Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide To The Shinkansen
Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen
Related Articles: Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen
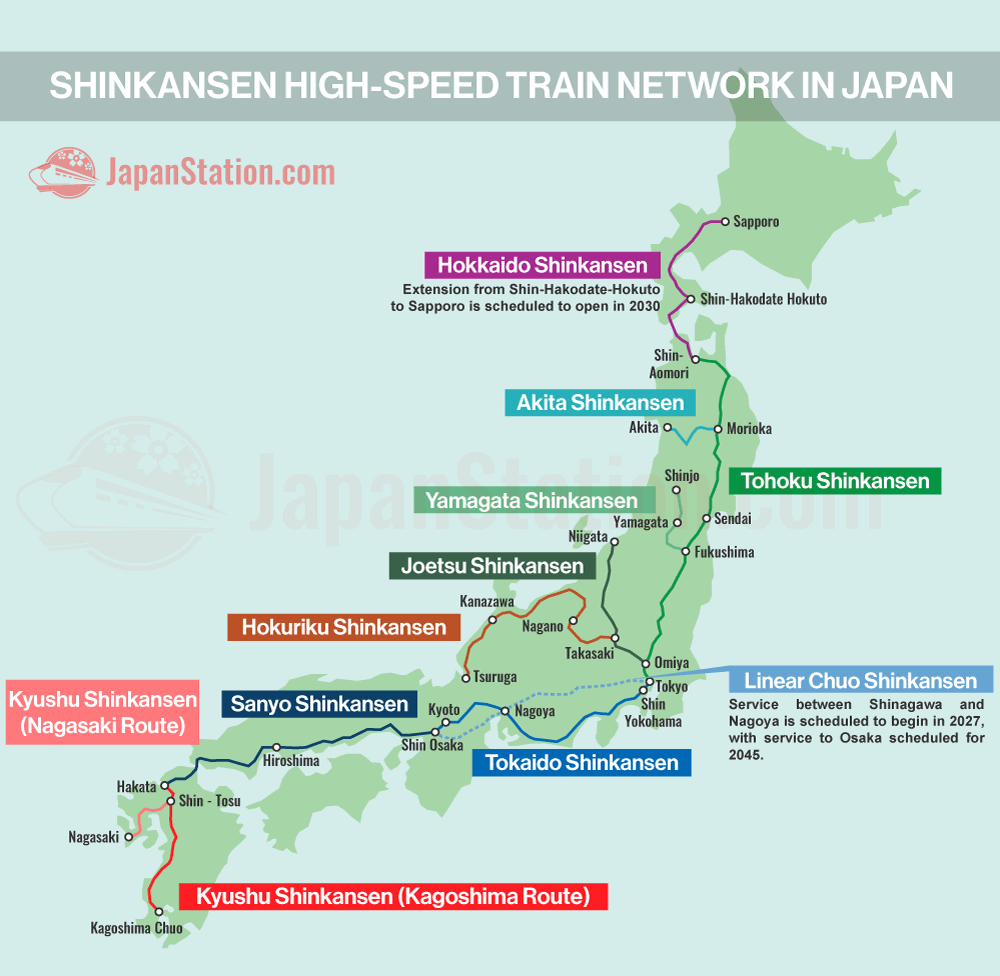
The Shinkansen, Japan’s iconic bullet train network, is a marvel of engineering and a testament to the country’s dedication to efficiency and innovation. This high-speed railway system seamlessly connects major cities across the archipelago, offering travelers a swift and comfortable journey. Understanding the intricate network of lines and routes is crucial for planning a smooth and enjoyable trip.
