Navigating The Landscape: The Power Of 3D Maps In Understanding Israel
Navigating the Landscape: The Power of 3D Maps in Understanding Israel
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: The Power of 3D Maps in Understanding Israel
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: The Power of 3D Maps in Understanding Israel. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: The Power of 3D Maps in Understanding Israel

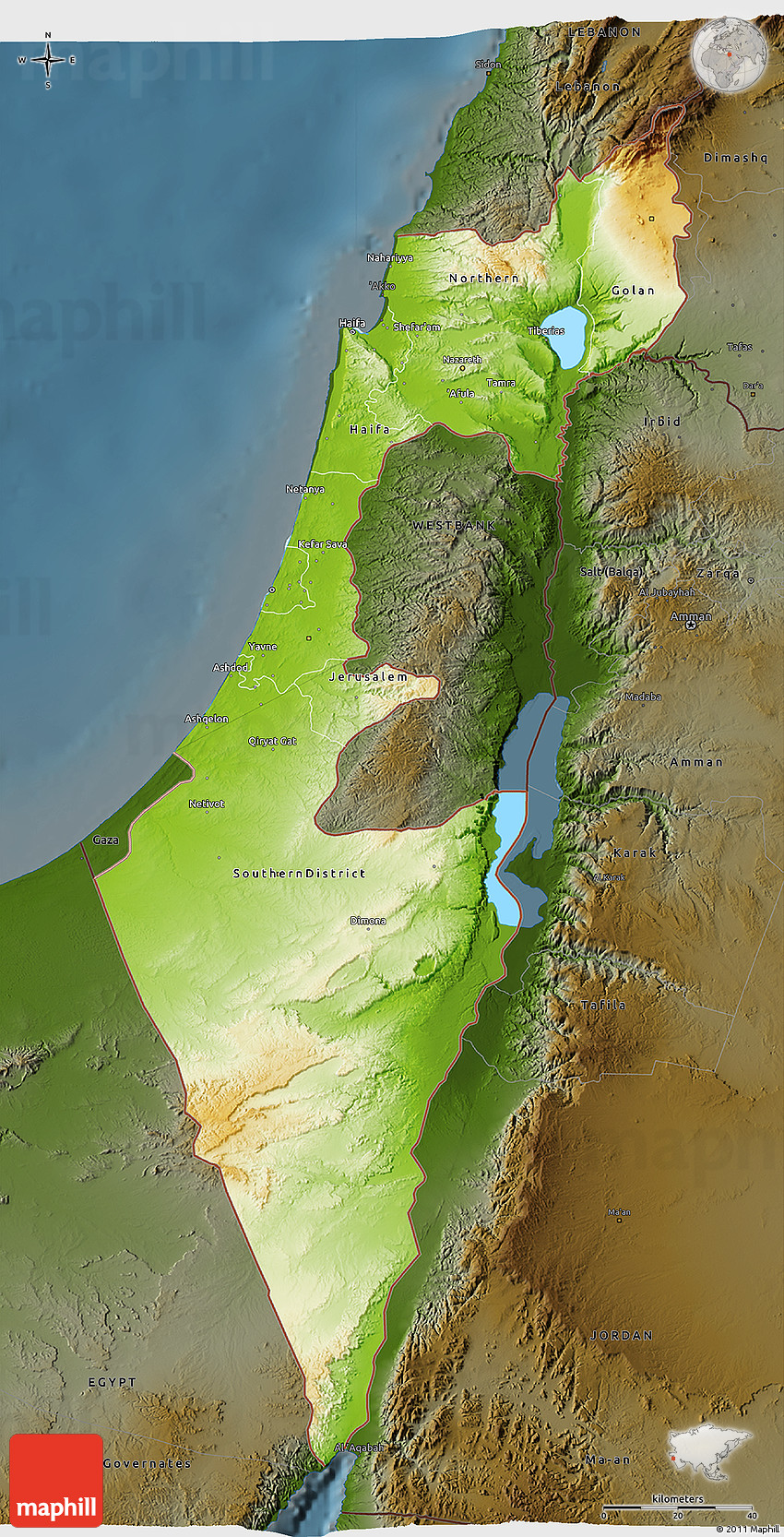
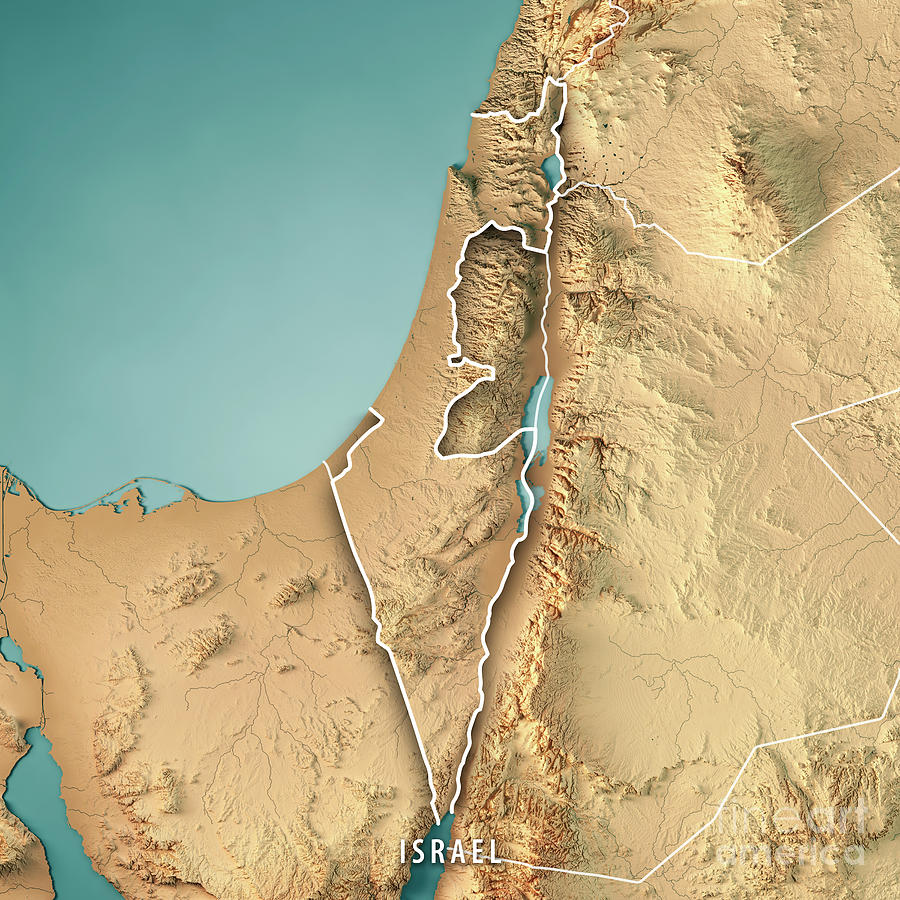
The Land of Israel, a region steeped in history, culture, and conflict, presents a complex landscape demanding nuanced understanding. Traditional two-dimensional maps, while useful, often fail to fully capture the intricate spatial relationships and topographic features that define the region. This is where three-dimensional (3D) maps emerge as a powerful tool, offering a transformative perspective on Israel’s geography and its impact on the lives of its people.
Beyond Flat Representations: The Advantages of 3D Mapping
3D maps transcend the limitations of flat representations by offering a more realistic and immersive portrayal of the terrain. They allow viewers to:
- Visualize Topography: 3D maps effectively depict the dramatic elevation changes, from the rolling hills of the Galilee to the Dead Sea’s deep depression, providing a clear understanding of the physical landscape. This is particularly crucial for understanding the strategic importance of specific locations, the challenges of infrastructure development, and the impact of natural disasters.
- Experience Spatial Relationships: By presenting a three-dimensional view, 3D maps facilitate a deeper understanding of the spatial relationships between different geographic features. This enables viewers to grasp the proximity of cities, the flow of water resources, and the impact of borders on human movement.
