Mapping The Land Of The Bible: A Geographical Journey Through Ancient Israel
Mapping the Land of the Bible: A Geographical Journey through Ancient Israel
Related Articles: Mapping the Land of the Bible: A Geographical Journey through Ancient Israel
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Land of the Bible: A Geographical Journey through Ancient Israel. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Land of the Bible: A Geographical Journey through Ancient Israel
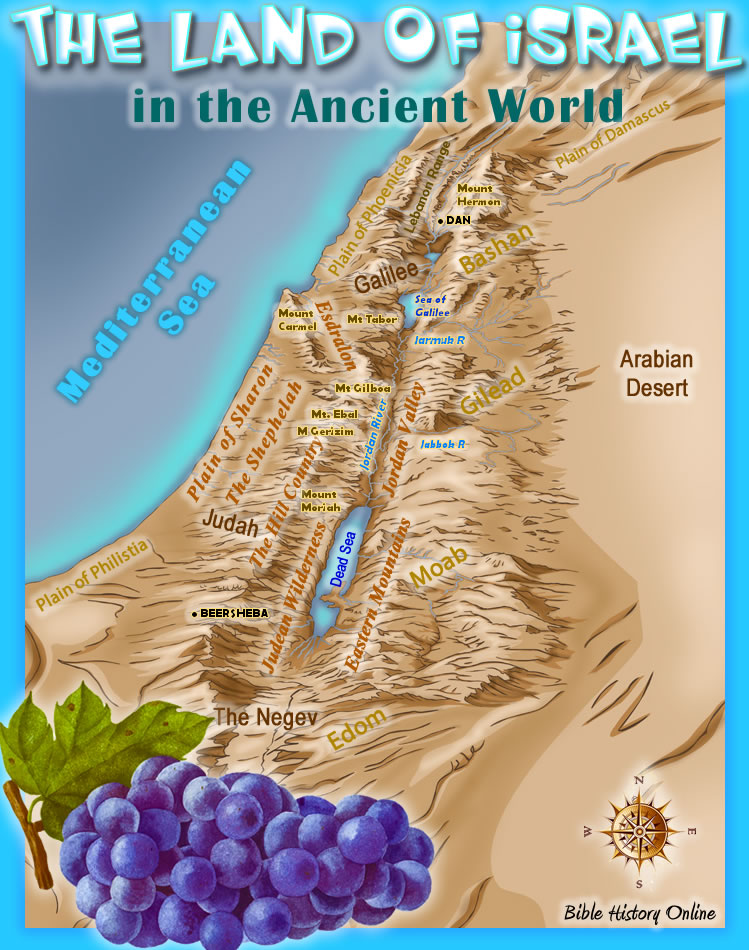
The land of Israel, a small region nestled between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, holds a unique place in human history. It is the birthplace of three major world religions – Judaism, Christianity, and Islam – and its landscape has been the stage for countless narratives, both historical and mythical. Understanding the geography of ancient Israel is crucial for comprehending the events, cultures, and beliefs that shaped these religions and continue to resonate across the globe.
The Physical Landscape: A Mosaic of Diverse Environments
Ancient Israel, unlike many other ancient civilizations, was not confined to a single fertile plain or river valley. Instead, it encompassed a mosaic of distinct environments, each with its own unique characteristics and influencing the lives of its inhabitants.
-
The Coastal Plain: This fertile strip of land along the Mediterranean coast provided access to trade routes and resources from the sea. Its temperate climate supported agriculture, while its harbors facilitated maritime trade. Cities like Jaffa and Ashdod thrived in this region.
-
The Shephelah: Rolling hills and valleys characterize this transition zone between the coastal plain and the highlands. Its fertile soil supported agriculture, while its strategic location made it a contested zone between coastal and highland populations.
-
The Central Highlands: This mountainous region, dominated by the Judean Hills and the Samaritan Mountains, provided a natural defense against invaders. Its rugged terrain was less hospitable for agriculture, leading to a more pastoral lifestyle. Jerusalem, a city of immense religious and political significance, was located in this region.
-
The Jordan Valley: This rift valley, running along the eastern edge of the land, is characterized by its extreme heat and aridity. It was a crucial trade route, connecting the highlands to the Dead Sea and the Arabian Peninsula. Jericho, one of the oldest cities in the world, was located in this region.
