Navigating Data With JavaScript: Mastering Map And Filter
Navigating Data with JavaScript: Mastering Map and Filter
Related Articles: Navigating Data with JavaScript: Mastering Map and Filter
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Data with JavaScript: Mastering Map and Filter. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating Data with JavaScript: Mastering Map and Filter
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating Data with JavaScript: Mastering Map and Filter
- 3.1 Understanding Map: Transforming Data Elements
- 3.2 Filtering Data with Filter: Selecting Desired Elements
- 3.3 The Power of Combining Map and Filter
- 3.4 Benefits of Using Map and Filter
- 3.5 FAQs about Map and Filter
- 3.6 Tips for Using Map and Filter Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating Data with JavaScript: Mastering Map and Filter
In the realm of JavaScript programming, manipulating and transforming data is a fundamental task. While basic loops can achieve this, JavaScript offers powerful built-in functions like map and filter that streamline data processing, enhance code readability, and optimize performance. This article delves into the functionality of these methods, exploring their practical applications and showcasing their significance in modern JavaScript development.
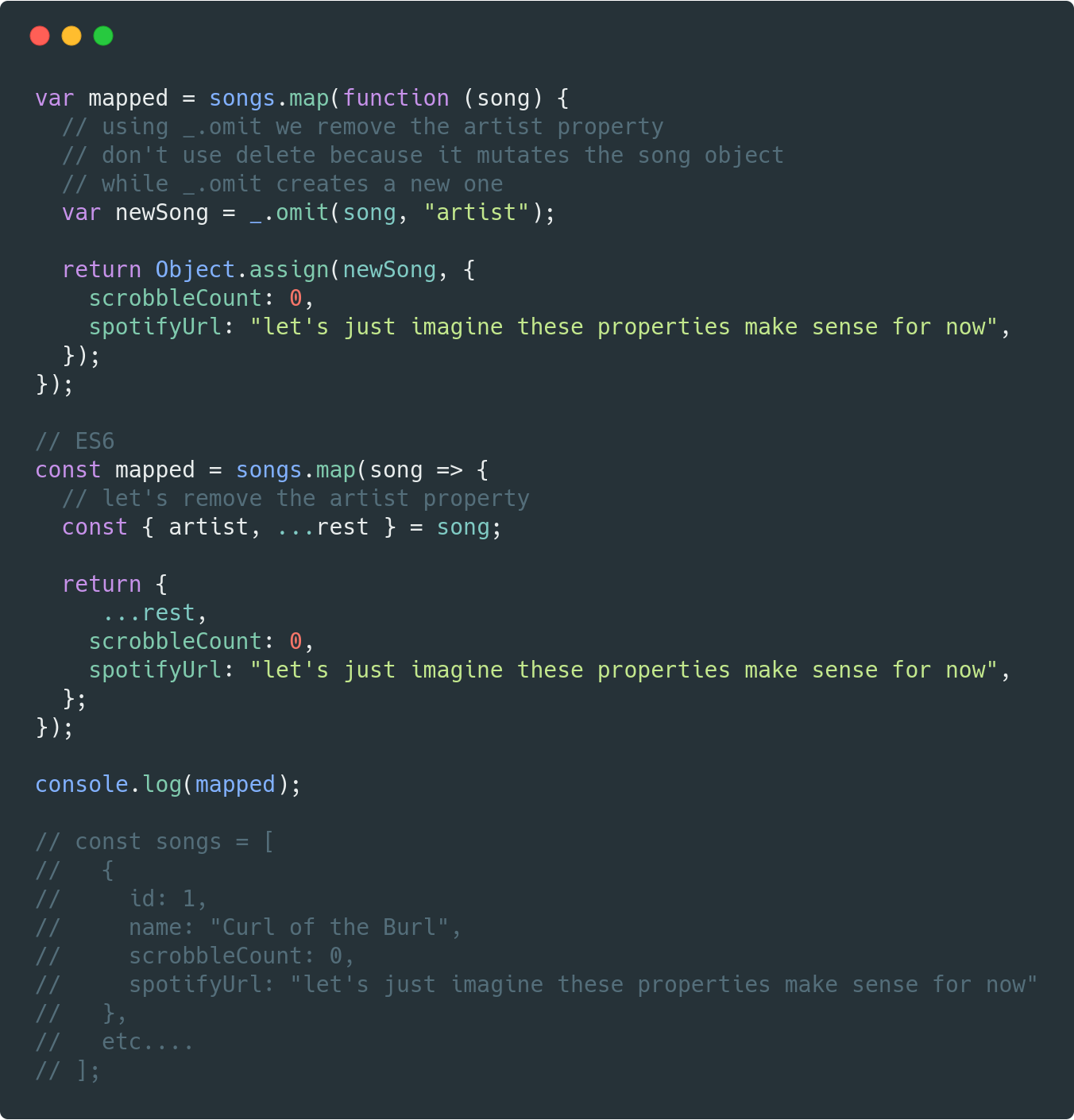
Understanding Map: Transforming Data Elements
The map method serves as a versatile tool for creating a new array by applying a function to each element of an existing array. It iterates through the original array, executes the provided function on each element, and constructs a new array with the results.
