Navigating The Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide To Japan’s Prefectures
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Prefectures
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Prefectures
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Prefectures. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Prefectures
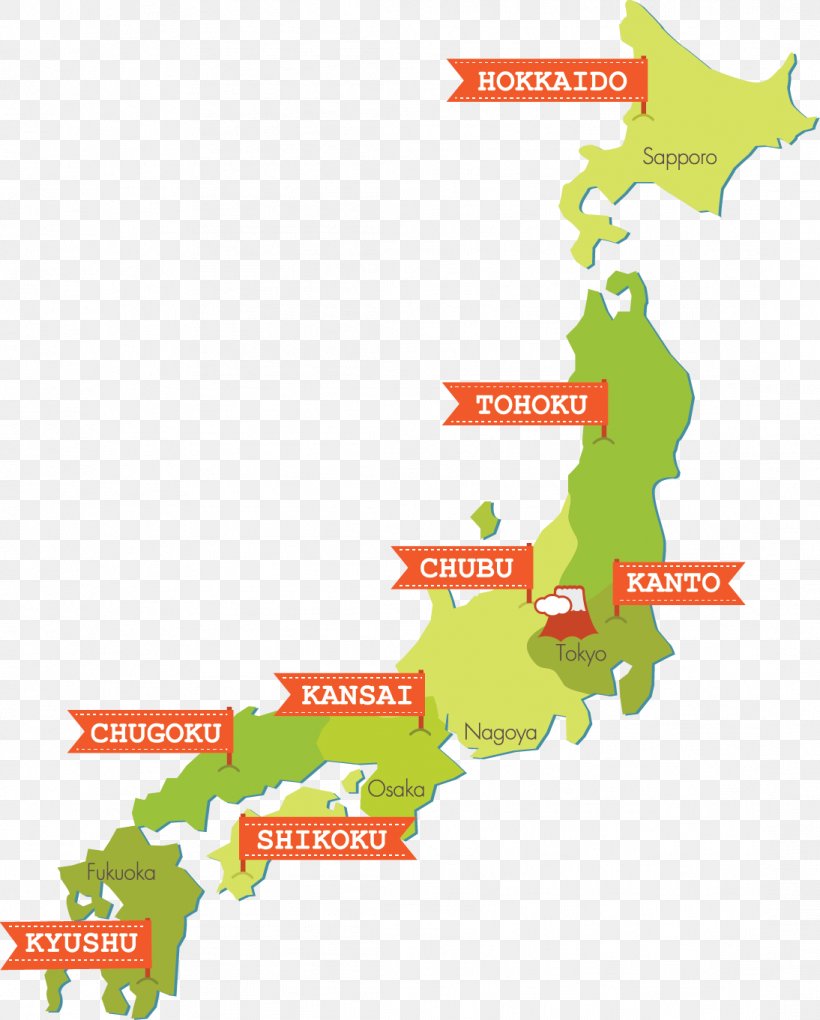
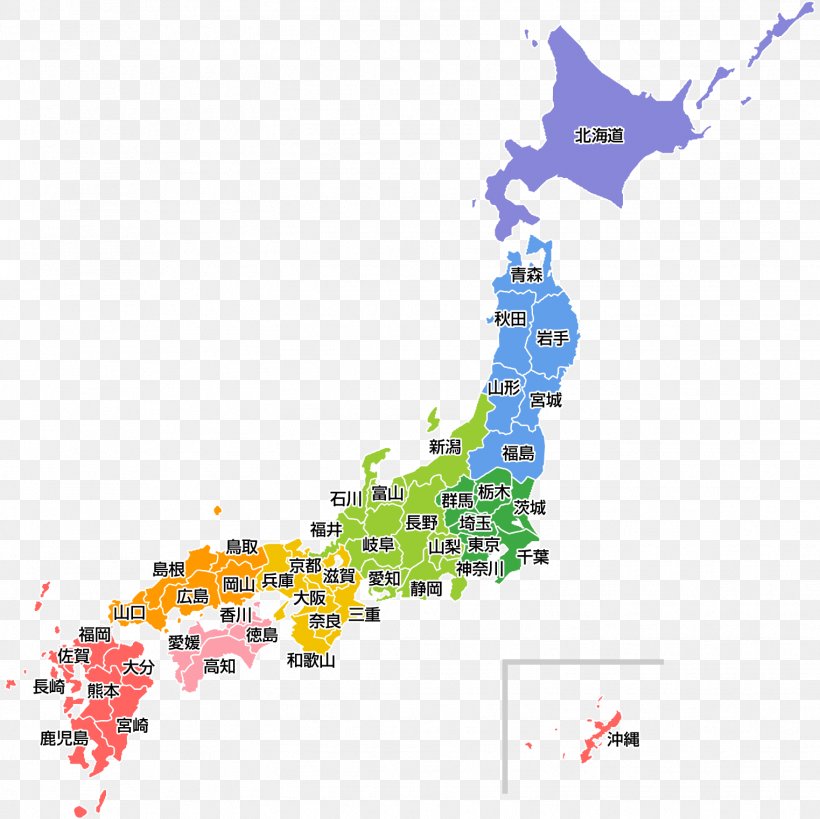
Japan, a nation of islands, is a tapestry of diverse cultures, landscapes, and histories. Its administrative structure, defined by 47 prefectures, reflects this intricate tapestry, offering a unique lens through which to understand the country’s complexities. This article delves into the intricate geography of Japan’s prefectures, outlining their historical significance, geographic characteristics, and cultural nuances.