- Explore Hidden Dimensions: 3D maps can integrate various data layers, such as population density, historical sites, or infrastructure networks, onto the terrain. This allows for a multi-faceted analysis, revealing the interconnectedness of different aspects of life in Israel.
Applications of 3D Maps in Understanding Israel
The application of 3D maps in understanding Israel is multifaceted, extending beyond the realm of academia to encompass various fields:
- Archaeology and History: 3D maps play a crucial role in archaeological investigations, facilitating the reconstruction of ancient settlements and understanding the evolution of the landscape over time. They allow researchers to visualize the spatial relationships between archaeological sites, providing insights into past societies and their interaction with the environment.
- Urban Planning and Development: 3D maps are invaluable tools for urban planners, enabling them to visualize the impact of proposed development projects on the existing landscape. They facilitate the analysis of traffic flow, accessibility, and environmental impact, ensuring sustainable and well-planned urban development.
- Environmental Management: 3D maps aid in understanding the impact of climate change, deforestation, and other environmental issues on the landscape. They provide a platform for analyzing the distribution of natural resources, identifying potential environmental hazards, and developing strategies for sustainable management.
- Military and Security: The ability to visualize terrain in three dimensions is vital for military planning and operations. 3D maps facilitate the identification of strategic locations, the assessment of potential threats, and the development of effective defense strategies.
