Navigating The Indonesian Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Provinces
Navigating the Indonesian Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces
Related Articles: Navigating the Indonesian Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Indonesian Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Indonesian Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces

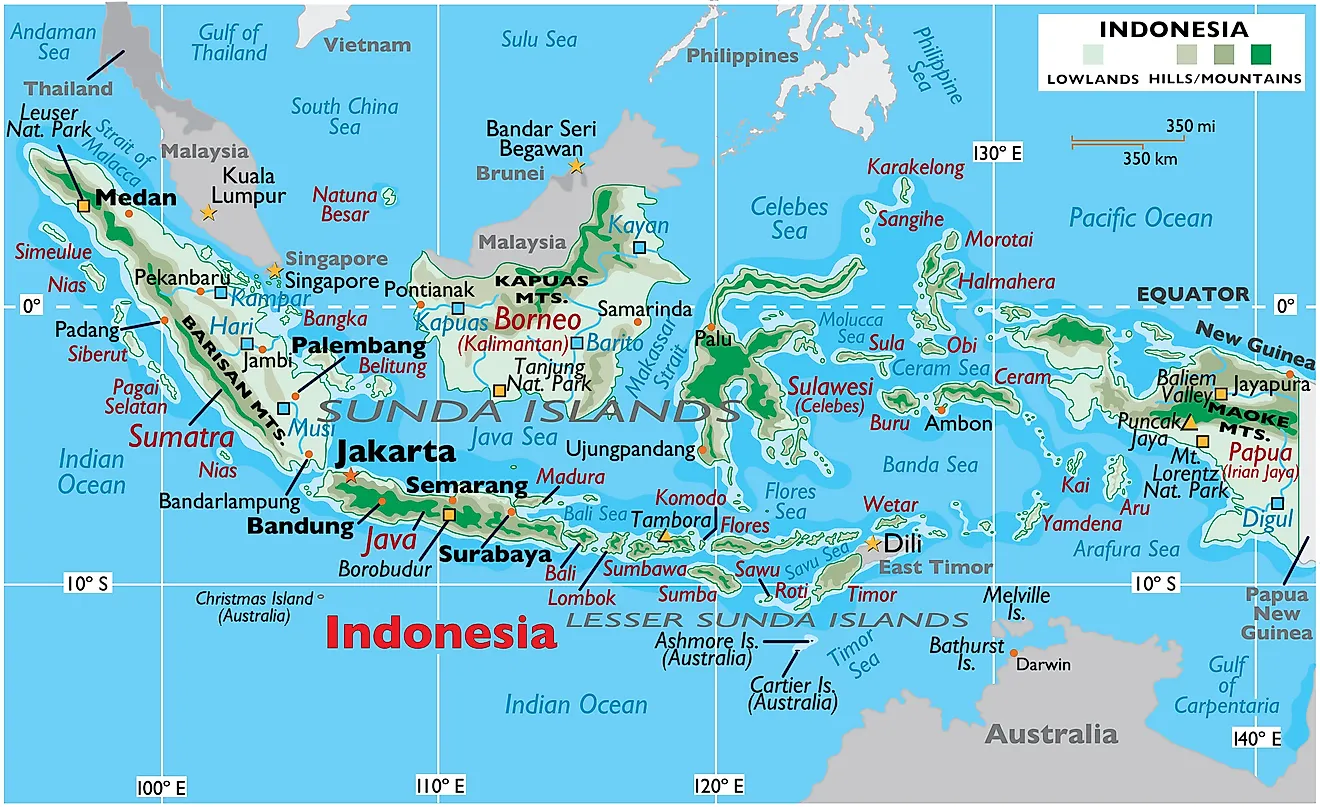
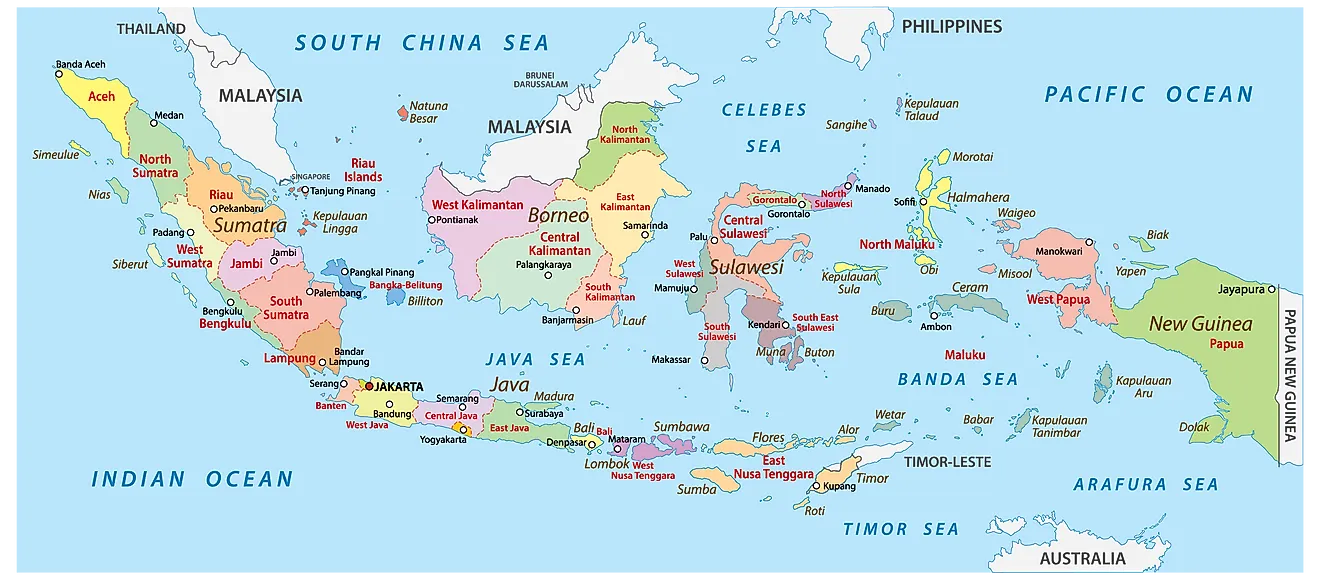
