respect the environment: Be mindful of the fragile ecosystems and contribute to sustainable tourism practices.
Conclusion: The Archipelago’s Enduring Significance
The Indonesian archipelago is a testament to the power of nature and the resilience of its people. Its diverse islands, each with its unique history, culture, and natural beauty, offer a glimpse into the extraordinary tapestry of life on Earth. Understanding the geography of this vast nation is essential for appreciating its cultural richness, ecological significance, and economic potential. As Indonesia continues to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, a deep understanding of its islands will be crucial for sustainable development and a brighter future for all Indonesians.



.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Archipelago of Indonesia: A Geographic Tapestry of Diversity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!