- Tourism and Education: 3D maps enhance the tourism experience by providing interactive and engaging ways to explore the country. They can be used to guide visitors to historical sites, natural wonders, and cultural attractions, enriching their understanding of the region. Additionally, 3D maps serve as powerful educational tools, bringing the geography of Israel to life for students of all ages.
Examples of 3D Maps in Action
Numerous projects showcase the power of 3D maps in illuminating the intricacies of Israel’s landscape:
- The Digital Jerusalem Project: This ambitious project aims to create a comprehensive 3D model of Jerusalem, encompassing both its historical and modern aspects. The project utilizes various data sources, including aerial photography, laser scanning, and archaeological records, to reconstruct the city’s evolution over time.
- The Israeli National Geographic Information System (IGNIS): IGNIS is a national-scale initiative that provides a comprehensive 3D model of Israel, including its terrain, infrastructure, and population distribution. The platform serves as a valuable resource for researchers, planners, and decision-makers, facilitating informed decision-making across various sectors.
- Interactive 3D Maps for Tourism: Several companies have developed interactive 3D maps specifically designed for tourism. These maps allow visitors to explore the country’s major attractions, navigate through cities, and discover hidden gems, enhancing their travel experience.
FAQs about 3D Maps of Israel
1. What are the different types of 3D maps available for Israel?
3D maps of Israel can be broadly categorized into:
- Terrain-based maps: These maps primarily focus on the physical landscape, showcasing elevation changes, geological features, and natural resources.
- Infrastructure maps: These maps highlight the network of roads, railways, airports, and other infrastructure elements, providing insights into connectivity and accessibility.
- Population density maps: These maps visualize the distribution of population across different regions, providing insights into demographic trends and urban development.
- Historical maps: These maps integrate historical data, showcasing the evolution of the landscape over time, highlighting archaeological sites, and illustrating the impact of past events.
2. How are 3D maps of Israel created?
The creation of 3D maps involves a multi-step process, typically employing the following techniques:
- Aerial photography: High-resolution aerial photographs are used to capture the landscape from above, providing a comprehensive overview of the terrain.
- Laser scanning (LiDAR): LiDAR technology emits laser pulses that measure the distance to the ground, generating detailed elevation data that can be used to create accurate 3D models.
- Satellite imagery: Satellite imagery provides a wide-angle perspective of the landscape, capturing large-scale features and providing valuable data for 3D map creation.
- Geographic Information System (GIS) software: GIS software is used to process and integrate data from various sources, creating a unified 3D model of the landscape.
3. What are the benefits of using 3D maps for understanding Israel?
3D maps offer a multitude of benefits for understanding Israel, including:
- Improved visualization: 3D maps provide a more realistic and immersive view of the landscape, facilitating a deeper understanding of its features and complexities.
- Enhanced spatial analysis: 3D maps allow for the analysis of spatial relationships between different geographic features, providing insights into connectivity, accessibility, and the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Data integration: 3D maps can integrate various data layers, including historical, environmental, and demographic information, providing a comprehensive and multi-faceted understanding of the region.
- Effective communication: 3D maps offer a powerful tool for communicating complex geographic information to a wider audience, making it easier to understand and engage with the landscape.
4. What are the limitations of 3D maps of Israel?
Despite their advantages, 3D maps have some limitations:
- Data availability: The accuracy and detail of 3D maps depend on the availability of high-quality data. Data gaps or inaccuracies can lead to limitations in the maps’ reliability.
- Computational requirements: Creating and rendering 3D maps can require significant computational resources, potentially limiting accessibility for some users.
- User experience: The effectiveness of 3D maps depends on the user’s ability to navigate and interpret the data presented. Users may need training or guidance to fully utilize the potential of these maps.
Tips for Using 3D Maps of Israel Effectively
- Choose the right map for your needs: Consider the purpose of your analysis and select a 3D map that provides the relevant data and features.
- Explore different perspectives: Rotate and zoom the map to gain different viewpoints and understand the landscape from various angles.
- Utilize data layers: Explore the available data layers and integrate them into your analysis to gain a multi-faceted understanding of the region.
- Interact with the map: Use interactive features, such as zoom, pan, and layer control, to explore the map and gain a deeper understanding of the data.
- Compare and contrast: Use different 3D maps to compare and contrast different data sets and perspectives on the landscape.
Conclusion
3D maps are a powerful tool for understanding the complex landscape of Israel. They provide a more realistic and immersive view of the terrain, facilitate spatial analysis, and enable the integration of various data layers. By leveraging the capabilities of 3D maps, researchers, planners, and decision-makers can gain a deeper understanding of Israel’s geography, its impact on the lives of its people, and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. As technology continues to advance, 3D maps will likely play an even more significant role in shaping our understanding of this fascinating and complex region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: The Power of 3D Maps in Understanding Israel. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!