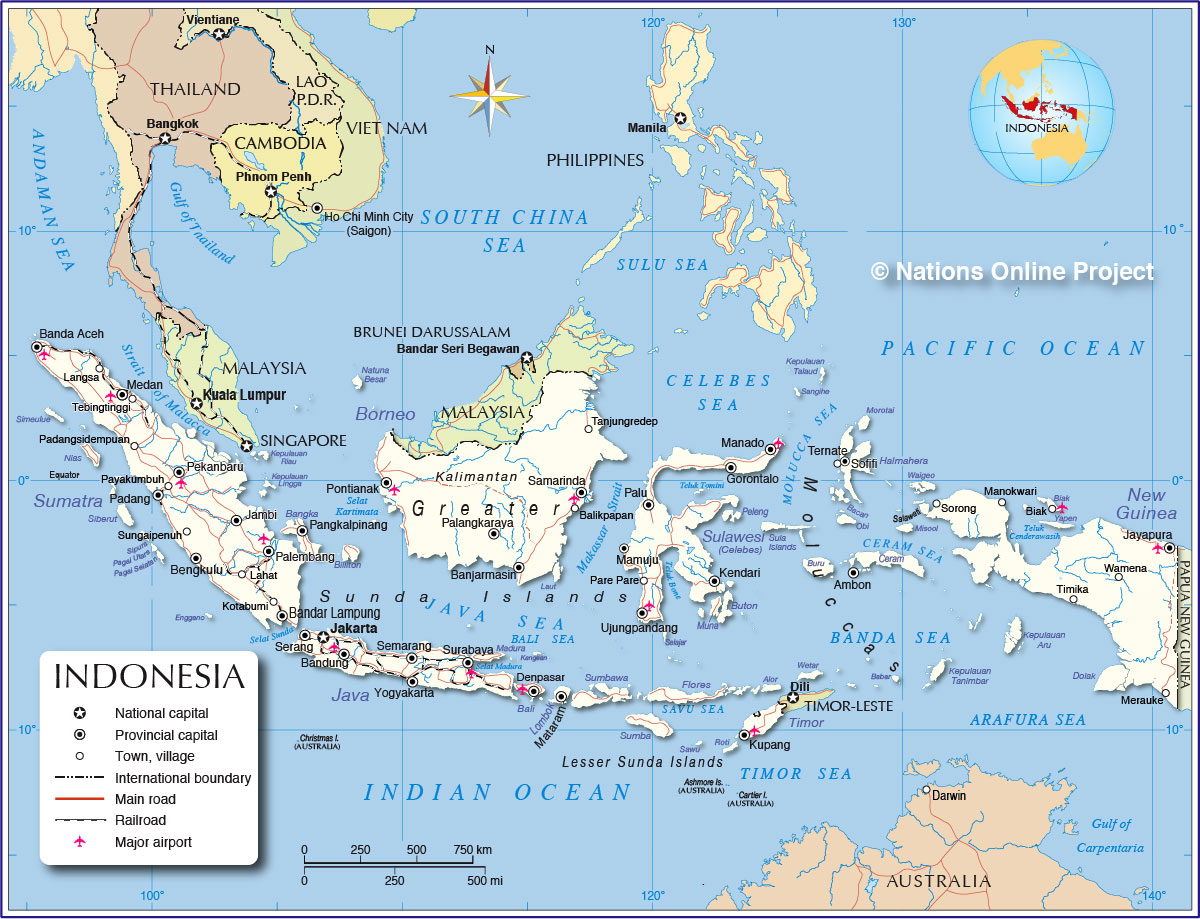
The Republic of Indonesia, an archipelago nation sprawling across Southeast Asia, is a tapestry of diverse cultures, languages, and landscapes. Its geographical expanse, encompassing over 17,000 islands, is further divided into 34 provinces, each with its own unique character and contribution to the national fabric. Understanding the map of Indonesian provinces is crucial for appreciating the nation’s complexity and the interconnectedness of its people and regions.
