Navigating The Archipelago: Understanding The Names Of Japan’s Islands
Navigating the Archipelago: Understanding the Names of Japan’s Islands
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: Understanding the Names of Japan’s Islands
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: Understanding the Names of Japan’s Islands. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: Understanding the Names of Japan’s Islands
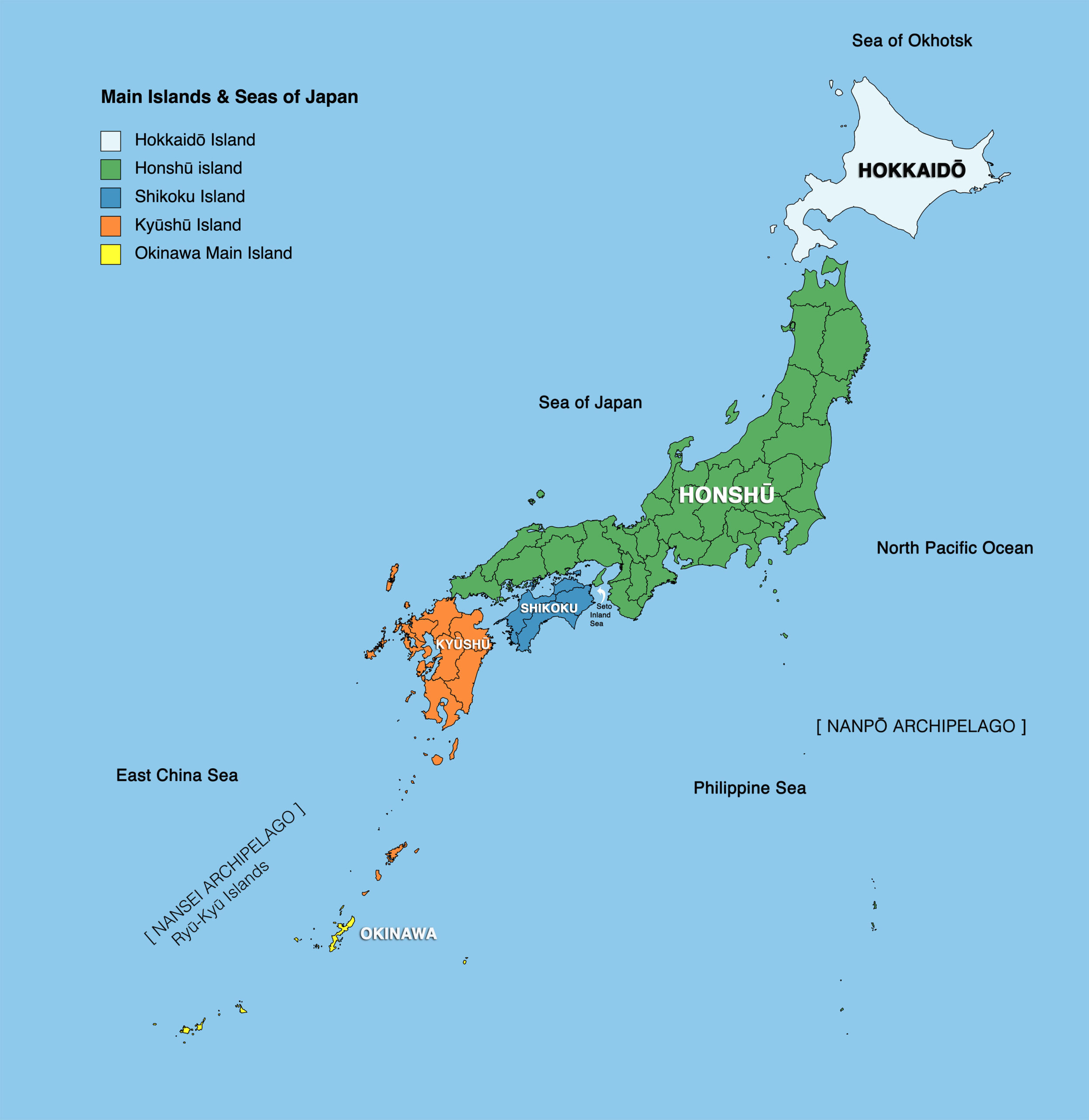
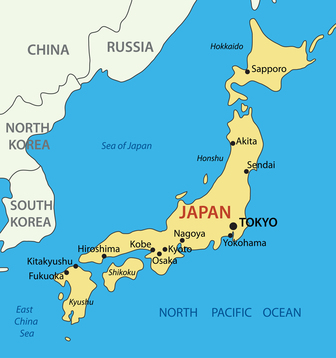
Japan, a nation renowned for its rich culture and stunning landscapes, is an archipelago comprised of over 6,800 islands. While many associate Japan with the four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – the nation’s intricate geography encompasses a vast array of smaller islands, each with its unique history and identity. This article delves into the fascinating world of Japanese island names, exploring their origins, meanings, and the cultural significance they hold.
