Navigating Japan’s Electrical Grid: A Comprehensive Guide To The 50Hz/60Hz Divide
Navigating Japan’s Electrical Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50Hz/60Hz Divide
Related Articles: Navigating Japan’s Electrical Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50Hz/60Hz Divide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Japan’s Electrical Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50Hz/60Hz Divide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Japan’s Electrical Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50Hz/60Hz Divide
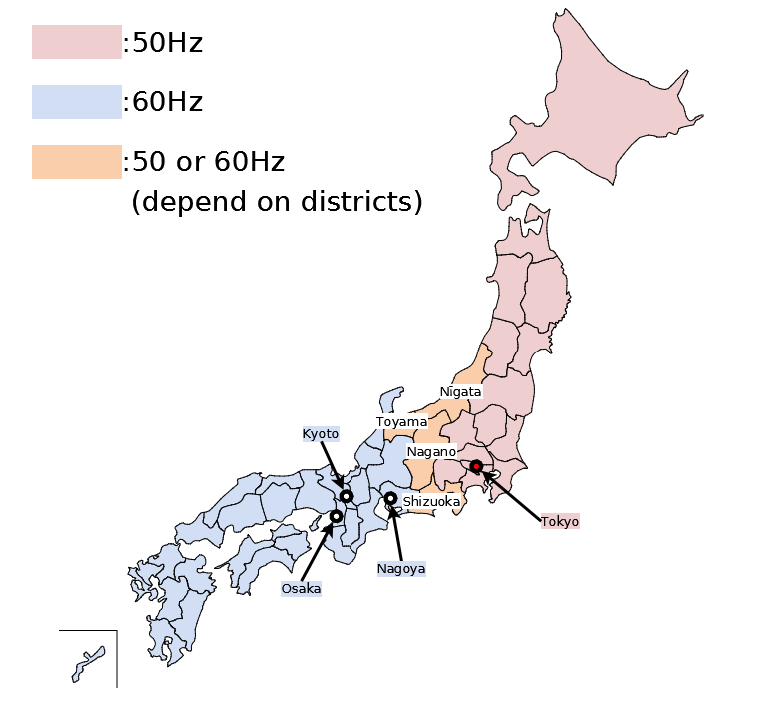
Japan’s electrical grid is a fascinating example of how historical factors can influence modern infrastructure. The country is divided into two distinct regions with differing electrical frequencies: 50Hz in the eastern region and 60Hz in the western region. This seemingly small distinction has significant implications for everyday life, impacting everything from appliances to industrial operations. Understanding this division is crucial for anyone traveling or conducting business in Japan.
The Historical Roots of the 50Hz/60Hz Divide
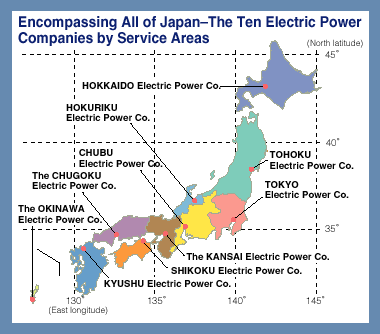
The origins of this divide trace back to the early 20th century, when Japan was rapidly industrializing. At that time, two major electrical companies, Tokyo Electric Power (TEPCO) and Kansai Electric Power (KEPCO), were responsible for building power grids in their respective regions. TEPCO, based in the east, adopted the 50Hz frequency standard used in Europe, while KEPCO, based in the west, chose the 60Hz standard prevalent in North America. This decision, made for largely practical reasons, ultimately resulted in a permanent division of the country’s electrical grid.
The Implications of the 50Hz/60Hz Divide
The 50Hz/60Hz difference might seem insignificant at first glance, but its impact is felt across various aspects of life in Japan.
- Appliance Compatibility: One of the most immediate consequences is the incompatibility of electrical appliances between the two regions. A 50Hz appliance will not operate on a 60Hz circuit, and vice versa. This necessitates the purchase of region-specific appliances or the use of transformers for compatibility. For travelers, this means carefully checking the frequency requirements of their electronics before bringing them to Japan.
- Industrial Applications: The frequency difference also affects industrial operations, particularly in areas like manufacturing and heavy machinery. Equipment designed for one frequency may not function properly or at all on the other. This necessitates careful planning and the use of specialized equipment for industries operating across both regions.
