Navigating The Electrical Landscape Of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide To The 50/60 Hz Divide
Navigating the Electrical Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50/60 Hz Divide
Related Articles: Navigating the Electrical Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50/60 Hz Divide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Electrical Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50/60 Hz Divide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Electrical Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50/60 Hz Divide
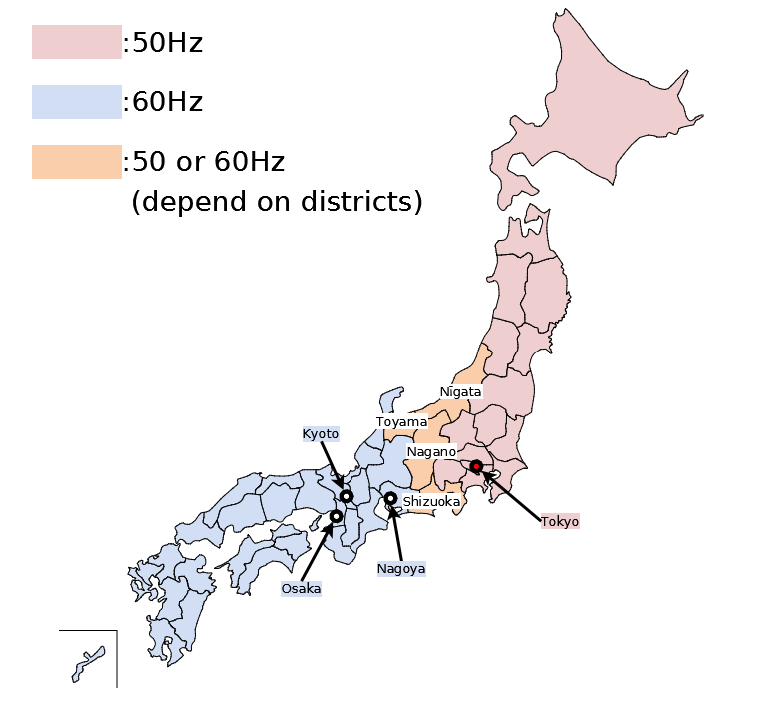
Japan, a technological powerhouse, presents a unique challenge to travelers and businesses alike: a split electrical grid operating at two distinct frequencies. Understanding