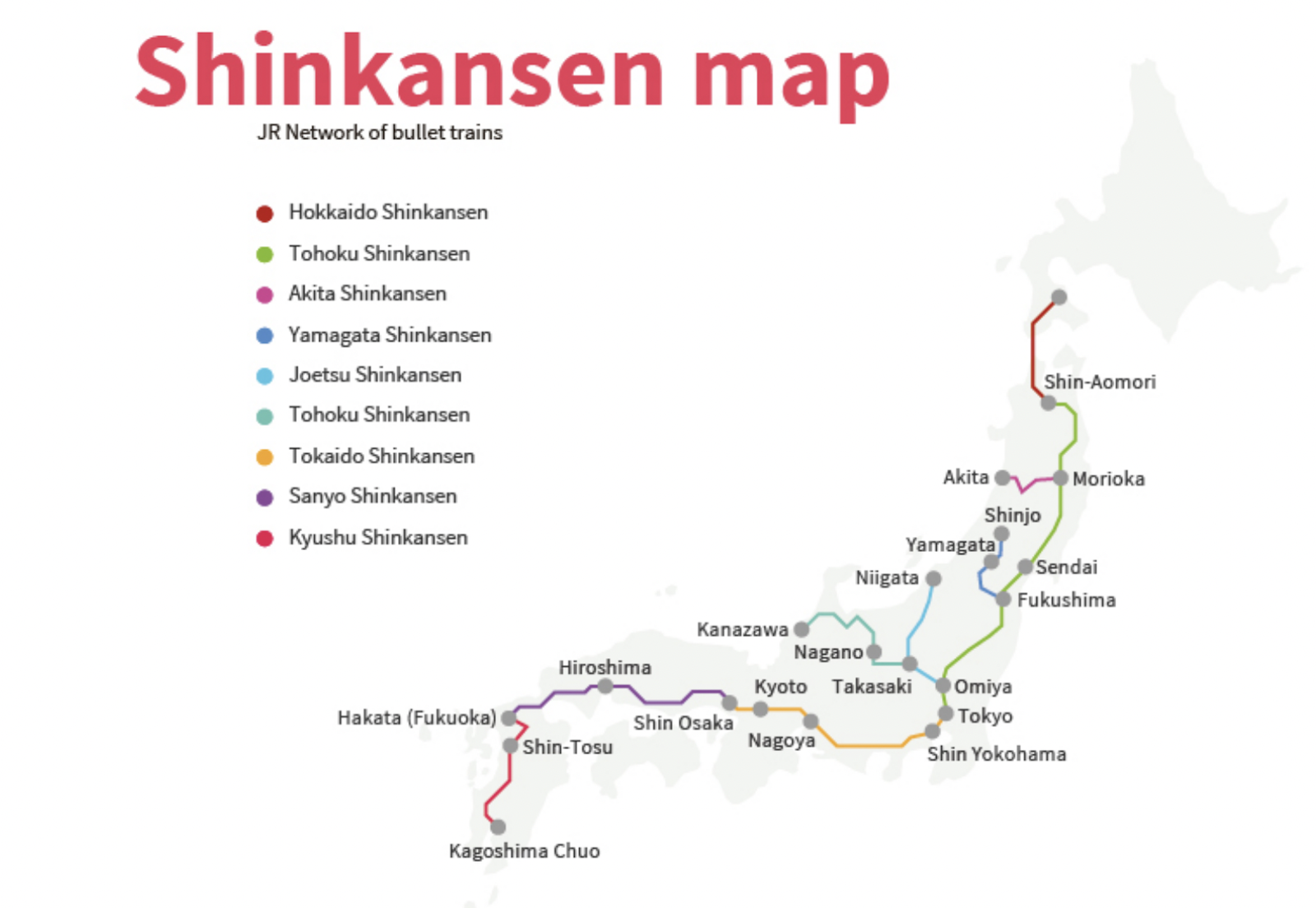
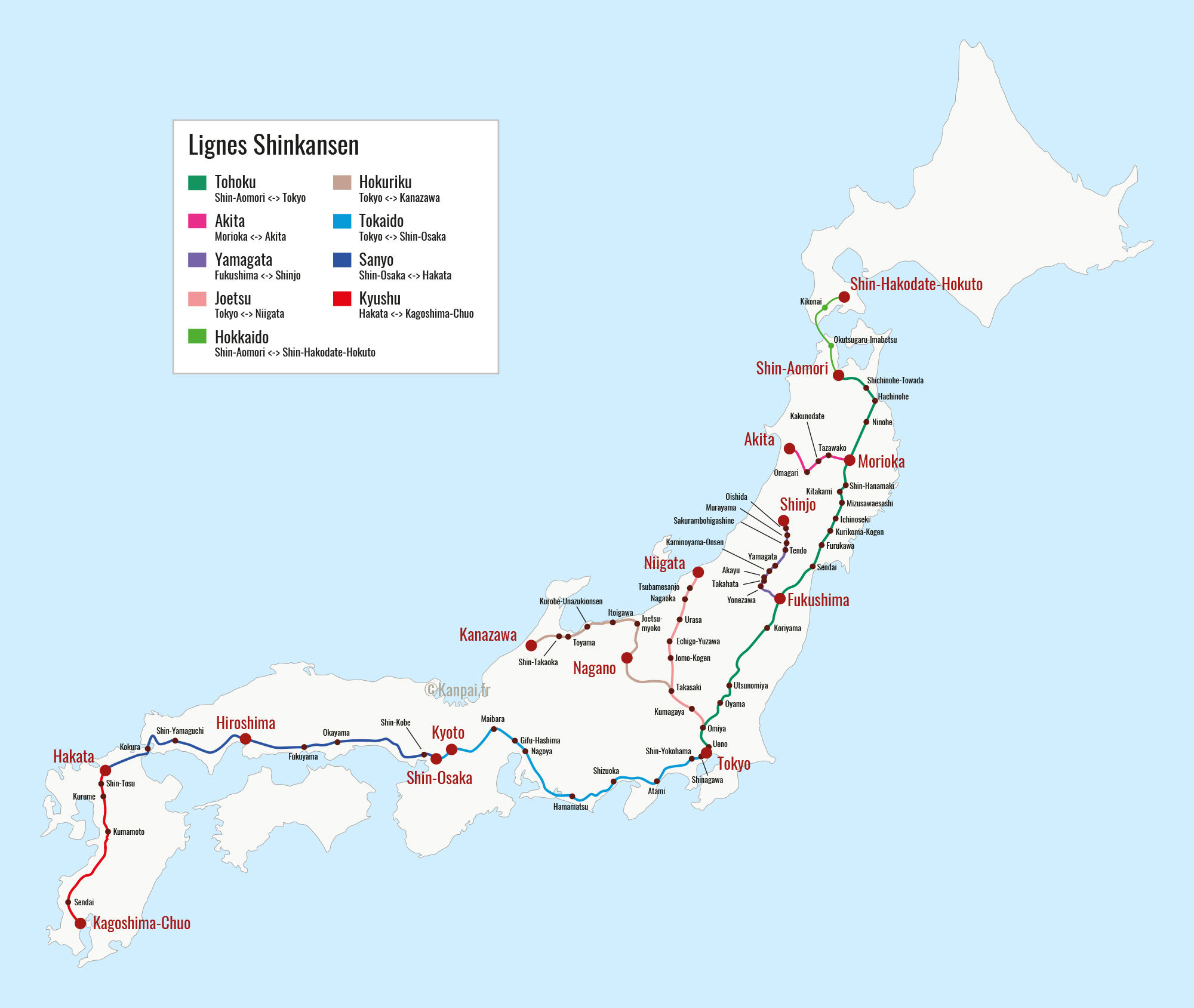
A Network of Lines and Routes
The Shinkansen network is comprised of multiple lines, each with its own distinct route and destinations. The primary lines, often referred to by their color-coded designations, are:
- Tōkaidō Shinkansen (Green): The original and most extensive line, connecting Tokyo to Osaka and extending further to Hakata in Kyushu.
- Sanyō Shinkansen (Blue): Branching off the Tōkaidō line in Osaka, it travels westward to Hakata, offering access to major cities like Hiroshima and Okayama.