Understanding the Names: A Glimpse into History and Culture
The names of Japan’s islands, often imbued with historical narratives and cultural symbolism, offer a window into the nation’s past. Many names are rooted in ancient Japanese mythology and folklore, reflecting the deep connection between the Japanese people and their land.
Hokkaido: This northernmost island, known for its rugged beauty and abundant natural resources, derives its name from the Ainu language, the indigenous people of Hokkaido. "Hokkaido" translates to "the way of the sea," reflecting the island’s proximity to the Pacific Ocean and its importance as a maritime route.
Honshu: The largest and most populous island, Honshu, encompasses Tokyo, the nation’s capital, and numerous other major cities. The name "Honshu" means "mainland," signifying its central role in Japanese history and culture.
Shikoku: This island, known for its picturesque mountains and serene temples, derives its name from the ancient Japanese word "Shikoku," which literally means "four countries." This name reflects the island’s historical division into four provinces.
Kyushu: The southernmost of the four main islands, Kyushu, is renowned for its volcanic landscapes and warm climate. Its name, "Kyushu," translates to "nine provinces," highlighting its historical administrative division.
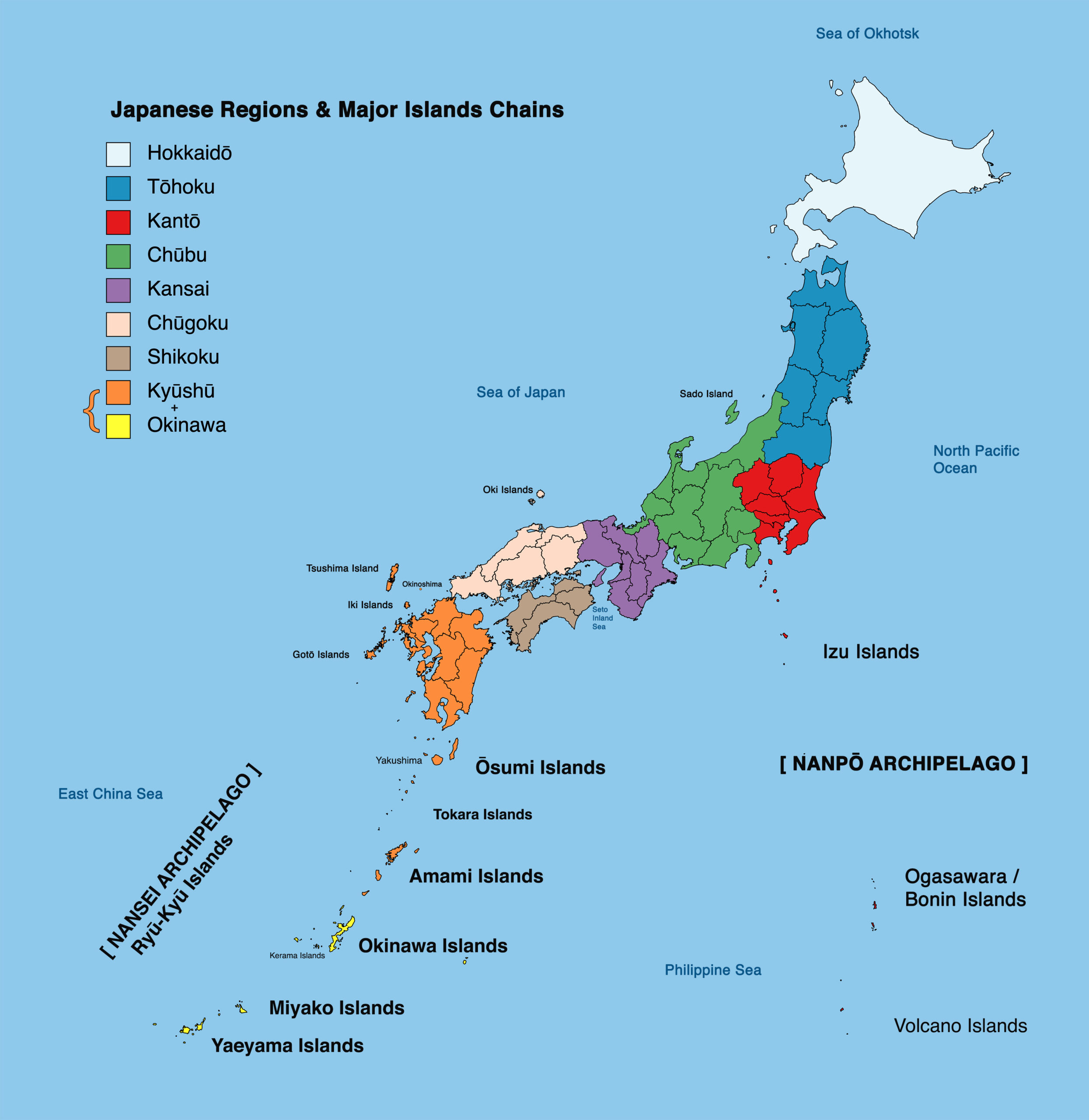
Beyond the Four Main Islands:
While Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu are the most prominent islands, Japan’s geographic tapestry extends far beyond. Numerous smaller islands, often grouped into island chains, contribute to the nation’s unique landscape and cultural diversity.