this division, commonly referred to as the "50/60 Hz map," is crucial for ensuring compatibility of electronic devices and avoiding potential damage. This article provides a comprehensive overview of this phenomenon, its historical origins, practical implications, and strategies for navigating it successfully.
The 50/60 Hz Divide: A Historical Perspective
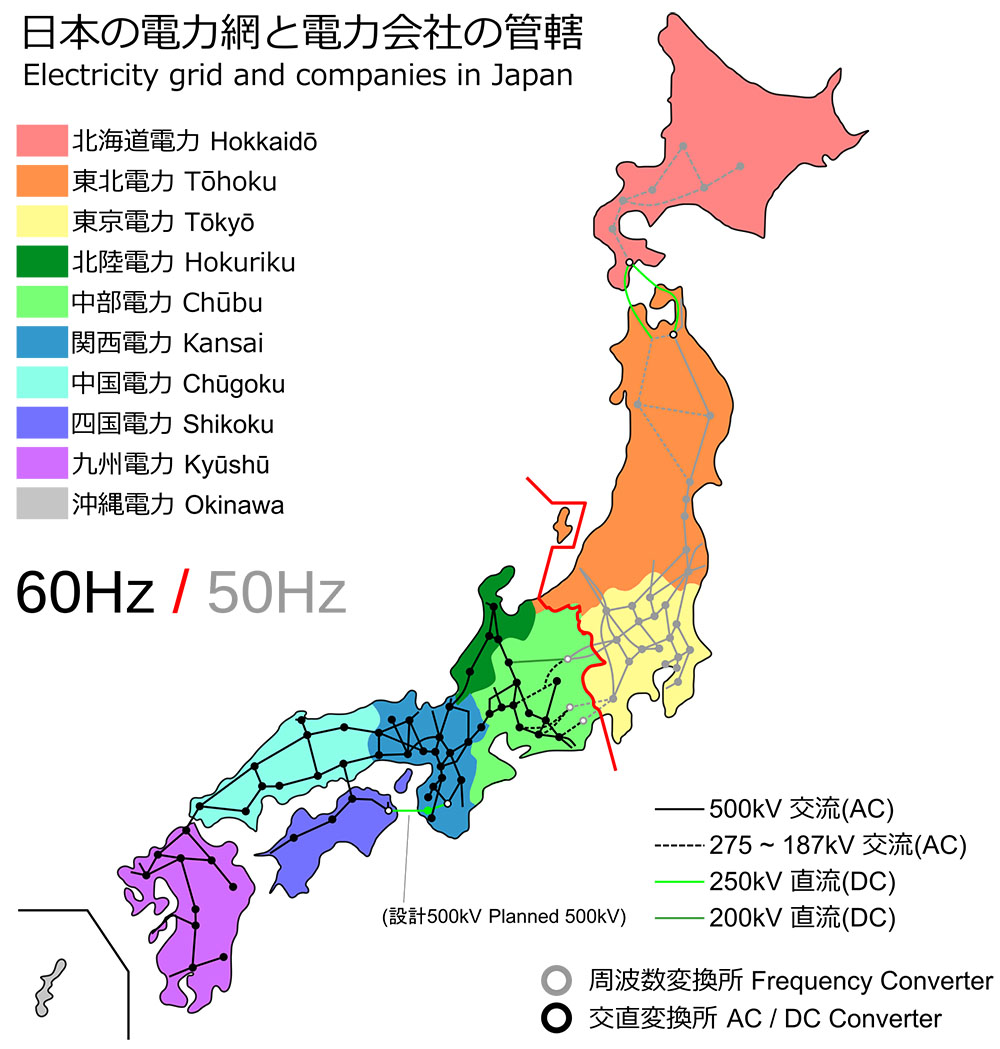
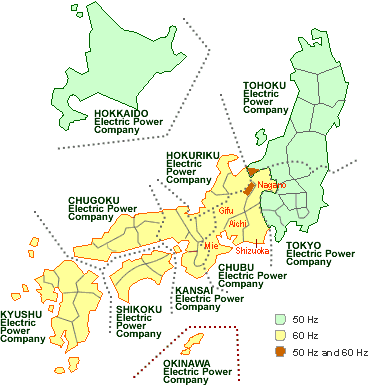
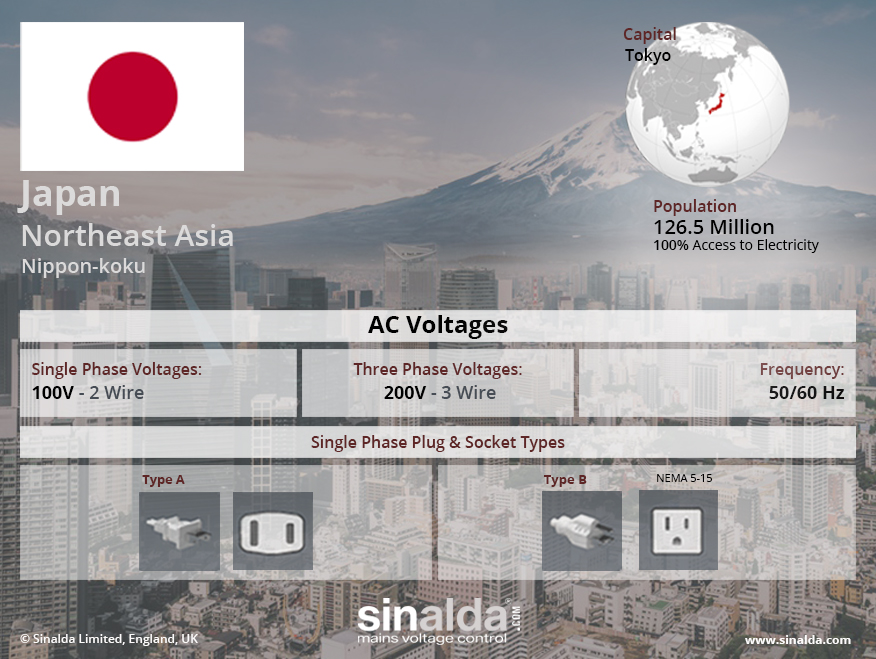
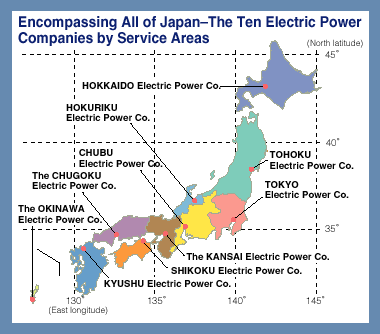
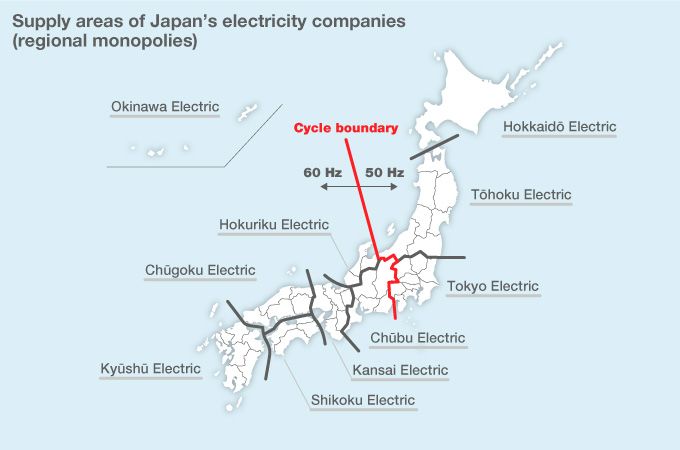
The electrical grid in Japan operates at two distinct frequencies: 50 Hz in the eastern region and 60 Hz in the western region. This seemingly arbitrary division stems from the nation’s early industrial development.
