Navigating The Complexities Of The Map Of Israel Today
Navigating the Complexities of the Map of Israel Today
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of the Map of Israel Today
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of the Map of Israel Today. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of the Map of Israel Today
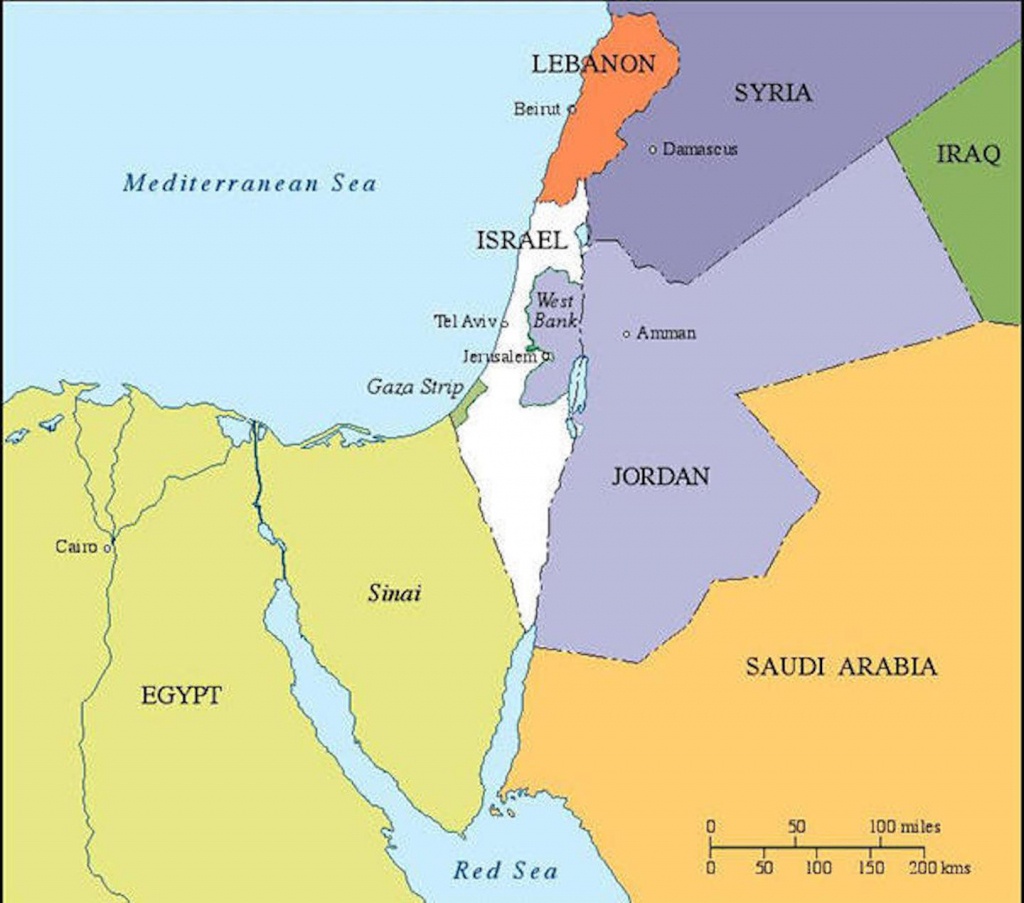
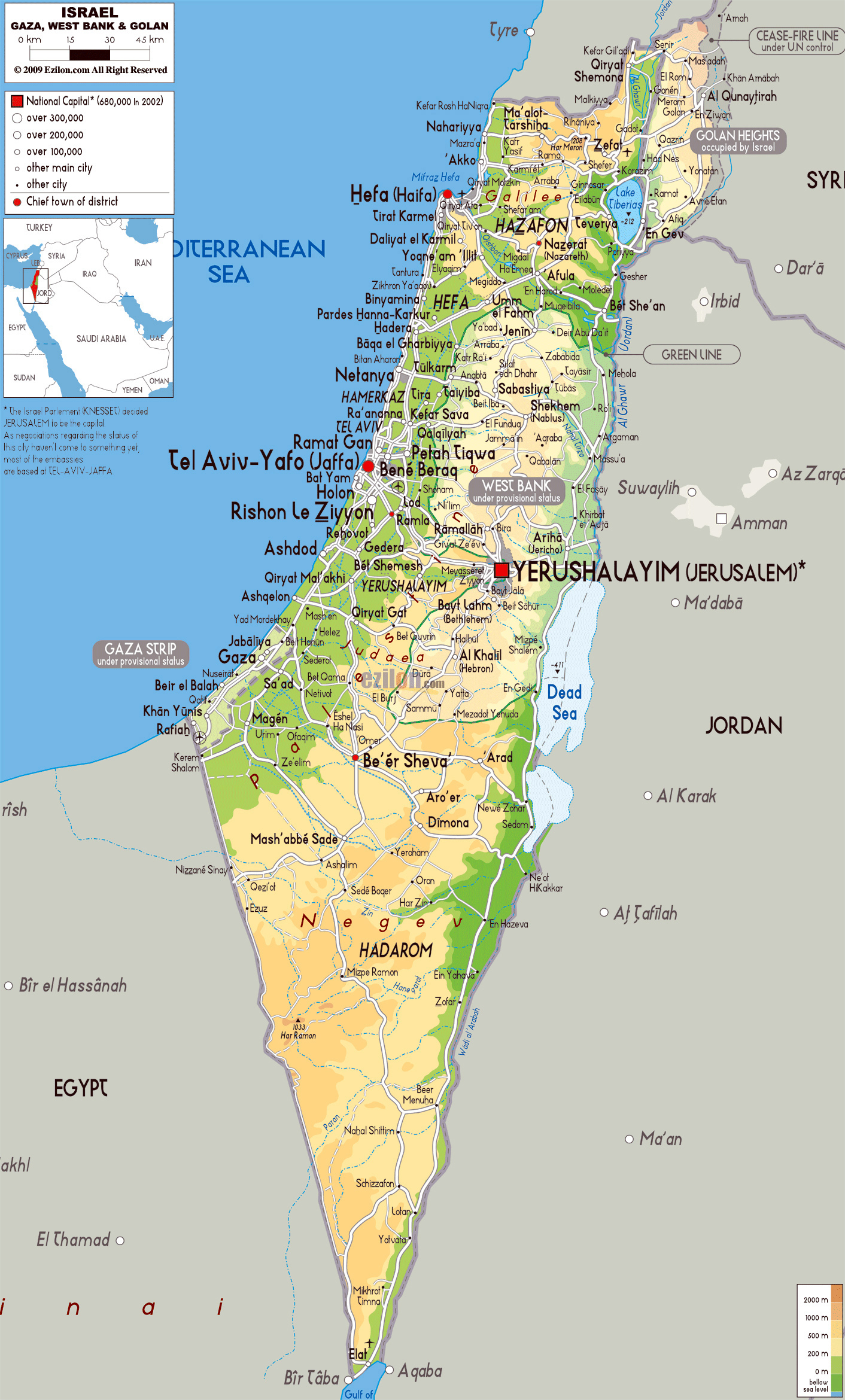
The map of Israel today presents a complex and dynamic landscape, shaped by historical, political, and social forces. Understanding its intricacies requires navigating a web of contested territories, disputed borders, and diverse populations. This article delves into the key elements of the modern Israeli map, exploring its historical context, political realities, and the challenges it faces.
Historical Context: A Land of Contested Claims
The land known as Israel today has been a focal point of conflict and struggle for millennia. The region has been home to various empires and civilizations, each leaving their mark on the landscape and its inhabitants. The ancient Israelites, who gave the land its name, established their kingdom in the 10th century BCE, and their history is intertwined with the development of Judaism.
Following the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE, Jewish communities dispersed throughout the world. The land remained under various foreign powers, including the Roman Empire, the Byzantine Empire, and the Ottoman Empire. The Zionist movement, which emerged in the 19th century, aimed to establish a Jewish homeland in Palestine. This movement gained momentum following the Holocaust, leading to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948.
