Navigating The Japanese Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide To The Shinkansen Network
Navigating the Japanese Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Japanese Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Network
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Japanese Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Japanese Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Network

The Shinkansen, Japan’s high-speed rail network, is a marvel of modern engineering and a testament to the nation’s commitment to efficient transportation. Its intricate network of lines crisscrosses the Japanese archipelago, connecting major cities and offering a seamless and comfortable journey for millions of travelers each year.
This article delves into the intricate web of the Shinkansen network, exploring its history, key lines, operational characteristics, and the profound impact it has had on Japanese society and culture.
A Brief History of the Shinkansen
The concept of a high-speed rail network in Japan emerged in the 1950s, fueled by the need for a faster and more efficient mode of transportation to connect major cities. The first Shinkansen line, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, opened in 1964, coinciding with the Tokyo Olympics. This groundbreaking achievement marked the beginning of a new era in Japanese transportation, revolutionizing travel within the country.
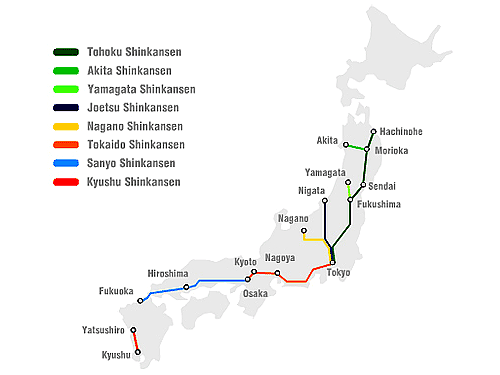