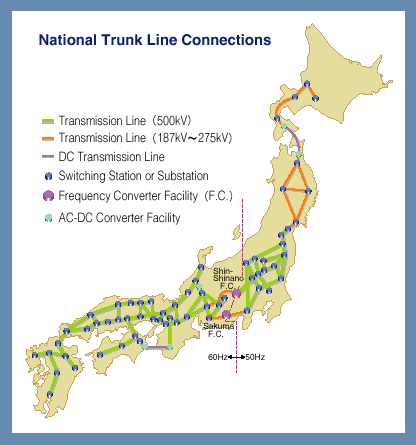
- Electrical Infrastructure: The 50Hz/60Hz divide also presents challenges for the development and maintenance of the national power grid. Connecting the two regions requires specialized equipment and careful coordination to ensure seamless operation and prevent potential disruptions.
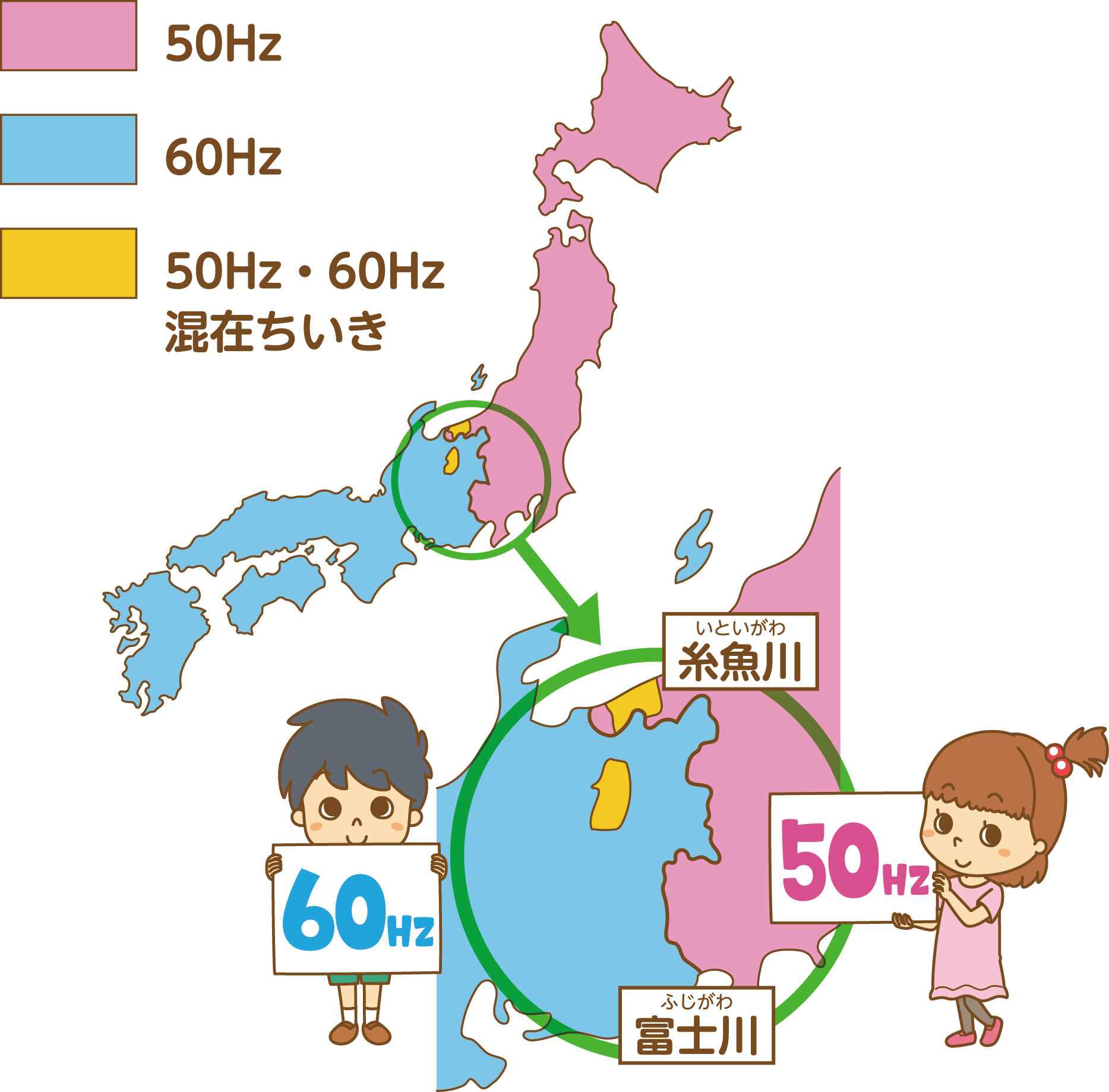
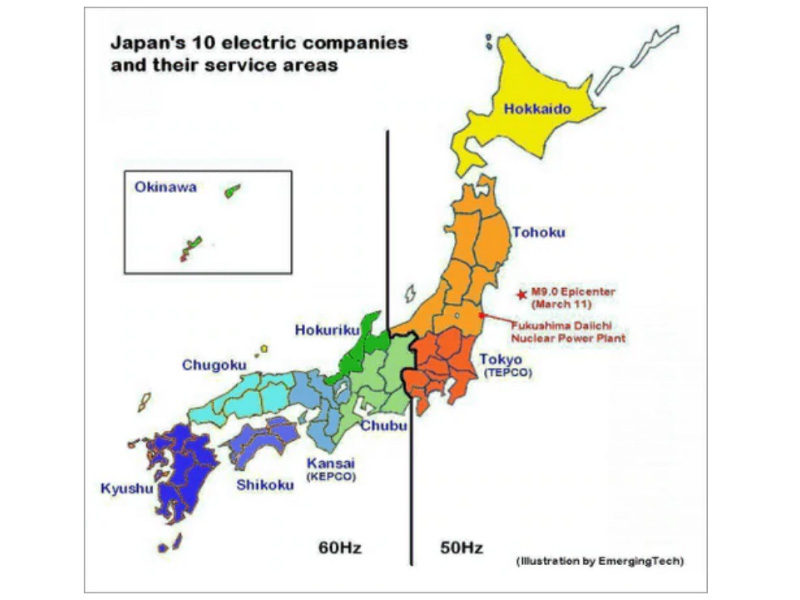
The 50Hz/60Hz Map: A Visual Representation of the Division
The 50Hz/60Hz map of Japan visually depicts this division, highlighting the boundary line that separates the two regions. The eastern region, encompassing Tokyo, the capital, and surrounding areas, operates on 50Hz. The western region, including Osaka and Kyoto, uses 60Hz. This map serves as a crucial reference for individuals and organizations operating in both regions, ensuring compatibility and avoiding potential issues related to the frequency difference.
Navigating the 50Hz/60Hz Divide: Practical Tips for Travelers and Businesses
For travelers and businesses operating in Japan, understanding the 50Hz/60Hz divide is crucial for a smooth and efficient experience. Here are some practical tips:
- Check Appliance Compatibility: Before bringing any electrical appliances to Japan, ensure they are compatible with the region’s frequency. If unsure, it’s best to purchase appliances locally or use a voltage converter.
- Research Local Power Standards: Before traveling or setting up business operations in Japan, familiarize yourself with the local electrical standards, including frequency and voltage. This will help avoid potential problems with appliances and equipment.
- Consult with Local Experts: If you are dealing with complex industrial applications or infrastructure projects, consult with local experts familiar with the 50Hz/60Hz divide. They can provide valuable insights and guidance on ensuring compatibility and avoiding potential issues.