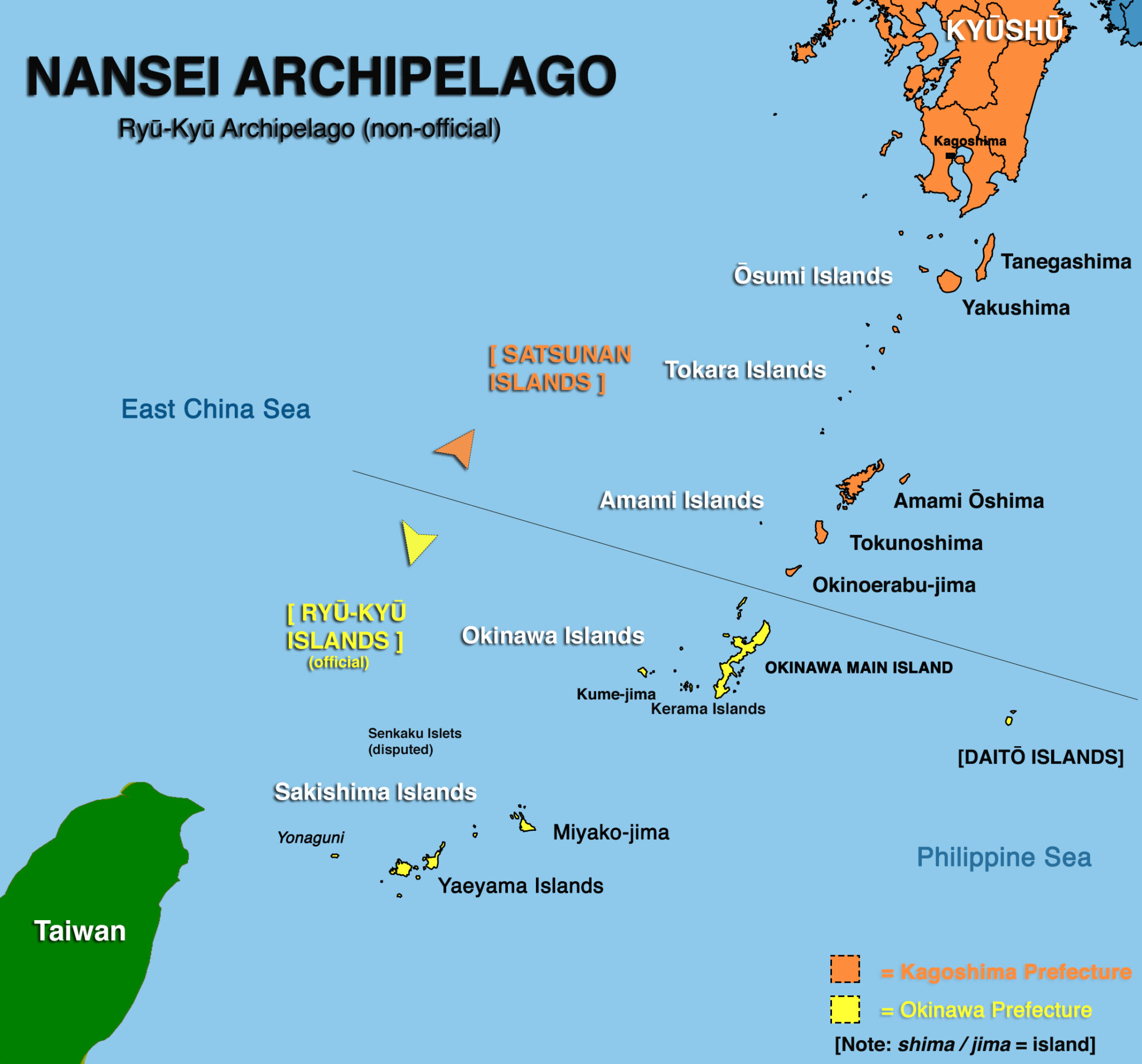
The Ryukyu Islands: This chain of islands, located south of Kyushu, is known for its vibrant culture and rich history. The name "Ryukyu" originates from the ancient kingdom that once ruled the islands, leaving behind a legacy of unique traditions and customs.