Over the decades, the Shinkansen network has expanded significantly, with new lines branching out to connect more cities and regions. The network currently comprises eight distinct lines, each with its own unique characteristics and destinations:
- Tōkaidō Shinkansen: The original and most heavily used line, connecting Tokyo with Osaka and Nagoya.
- Sanyō Shinkansen: Extends the Tōkaidō Shinkansen line westward, reaching cities like Hiroshima and Fukuoka.
- Tōhoku Shinkansen: Connects Tokyo with cities in the Tohoku region, including Sendai and Aomori.
- Jōetsu Shinkansen: Runs parallel to the Tōhoku Shinkansen, connecting Tokyo with Niigata.
- Hokuriku Shinkansen: Connects Tokyo with Kanazawa and Toyama, traversing the mountainous Hokuriku region.
- Kyushu Shinkansen: Connects Hakata (Fukuoka) with Kagoshima, traversing the island of Kyushu.
- Yamagata Shinkansen: Connects Fukushima with Shinjō, serving the Yamagata Prefecture.
- Akita Shinkansen: Connects Akita with Morioka, connecting the Akita Prefecture to the Tōhoku Shinkansen network.
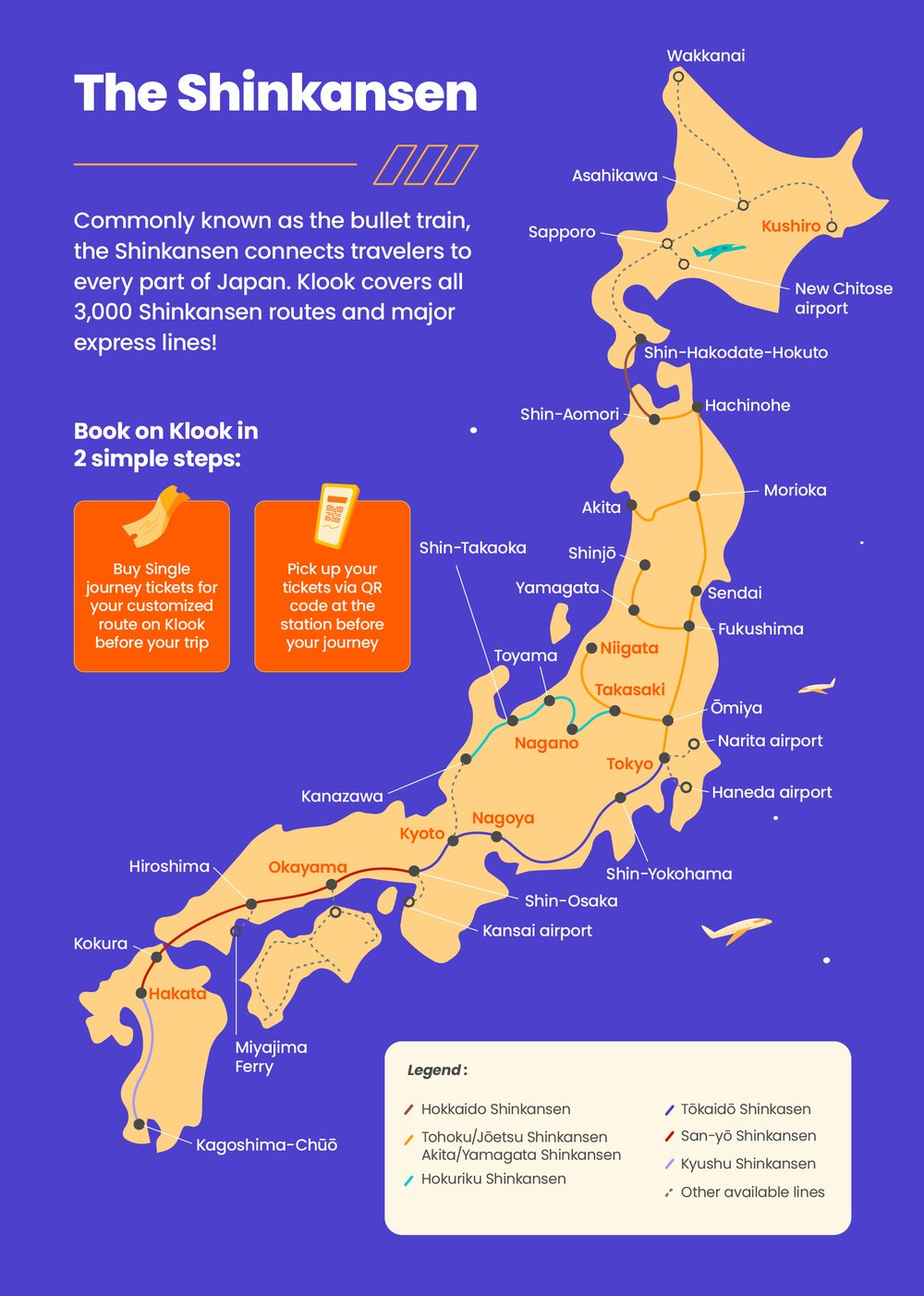
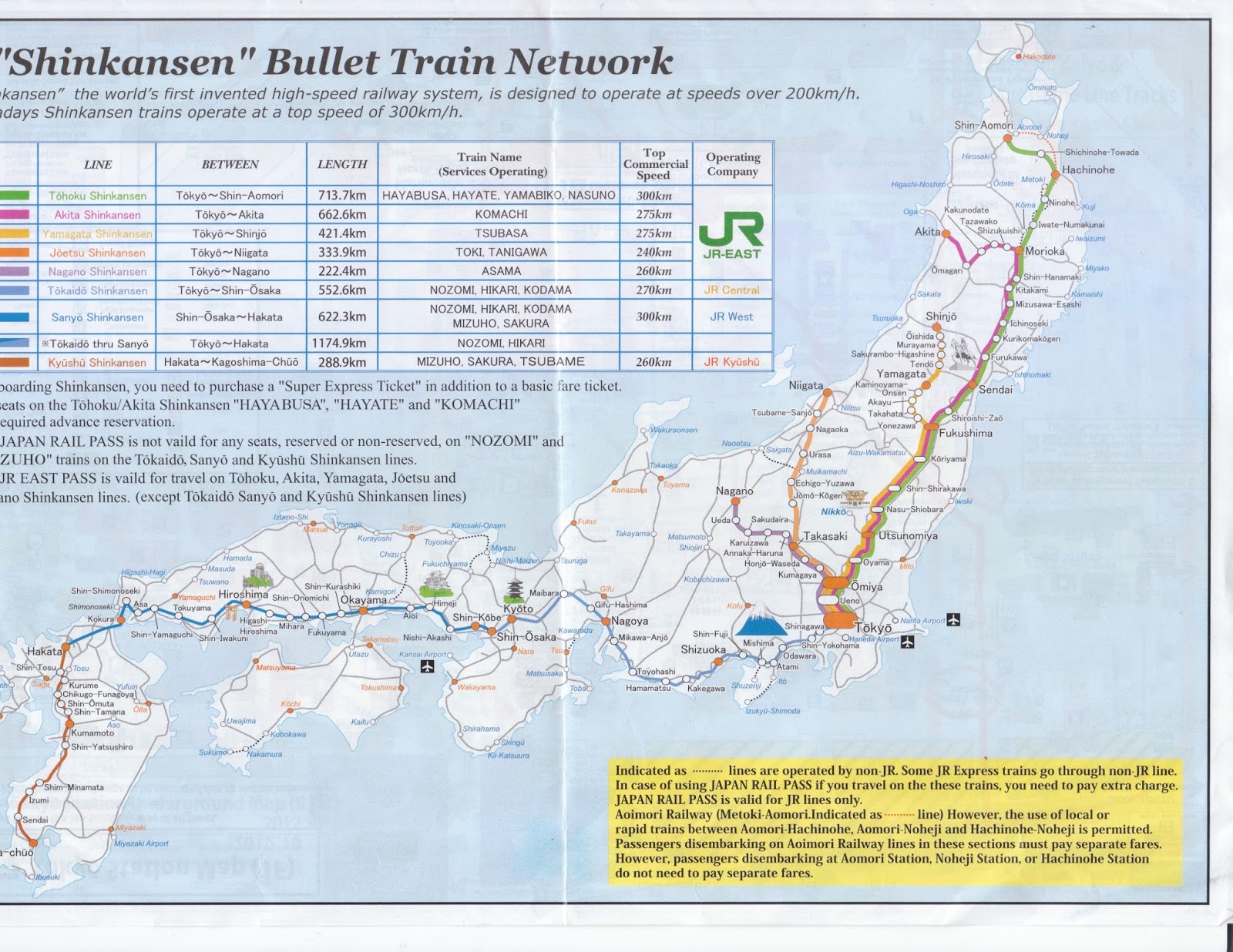
Understanding the Shinkansen Map
Navigating the Shinkansen network requires understanding the intricate map, which depicts the various lines, stations, and key destinations. The map is color-coded to differentiate between lines, with each line having its own distinct color and symbol. Stations are marked with their names, often accompanied by their Romanized spellings.