- Tōhoku Shinkansen (Pink): Stretching north from Tokyo, this line connects to major cities in the Tohoku region, including Sendai, Morioka, and Aomori.
- Hokkaidō Shinkansen (Yellow): The newest addition, extending from Aomori to Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto in Hokkaido, offering access to the northernmost island.
- Jōetsu Shinkansen (Orange): Connecting Tokyo to Niigata on the Japan Sea coast, this line offers an alternative route to the north.
- Nagano Shinkansen (Purple): Branching off the Jōetsu line, it connects to Nagano, renowned for its winter sports and hot springs.
- Kyushu Shinkansen (Red): Connecting Hakata to Kagoshima in Kyushu, this line offers access to the southern island’s unique landscapes and culture.
Beyond the Major Lines
Beyond the primary lines, several smaller lines and extensions contribute to the comprehensive reach of the Shinkansen. These include:
- Hokuriku Shinkansen: Connecting Tokyo to Kanazawa and further to Osaka via the Hokuriku region.
- Yamagata Shinkansen: Connecting Fukushima to Shinjō, offering access to the Yamagata prefecture.
- Akita Shinkansen: Connecting Akita to Morioka, providing a link to the Akita prefecture.
Navigating the Network: Understanding the Map
The Shinkansen map is an essential tool for planning your journey. It visually depicts the network’s layout, highlighting the lines, stations, and key destinations.
- Lines and Colors: The map typically uses different colors to represent each line, allowing for easy identification.
- Stations: Major stations are clearly marked, with their names and locations indicated.
- Route Information: The map shows the direction of travel for each line, enabling travelers to determine the appropriate route for their destination.
- Transfer Points: Transfer points between lines are highlighted, facilitating seamless travel between different routes.
Benefits of the Shinkansen Network
The Shinkansen network offers numerous benefits to travelers and the Japanese economy:
- Speed and Efficiency: Bullet trains travel at speeds exceeding 200 km/h, significantly reducing travel time between cities. This efficiency saves valuable time for both business travelers and tourists.
- Comfort and Convenience: Shinkansen trains are renowned for their comfort and amenities. Spacious seating, onboard restrooms, and often, power outlets and Wi-Fi enhance the travel experience.
- Reliability and Punctuality: The Shinkansen system is renowned for its reliability and punctuality. Trains operate on a strict schedule, minimizing delays and ensuring predictable travel times.
- Accessibility and Connectivity: The network’s extensive reach connects major cities and regions, offering convenient access to diverse attractions and cultural experiences.
- Economic Impact: The Shinkansen network contributes significantly to Japan’s economy by facilitating tourism, business travel, and transportation of goods.
FAQs About the Shinkansen Network
Q: What is the average speed of a Shinkansen train?
A: The average speed of a Shinkansen train varies depending on the line and track conditions, but generally ranges from 240 to 300 km/h.
Q: How often do Shinkansen trains run?
A: Train frequency varies depending on the line and time of day. However, trains typically run every 15 to 30 minutes during peak hours and less frequently during off-peak hours.
Q: Are there different classes of seating on Shinkansen trains?
A: Yes, most Shinkansen trains offer different seating classes, including standard, green (first class), and sometimes, even luxury options.
Q: How can I purchase tickets for the Shinkansen?
A: Tickets can be purchased at major train stations, convenience stores with ticketing machines, or online through official websites.
Q: Are there any discounts available for Shinkansen tickets?
A: Yes, discounts are available for children, seniors, and group travelers. Additionally, Japan Rail Pass offers unlimited travel on the Shinkansen network for a set period.
Tips for Using the Shinkansen Network
- Plan in Advance: Reserve tickets in advance, especially during peak travel seasons or for popular routes.
- Check Train Schedules: Verify train schedules and departure times before arriving at the station.
- Arrive Early: Allow ample time for check-in, baggage handling, and navigating the station.
- Utilize Station Amenities: Take advantage of station amenities, such as restrooms, luggage lockers, and information desks.
