Optimizing Java Performance: Exploring The Fastest Map Implementations
Optimizing Java Performance: Exploring the Fastest Map Implementations
Related Articles: Optimizing Java Performance: Exploring the Fastest Map Implementations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Optimizing Java Performance: Exploring the Fastest Map Implementations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Optimizing Java Performance: Exploring the Fastest Map Implementations

In the realm of Java programming, maps are indispensable data structures that associate keys with values, providing efficient access and retrieval. Choosing the right map implementation is crucial for achieving optimal performance, especially in applications demanding high throughput and low latency. This article delves into the world of Java maps, exploring the fastest implementations and highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Understanding Java Map Implementations
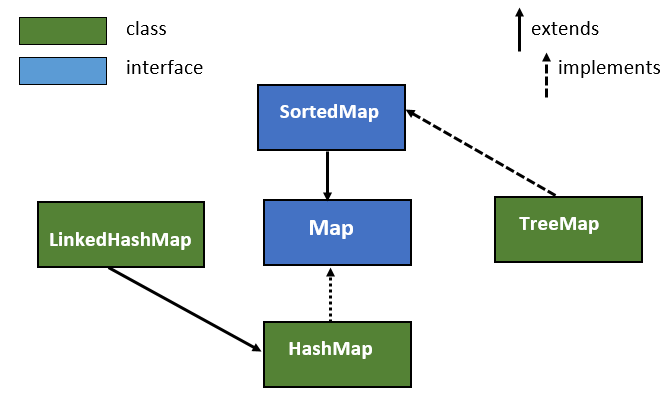
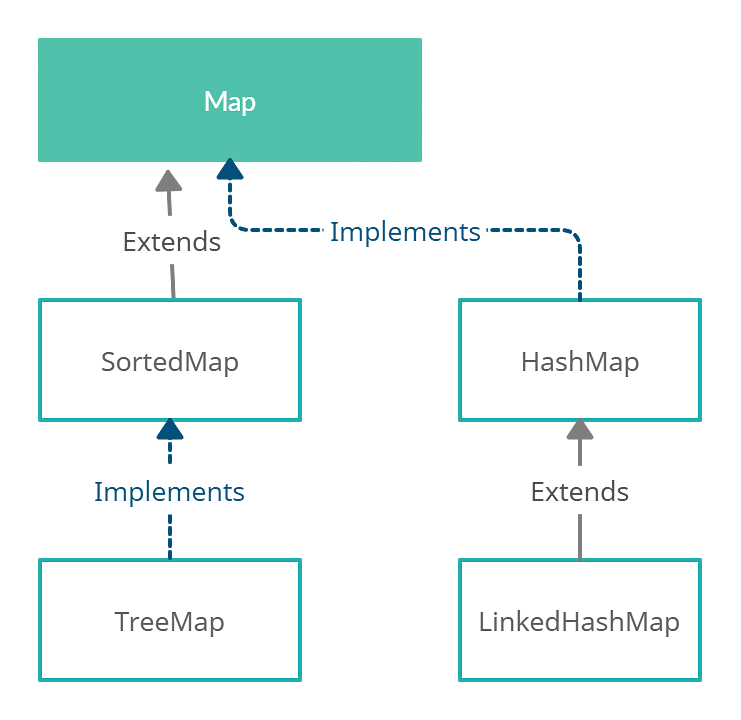
Java’s java.util.Map interface defines the fundamental contract for map functionality. Several concrete implementations exist, each with its own trade-offs in terms of performance, memory usage, and feature set. The most commonly used implementations include:
-
HashMap: The ubiquitous
HashMapis a hash table-based implementation. It offers excellent performance for most common operations like insertion, retrieval, and deletion, with average time complexity of O(1). However, it provides no ordering guarantee for key-value pairs. -
TreeMap:
TreeMapis a red-black tree-based implementation, ensuring that keys are sorted in ascending order. It provides logarithmic time complexity for most operations (O(log n)), making it suitable for scenarios requiring sorted key access. -
LinkedHashMap:
LinkedHashMapextendsHashMapby maintaining the insertion order of key-value pairs. It achieves this by using a doubly linked list, resulting in slightly slower performance thanHashMapbut offering predictable iteration order. -
ConcurrentHashMap: Designed for concurrent access,
ConcurrentHashMaputilizes a segmented lock approach to enable multiple threads to operate on different parts of the map simultaneously. It offers significant performance improvements in multi-threaded environments compared to synchronized versions of other maps.
