Navigating The Email Landscape: Understanding IMAP And POP3
Navigating the Email Landscape: Understanding IMAP and POP3
Related Articles: Navigating the Email Landscape: Understanding IMAP and POP3
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Email Landscape: Understanding IMAP and POP3. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Email Landscape: Understanding IMAP and POP3
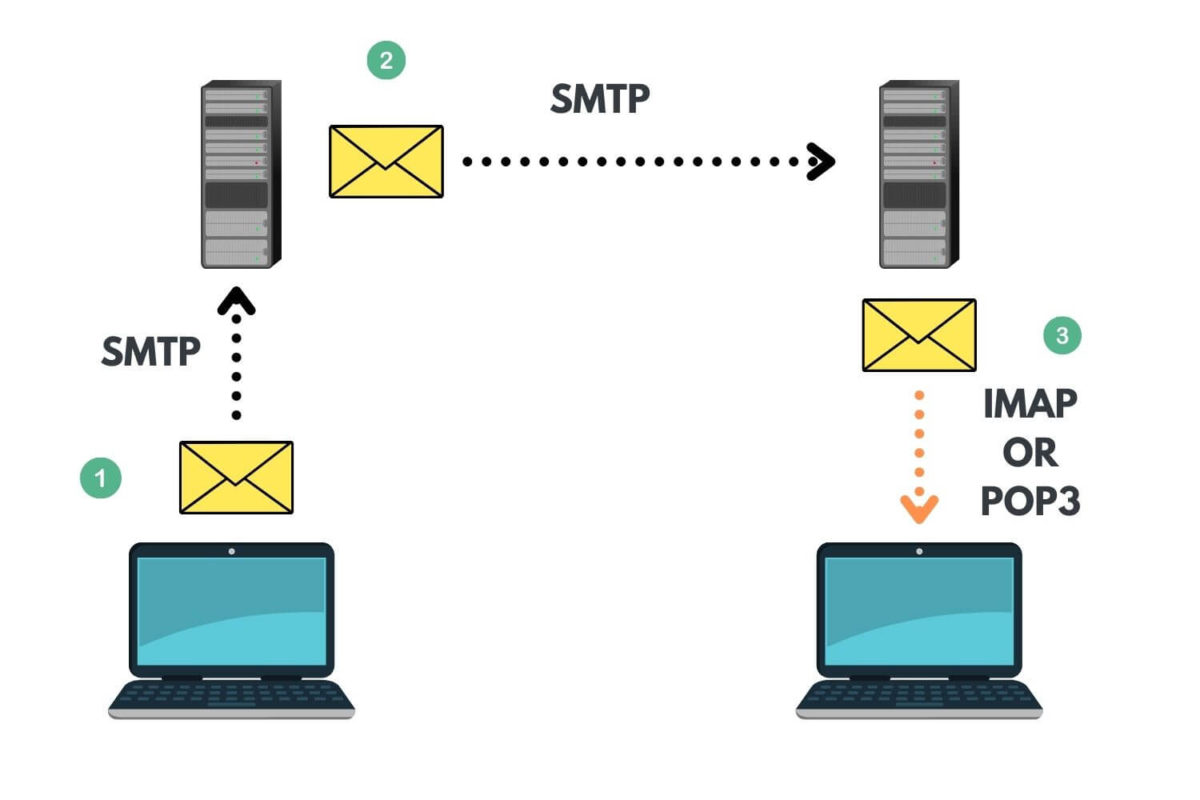
In the digital age, email communication has become an indispensable tool for individuals and businesses alike. Efficiently managing email necessitates understanding the underlying protocols that govern email retrieval and storage. Two prominent protocols, IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) and POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3), serve as the foundation for email access, but they differ significantly in their approach to email handling. This article delves into the intricacies of IMAP and POP3, highlighting their distinctive features, advantages, and disadvantages to enable informed decision-making when selecting the most suitable protocol for your email needs.
IMAP: A Centralized Email Hub
IMAP operates as a centralized email management system, allowing users to access their emails from multiple devices simultaneously. The protocol synchronizes email data across all connected devices, ensuring that any changes made on one device are reflected on all others. This seamless integration fosters a unified email experience, irrespective of the device being used.
Key Features of IMAP:
- Centralized Storage: IMAP stores all emails on the server, eliminating the need to download and store them locally on each device. This centralized approach ensures that emails are readily accessible from any location with an internet connection.
- Synchronization Across Devices: Changes made to emails, such as marking them as read or deleting them, are automatically synchronized across all connected devices. This real-time synchronization ensures consistency and eliminates the need to manually manage email folders across multiple devices.
- Offline Access: IMAP allows users to access emails offline, even when not connected to the internet. This feature is particularly valuable for users who frequently travel or work in areas with limited internet connectivity.