The Historical Foundation of Prefectures
The concept of prefectures in Japan, known as "ken" (県), traces its roots to the Meiji Restoration of 1868. Prior to this period, Japan was divided into feudal domains, each governed by a lord. The Meiji government, seeking to centralize power and establish a modern nation-state, abolished these domains and implemented a system of prefectures. This administrative reform aimed to standardize governance, streamline tax collection, and promote economic development across the archipelago.
A Geographic Mosaic: Exploring the Prefectures
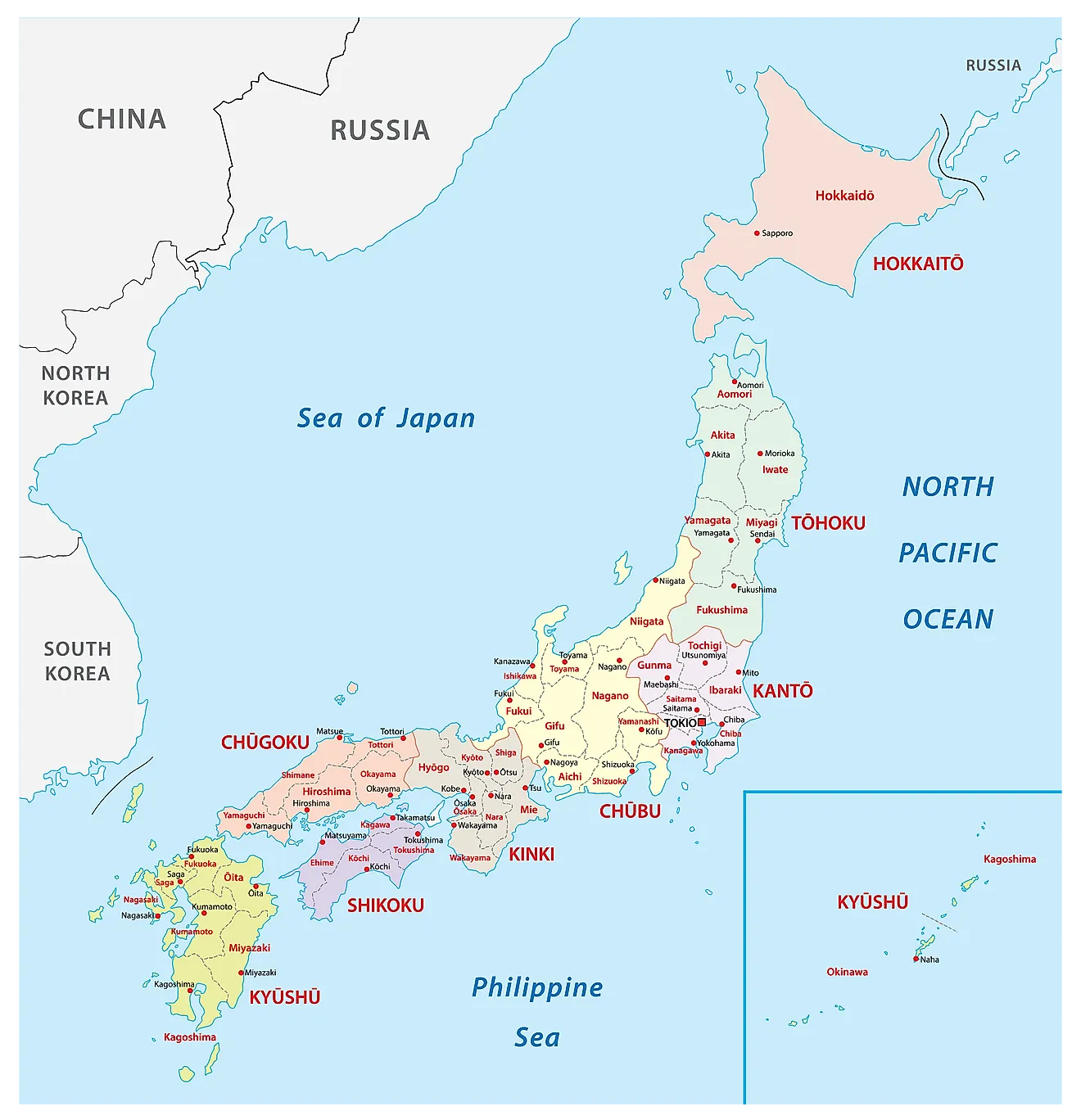
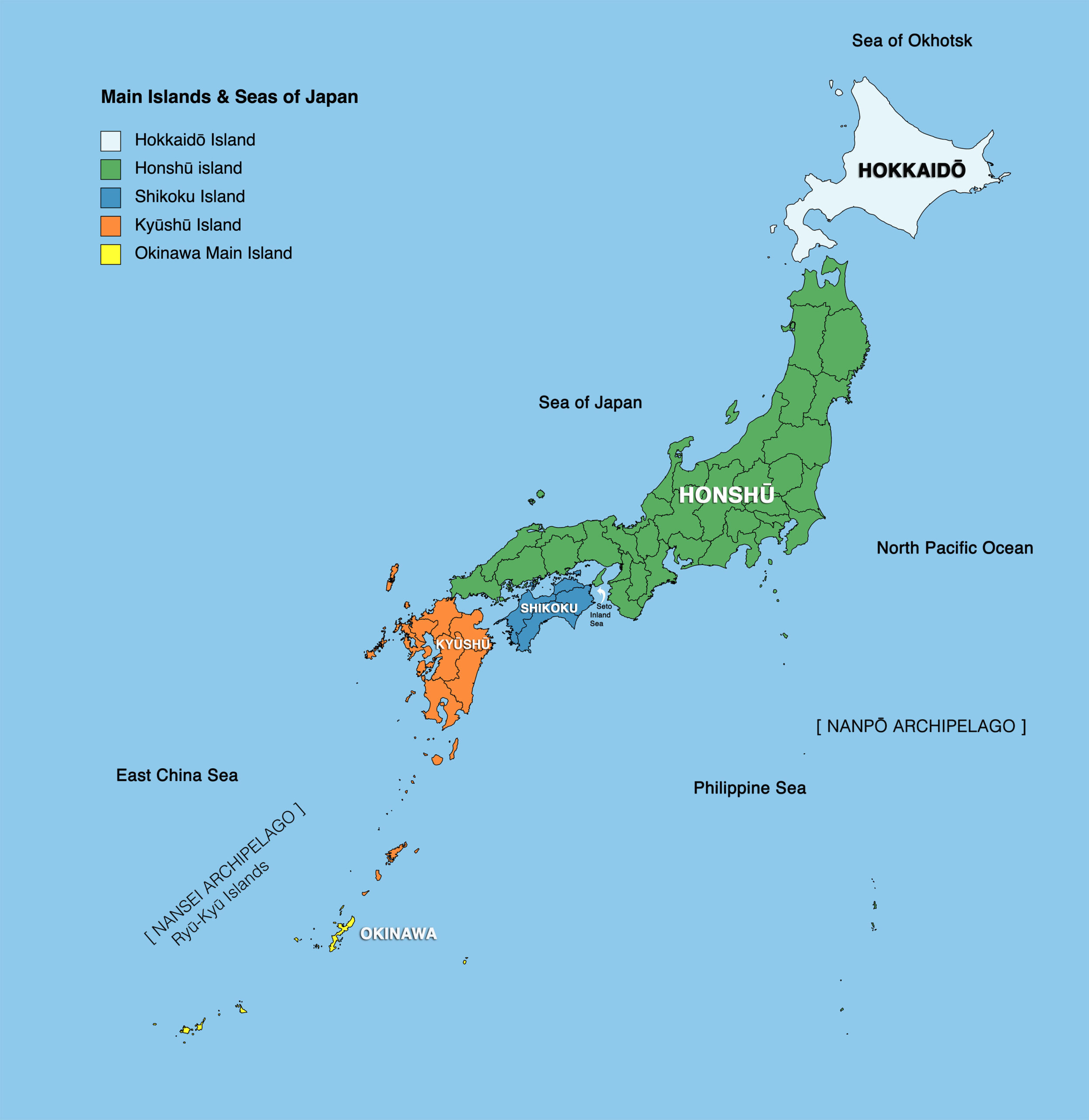