Factors Influencing Map Performance
The choice of the fastest map implementation is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Several factors influence performance, including:
-
Data size: For small datasets, the performance difference between implementations might be negligible. However, as the dataset grows, the choice of implementation becomes increasingly important.
-
Access patterns: If the application requires frequent insertions and deletions,
HashMapmight be the best choice. If sorted key access is essential,TreeMapwould be more suitable. -
Concurrency: In multi-threaded environments,
ConcurrentHashMapexcels at handling concurrent access, ensuring thread safety and minimizing contention. -
Memory constraints: Different implementations have varying memory footprints.
HashMapis generally more memory-efficient thanTreeMap, which requires additional overhead for maintaining its tree structure.
Benchmarking and Performance Analysis
To objectively evaluate the performance of different map implementations, benchmarking is crucial. Various frameworks and libraries are available for conducting comprehensive performance analysis, including:
-
JMH (Java Microbenchmark Harness): JMH is a highly recommended tool for benchmarking Java code. It provides features like warm-up, multiple iterations, and statistical analysis to ensure accurate and reliable results.
-
Apache JMeter: JMeter is a popular tool for performance testing web applications. It can be utilized to benchmark map operations by simulating various load scenarios.
-
Google Caliper: Caliper is another powerful benchmarking framework that offers advanced features like microbenchmarking, statistical analysis, and reporting.
Optimizing Map Performance
Beyond choosing the right implementation, several techniques can further enhance map performance:
-
Key hashing: Effective hashing algorithms are crucial for
HashMapperformance. Poorly designed hash functions can lead to collisions and degrade performance. -
Load factor: The load factor determines the ratio of entries to the number of buckets in a
HashMap. A higher load factor can reduce memory usage but increase the likelihood of collisions. -
Concurrency control: For concurrent operations, using
ConcurrentHashMapis recommended. Implementing custom locking mechanisms can also be beneficial in specific scenarios. -
Data structure optimization: If memory usage is a concern, consider using more compact data structures like
IntHashMapfor integer keys.
Real-World Applications of Fast Maps
Fast map implementations are essential in various real-world scenarios:
-
Caching: Maps are extensively used in caching systems to store frequently accessed data for quick retrieval.
-
Database indexing: Databases often employ maps for efficient indexing, enabling fast lookups based on keys.
-
Web applications: Maps are crucial for handling user sessions, managing application state, and storing configuration data in web applications.
-
Game development: Fast maps are essential for storing game data like player positions, inventory items, and world objects.
FAQs
Q: What is the fastest map implementation in Java?
A: There is no single "fastest" map. The optimal implementation depends on the specific use case and factors like data size, access patterns, and concurrency requirements.
Q: When should I use HashMap vs. TreeMap?
**A: HashMap is suitable for general-purpose usage, offering fast operations and no ordering guarantee. TreeMap is preferred when sorted key access is crucial, but it incurs a performance overhead.
Q: How can I improve the performance of HashMap?
A: Ensure effective key hashing, choose an appropriate load factor, and avoid excessive resizing operations.
Q: Is ConcurrentHashMap always faster than synchronized HashMap?
A: ConcurrentHashMap is generally faster for concurrent operations, but its performance can vary depending on the workload and contention levels.
Tips
-
Benchmark different implementations: Before choosing a map, benchmark its performance against your specific workload.
-
Optimize key hashing: Ensure that your key objects have effective
hashCode()andequals()methods. -
Consider data structure alternatives: If memory usage is a concern, explore more compact data structures like
IntHashMapfor integer keys. -
Profile your code: Use profiling tools to identify performance bottlenecks related to map operations.
Conclusion
Choosing the fastest map implementation in Java requires careful consideration of the specific use case and performance requirements. HashMap generally offers the best performance for most scenarios, but TreeMap is suitable for sorted key access, and ConcurrentHashMap excels in concurrent environments. Benchmarking and profiling are crucial for identifying performance bottlenecks and optimizing map operations. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different map implementations and employing best practices, developers can achieve optimal performance and efficiency in their Java applications.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Optimizing Java Performance: Exploring the Fastest Map Implementations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!