- Eastern Region (50 Hz): Tokyo, the capital, adopted a 50 Hz system in the early 20th century, based on the influence of German engineers who were involved in the initial development of the Japanese power grid.
- Western Region (60 Hz): Osaka, a major industrial hub, opted for a 60 Hz system, largely influenced by American engineers who played a significant role in the region’s power infrastructure.
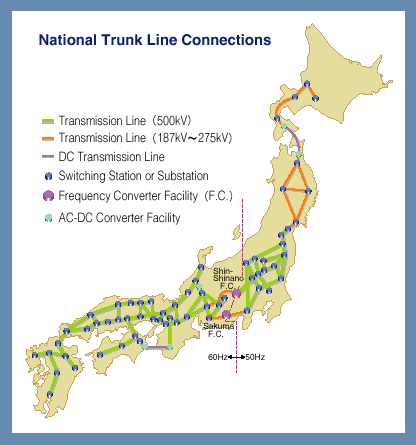
This historical divergence resulted in a permanent split, with the boundary line roughly following the 135th meridian east. The two systems remain incompatible, meaning devices designed for one frequency cannot be directly plugged into the other without risking damage.
Practical Implications of the 50/60 Hz Divide
The 50/60 Hz divide poses several practical challenges:
- Device Compatibility: Electronics designed for one frequency may malfunction or be damaged when used on the other. Appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners are particularly vulnerable.
- Voltage Conversion: While the voltage in both regions is 100V, the frequency difference necessitates voltage converters for devices designed for different frequencies.
- Travel and Business: Travelers and businesses need to be aware of the frequency difference when bringing electronics to Japan. This includes ensuring the compatibility of laptops, smartphones, chargers, and other essential devices.
- Industrial Considerations: The frequency difference can complicate the operation of industrial equipment and machinery, especially those with motors and other sensitive components.
Navigating the Frequency Difference: A Guide for Travelers and Businesses
Understanding the 50/60 Hz divide is essential for smooth travel and business operations in Japan. Here’s a breakdown of key considerations:
- Device Compatibility: Always check the frequency specifications of electronic devices before bringing them to Japan. Devices labeled as "dual voltage" or "universal" are generally compatible with both 50 Hz and 60 Hz systems.
- Voltage Converters: For devices that are not dual voltage, voltage converters are essential for safe and efficient operation. Ensure the converter is rated for the correct voltage and frequency.
- Frequency Adapters: Frequency adapters are not necessary for most devices, as voltage conversion typically addresses frequency differences. However, some sensitive electronics may require a frequency adapter, particularly for long-term use.
- Local Power Supplies: In many hotels and public areas, power outlets are labeled with the appropriate frequency. Always check the label before plugging in any device.
- Consult with Manufacturers: If you have any concerns about the compatibility of specific devices, consult the manufacturer’s website or contact their customer support.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the 50/60 Hz Divide
Q: What happens if I plug a 60 Hz device into a 50 Hz outlet?
A: The device may malfunction or be damaged. The motor speed of appliances like refrigerators and washing machines may be affected, potentially leading to overheating or failure.
Q: Can I use a voltage converter for both voltage and frequency conversion?
A: While some voltage converters claim to handle both voltage and frequency, it is generally not recommended. Frequency conversion requires specialized equipment and may not be reliable.
Q: Is there a universal power adapter for Japan?
A: There is no single universal adapter that covers both voltage and frequency. You may need a combination of voltage converters and frequency adapters depending on the specific devices you are using.
Q: Are there any areas in Japan where the frequency is different?
A: No, the 50 Hz and 60 Hz regions are clearly defined, and there are no known areas with mixed frequencies.
Tips: Ensuring Compatibility and Avoiding Problems
- Research Before You Travel: Check the frequency requirements of all electronic devices you plan to bring to Japan.
- Pack Dual Voltage Devices: Prioritize devices that are compatible with both 50 Hz and 60 Hz.
- Invest in Quality Converters: Choose reliable and certified voltage converters for devices that require them.
- Be Aware of Outlet Labels: Pay attention to the frequency labels on power outlets in hotels, restaurants, and other public areas.
- Consult with Local Experts: If you have any doubts or concerns, seek assistance from local experts or hotel staff.
Conclusion: A Navigable Challenge
The 50/60 Hz divide in Japan may seem like a complex issue, but with careful planning and awareness, it can be easily navigated. By understanding the historical context, practical implications, and available solutions, travelers and businesses can ensure the smooth operation of their electronic devices and avoid potential damage. The key is to be informed, prepared, and proactive in addressing this unique aspect of Japan’s electrical infrastructure.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Electrical Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50/60 Hz Divide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!