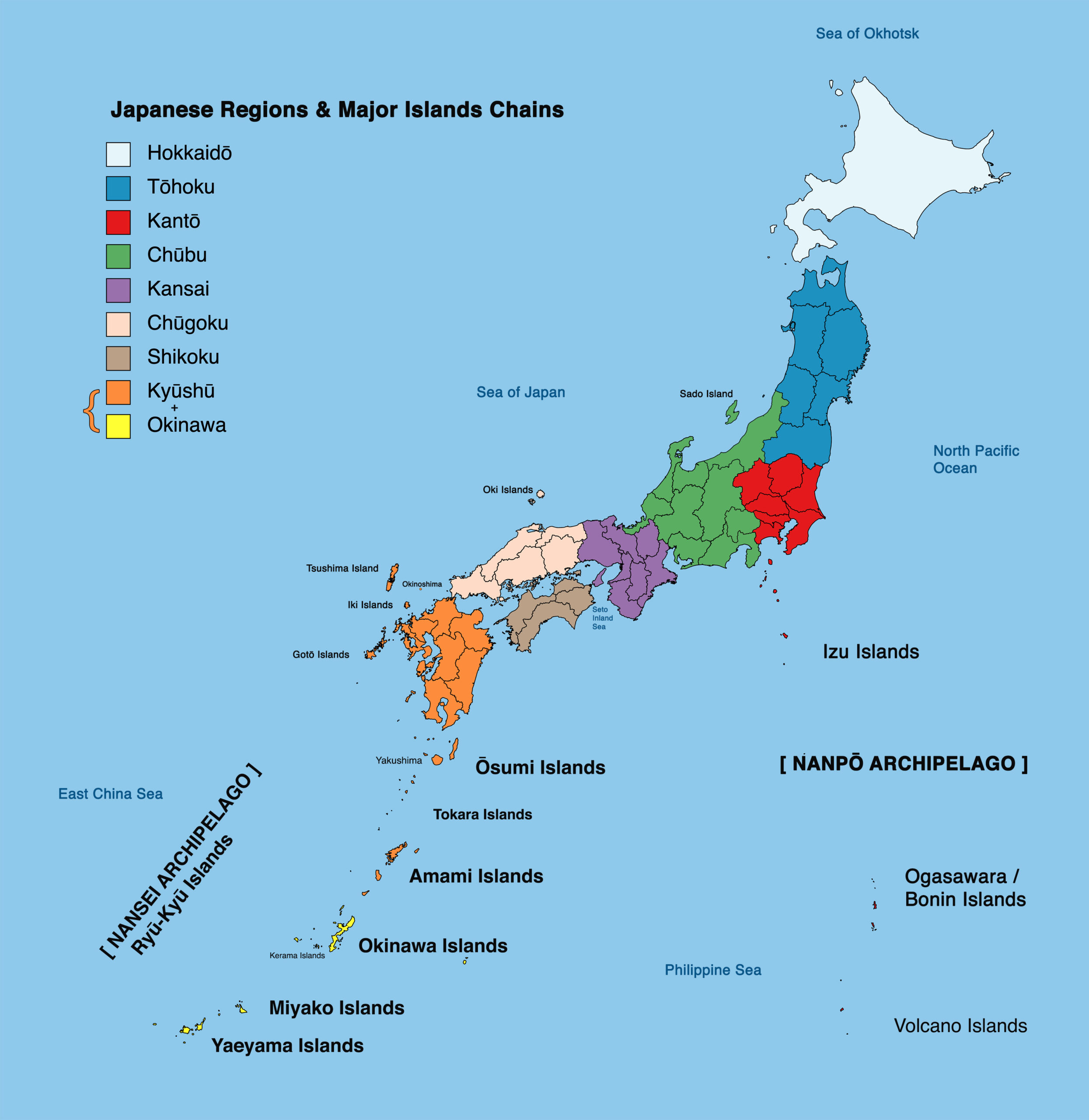
Japan’s 47 prefectures are spread across four main islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, along with numerous smaller islands. Each prefecture boasts distinct geographical features, shaping its unique landscape, climate, and cultural identity.
