Navigating The Indian Ocean: A Geographical And Strategic Overview
Navigating the Indian Ocean: A Geographical and Strategic Overview
Related Articles: Navigating the Indian Ocean: A Geographical and Strategic Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Indian Ocean: A Geographical and Strategic Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Indian Ocean: A Geographical and Strategic Overview
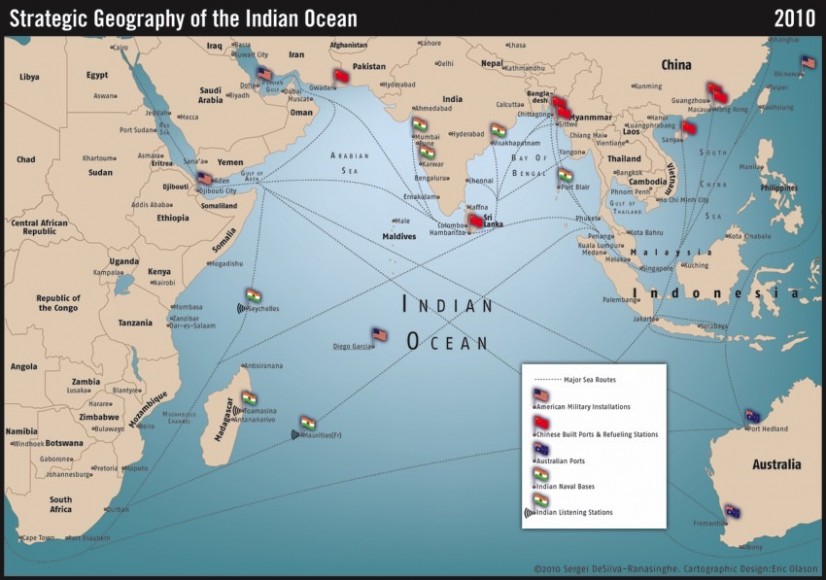
The Indian Ocean, the third largest of the world’s five oceans, is a vast expanse of water that plays a crucial role in global trade, climate, and geopolitics. Its shores are home to a diverse array of countries, each with its own unique history, culture, and challenges. Understanding the geography and strategic importance of these nations is essential for comprehending the complexities of the region and its impact on the world.
A Diverse Tapestry of Nations:
The Indian Ocean basin encompasses a vast swathe of land, spanning from the eastern coast of Africa to the western shores of Southeast Asia. This region includes:
- Africa: The eastern coast of Africa, including nations like Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, and South Africa, forms a significant part of the Indian Ocean’s geography. These countries are characterized by their diverse ecosystems, from coastal plains to mountainous regions, and play a key role in trade routes connecting Africa with Asia and the Middle East.
- The Arabian Peninsula: The Arabian Peninsula, home to nations like Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates, is a major oil-producing region and holds significant geopolitical influence. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Africa, Asia, and Europe makes it a crucial player in global affairs.
- The Indian Subcontinent: India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives form the Indian subcontinent, a densely populated region with rich cultural heritage and a long history of trade and maritime activity. These countries are major players in the global economy and hold significant influence within the Indian Ocean region.
- Southeast Asia: Nations like Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand, along with smaller island nations, contribute to the diverse cultural and economic landscape of the Indian Ocean. These countries are crucial to global trade, particularly in the technology and manufacturing sectors.
- Australia: Although geographically located in Oceania, Australia’s northern coastline borders the Indian Ocean and plays a significant role in regional affairs. Its vast resources and strategic location make it a crucial player in the Indian Ocean’s geopolitical landscape.
The Importance of the Indian Ocean:
The Indian Ocean’s significance stems from several factors:
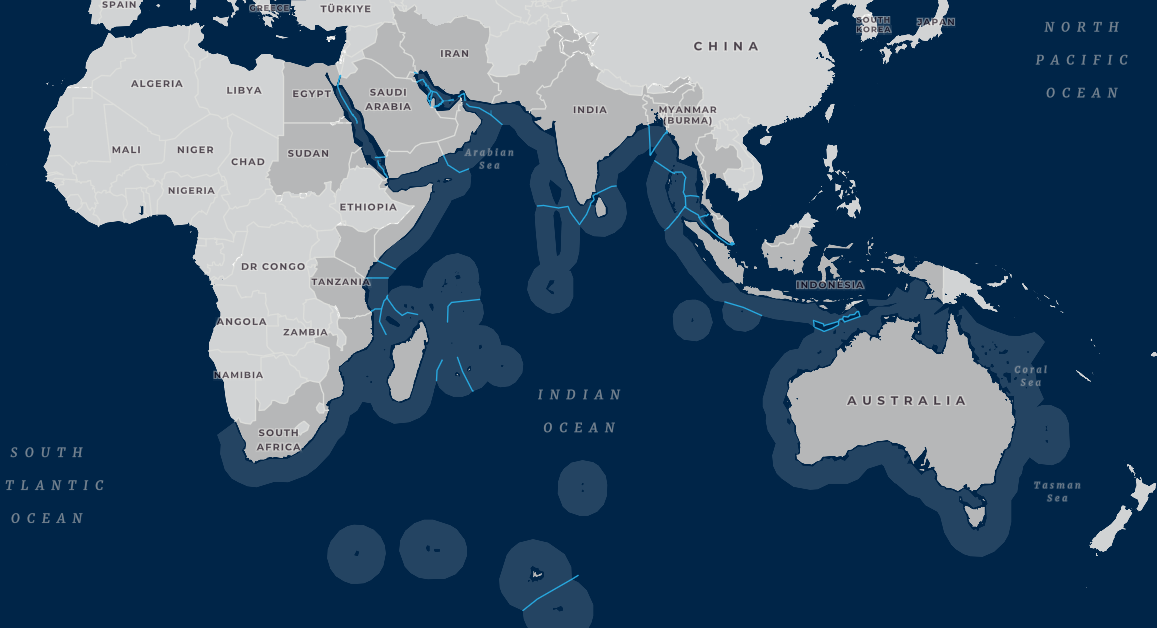
- Trade Routes: Historically, the Indian Ocean has been a major trade route connecting the East and West, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. This legacy continues today, with the Indian Ocean playing a crucial role in global trade, particularly for oil, gas, and other commodities.