- Respect Train Etiquette: Be mindful of train etiquette, such as keeping noise levels low and refraining from using mobile phones during quiet hours.
Conclusion
The Shinkansen network is an integral part of Japan’s transportation infrastructure and a symbol of the country’s technological prowess. It offers travelers a convenient, efficient, and comfortable way to explore the diverse regions of Japan. By understanding the network’s layout, routes, and benefits, travelers can fully embrace the unique experience of high-speed rail travel in Japan. Whether embarking on a sightseeing adventure or a business trip, the Shinkansen provides a seamless and memorable journey across the Land of the Rising Sun.
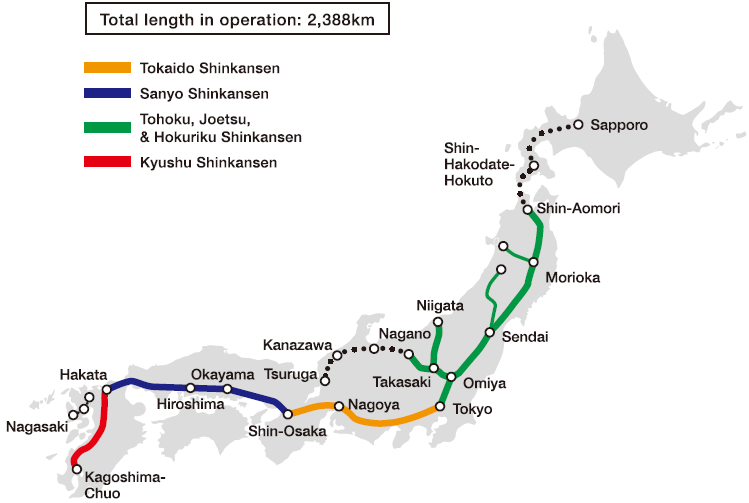


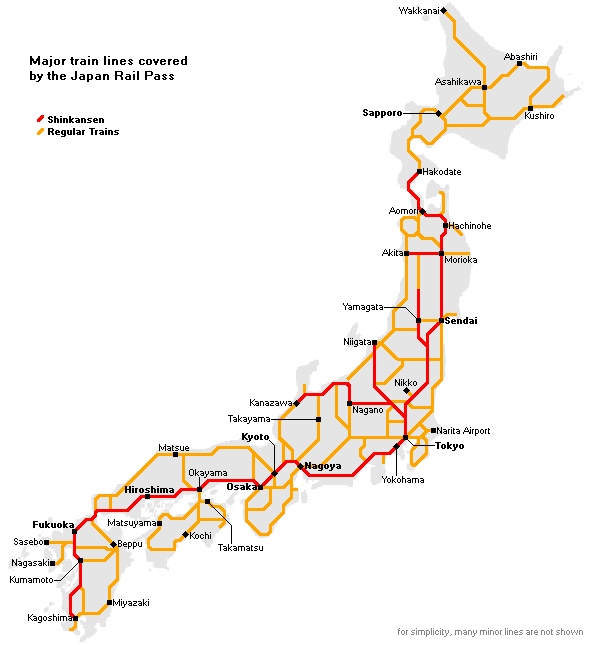
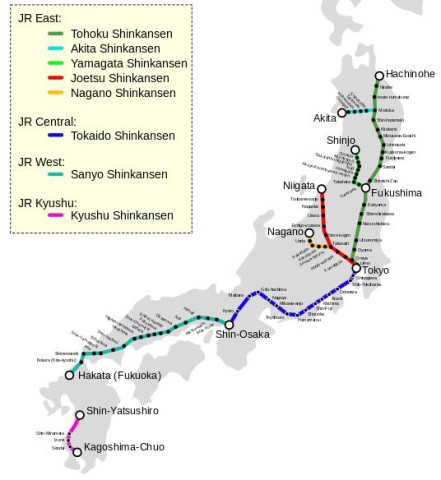

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!