The creation of Israel triggered the first Arab-Israeli War, resulting in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians. The war also left Israel in control of territories beyond its declared borders, including the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip. These territories remain at the heart of the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Political Realities: A Complex Mosaic of Control and Dispute
The map of Israel today reflects the intricate political landscape of the region. The country is divided into distinct areas, each with its own legal and administrative status.
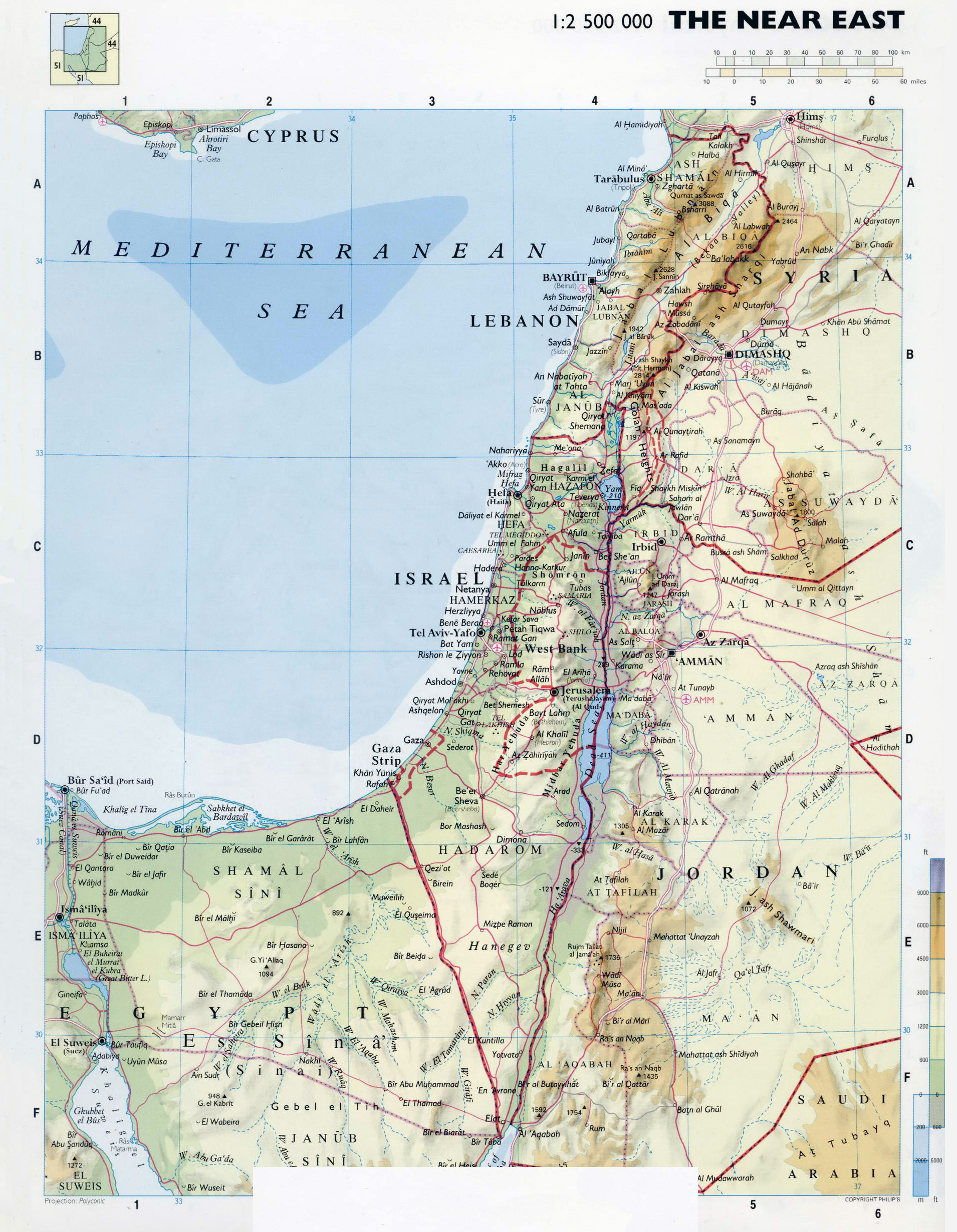
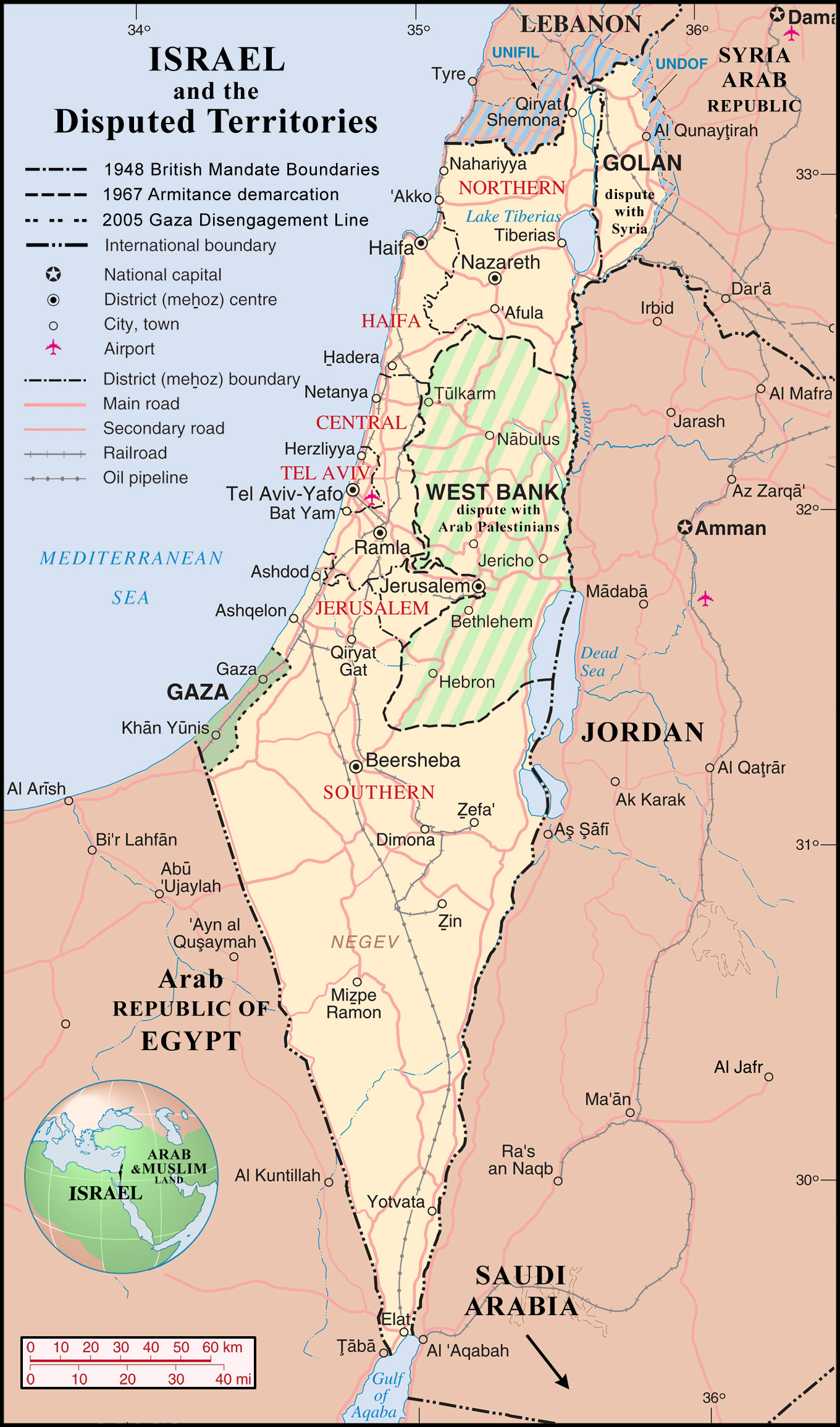
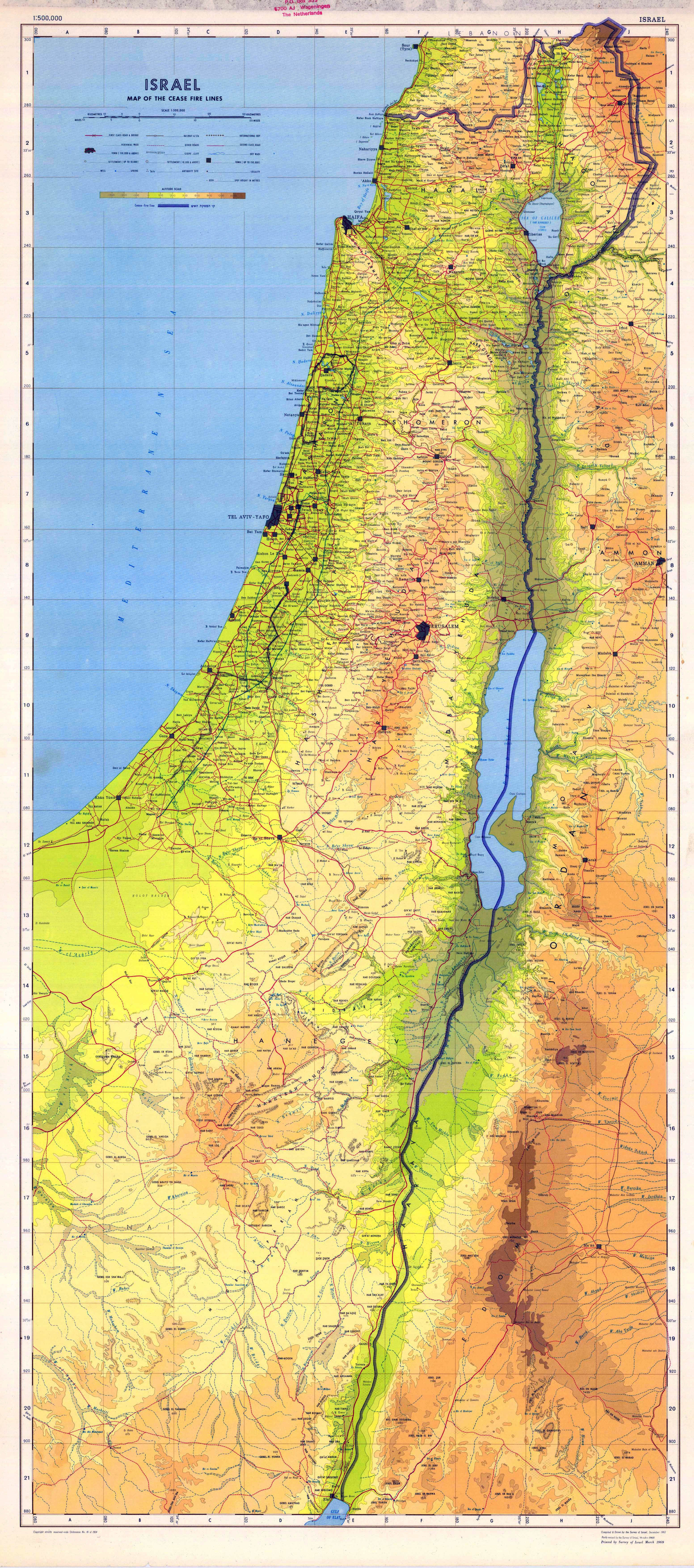
- Israel Proper: This area comprises the territory controlled by Israel since its independence in 1948. It encompasses the coastal plain, the Galilee region, and the Negev desert. This area is considered the core of the Israeli state, and it houses the majority of its population.
- The West Bank: This territory, located west of the Jordan River, is considered occupied by Israel under international law. It is home to a significant Palestinian population, with the majority residing in the cities of Ramallah, Hebron, and Bethlehem. The West Bank is divided into Area A, controlled by the Palestinian Authority, Area B, with shared control, and Area C, under full Israeli control.
- East Jerusalem: This area, captured by Israel in 1967, is claimed by both Israel and Palestine. Israel annexed East Jerusalem in 1980, a move not recognized by the international community. The city is home to important religious sites for Jews, Christians, and Muslims, making it a focal point of religious and political tension.