A Geographical Overview:
The Indonesian archipelago, situated between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, is a land of dramatic contrasts. From the towering peaks of Papua to the fertile plains of Java, the landscape varies significantly, influencing the provinces’ economic activities and cultural identities. The provinces can be broadly categorized into five main regions:
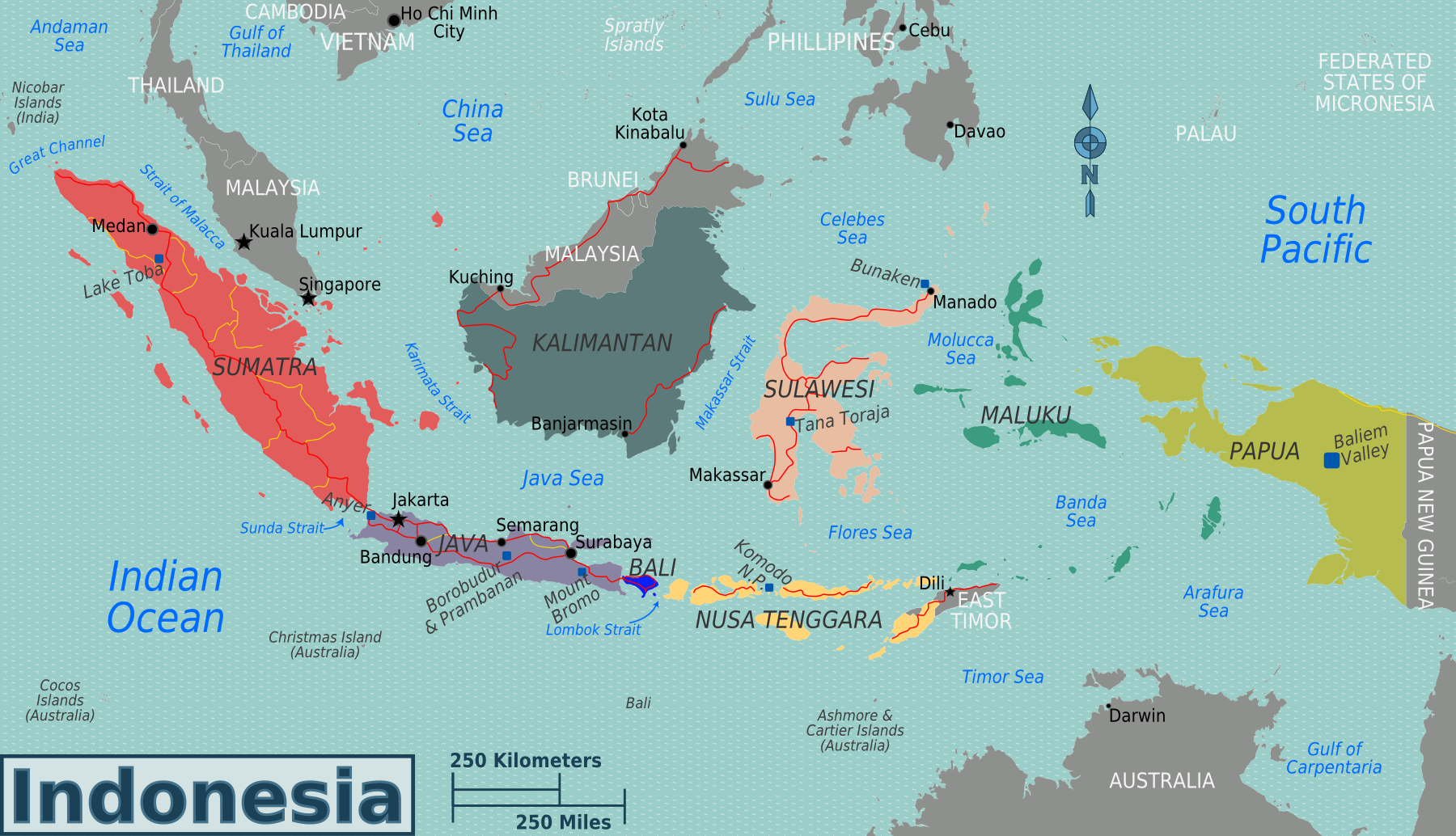
- Sumatra: The largest island in Indonesia, Sumatra is home to 10 provinces, each with its own distinct features. The northern provinces, such as Aceh and North Sumatra, are known for their cultural heritage and Islamic traditions. The central and southern provinces, including Riau and Jambi, are characterized by their rich natural resources, including oil and gas.