- Multiple Folders: IMAP supports the creation of multiple folders for organizing emails, enabling users to categorize emails based on their content, sender, or other criteria. This structured approach enhances email management and facilitates efficient retrieval.
- Search Functionality: IMAP provides robust search capabilities, allowing users to easily find specific emails based on keywords, senders, dates, and other criteria. This powerful search function streamlines email retrieval and eliminates the need to manually sift through numerous emails.
POP3: A Local Email Download
In contrast to IMAP’s centralized approach, POP3 operates by downloading emails to the local device. Each email is downloaded and stored on the device, effectively making a copy of the email on the server. This local storage approach provides a degree of autonomy, but it comes with certain limitations.
Key Features of POP3:
- Local Storage: POP3 downloads emails to the local device, making them accessible even without an internet connection. This offline access is a key advantage for users who require email access in areas with limited internet connectivity.
- Limited Synchronization: POP3 does not synchronize email data across multiple devices. Changes made on one device are not reflected on other devices. This lack of synchronization can lead to inconsistencies and require manual management of emails across different devices.
- Email Deletion: POP3 typically deletes emails from the server once they are downloaded to the local device. This deletion can be problematic if users need to access the same email from multiple devices or require a backup copy of their emails.
- Limited Functionality: POP3 offers limited functionality compared to IMAP. It does not support features such as multiple folders, synchronization, or robust search capabilities.
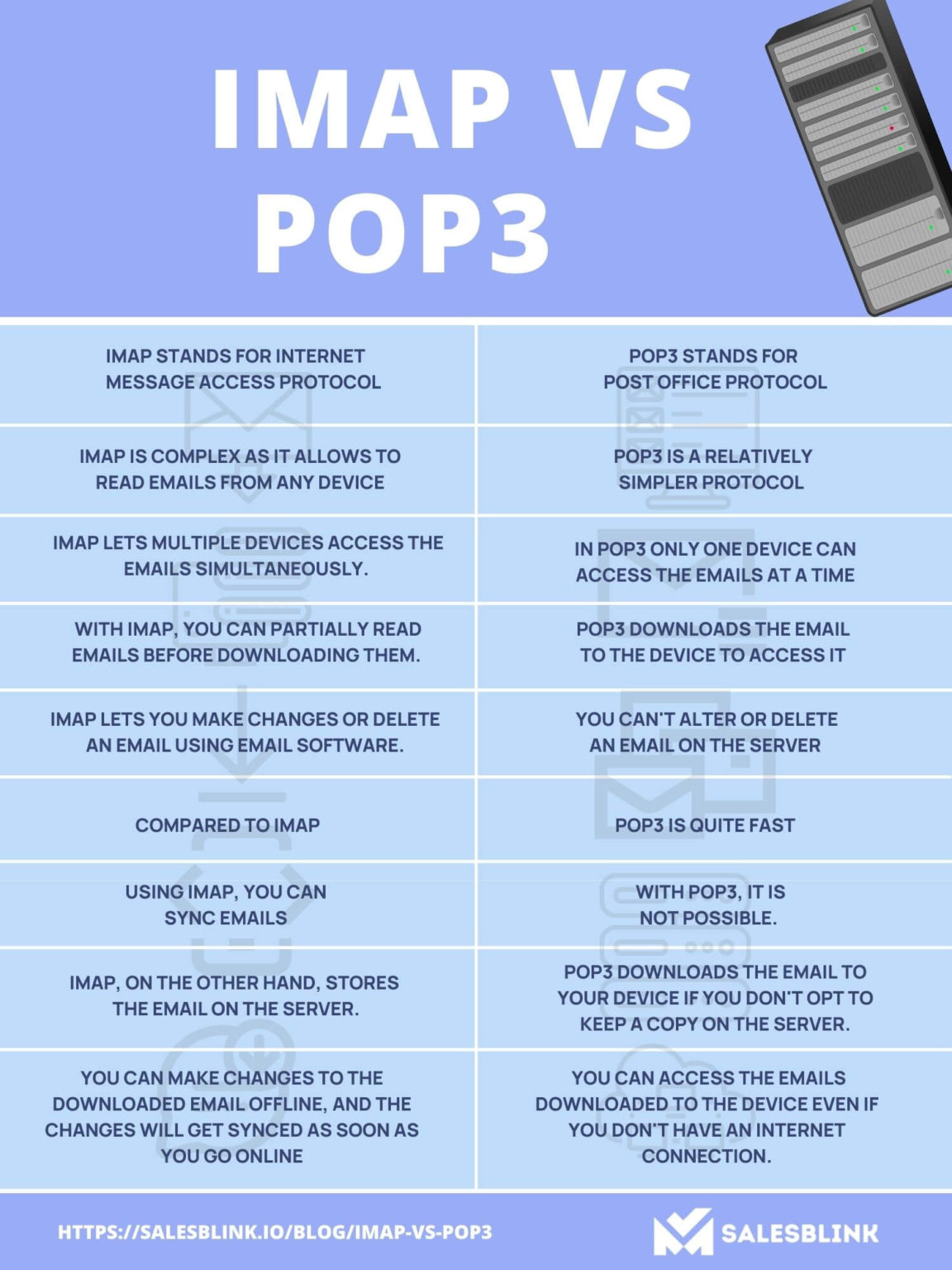
Choosing the Right Protocol: A Comparative Analysis
The choice between IMAP and POP3 hinges on individual email usage patterns and preferences. IMAP offers a centralized, synchronized, and feature-rich email management experience, making it an ideal choice for users who frequently access emails from multiple devices or require a robust email organization system. POP3, on the other hand, provides a local storage approach with offline access, making it suitable for users who prioritize offline email access and do not require extensive email management capabilities.