- The Gaza Strip: This coastal territory, separated from the West Bank by Israeli territory, is governed by the Hamas movement, which has been engaged in conflict with Israel since 2007. The territory is densely populated and faces significant economic and humanitarian challenges.
These distinct areas highlight the complex mosaic of control and dispute that defines the Israeli map. The legal and political status of these territories remains a source of ongoing conflict, with both Israelis and Palestinians claiming rights to the land.
Challenges and Controversies: A Spectrum of Perspectives
The map of Israel today is not only a geographical representation but also a reflection of ongoing challenges and controversies. These include:
- The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The conflict between Israel and Palestine remains the defining issue in the region. The two-state solution, which proposes the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, has been the dominant framework for peace negotiations. However, the lack of progress in negotiations and the ongoing disputes over land, borders, and Jerusalem have cast doubt on the viability of this solution.
- Settlements: The construction of Israeli settlements in the West Bank, considered illegal under international law, has been a significant point of contention. Settlements contribute to the fragmentation of the West Bank and hinder the possibility of a contiguous Palestinian state.
- Security: Israel’s security concerns are deeply intertwined with its territorial claims and its relationship with its neighbors. The country has faced numerous terrorist attacks and military conflicts, leading to a focus on security measures and the development of a powerful military force.
- Demographics: The demographic composition of Israel is changing rapidly. The Palestinian population in the West Bank and Gaza is growing at a faster rate than the Israeli population. This shift raises concerns about the long-term viability of a two-state solution and the future of the region.
- International Relations: Israel’s relationship with the international community is complex and often strained. The country faces criticism over its treatment of Palestinians, its settlements, and its military actions. International pressure and sanctions have been applied in an attempt to influence Israeli policy.
These challenges and controversies highlight the complex and often conflicting perspectives surrounding the map of Israel today. Navigating these issues requires a nuanced understanding of the historical context, political realities, and the diverse voices involved.
FAQs on the Map of Israel Today
1. What is the status of the West Bank?
The West Bank is considered occupied territory under international law, with Israel controlling most of the land and resources. The Palestinian Authority governs certain areas of the West Bank, but its authority is limited by Israeli control.
2. What is the status of East Jerusalem?
East Jerusalem was annexed by Israel in 1980, a move not recognized by the international community. Both Israel and Palestine claim sovereignty over the city.
3. What is the two-state solution?
The two-state solution proposes the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, with both states coexisting peacefully. This solution has been the dominant framework for peace negotiations, but it has faced significant challenges and setbacks.
4. What is the role of the United Nations in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict?
The United Nations has been actively involved in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict since its inception. The organization has passed numerous resolutions condemning Israeli actions and calling for a two-state solution. The UN also provides humanitarian assistance to Palestinians in the West Bank and Gaza.
5. What are the main challenges facing Israel today?
Israel faces a range of challenges, including the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the security threat posed by Hamas and other militant groups, the economic impact of the conflict, and the growing international criticism over its policies.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Israel Today
- Consult reliable sources: Seek information from credible news organizations, academic institutions, and international organizations.
- Consider multiple perspectives: Engage with a variety of viewpoints on the conflict, including those of Israelis, Palestinians, and international actors.
- Learn about the history of the region: Understanding the historical context is crucial for understanding the current situation.
- Be aware of the complexities: The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a complex issue with no easy solutions. Avoid simplistic narratives and recognize the nuances involved.
- Engage in respectful dialogue: Engage in discussions about the conflict with an open mind and a willingness to listen to different perspectives.
Conclusion: A Path Forward for the Map of Israel Today
The map of Israel today represents a complex and dynamic landscape, shaped by historical grievances, political realities, and the aspirations of its diverse populations. Achieving a lasting peace in the region requires a commitment to dialogue, compromise, and a shared vision for a future where Israelis and Palestinians can live in peace and security. Navigating the challenges of the present necessitates a deep understanding of the past, a willingness to address the concerns of all parties involved, and a commitment to finding common ground. The map of Israel today is not just a geographical representation but a roadmap for a future that remains to be written.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of the Map of Israel Today. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!