Navigating The Roads Of Northern Ireland: A Comprehensive Guide To The Road Network
Navigating the Roads of Northern Ireland: A Comprehensive Guide to the Road Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Roads of Northern Ireland: A Comprehensive Guide to the Road Network
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Roads of Northern Ireland: A Comprehensive Guide to the Road Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Roads of Northern Ireland: A Comprehensive Guide to the Road Network
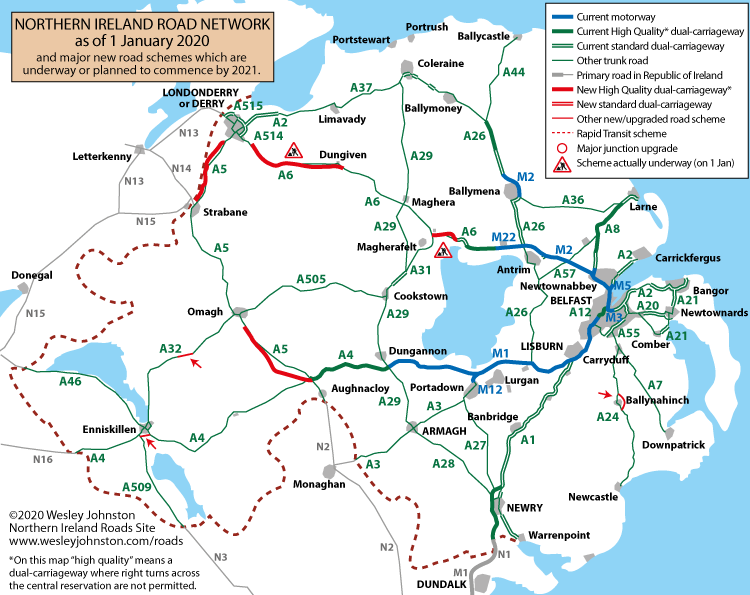
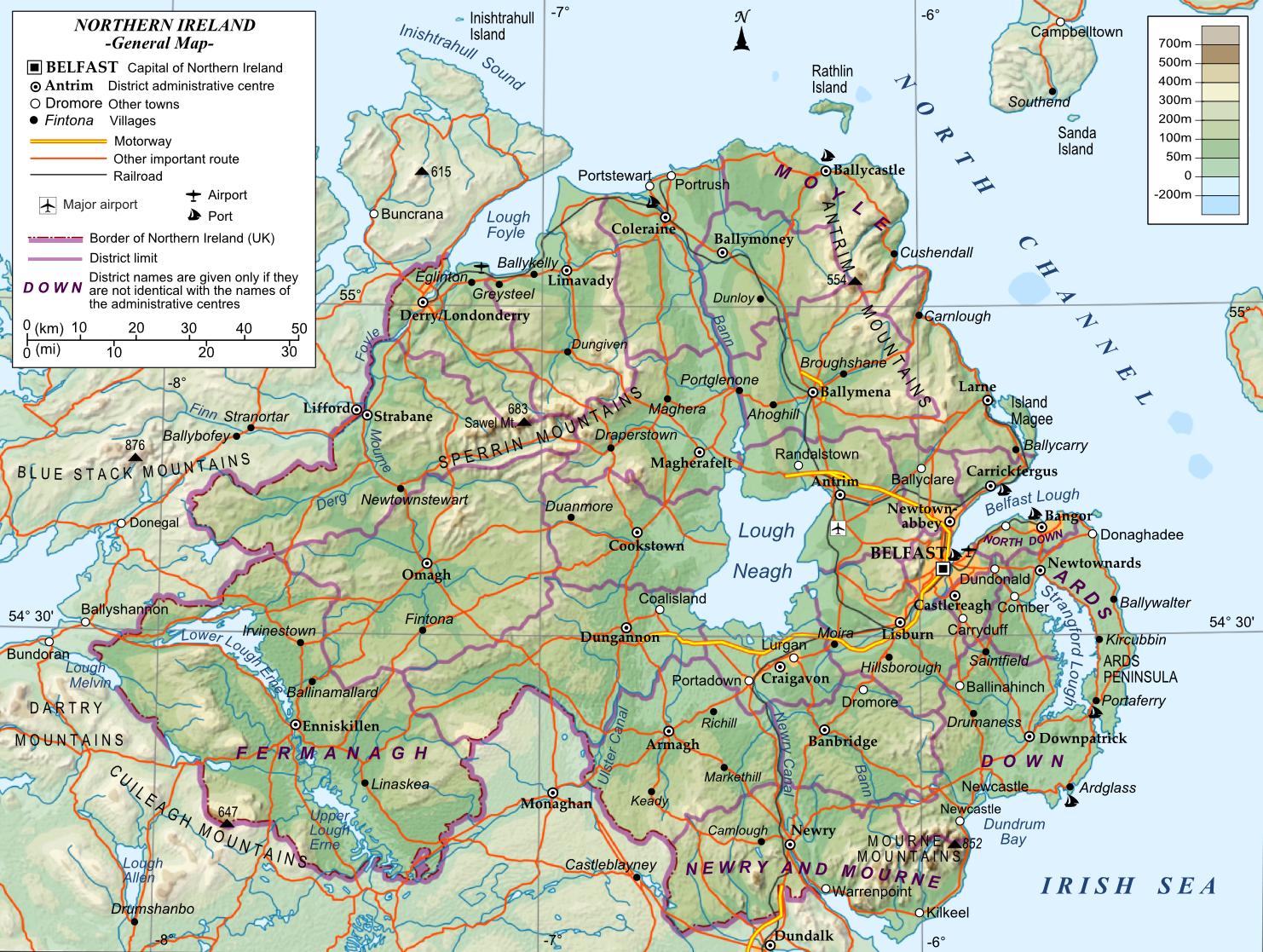
Northern Ireland, a picturesque land of rolling hills, rugged coastlines, and vibrant cities, boasts a well-developed road network that connects its diverse landscapes and communities. Understanding this intricate system is crucial for travelers, residents, and anyone seeking to explore the region’s beauty and rich history. This article delves into the complexities of the Northern Irish road network, offering a comprehensive overview of its features, challenges, and significance.
A History of Road Development
The development of Northern Ireland’s road network reflects a gradual evolution from rural pathways to modern highways. Early roads, primarily serving agricultural needs, were often narrow and poorly maintained. The advent of the automobile in the early 20th century spurred a rapid expansion of road infrastructure, with the construction of major arterial routes connecting key cities and towns. This period also saw the introduction of road signs, traffic lights, and other essential traffic management systems.
Following World War II, the Northern Ireland Ministry of Commerce undertook a significant program of road improvements, focusing on widening existing roads and introducing new bypasses to alleviate traffic congestion in urban areas. The 1960s saw the introduction of motorways, a major advancement in road infrastructure, with the M1 motorway connecting Belfast to the border with the Republic of Ireland.
Key Features of the Road Network
