Navigating The Landscape Of Array Manipulation: A Deep Dive Into Filter And Map In JavaScript
Navigating the Landscape of Array Manipulation: A Deep Dive into Filter and Map in JavaScript
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Array Manipulation: A Deep Dive into Filter and Map in JavaScript
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Array Manipulation: A Deep Dive into Filter and Map in JavaScript. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Array Manipulation: A Deep Dive into Filter and Map in JavaScript
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Array Manipulation: A Deep Dive into Filter and Map in JavaScript
- 3.1 Filter: Extracting the Desired Elements
- 3.2 Map: Transforming Elements with a Function
- 3.3 Choosing the Right Tool: Filter vs. Map
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Combining Filter and Map
- 3.5 FAQs about Filter and Map
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use of Filter and Map
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Array Manipulation
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Array Manipulation: A Deep Dive into Filter and Map in JavaScript
JavaScript, a dynamic and versatile language, offers an array of powerful tools for manipulating data. Among these, the filter and map methods stand out as essential building blocks for data transformation and analysis. Understanding their distinct roles and capabilities is crucial for writing efficient and elegant code. This article delves into the intricacies of these methods, providing a comprehensive understanding of their functionality, use cases, and the benefits they offer.
Filter: Extracting the Desired Elements
The filter method acts as a discerning sieve, allowing you to select specific elements from an array based on a given condition. It iterates through each element, applying a provided function (a "predicate") to determine its eligibility for inclusion in the resulting array. If the predicate returns true, the element is kept; if it returns false, the element is discarded.
Illustrative Example:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
const evenNumbers = numbers.filter(number => number % 2 === 0);
console.log(evenNumbers); // Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]In this example, the filter method, with the predicate number => number % 2 === 0, identifies and extracts all the even numbers from the numbers array.
Key Points:
-
Immutability:
filteralways returns a new array, leaving the original array untouched. This ensures data integrity and predictable behavior. - Conditional Selection: The predicate function acts as a gatekeeper, determining which elements are included in the output array.
-
Clarity and Readability: Using
filterfor selective extraction enhances code readability and maintainability, making it easier to grasp the purpose of the code.
Map: Transforming Elements with a Function
The map method, on the other hand, is a powerful tool for transforming each element of an array. It applies a function to every element, generating a new array with the transformed elements. This function can perform various operations, such as adding a constant value, changing data types, or applying complex calculations.
Illustrative Example:
const temperaturesCelsius = [10, 20, 30, 40];
const temperaturesFahrenheit = temperaturesCelsius.map(celsius => (celsius * 9/5) + 32);
console.log(temperaturesFahrenheit); // Output: [50, 68, 86, 104]Here, the map method, with the function celsius => (celsius * 9/5) + 32, transforms each Celsius temperature into its Fahrenheit equivalent, creating a new array of Fahrenheit values.
Key Points:
-
Element-wise Transformation:
mapapplies the provided function to each element individually, generating a new array with the transformed results. - Data Manipulation: It allows for flexible transformations, enabling you to manipulate data in various ways, from simple arithmetic to complex calculations.
-
Functional Programming Paradigm:
mappromotes a functional programming style, where data transformations are achieved through pure functions, enhancing code reusability and predictability.
Choosing the Right Tool: Filter vs. Map
While both filter and map operate on arrays, their core functionalities differ significantly. Choosing the appropriate method depends on the specific task at hand:
-
Filter: When you need to select specific elements based on a condition,
filteris your go-to method. It effectively sifts through the array, keeping only the elements that meet the defined criteria. -
Map: When you need to transform each element of an array,
mapis the ideal choice. It allows you to apply a function to each element, producing a new array with the transformed results.
Practical Scenarios:
-
Filtering a List of Products: You might use
filterto extract products that are on sale or meet specific price criteria from a list of products. -
Converting Units: You could use
mapto convert a list of temperatures from Celsius to Fahrenheit or vice versa. -
Generating a List of Squares: You could use
mapto create a new array containing the squares of all numbers in an existing array.
Beyond the Basics: Combining Filter and Map
The true power of filter and map lies in their ability to be combined, creating sophisticated data manipulation chains. This allows you to perform multiple operations in a sequential manner, efficiently transforming data according to your specific needs.
Illustrative Example:
const products = [
name: "Laptop", price: 1000, onSale: true ,
name: "Keyboard", price: 50, onSale: false ,
name: "Mouse", price: 25, onSale: true ,
name: "Monitor", price: 300, onSale: false
];
const discountedProducts = products
.filter(product => product.onSale)
.map(product => ( ...product, price: product.price * 0.9 ));
console.log(discountedProducts);In this example, we first use filter to select only products that are on sale. Then, we use map to apply a 10% discount to the price of each selected product. This chained approach effectively combines filtering and transformation to achieve a specific result.
FAQs about Filter and Map
Q1: Can I use filter and map together in a single line of code?
A: While it is possible to combine filter and map in a single line, it’s generally recommended to separate them for improved readability and maintainability. This approach makes it easier to understand the individual steps involved in the data transformation process.
Q2: Are filter and map the only array manipulation methods in JavaScript?