Syntax:
const newArray = originalArray.map(function(element, index, array)
// Perform transformation on element
return transformedElement;
);The map function accepts a callback function as its argument. This callback function receives three parameters:
- element: The current element being processed.
- index: The index of the current element in the original array.
- array: The original array itself.
The callback function is responsible for transforming the current element. It can perform various operations, such as:
- Simple transformations: Multiplying each element by a constant, adding a value, or converting strings to numbers.
- Complex calculations: Applying mathematical formulas or custom logic to manipulate data.
- String manipulation: Modifying strings by adding prefixes, suffixes, or changing their case.
Example:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// Double each element in the array
const doubledNumbers = numbers.map(number => number * 2);
console.log(doubledNumbers); // Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]In this example, the map method iterates through the numbers array, multiplying each element by 2. The result is a new array doubledNumbers containing the transformed values.
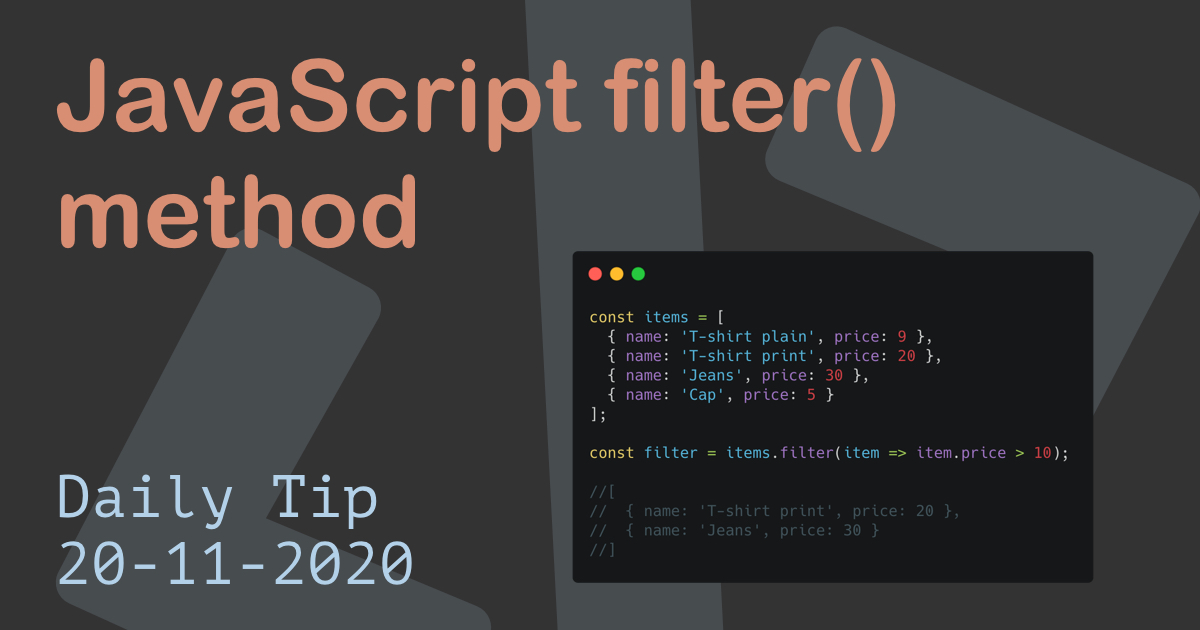
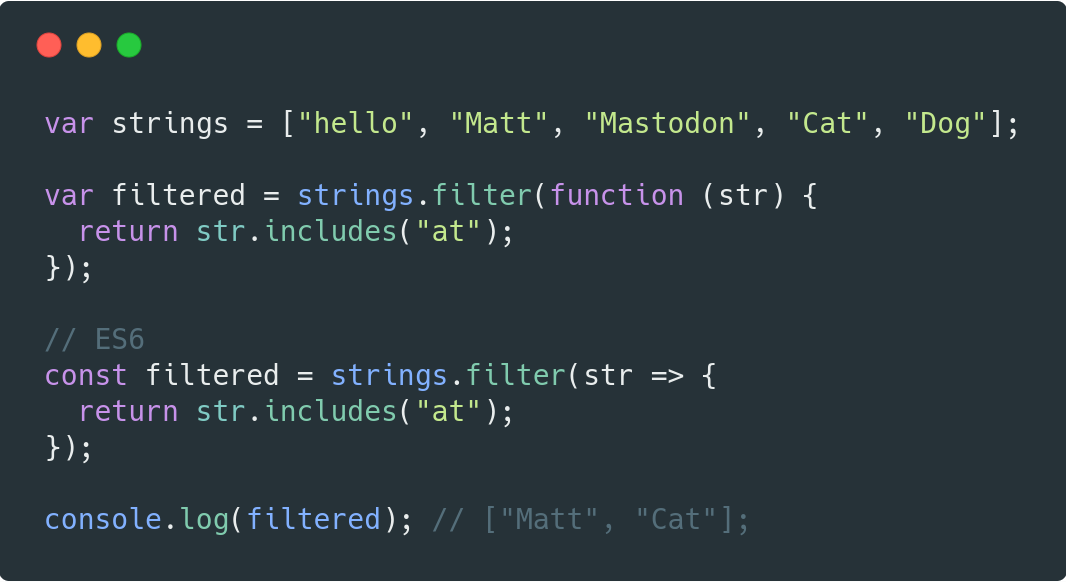
Filtering Data with Filter: Selecting Desired Elements
The filter method empowers developers to create a new array containing only the elements that meet a specific condition. It iterates through the original array, applies a test function to each element, and includes only those elements that pass the test in the new array.