Table: Comparing IMAP and POP3
| Feature | IMAP | POP3 |
|---|---|---|
| Email Storage | Server-based | Local device |
| Synchronization | Yes | No |
| Offline Access | Yes | Yes |
| Multiple Folders | Yes | No |
| Search Functionality | Yes | Limited |
| Email Deletion | Remains on server | Deleted from server |
| Device Compatibility | Wide | Limited |
Advantages of IMAP:
- Centralized Email Management: IMAP simplifies email management by providing a single point of access for all emails.
- Synchronization Across Devices: IMAP ensures that email data is consistent across all connected devices, eliminating the need for manual management.
- Offline Access: IMAP allows users to access emails even when offline, ensuring uninterrupted email access.
- Robust Search Capabilities: IMAP’s advanced search functionality streamlines email retrieval and facilitates efficient email management.
- Multiple Folder Support: IMAP enables users to organize emails into multiple folders, enhancing email organization and retrieval.
Advantages of POP3:
- Offline Access: POP3 provides offline access to emails, making it suitable for users who require email access in areas with limited internet connectivity.
- Simplified Setup: POP3 is relatively straightforward to set up and configure, making it an attractive option for users who prefer a simple email setup.
Disadvantages of IMAP:
- Internet Dependence: IMAP relies on a constant internet connection for email access, making it unsuitable for users who frequently work offline.
- Potential for Data Loss: If the server storing IMAP emails encounters a failure, users could potentially lose access to their emails.
Disadvantages of POP3:
- Limited Functionality: POP3 lacks the advanced features and capabilities of IMAP, such as synchronization, multiple folders, and robust search capabilities.
- Email Deletion: POP3 typically deletes emails from the server after downloading them, which can lead to data loss or accessibility issues.
- Lack of Synchronization: POP3 does not synchronize email data across devices, leading to inconsistencies and requiring manual management.
FAQs: Deciphering the Protocol Puzzle
1. Which protocol is better for me?
The best protocol for you depends on your individual email usage patterns and preferences. If you frequently access emails from multiple devices, require email synchronization, and prefer a centralized email management system, IMAP is the better choice. If you prioritize offline access and do not require extensive email management features, POP3 may be more suitable.
2. Can I switch protocols?
Yes, you can switch between IMAP and POP3 protocols. However, switching protocols may require reconfiguring your email client and potentially transferring emails between the server and your local device.
3. How do I configure IMAP or POP3 in my email client?
The configuration process for IMAP and POP3 varies depending on the email client you are using. Consult your email client’s documentation for instructions on configuring the desired protocol.
4. What is the difference between IMAP and POP3 security?
Both IMAP and POP3 can be secured using SSL/TLS encryption, which protects email communication from eavesdropping. However, the level of security may vary depending on the email provider and the specific implementation of the protocol.
5. What are the benefits of using IMAP?
IMAP offers a centralized, synchronized, and feature-rich email management experience, making it ideal for users who require a robust email organization system and access emails from multiple devices.
6. What are the benefits of using POP3?
POP3 provides offline access to emails, making it suitable for users who prioritize offline access and do not require extensive email management features.
Tips: Mastering Email Management
- Choose the right protocol: Select the protocol that aligns with your email usage patterns and preferences.
- Configure your email client correctly: Ensure that your email client is properly configured for the chosen protocol.
- Back up your emails: Regularly back up your emails to protect against data loss.
- Use email filters: Implement filters to automatically organize and manage incoming emails.
- Keep your email client updated: Install the latest updates for your email client to ensure optimal performance and security.
Conclusion: Navigating the Email Landscape with Confidence
Understanding the nuances of IMAP and POP3 empowers users to make informed decisions about email management. IMAP, with its centralized storage, synchronization capabilities, and robust features, offers a comprehensive and efficient approach to email management. POP3, while limited in functionality, provides offline access, making it suitable for users who prioritize offline access and require a simpler email setup. By carefully considering individual email needs and preferences, users can choose the protocol that best aligns with their email management goals, ensuring a smooth and efficient email experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Email Landscape: Understanding IMAP and POP3. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