- Energy Security: The Indian Ocean is home to significant oil and gas reserves, making it a crucial source of energy for many countries. The region’s geopolitical stability and the security of these energy resources are vital for global economic stability.
- Climate Change: The Indian Ocean is susceptible to climate change, with rising sea levels, changes in ocean currents, and more frequent extreme weather events. These changes have significant implications for coastal communities, fisheries, and overall regional stability.
- Geopolitical Influence: The Indian Ocean is a strategically important region, with several major powers vying for influence. The United States, China, India, and other nations are increasing their military presence in the region, leading to heightened tensions and competition.
- Biodiversity: The Indian Ocean is home to a vast array of marine life, including whales, dolphins, sharks, and coral reefs. This biodiversity is threatened by pollution, overfishing, and climate change, highlighting the need for sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
Navigating the Challenges:
The Indian Ocean faces numerous challenges, including:
- Maritime Security: Piracy, terrorism, and other security threats pose significant risks to maritime trade and regional stability. International cooperation is crucial to address these challenges and ensure the safety of shipping lanes.
- Environmental Degradation: Pollution, overfishing, and climate change are impacting the health of the Indian Ocean’s ecosystems. Sustainable practices and international cooperation are essential to mitigate these threats and protect the region’s biodiversity.
- Economic Inequality: The Indian Ocean region is characterized by significant economic disparities, with some countries experiencing rapid growth while others struggle with poverty and inequality. Addressing these disparities is crucial for regional stability and development.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Rising competition for influence between major powers in the Indian Ocean creates geopolitical tensions. Diplomatic efforts and dialogue are essential to manage these tensions and prevent conflicts.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major maritime trade routes in the Indian Ocean?
A: The Indian Ocean is home to several key maritime trade routes, including:
- The Suez Canal: Connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, the Suez Canal is a vital waterway for global trade, facilitating the movement of goods between Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- The Strait of Malacca: Located between Malaysia and Indonesia, the Strait of Malacca is one of the busiest shipping lanes in the world, carrying a significant amount of global trade.
- The Bab el-Mandeb Strait: Connecting the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden, the Bab el-Mandeb Strait is a crucial route for oil tankers and other vessels travelling between the Middle East and Europe.
- The Cape of Good Hope: Located at the southern tip of Africa, the Cape of Good Hope is a historic maritime route connecting the Atlantic and Indian Oceans.
Q: How does climate change affect the Indian Ocean?
A: Climate change has significant impacts on the Indian Ocean, including:
- Rising Sea Levels: Sea levels are rising due to melting glaciers and thermal expansion of ocean water, posing threats to coastal communities and infrastructure.
- Changes in Ocean Currents: Climate change is altering ocean currents, affecting marine ecosystems and weather patterns.
- Increased Frequency and Intensity of Extreme Weather Events: The Indian Ocean region is experiencing more frequent and intense cyclones, floods, and droughts, impacting livelihoods and infrastructure.
Q: What are the major geopolitical players in the Indian Ocean?
A: Several major powers are vying for influence in the Indian Ocean, including:
- The United States: The United States maintains a strong military presence in the Indian Ocean, with bases in Diego Garcia and other locations.
- China: China is rapidly expanding its economic and military influence in the region, investing heavily in infrastructure projects and establishing naval bases.
- India: India views the Indian Ocean as its strategic backyard and is actively increasing its military capabilities and diplomatic engagement in the region.
- Other Nations: Other countries, including Japan, Australia, France, and Russia, are also seeking to increase their influence in the Indian Ocean.
Tips for Navigating the Indian Ocean’s Complexities:
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of current events and developments in the Indian Ocean region through news sources, think tanks, and academic publications.
- Foster Dialogue and Cooperation: Promote dialogue and cooperation between countries in the region to address shared challenges and build trust.
- Support Sustainable Practices: Promote sustainable practices in fisheries, shipping, and other sectors to protect the Indian Ocean’s environment.
- Invest in Infrastructure: Invest in infrastructure projects that enhance connectivity and facilitate trade within the region.
Conclusion:
The Indian Ocean is a region of immense diversity, strategic importance, and complex challenges. Its geography, history, and current dynamics shape global trade, climate, and security. Understanding the nuances of the Indian Ocean’s landscape is crucial for navigating the complexities of the 21st century. By promoting dialogue, cooperation, and sustainable practices, the nations of the Indian Ocean can harness the region’s potential and build a more prosperous and secure future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Indian Ocean: A Geographical and Strategic Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!