Syntax:
const filteredArray = originalArray.filter(function(element, index, array)
// Check if element meets the condition
return conditionMet;
);Similar to map, the filter method accepts a callback function as its argument. This callback function also receives three parameters:
- element: The current element being evaluated.
- index: The index of the current element in the original array.
- array: The original array itself.
The callback function must return a Boolean value:
- true: If the current element meets the condition, it is included in the new array.
- false: If the current element does not meet the condition, it is excluded from the new array.
Example:
const ages = [18, 25, 16, 30, 22];
// Filter for ages greater than or equal to 18
const adults = ages.filter(age => age >= 18);
console.log(adults); // Output: [18, 25, 30, 22]In this example, the filter method iterates through the ages array, testing each element against the condition age >= 18. Only the elements that satisfy this condition are included in the new array adults.
The Power of Combining Map and Filter
The true power of map and filter lies in their ability to work together seamlessly. By combining these methods, developers can perform complex data transformations and filtering operations in a concise and elegant manner.
Example:
const products = [
name: "Apple", price: 1.20, quantity: 5 ,
name: "Banana", price: 0.80, quantity: 3 ,
name: "Orange", price: 1.50, quantity: 2 ,
];
// Calculate the total cost of each product and filter for products with a cost greater than 3
const expensiveProducts = products
.map(product => ( ...product, totalCost: product.price * product.quantity ))
.filter(product => product.totalCost > 3);
console.log(expensiveProducts);
// Output: [
// name: "Apple", price: 1.20, quantity: 5, totalCost: 6 ,
// name: "Banana", price: 0.80, quantity: 3, totalCost: 2.4 ,
// ]In this example, we first use map to calculate the totalCost for each product. Then, we use filter to select only the products whose totalCost is greater than 3. This demonstrates how map and filter can be chained together to perform multi-step data manipulation.
Benefits of Using Map and Filter
-
Code Readability:
mapandfilterpromote a more declarative style of programming, making code easier to understand and maintain. - Conciseness: They eliminate the need for verbose loops, resulting in shorter and more concise code.
- Performance: These methods are optimized for performance, especially when dealing with large datasets.
-
Functional Programming:
mapandfilteralign with functional programming principles, emphasizing immutability and side-effect-free operations.
FAQs about Map and Filter
1. Can map modify the original array?
No, map does not modify the original array. It creates a new array containing the transformed elements.
2. Can filter modify the original array?
Similarly, filter does not modify the original array. It creates a new array containing only the elements that satisfy the condition.
3. What happens if the callback function in map or filter returns undefined?
In map, if the callback function returns undefined, the corresponding element in the new array will be undefined. In filter, if the callback function returns undefined, the element will be excluded from the new array.
4. Can I use map and filter with nested arrays?
Yes, you can use map and filter with nested arrays by applying them to the nested arrays themselves.
5. What are some common use cases for map and filter?
- Data transformation: Converting data from one format to another.
- Data filtering: Selecting specific elements based on certain criteria.
- Data aggregation: Combining data from multiple sources.
- Array manipulation: Performing operations like sorting, reversing, or removing duplicates.
Tips for Using Map and Filter Effectively
- Keep callback functions concise: Aim for clear and focused callback functions that perform a single task.
- Use arrow functions: Arrow functions provide a more concise syntax for defining callback functions.
-
Chain methods for complex operations: Combine
mapandfilterwith other array methods to achieve complex data transformations. -
Consider performance implications: While
mapandfilterare generally efficient, be mindful of their impact on performance when working with very large datasets.
Conclusion
map and filter are essential tools in the JavaScript developer’s arsenal. They offer a powerful and elegant way to manipulate and transform data, enhancing code readability, conciseness, and performance. By understanding their functionality and best practices, developers can leverage these methods to effectively process and manage data in their applications. As JavaScript continues to evolve, map and filter remain fundamental building blocks for efficient and effective data manipulation, solidifying their place as essential tools in the modern JavaScript developer’s toolkit.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Data with JavaScript: Mastering Map and Filter. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!