Frequently Asked Questions about Japan’s 50Hz/60Hz Divide
Q: Can I use a 50Hz appliance in a 60Hz region or vice versa?
A: No, you cannot. Appliances designed for one frequency will not operate on the other.
Q: What happens if I try to use a 50Hz appliance in a 60Hz region?
A: The appliance will likely not function at all, or it may malfunction and potentially damage itself or other connected devices.
Q: What are the benefits of the 50Hz/60Hz divide?
A: While the divide presents challenges, it also allows for the use of specific equipment and technologies optimized for each frequency. This can be advantageous for certain industrial applications.
Q: Is there any effort to unify the electrical grid in Japan?
A: There have been discussions and studies on unifying the grid, but it remains a complex and costly undertaking. The potential benefits must be weighed against the significant logistical and financial challenges involved.
Conclusion
Japan’s 50Hz/60Hz divide is a unique feature of the country’s electrical infrastructure, resulting from historical decisions and impacting various aspects of life. Understanding this divide is crucial for travelers, businesses, and anyone working with electrical systems in Japan. By being aware of the implications and utilizing available resources, individuals and organizations can navigate this unique aspect of Japan’s electrical landscape effectively. While the divide presents challenges, it also highlights the complex interplay between historical factors, technological advancements, and the evolution of infrastructure in a modern, technologically advanced society.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Japan’s Electrical Grid: A Comprehensive Guide to the 50Hz/60Hz Divide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!