Northern Ireland’s road network comprises a diverse range of roads, each serving specific functions:
- Motorways: The M1, M2, and M12 motorways form the backbone of the network, providing high-speed connections between major cities and towns. These roads are characterized by their dedicated lanes, limited access points, and high speed limits.
- Dual Carriageways: These roads feature two lanes in each direction, separated by a central reservation. They offer a smoother and safer driving experience compared to single carriageways, particularly on routes with high traffic volumes.
- Single Carriageways: These roads typically have one lane in each direction, with occasional passing opportunities. They are prevalent in rural areas and often connect smaller towns and villages.
- A-Roads: These are major roads connecting towns and cities, often carrying significant traffic volumes. They are generally of good quality but can be subject to congestion during peak hours.
- B-Roads: These are secondary roads connecting smaller towns and villages. They are typically narrower and less busy than A-roads but can offer scenic views and a more intimate driving experience.
- C-Roads: These are local roads primarily serving rural areas. They are often narrow and winding, with limited passing opportunities.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Northern Ireland’s road network has undergone significant improvements, it faces ongoing challenges:
- Traffic Congestion: Urban areas, particularly Belfast, experience significant traffic congestion during peak hours. This issue is exacerbated by the limited capacity of some key roads and the increasing number of vehicles on the roads.
- Road Safety: While road safety has improved in recent years, accidents remain a concern. Factors contributing to accidents include speeding, driver fatigue, and poor road conditions.
- Infrastructure Investment: Maintaining and improving the road network requires significant financial investment. This is particularly challenging in light of ongoing budget constraints.