- Java: The most populous island in Indonesia, Java boasts 5 provinces, each playing a crucial role in the nation’s economy and culture. West Java, with its bustling capital Jakarta, is the heart of Indonesian industry and commerce. Central Java, home to the ancient temples of Borobudur and Prambanan, is a center of Javanese culture and spirituality. East Java, known for its vibrant cultural traditions and stunning natural beauty, is a popular tourist destination.
- Kalimantan: The third-largest island in the world, Kalimantan is divided into 5 provinces, all of which are rich in natural resources, particularly timber and oil palm plantations. The provinces of West Kalimantan and East Kalimantan are also home to diverse indigenous communities, preserving their traditions and cultures.
- Sulawesi: This island, known for its unique shape resembling a "K", is divided into 6 provinces, each with its own distinct identity. North Sulawesi, with its stunning beaches and volcanic landscapes, is a popular tourist destination. South Sulawesi, known for its vibrant cultural heritage and historical sites, is a center of trade and commerce.
- Maluku and Papua: These easternmost provinces, comprising 10 islands in total, are characterized by their unique cultures, diverse landscapes, and rich biodiversity. Maluku, known for its spice trade and stunning beaches, is a popular destination for diving and snorkeling. Papua, with its rugged mountains and dense rainforests, is home to a diverse range of indigenous cultures and unique wildlife.
The Significance of Provincial Boundaries:
The division of Indonesia into provinces serves several crucial purposes:
- Administrative Efficiency: By dividing the country into smaller, manageable units, the government can effectively manage and deliver services to its citizens. Each province has its own elected governor, legislature, and bureaucracy, allowing for localized decision-making and responsive governance.
- Cultural Preservation: The provincial boundaries often reflect the distinct cultural identities of different regions. This allows for the preservation of local languages, traditions, and customs, fostering a sense of belonging and cultural diversity within the nation.
- Economic Development: Each province possesses unique resources and strengths, allowing for specialized economic development strategies. This fosters regional growth and contributes to the overall economic prosperity of the nation.
- Resource Management: Dividing the country into provinces enables more efficient and localized management of natural resources, ensuring their sustainable use and preservation for future generations.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the provincial system plays a crucial role in Indonesia’s development, it also presents challenges:
- Regional Disparities: Despite economic growth, significant disparities exist between provinces, with some lagging behind in terms of infrastructure, education, and healthcare. Addressing these disparities requires targeted policies and investments.
- Interprovincial Conflicts: Differences in resource allocation, cultural identities, and political aspirations can lead to tensions and conflicts between provinces. Promoting interprovincial cooperation and dialogue is essential for maintaining national unity.
- Environmental Challenges: The provinces face various environmental challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. Collaborative efforts are needed to ensure sustainable development and environmental protection.
FAQs about Indonesian Provinces:
Q: What is the most populous province in Indonesia?
A: West Java is the most populous province, with a population exceeding 48 million.
Q: Which province has the highest GDP?
A: Jakarta, the capital city, holds the highest GDP, followed by East Java and West Java.
Q: What are some of the most popular tourist destinations in Indonesia?
A: Popular tourist destinations include Bali, Lombok, Yogyakarta, Raja Ampat, and the Komodo National Park.
Q: How many provinces are there in Indonesia?
A: Indonesia is currently divided into 34 provinces.
Tips for Exploring Indonesian Provinces:
- Research your destination: Each province offers unique experiences. Research local customs, traditions, and attractions before your trip.
- Embrace cultural diversity: Indonesia is a melting pot of cultures. Engage with local communities, learn about their traditions, and appreciate their unique perspectives.
- Respect local customs: Dress modestly, be mindful of local etiquette, and avoid offensive behavior.
- Consider the best time to visit: Indonesia’s climate varies significantly across provinces. Research the best time to visit for optimal weather conditions.
- Support local businesses: Patronize local restaurants, shops, and tour operators to contribute to the local economy.
Conclusion:
Understanding the map of Indonesian provinces is key to comprehending the nation’s rich tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and resources. Each province contributes uniquely to the national fabric, showcasing the diversity and dynamism of this archipelago nation. By acknowledging the challenges and opportunities associated with the provincial system, Indonesia can strive for inclusive and sustainable development, ensuring a brighter future for all its citizens.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Indonesian Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!