Hokkaido: The Northern Frontier
Hokkaido, the northernmost island, is a land of rugged mountains, vast forests, and fertile plains. Its largest city, Sapporo, is known for its beer and annual snow festival. Hokkaido’s prefecture system, established in 1869, reflects its distinct history and culture, separate from the mainland.
Honshu: The Heart of Japan
Honshu, the largest island, encompasses the majority of Japan’s population and major cities, including Tokyo, Osaka, and Kyoto. The island’s diverse landscape includes the towering Japanese Alps, rolling plains, and the Pacific coast. Honshu’s prefectures, established in the late 19th century, represent a blend of historical, cultural, and economic influences.
Shikoku: The Island of Pilgrimage
Shikoku, the smallest of the four main islands, is known for its serene beauty and historical significance. It is home to the famous Shikoku Pilgrimage, a 1,200-kilometer route of 88 temples. Shikoku’s prefectures, with their unique cultural traditions and natural wonders, offer a glimpse into Japan’s spiritual heart.
Kyushu: The Southern Gateway
Kyushu, the southernmost island, is characterized by its volcanic landscapes, warm climate, and vibrant culture. It is home to the city of Fukuoka, a major economic hub, and the island of Okinawa, known for its unique culture and stunning beaches. Kyushu’s prefectures reflect the island’s rich history, influenced by trade with mainland Asia and its unique cultural heritage.
Beyond the Main Islands: A Tapestry of Diversity
Beyond the four main islands, numerous smaller islands, collectively known as the Ryukyu Islands, are also divided into prefectures. These islands, with their distinct cultural traditions and unique landscapes, offer a glimpse into Japan’s diverse and fascinating maritime history.
The Importance of Prefectures
Japan’s prefecture system serves as the primary level of local government, responsible for administering a wide range of services, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure. Each prefecture has its own elected governor and assembly, allowing for decentralized decision-making and a strong sense of local identity.
Benefits of the Prefectural System
The prefecture system offers several benefits:
- Local Governance: Decentralized governance allows for tailored policies and services that address specific regional needs.
- Cultural Preservation: Prefectures play a vital role in preserving and promoting local traditions, languages, and cultural heritage.
- Economic Development: Prefectures are responsible for attracting investment, promoting tourism, and fostering economic growth within their respective regions.
- Disaster Management: Prefectures are crucial in coordinating disaster response and recovery efforts, leveraging local knowledge and resources.
Understanding the Map of Japan’s Prefectures
Navigating the map of Japan’s prefectures is essential for understanding the country’s geography, culture, and history. The map showcases the diverse landscapes, urban centers, and historical sites that make up the Japanese archipelago.
FAQs on Japan’s Prefectures
Q: What is the smallest prefecture in Japan?
A: The smallest prefecture in Japan is Tokyo, with an area of 2,188 square kilometers.
Q: What is the largest prefecture in Japan?
A: The largest prefecture in Japan is Hokkaido, with an area of 83,456 square kilometers.
Q: Which prefecture is the most populous?
A: The most populous prefecture is Kanagawa, with a population of over 9.2 million.
Q: What is the capital city of Japan?
A: The capital city of Japan is Tokyo, which is also the capital of Tokyo Prefecture.
Tips for Exploring Japan’s Prefectures
- Research specific prefectures: Identify prefectures that align with your interests, whether it be historical sites, natural beauty, or cultural experiences.
- Utilize online resources: Websites, travel blogs, and social media platforms offer valuable information on attractions, transportation, and accommodation options.
- Consider regional specialties: Explore local cuisine, crafts, and festivals unique to each prefecture.
- Embrace the local culture: Interact with locals, learn basic Japanese phrases, and immerse yourself in the region’s unique traditions.
Conclusion
Japan’s prefectures are not merely administrative divisions; they are the building blocks of a nation rich in history, culture, and diversity. Understanding the map of Japan’s prefectures offers a profound insight into the country’s geographical, cultural, and historical complexities. By exploring each prefecture’s unique characteristics, one can truly appreciate the intricate tapestry that makes up the Japanese archipelago.



![Japanese Archipelago Entering Prefecture Names - Stock Illustration [33334876] - PIXTA](https://en.pimg.jp/033/334/876/1/33334876.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Prefectures. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!