The Izu Islands: Located south of Tokyo, the Izu Islands are volcanic in origin and offer a glimpse into Japan’s natural wonders. The name "Izu" is believed to be derived from the Ainu word "izu," meaning "island."
The Ogasawara Islands: Situated far south of Tokyo, the Ogasawara Islands are renowned for their pristine natural beauty and diverse ecosystem. The name "Ogasawara" is believed to be derived from the name of a local chieftain who ruled the islands in the past.
Cultural Significance and Identity:
The names of Japan’s islands are not mere geographic labels; they are intertwined with the nation’s cultural identity and historical narratives. Each island carries a unique story, reflected in its name, its landscape, and the lives of its people.
Hokkaido: The island’s Ainu heritage is deeply rooted in its name and culture, highlighting the importance of indigenous traditions and the interconnectedness of nature and human life.
Honshu: The name "Honshu" embodies the island’s central role in Japanese history and culture, serving as a hub for political, economic, and social development.
Shikoku: The name "Shikoku" reflects the island’s historical division into four provinces, highlighting the importance of regional identities and the diverse cultural tapestry of Japan.
Kyushu: The name "Kyushu" emphasizes the island’s historical administrative division, showcasing the evolution of Japanese governance and the interconnectedness of different regions.
The Ryukyu Islands: The name "Ryukyu" represents the rich cultural heritage of the islands, highlighting the unique traditions, customs, and history of the Ryukyuan people.
The Izu Islands: The name "Izu" reflects the volcanic origins of the islands, showcasing the power of nature and the beauty of volcanic landscapes.
The Ogasawara Islands: The name "Ogasawara" connects the islands to their historical past, highlighting the legacy of local leadership and the unique cultural identity of the Ogasawara people.
FAQs about Japanese Island Names:
Q: What is the significance of the names of Japan’s islands?
A: The names of Japan’s islands are more than just geographic labels; they are imbued with historical narratives, cultural symbolism, and the stories of the people who inhabit them. They reflect the nation’s rich history, diverse cultural tapestry, and deep connection to the natural world.
Q: How did the names of the main islands originate?
A: The names of the main islands, Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, have diverse origins. Hokkaido’s name derives from the Ainu language, while Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu are based on ancient Japanese words reflecting the islands’ historical divisions and geographic significance.
Q: What is the significance of the Ryukyu Islands’ name?
A: The name "Ryukyu" represents the ancient kingdom that once ruled the islands, highlighting their rich cultural heritage and unique traditions.
Q: What is the importance of understanding the names of Japan’s islands?
A: Understanding the names of Japan’s islands provides insights into the nation’s history, culture, and the stories of its people. It allows us to appreciate the diverse landscape, the unique traditions, and the interconnectedness of different regions.
Tips for Exploring Japanese Island Names:
- Delve into Japanese mythology and folklore: Many island names are rooted in ancient stories and legends, offering a deeper understanding of their cultural significance.
- Explore the origins of the names: Research the etymology of island names to uncover their historical context and cultural significance.
- Learn about the local history and traditions: Each island has a unique history and cultural identity, reflected in its name and the stories of its people.
- Travel to different islands: Experience the diverse landscapes, traditions, and cultures of Japan’s islands firsthand.
Conclusion:
The names of Japan’s islands are more than just geographic labels; they are windows into the nation’s history, culture, and the stories of its people. From the ancient Ainu heritage of Hokkaido to the vibrant traditions of the Ryukyu Islands, each island name reflects a unique identity and a connection to the nation’s past. By exploring these names, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of Japanese culture and the beauty of the archipelago’s diverse landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: Understanding the Names of Japan’s Islands. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!