-
The Negev Desert: This vast desert region in the south was sparsely populated and largely uninhabitable. Its harsh conditions limited human activity, although some nomadic tribes lived in the area, relying on oases and seasonal rainfall.
The Human Landscape: A Tapestry of Cultures and Empires
The geography of ancient Israel not only shaped its natural environment but also influenced its human landscape. Over centuries, various cultures and empires rose and fell, leaving their mark on the land and its people.
-
The Canaanites: This Bronze Age civilization dominated the region before the arrival of the Israelites. They developed sophisticated city-states, practiced polytheistic religion, and engaged in extensive trade. Their legacy can be seen in archaeological sites like Megiddo and Hazor.
-
The Israelites: The arrival of the Israelites, believed to have migrated from Mesopotamia, marked a significant shift in the region’s history. They established a kingdom, developed a unique monotheistic religion, and left a lasting impact on the cultural and spiritual landscape of the land.
-
The Philistines: These seafaring people, originating from the Aegean region, settled along the Mediterranean coast and clashed with the Israelites. Their influence is evident in their sophisticated ironworking and their military prowess, as depicted in the biblical story of David and Goliath.
-
The Assyrians and Babylonians: These powerful empires conquered Israel and Judah, leading to periods of exile and upheaval. Their impact on the region’s political and cultural landscape was profound, influencing its development for centuries to come.
-
The Persians, Greeks, and Romans: These empires, in turn, ruled over the region, leaving their own imprint on its history and culture. They introduced new administrative structures, architectural styles, and religious ideas, further shaping the diverse mosaic of ancient Israel.
The Importance of Geographical Understanding
Understanding the geographical context of ancient Israel is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and religion. The land’s diverse landscape and its strategic location influenced the rise and fall of civilizations, the development of trade routes, and the spread of religious ideas.
-
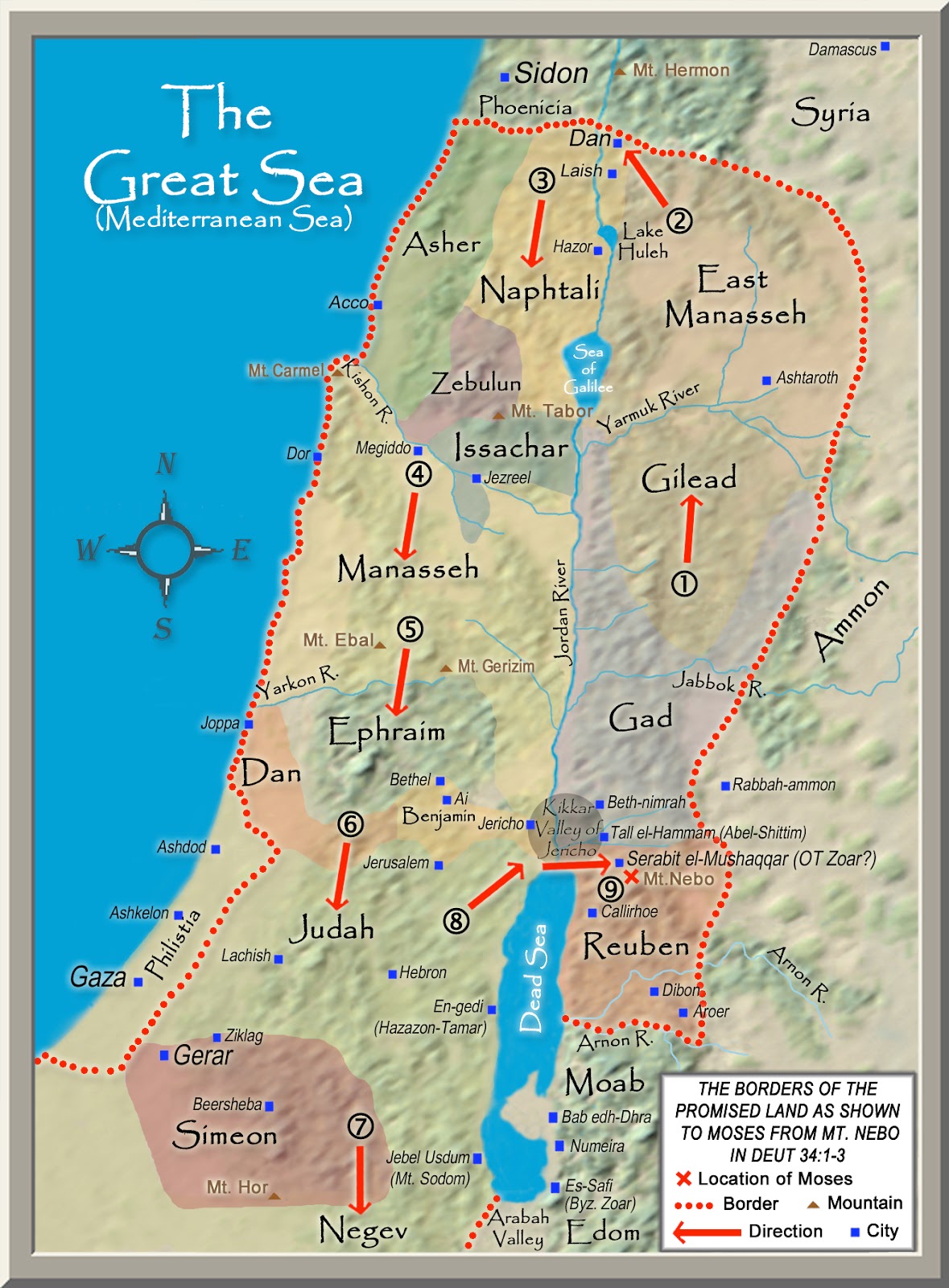
Historical Context: Maps of ancient Israel provide a visual representation of the locations where key events took place, helping us understand the spatial relationships between different cities, empires, and battlefields. For example, mapping the routes of the Israelite exodus from Egypt, or the locations of the major battles between Israel and its enemies, sheds light on the historical narratives that shaped the region.
-
Cultural Understanding: The geographical context illuminates the cultural differences between various groups inhabiting the land. The mountainous terrain of the highlands fostered a more pastoral lifestyle, while the coastal plain fostered maritime trade and urban development. This understanding helps us appreciate the diversity of cultural practices, beliefs, and social structures that existed in ancient Israel.
-