Despite these challenges, Northern Ireland’s road network presents opportunities for further development:
- Sustainable Transport: Promoting sustainable transport options, such as cycling and public transport, can reduce traffic congestion and improve air quality.
- Smart Road Infrastructure: Investing in smart technologies, such as traffic monitoring systems and adaptive traffic lights, can optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Road Safety Initiatives: Implementing targeted road safety campaigns and improving road infrastructure can reduce the number of accidents and fatalities.
The Importance of the Road Network
Northern Ireland’s road network plays a vital role in the region’s economy, society, and daily life. It:
- Connects People and Places: The network facilitates travel between communities, allowing people to access essential services, visit family and friends, and engage in leisure activities.
- Supports Economic Growth: The efficient movement of goods and services is crucial for economic growth. The road network provides the vital infrastructure for businesses to operate and trade.
- Promotes Tourism: The network allows visitors to explore the region’s stunning natural beauty and rich cultural heritage, contributing to the tourism industry.
- Enhances Quality of Life: The road network enables people to access employment opportunities, education, healthcare, and other essential services, contributing to a higher quality of life.
Navigating the Network: Tips and Resources
For travelers and residents alike, understanding the intricacies of Northern Ireland’s road network is crucial for safe and efficient journeys. Here are some tips and resources:
- Plan Your Route: Utilize online mapping tools and navigation apps to plan your route, considering traffic conditions, road closures, and alternative routes.
- Be Aware of Road Signs: Pay close attention to road signs, including speed limits, traffic regulations, and directions.
- Drive Safely: Always drive defensively, respecting speed limits, and avoiding distractions.
- Check Weather Conditions: Be aware of weather conditions, as heavy rain, snow, or fog can significantly impact road conditions and visibility.
- Plan for Delays: Allow extra time for your journey, especially during peak hours or in areas prone to traffic congestion.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on road closures and traffic disruptions through local news outlets, social media, and official transportation websites.
- Consider Alternative Transportation: Explore alternative transportation options, such as public transport, cycling, or walking, especially for short distances or in congested areas.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main roads connecting Belfast to other major cities in Northern Ireland?
The M1 motorway connects Belfast to the border with the Republic of Ireland, providing a high-speed route to Dublin and other cities in the south. The M2 motorway connects Belfast to Derry/Londonderry, while the A2 road connects Belfast to Bangor and the eastern coast.
2. Are there any tolls on roads in Northern Ireland?
There are no tolls on roads in Northern Ireland.
3. What are the speed limits on roads in Northern Ireland?
The speed limit on motorways is 70 mph, while on dual carriageways it is 60 mph. On single carriageways, the speed limit is generally 60 mph, but it can be lower in built-up areas or on specific stretches of road.
4. What are the best resources for planning a road trip in Northern Ireland?
Several online resources can assist in planning a road trip, including:
- Google Maps: Offers detailed maps, traffic conditions, and navigation instructions.
- AA Route Planner: Provides route planning, traffic updates, and travel information.
- RAC Route Planner: Offers similar features to the AA Route Planner.
- Northern Ireland Tourist Board Website: Provides information on attractions, accommodation, and travel planning resources.
5. What are some scenic routes to consider for a road trip in Northern Ireland?
Northern Ireland offers numerous scenic routes, including:
- The Causeway Coastal Route: A stunning coastal route that follows the dramatic coastline of County Antrim, featuring iconic landmarks such as the Giant’s Causeway and Carrick-a-Rede Rope Bridge.
- The Mourne Mountains Drive: A scenic route through the stunning Mourne Mountains, offering breathtaking views and challenging driving conditions.
- The Sperrin Mountains Drive: A picturesque route through the Sperrin Mountains, featuring rolling hills, ancient forests, and charming villages.
Conclusion
Northern Ireland’s road network is a testament to the region’s development, connecting its diverse landscapes, communities, and industries. Understanding the complexities of this network is crucial for safe and efficient travel, allowing individuals to explore the region’s beauty and rich heritage. By embracing sustainable transportation solutions, investing in smart infrastructure, and prioritizing road safety, Northern Ireland can continue to enhance its road network, fostering economic growth, promoting tourism, and enhancing the quality of life for its residents.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Roads of Northern Ireland: A Comprehensive Guide to the Road Network. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!