The map also indicates the distance between stations, the travel time, and the types of trains operating on each line. It is essential to note that not all trains stop at every station, and some trains are express services that only stop at major stations.
The Benefits of the Shinkansen
The Shinkansen network has profoundly impacted Japanese society, offering numerous benefits:
- Speed and Efficiency: The Shinkansen is renowned for its speed, reaching speeds of up to 300 kilometers per hour. This allows for quick and efficient travel between major cities, significantly reducing travel time compared to conventional train or road travel.
- Comfort and Convenience: Shinkansen trains are known for their comfort and convenience. They offer spacious seating, ample legroom, and amenities like power outlets, Wi-Fi, and onboard restrooms.
- Reliability and Punctuality: The Shinkansen network is renowned for its reliability and punctuality. Trains operate on a strict schedule, and delays are rare. This makes it a dependable and predictable mode of transportation for business travelers and tourists alike.
- Safety and Security: The Shinkansen network has an exceptional safety record. Strict safety protocols are in place, and the network is meticulously maintained, ensuring a safe and secure journey for all passengers.
- Economic Development: The Shinkansen network has played a vital role in the economic development of Japan. It has facilitated trade and tourism, connecting major cities and regions, and stimulating economic growth.
- Environmental Sustainability: The Shinkansen network is an environmentally sustainable mode of transportation. It emits significantly less carbon dioxide than air travel, contributing to a greener future.
FAQs about the Shinkansen Network
1. What is the cost of Shinkansen tickets?
Ticket prices for the Shinkansen vary depending on the distance traveled, the type of train, and the time of day. It is generally more expensive to travel during peak hours.
2. How do I purchase Shinkansen tickets?
Tickets can be purchased at train stations, online through the Japan Rail Pass website, or through travel agencies.
3. Is there a discount for children or seniors?
Children under six years old travel free, while children between six and 11 years old receive a discount. Seniors over 65 years old may be eligible for discounts on certain tickets.
4. Can I use a Japan Rail Pass on the Shinkansen?
Yes, the Japan Rail Pass, a tourist-oriented pass, allows unlimited travel on the Shinkansen network, except for some limited express trains.
5. Are there any luggage restrictions on the Shinkansen?
There are no specific luggage restrictions on the Shinkansen. However, it is recommended to keep luggage within manageable size and weight to ensure easy movement on and off the train.
6. What are the amenities available on Shinkansen trains?
Shinkansen trains offer a variety of amenities, including spacious seating, ample legroom, power outlets, Wi-Fi, onboard restrooms, and vending machines.
7. How do I find my seat on the Shinkansen?
Your ticket will indicate your seat number and car number. Follow the signs and announcements to locate your designated seat.
Tips for Traveling on the Shinkansen
- Book your tickets in advance: To ensure your desired seat, especially during peak travel seasons, it is recommended to book tickets in advance, either online or at a train station.
- Arrive at the station early: Allow ample time to navigate the station, find your platform, and board the train.
- Pay attention to announcements: Announcements are made in Japanese and English, providing information about departures, arrivals, and changes to the schedule.
- Keep your belongings close: Be mindful of your belongings, especially during crowded hours.
- Respect other passengers: Maintain a quiet environment and avoid loud conversations or disruptive behavior.
- Take advantage of the amenities: Utilize the onboard amenities, such as power outlets, Wi-Fi, and restrooms, to enhance your travel experience.
Conclusion
The Shinkansen network is an integral part of Japanese life, connecting major cities and regions, facilitating trade and tourism, and contributing to the nation’s economic growth. Its speed, comfort, reliability, and safety have made it a preferred mode of transportation for millions of travelers each year. As the network continues to expand and modernize, it is poised to play an even more vital role in shaping the future of transportation in Japan and beyond.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Japanese Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Network. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!