Religious Interpretation: The land of Israel holds immense religious significance, serving as the setting for key events and narratives in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Maps help us visualize the locations associated with these narratives, such as the Temple Mount in Jerusalem, the site of the Second Temple, or the Sea of Galilee, where Jesus performed many miracles.
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of Jerusalem in ancient Israel?
A: Jerusalem, located in the Judean Hills, was a city of immense religious and political importance. It was the capital of the Israelite kingdoms of Judah and Israel, and it housed the Temple, the center of Jewish religious life. Its strategic location made it a contested zone between various empires, and its religious significance continues to make it a focal point of international conflict today.
Q: How did the geography of ancient Israel influence its agriculture?
A: The diverse geography of ancient Israel resulted in varied agricultural practices. The coastal plain, with its fertile soil and temperate climate, supported the cultivation of grains, fruits, and vegetables. The highlands, with its rugged terrain, were more suitable for pastoralism, with sheep, goats, and cattle being raised. The Jordan Valley, with its arid climate, required irrigation systems for agriculture.
Q: What are some of the major archaeological sites in ancient Israel?
A: Ancient Israel is home to numerous archaeological sites that offer insights into its history and culture. Some of the most notable include:
- Masada: A fortified hilltop in the Judean Desert, known for its role in the Jewish revolt against Rome.
- Megido: An ancient city located in the Jezreel Valley, known for its strategic importance and its role in several battles.
- Hazor: A large Canaanite city located in the Upper Galilee, known for its extensive archaeological remains.
- Jericho: One of the oldest cities in the world, located in the Jordan Valley, known for its ancient walls and its strategic importance.
Tips
- Use a variety of maps: Different types of maps can be used to explore ancient Israel, including topographical maps, historical maps, and thematic maps.
- Combine maps with historical texts: Maps can be used in conjunction with historical texts to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the events and cultures of ancient Israel.
- Engage in active learning: Use maps to create timelines, trace trade routes, or map out the spread of religious ideas.
- Explore the archaeological evidence: Visit archaeological sites in Israel to see firsthand the evidence of ancient civilizations and their cultures.
Conclusion
The map of ancient Israel is a powerful tool for understanding the history, culture, and religion of this pivotal region. It provides a visual framework for comprehending the interplay between the land’s diverse geography and the lives of its inhabitants. By exploring the physical landscape, the rise and fall of empires, and the development of religious traditions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of ancient Israel and its enduring legacy in the modern world.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Land of the Bible: A Geographical Journey through Ancient Israel. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!