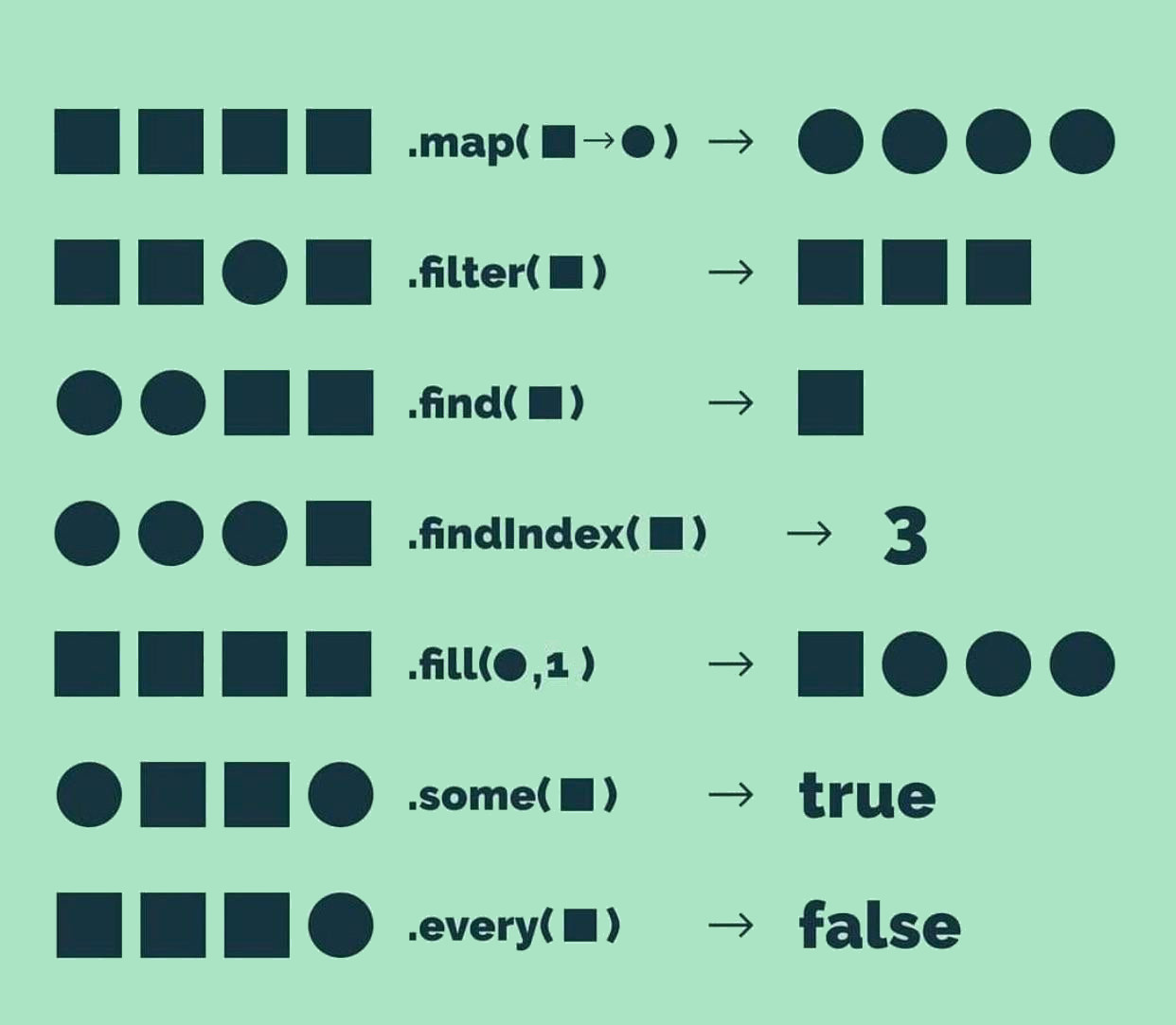
A: No. JavaScript offers a plethora of array manipulation methods, including forEach, reduce, some, every, and find. Each method serves a specific purpose, providing a wide range of tools for working with arrays.
Q3: Can I use filter and map on objects?
A: While filter and map primarily work with arrays, they can also be applied to objects indirectly. You can use Object.keys to get an array of keys from an object and then apply filter or map to that array.
Q4: What are the performance implications of using filter and map?
A: Both filter and map are relatively efficient methods. However, their performance can be affected by the complexity of the predicate or transformation function. For large arrays, it’s essential to optimize these functions to minimize processing time.
Tips for Effective Use of Filter and Map
- Use Descriptive Function Names: Choose meaningful names for the predicate and transformation functions to enhance code clarity and readability.
-
Avoid Side Effects: Ensure that the functions used with
filterandmapare pure functions, meaning they do not modify external variables or have side effects. -
Chain Methods for Complex Operations: Combine
filterandmapwith other array methods, likereduce, to achieve complex data transformations in a concise and elegant manner. -
Test Thoroughly: Thoroughly test your code to ensure that
filterandmapare functioning as expected, particularly when dealing with large datasets.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Array Manipulation
The filter and map methods are invaluable tools in the JavaScript developer’s arsenal. They provide efficient and elegant ways to manipulate arrays, enabling you to extract specific elements, transform data, and achieve complex data analysis tasks. By understanding their functionalities and applying them effectively, you can write cleaner, more maintainable, and efficient code, unlocking the full potential of JavaScript for data manipulation.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Array Manipulation: A Deep Dive into Filter and Map in JavaScript. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
