Navigating The Landscape Of Java Data Structures: A Comprehensive Look At Dictionaries And Maps
Navigating the Landscape of Java Data Structures: A Comprehensive Look at Dictionaries and Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Java Data Structures: A Comprehensive Look at Dictionaries and Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Java Data Structures: A Comprehensive Look at Dictionaries and Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Java Data Structures: A Comprehensive Look at Dictionaries and Maps
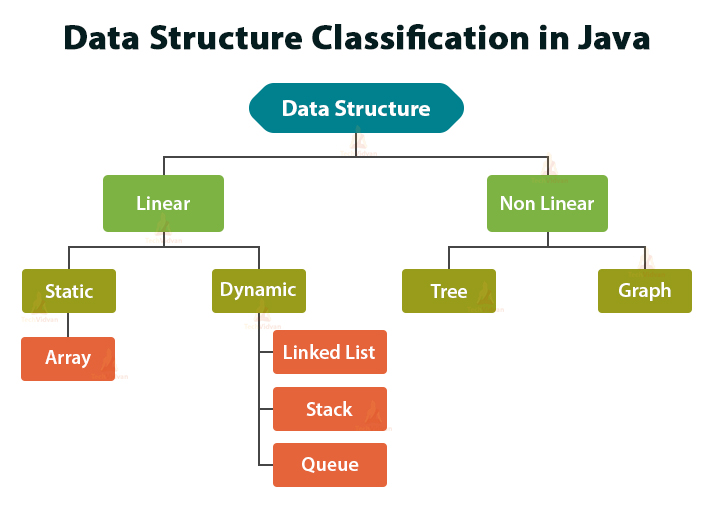
In the realm of Java programming, data structures serve as the foundation upon which complex applications are built. They provide efficient mechanisms for organizing and storing data, enabling programmers to retrieve, manipulate, and process information effectively. Among these structures, dictionaries and maps hold a prominent position, offering a powerful means to represent key-value pairs. While often used interchangeably, a closer examination reveals distinct characteristics that differentiate these two structures.
Understanding the Concept of Key-Value Pairs
At their core, both dictionaries and maps rely on the concept of key-value pairs. This paradigm allows for the association of a unique identifier, the "key," with a corresponding data element, the "value." This association creates a logical connection, enabling quick access to the value based on its associated key.
The Dictionary: A Conceptual Foundation
The dictionary, while not a concrete data structure in Java, serves as a conceptual foundation for understanding the concept of key-value pairs. It embodies the fundamental idea of associating words with their definitions, much like a physical dictionary. This association allows users to readily find the meaning of a word by referencing its corresponding entry.
The Map: A Powerful Implementation in Java
In contrast to the conceptual dictionary, the map is a concrete data structure in Java, providing a practical implementation of the key-value pair concept. The java.util.Map interface defines the fundamental operations for managing key-value pairs, including methods for insertion, retrieval, update, and removal.
Key Differences: Exploring the Nuances
While both dictionaries and maps revolve around key-value pairs, several key differences distinguish them:
1. Implementation: Dictionaries, being conceptual, lack a specific implementation in Java. Maps, however, are implemented using various concrete classes like HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap, each offering unique characteristics and performance trade-offs.
2. Ordering: Dictionaries, as a conceptual representation, do not inherently impose an order on key-value pairs. Maps, on the other hand, can be ordered based on the underlying implementation. TreeMap, for example, maintains keys in sorted order, while HashMap does not guarantee any specific order.
3. Key Uniqueness: Dictionaries, by their nature, assume that each key is unique. Maps, while generally designed to handle unique keys, can allow for duplicate keys depending on the implementation. For instance, HashMap does not enforce uniqueness, allowing multiple entries with the same key.
4. Data Structure: Dictionaries, being conceptual, do not specify a specific underlying data structure. Maps, however, leverage various data structures internally, such as hash tables, trees, or linked lists, depending on the implementation.
Choosing the Right Tool: Navigating the Trade-offs
The choice between dictionaries and maps in Java depends heavily on the specific requirements of the application.
Dictionaries excel in conceptual clarity, emphasizing the core concept of associating keys with values. They are particularly useful for understanding the fundamental principles of key-value pair management.
Maps provide a practical implementation in Java, offering a wide range of options for storing and manipulating key-value pairs. The choice of a specific map implementation depends on factors such as performance requirements, ordering needs, and the necessity for key uniqueness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the benefits of using maps in Java?
A: Maps offer several benefits:
- Efficient Retrieval: Maps allow for quick access to values based on their associated keys.
- Flexibility: They support various data types for both keys and values, providing flexibility in storing and retrieving diverse data.
- Dynamic Size: Maps can grow or shrink dynamically as needed, accommodating changes in data volume.
Q: When should I use a HashMap over a TreeMap in Java?
A: HashMap is preferred when:
-
Order is not critical:
HashMapdoes not maintain a specific order of key-value pairs. -
Performance is paramount:
HashMapoffers faster insertion, retrieval, and deletion operations compared toTreeMap. -
Key uniqueness is not strictly enforced:
HashMapallows for multiple entries with the same key.
TreeMap, on the other hand, is suitable when:
-
Sorted keys are required:
TreeMapmaintains keys in sorted order, allowing for efficient range queries and sorted iteration. -
Unique keys are essential:
TreeMapenforces key uniqueness, preventing duplicate keys.
Q: How can I iterate over a map in Java?
A: Java provides several ways to iterate over a map:
-
Key Set: You can obtain a set of keys using the
keySet()method and iterate over it. -
Entry Set: You can obtain a set of key-value pairs using the
entrySet()method and iterate over it, accessing both keys and values. -
Lambda Expressions: Java 8 introduced lambda expressions, providing a concise way to iterate over maps using the
forEach()method.
Tips for Effective Map Usage
- Choose the right map implementation: Carefully consider the requirements of your application and select the most appropriate map implementation based on performance, ordering, and key uniqueness needs.
- Handle null keys and values: Be mindful of null values, as they can lead to unexpected behavior. Consider using a dedicated null object or handling null values explicitly.
-
Utilize the appropriate methods: Leverage the rich set of methods provided by the
Mapinterface to perform common operations such as insertion, retrieval, update, and removal. - Optimize for performance: Consider using efficient data structures like hash tables for faster lookups, particularly when dealing with large datasets.
- Maintain code clarity: Use meaningful variable names and comments to enhance code readability and maintainability.
Conclusion
Dictionaries and maps play a vital role in Java programming, providing powerful mechanisms for managing key-value pairs. While dictionaries serve as a conceptual foundation, maps offer concrete implementations, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. By understanding the differences between these data structures and carefully considering their respective benefits, developers can choose the most appropriate tool for their specific needs, ensuring efficient and effective data management in their Java applications.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Java Data Structures: A Comprehensive Look at Dictionaries and Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
